04.03.2022 11 217 VAZ 2110
Author: Ivan Baranov
The ECU is the main control module in any car. Thanks to the control unit, the optimal parameters for the operation of the power unit are determined, so this module must always work exactly like a clock. Where is the VAZ 2110 ECU located, what malfunctions are typical for it and how to change the device if necessary - we will talk about this below.
[Hide]
Description of "brains"
The VAZ 2110 is considered the first vehicle in the domestic automobile industry equipped with an injection engine. The power unit is controlled by an ECU, an electronic device that determines the basic parameters of engine operation in accordance with sensor signals. In fact, the ECU of a VAZ 2110, VAZ 2112 or any other model is the “brains” of the car, the operation of which affects the functionality of the vehicle as a whole.
Control controller in VAZ 2110
In the “Tens”, as well as the VAZ 2112, there are 16 valves and other models equipped with BOSCH 7.9.7 or January 7.2 systems, one M6 screw is installed in the head. From this screw the mass is taken to the ignition coils, and the mass is taken directly to the control model in the cabin. Typically, the mass is a welded stud mounted on the ECM bracket, particularly behind the center console, behind the left screen. In this case, the mass is transferred to the bracket through a pin, which is welded on the engine shield in the middle. It should also be noted that the nut on this stud is not usually tightened.
Control unit location
Now let's consider the location of the VAZ 2110 ECU. This device in the Ten is located under the center console, in its lower part, in particular, under the control panel. In order to gain access to the control module, you must remove the plastic panel on the passenger side, to do this you will have to use a Phillips screwdriver. Once you remove the cover, you will see many different wires, plugs, and safety devices. The controller itself is located behind them, it is screwed to the bar in a horizontal position.
The arrow indicates the location of the ECM module behind the center console
Video “Why the ECM does not communicate during testing”
From the video below, you can find out why there may be no communication between the ECM and the laptop during diagnostics (the author of the video is the Billye espada channel).
The most common problems with the electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller) in a VAZ family car.
An electronic engine control unit, abbreviated as ECU, ECM, controller, is an electronic device that, using various signals from engine sensors, controls the composition and amount of fuel supplied to the engine. Having a built-in diagnostic system, it can recognize problems in the system, warning the driver about them through a warning lamp (Check engine). It also stores diagnostic codes that indicate areas of trouble to help technicians make repairs.
Symptoms of a malfunction of the electronic engine control unit:
— Lack of control signals for injectors, ignition, fuel pump, valve or idle mechanism, and other actuators. - No response to Lambda - regulation, temperature sensor, throttle position sensor, etc. - No communication with the diagnostic tool. — Physical damage (burnt radio elements, conductors).
You can purchase an electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller) from us!
DON'T STROKE - BUY CHEAPER! ! !
Causes of malfunction of the electronic engine control unit:
1. Unqualified intervention in the car’s electrical system when installing alarms and carrying out repairs. 2. “Lighting up” from a car with the engine running. 3. “Reversal of polarity” when connecting the battery. 4. Removing the battery terminal with the engine running. 5. Turning on the starter with the power bus disconnected; 6. Contact of the electrode during welding work with the sensors or wiring of the vehicle. 7. Water entering the ECM. 8. Broken or shorted wiring. 9. Malfunction of the high-voltage part of the ignition system: coils, wires, distributor
ECU diagnostics involves reading errors recorded in the controller’s memory. Reading is performed using special equipment: PC, cable, etc. via diagnostic K-line. You can also get by with an on-board computer that has the function of reading ECM errors.
The ECU stores diagnostic codes that indicate areas of trouble to assist technicians in making repairs.
If the ECM fails due to a problem in the wiring or actuator, a simple replacement may not give anything other than two, three, etc. burnt blocks.
To find out which controller is on your car, you will have to remove the side frame of the car's instrument panel console. Remember the number of your ECU and find it among the tables presented.
You can purchase an electronic engine control unit (ECU, ECM, controller) from us!
DON'T STROKE - BUY CHEAPER! ! !
The information will also be useful to you: Varieties of electronic engine control systems (ECM, controllers), which are installed on different models of the VAZ family car.
If you haven't found the answer you are looking for, then ask your question! We will respond shortly.
Don’t forget to share the information you find with your friends and acquaintances, as they may also need it - just click one of the social networking buttons.
Greetings, dear friends! I decided to devote today’s post entirely to the ECU (Electronic Engine Control Unit) of the VAZ 2114. After reading the article to the end, you will learn the following: what ECU is on the VAZ 2114 and how to find out its firmware version. I will give step-by-step instructions for its pinout, tell you about the popular ECU models January 7.2 and Itelma, and also talk about common errors and malfunctions.
Signs of the need for internal combustion engine repair
The reasons why the operation of the engine is disrupted are arranged in a small list, starting with refusal to start and ending with floating idle speed (this problem was removed on the 127 “engine”). Not all breakdowns end in capital damage - sometimes it’s enough to add oil, sometimes it’s enough to adjust the ECU settings.
Compression reduction
A decrease in cylinder compression below 16 atmospheres is a bad sign. Such a high limit corresponds to a compression ratio of 11.
Knocks in the engine
Engine knocks can come from several points. These could be hydraulic compressors, timing belt rollers or pins. The knocking noise could also be caused by low oil level. The answer to the question will be given by a thorough detailed inspection of all parts of the unit and checking the oil level.
Blue smoke from the exhaust pipe
The blue smoke that comes from the exhaust pipe appears when oil enters the combustion chamber. It can leak either from the valves or from under the piston. The result is the same: the oil is eaten up and blue smoke pours out of the chimney. Once the leak is located, half the problem will already be solved.
Troit motor
Sometimes in the cold the engine may stall - don’t be alarmed by this, because it may simply be one of the spark plugs that fails. In this case, we advise you to simply restart the engine and it will stop running.
How much does it cost to overhaul a Priora engine - average price
Self-repair of a Priora engine with 16 valves costs an average of 16-20 thousand rubles. The cost depends on the severity of the breakdown and may be lower or higher than this average range. Repairing a Priora engine can be entrusted to the wrong hands, but then you will have to pay for the work - sometimes the cost of repairs reaches as much as 40 thousand rubles.
This is an unreasonably inflated figure, because, as practice shows, you can rebuild the engine on a Priora, working at a moderate pace, in just three days - and three days of work is definitely not worth that kind of money. Don’t be afraid of not being able to cope - your Lada is easy to repair, and using the advice and “tutorials”, you will conquer even such a task that is impossible at first glance.
Benefits of tuning
The main advantage of this tuning is the ability to improve the performance characteristics of the car without interfering with the engine itself. There is no need to change the head, install different pistons or spider. It is enough to install a different firmware on the VAZ, then the car will become more responsive to the accelerator pedal. The next plus is the speed of installation. Upgrading the VAZ-2114 firmware will take no more than twenty minutes of time. In this case, you can always return the ECU to its factory settings.
Another advantage of the control unit firmware is the removal of engine errors. They can occur when the catalyst is removed or the oxygen sensor is faulty. Since many VAZ-2114 owners install a flame arrester instead of a catalyst, the “Check” is constantly lit on the instrument panel. With the new firmware, “Check” will not bother the owner. And with computer diagnostics there will be no errors in the exhaust system.
There are many programs for flashing VAZ firmware. One will allow you to achieve maximum fuel efficiency. The other will improve dynamic performance. The third will allow the 16-valve engine to run on 92 gasoline without detonation and overconsumption.
Physical location
The ECU of the “fourteenth” is located in the cabin directly under the instrument panel. If necessary, you can gain access to the “brains” from the passenger side; to do this, you will have to dismantle the decorative trim. If during the diagnostics a malfunction of the control unit was discovered, it will need to be dismantled for a more detailed study or repair. Before this, it is necessary to de-energize the car by disconnecting the terminals from the battery. Violation of the dismantling rules, as well as any experiments with voltage, can irreversibly damage the ECU.
ECUs of the following models were installed on the VAZ 2114-15:
- January (“4”, “5.1.Х”, “7.2”);
- BOSCH (“M1.5.4”, “M7.9.7”);
- ITELMA 5.1;
- GM-09.
What kind of ECUs are installed on the VAZ 2110
Earlier I already talked about what kind of ECUs are installed on the VAZ 2114, if you are interested, read this article! So, dozens of electronic control units are installed with similar ones.
January 4 – technical specifications for which VAZ 2110 models are installed
One of the most common ECUs installed on the VAZ 2110 is January 4.
Structural management system January 4
January 4 was installed on the first generation VAZ 2110 model of 1999. Of course, this is not the most advanced ECU for a VAZ, but it still has a number of advantages, which I will talk about later.
Bosch M1.5.4 - advantages and disadvantages of use in the VAZ 2110
For Euro-2 toxicity standards, new modifications of block M1.5.4 appear (has an unofficial index “N”, to create an artificial difference) 2111-1411020-60 and 2112-1411020-40, satisfying these standards and incorporating an oxygen sensor, catalytic neutralizer and adsorber.
ECU Bosch M1.5.4
Also, for Russian standards, an ECM was developed for 8-class. engine (2111-1411020-70), which is a modification of the very first ECM 2111-1411020. All modifications, except the very first, use a wideband knock sensor. This unit began to be produced in a new design - a lightweight, leak-proof stamped body with an embossed inscription “MOTRONIC” (popularly “tin can”). Subsequently, ECU 2112-1411020-40 also began to be produced in this design. Replacing the structure, in my opinion, is completely unjustified - sealed blocks were more reliable. New modifications most likely have differences in the circuit diagram towards simplification, since the detonation channel in them works less correctly, the “tins” “ring” more when using the same software.
January-5 – description and technical characteristics of the VAZ 2110 ECU
In parallel with the M1.5.4 system, AvtoVAZ, together with ELKAR, designed a functional analogue of the M1.5.4 block, which was called January-5.” Initially, versions were released for Euro-2 standards (2112-1411020-41) containing an oxygen sensor, catalytic converter and adsorber. Later, mass production and installation of systems based on control units began:
- “January-5.1.2” for 16 (2112-1411020-71).
- “January-5.1.1” for 8 (2111-1411020-71) valve engines.
All these units have software and calibrations developed by AvtoVAZ OJSC. For classic cars, the January 5.1.3 2104-1411020-01 modification is used in the Euro-2 configuration, without a knock sensor.
ECU VAZ 2110 January 5.1
It differs from version 5.1 only in the unsoldered elements of the detonation channel. In December 2005, NPP Avtel released for spare parts (this was never supplied to the VAZ conveyor!!!) ECU “January 5.1.x” with modified hardware.
ECU VAZ 2110 BOSCH MP7.0H
The next generation of ECUs for VAZ cars was Bosch MP 7.0. In this modification, both the hardware and software were developed by Bosch, the final calibration and fine-tuning of the systems was carried out by AvtoVAZ OJSC. This family is also expanding and has already been supplemented with systems meeting Euro-3 standards for 8 and 16-valve engines of front-wheel drive vehicles, as well as for all-wheel drive vehicles VAZ-21214 and VAZ-2123 (Euro-2 and Euro-3 standards).
A FLASH chip with a capacity of 256 Kb is used as ROM in these blocks, of which only 32 Kb contain calibration tables and can be read and rewritten. More precisely, you can write all 256 KB, but only read 32 KB. Reading/writing of these blocks (without opening the blocks) is supported only by Combiloader from SMS-Software. It is also possible to program the flash with an external programmer via an adapter connected to the ECU bus.
ECU VAZ 2110 BOSCH MP7.0H
This ECU uses a 16-bit B58590 processor (internal marking from Bosch), a 20-bit bus and 29F200 flash memory is used as ROM for storing software and calibrations. ECUs of different modifications differ in hardware. The ECU for E3 (-50) standards has an additional driver for the heater of the 2nd oxygen sensor. There may also be differences in the DTV channel. A beautiful paper sticker (there are such things), on top of the standard nameplate - most likely the brainchild of OPP, such blocks were installed on some Niva and Nadezhda cars, converted to OPP from ordinary Niva ones. This type of ECU supports non-disabled driver diagnostics. Therefore, when installing gas equipment on them, it is strictly necessary to use continuous shutdown of the injectors.
Historical reference
The car was equipped with a fuel injection distribution system that complies with the requirements of exhaust gas toxicity standards:
- The 16-valve power unit was equipped with an electronic system based on the M7.9.7 controller and complied with EURO 3;
- The 8-valve power unit complied with EURO 2 standards.
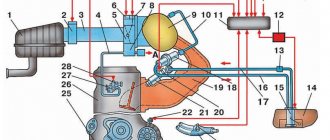
For reference: for brevity, the engine control system with distributed fuel injection is referred to in the diagrams as an abbreviation - SUD. For the EURO 3 engine it is equipped with a solenoid valve for purge the adsorber - in the diagram under No. 13.
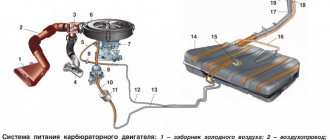
See also the wiring diagram for VAZ 21099 - carburetor.
EURO 3 – 16 valve version
The presented diagram shows the main components and sensors, thanks to which the control system organized the supply of the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders:
- The main components are the ignition coil, fuel injectors, controller and main relay (indicated in the diagram as numbers 1,2,3 and 4);
- A larger group of sensors includes several systems at once: power supply, cooling, air supply, engine operation, etc.
Control systems for monitoring the operation of the power unit include:
- throttle position sensor (No. 12);
- knock sensor (No. 18);
- diagnostic oxygen sensor (No. 16);
- crankshaft position sensor (No. 19);
- coolant temperature sensor (No. 13);
- immobilizer control unit (No. 20);
- coolant temperature indicator sensor (No. 26).
Visual surveillance systems include:
- immobilizer status indicator (No. 21);
- vehicle speed sensor (No. 23);
- oil pressure warning lamp sensor (No. 25);
- fuel level sensor (No. 24).
In addition, the VAZ 21124 wiring diagram also contains built-in protection elements:
- Main relay fuse (No. 5);
- Relay and fuse for electric cooling fan (No. 6 and 7);
- Fuel pump relay and fuse (No. 8 and 9);
For reference: G1, G2 indicated in the diagram are grounding points, A – ABS system block, B – diagnostic connector.
See also the wiring diagram for the VAZ 2112 (injector) - improving the performance of the lights.
EURO 2 compliant power unit
The electronic content of the car is similar to the 16-valve version:
- single controller for power units M7.9.7
- general factory instructions for cars with different power units.
In addition to the different markings of the sensors, the car circuits are identical with the exception of the solenoid valve for purge the adsorber, which is equipped with EURO 3 engines.
Video “No spark and blown fuse - repairing the ECU”
What to do if there is no spark and the fuses are constantly blowing - the video below shows the process of repairing the control controller in a garage (the author of the video is the Auto Practice channel).
I came across an article by McSystem. Actually, here it is below
In January - about Januarys. Again and in detail about the ECM-ECU masses
One of the rather serious problems affecting the stable operation of engines controlled by the January ECU (7.2, 7.2+, M73, 7.9.7) is the “mass problem” of the ECM. Moreover, the point is not so much in bad (or uncrimped) contacts and their fastenings, but rather in the rather incorrect wiring of the ECM harness itself. And the solution is not in “pulling a fancy cable (KG-25 or 50)” to the ECU. Therefore, this material will be devoted to a technically competent approach to solving this problem. What is described below is a kind of compilation, or an attempt to “chew” what has been published more than once, in particular on ChipTuner.ru, and to convey to readers the specifics of solving this problem. The articles by I.N. turned out to be the most complete and informative. Skrydlova, (aka Aktuator) “About the masses”, “MASS: AN UNEXHAUSTABLE SOURCE OF GLITCHES” “ONCE AGAIN ABOUT THE MASSES” Oleg Bratkov. Many years ago, having read and comprehended what was written, I implemented it on my typewriter. I completely agree with the conclusion of the author (aka Aktuator): “All the assurances of AVTOVAZ OJSC about improving the quality of electrical connections in manufactured vehicles are not worth a penny. In most cases, it is possible to achieve normal operation of the engine under the control of the ECM I 7.9.7 and January 7.2 only by carrying out additional, and not accepted by the manufacturer as a warranty, work to change the electrical circuit of the car.”
So, on to the topic! Classic ECM 21124 with ECU January 7.2(+) or M7.9.7 Electrical connection diagram of ECM EURO-2 M7.9.7, January 7.2 LADA 2110 with engine 21124. 21124-1411020-30, 21124-1411020-31.32
Fig. 1 ECM 21124 January 7.2, M7.9.7 Noticed, often described and characteristic problems - unstable idle speed, freezing speed, “jerking” of the engine at start and operation of the cooling fan, unreasonable jumps in the electrical parameters of the ECM during diagnostics. And this is not the entire list. And the whole problem is a rather incorrect wiring of the harness masses, not in relation to the body, but to the ECU. Therefore, in this article you will not see recommendations for tightening the “hoses” of additional mass to the ECU, due to its complete uselessness. This is not a newfangled “razmasovka” or “razminusovka”... Don’t get your hopes up!
The main idea voiced by the authors is that the wiring of the power lines of the ECU and fan and low-current sensor masses is fundamentally incorrect. Rice. 12
Fig.2 Ground connections of the ECM. S6, S7, S8
The sensors must be connected to the ground bus of the ECU board and not have contact with the body! There should be no flow of pulsed and direct currents of the ECU and IM in the sensor mass circuit. And the ECU is securely connected to the body. The rationale is to eliminate the influence of ECU currents (pulse and constant) and fan current on the reliability of sensor readings. Classic approach with data collection and processing systems! But not from AvtoVAZ designers, as usual... Now, in order
Fig. 3 Masses according to AvtoVAZ, or how not to do it
1. The ECU masses are combined into three crimps S6, S7, S8, which are combined with each other and TWO bends are already made from them to the body studs B3, B4. 2. A switched minus fan with a rated current of 12A is connected to S6, and at the peak at start - all 20A! ! ! Which in itself is terrible! 3. All this is connected (screwed) to the ECU bracket, which in turn is very flimsily connected to the body. The engine ECM consists of sensors and actuators (AM). Sensors can be easily divided into analog and discrete. Analogue – mass air flow sensor, air pressure sensor, diesel sensor, DD. The output signal of these sensors is a voltage in a certain small range, usually 0 - 5V. For this group, any (even small) interference has a serious impact on the result. Discrete ones - DC (to some approximation), DF, DS (Speed Sensor) - are less critical to interference, because the output signal has two fixed levels high and low, and intermediate levels are not interesting to the ECU. Actuators - ignition coils, injectors, canister valve, DC heating, IAC, relays and other sources of large pulsed and direct currents along the negative (mass) bus of the ECU. To understand what the developers were up to, let’s look at the diagram in Fig. 3 – this is a fragment of the main ECM diagram in expanded form. It immediately catches your eye - the masses of the most sensitive and responsible sensors, mass air flow sensors and diesel fuel sensors, are wired, although there are separate pins for them, 36 and 35, respectively. For what? Silence in response! S6-S7-S8 are connected by jumpers, which makes the situation even worse.
Malfunctions of electronic engine control units of VAZ LADA
VAZ Kalina cars, on which the engine control unit is structurally located under the interior heater radiator.
The most common malfunction of the units is a leak in the interior heater in the place where the engine ECU is installed. The result of this not very successful design solution may be complete failure of the control unit. In practice, the penetration of antifreeze into the ECU causes oxidation of the contacts and pins of the microcircuits, which manifests itself in the inability to start the engine, problems with the immobilizer, if the car starts, the engine starts to stall, etc.
Other most common malfunctions of electronic control units VS 5.1, January, Bosch, M73, M75
VAZ cars of the 2110, 2114, Kalina, Priora families are associated with the failure of the power MOSFET keys for controlling the ignition coils, the K-line driver, and the injector driver microcircuit.
The main signs of a faulty ECU of VAZ cars:
- lack of spark in one or more cylinders;
- no control of one or more nozzles;
- there is no control of the fuel pump relay;
- there is no control of the idle air regulator (IAC);
- the car does not go to diagnostics;
- when the ignition is turned on, the starter does not work, the fuel pump does not pump;
- control program checksum error.
Of course, for any malfunctions of this nature, you must assume that the ECU is operational and first check the fuses, wiring, relays, sensors, injectors, ignition coils, ignition module, etc. Most likely the reason will not be in the ECU and it is working properly. But if all options have been exhausted, contact us, we will carry out high-quality repairs of electronic control units with a guarantee.
Computer diagnostics of ECM Bosch M7.9.7
in this case it may show the following errors:
- P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204 - Open circuit in the injector control circuit of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th cylinder;
- P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270 - Short to ground in the injector control circuit of the 1,2,3, 4th cylinder;
- P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271 - Short circuit to the power supply of the injector control circuit of the 1,2,3, 4th cylinder;
- P0336 - Crankshaft position sensor - signal out of acceptable limits;
- P1135 - Circuit of the oxygen sensor heater to the converter: open, short to ground or to +12V;
- P1501, P1502, P1541 - Fuel pump relay control circuit;
- P0342, P0343 - Camshaft Position Sensor - Voltage Level Low or High.
Computer diagnostics of ECM Bosch ME17.9.7
in this case it may show the following errors:
- P0201,P0202,P0203,P0204 - Checking the injector control circuit for open circuit;
- P0261 - Checking the short circuit of the injector control circuit to ground;
- P0136, P0137, P0138 - Diagnostic oxygen sensor. The voltage is less than the lower threshold value or greater than the upper threshold value;
- P0300-P0304 - The number of misfires in cylinders 1-4 is greater than the threshold value;
- P0351, P0352 - Ignition coils. The primary circuit current is less than or greater than the threshold value;
- P0627, P0628, P0629 - Fuel pump relay. Checking for open circuit;
- P1578 - Throttle valve actuator. Adaptation value is out of range;
- P1545 - Throttle valve drive. The deviation of the actual throttle position from the desired one is greater than the threshold value;
- P2103,P2102,P2100 - Throttle valve actuator. Checking the short-circuit circuit for the on-board network, ground and open circuit;
A rare malfunction, but also occurs on ECU January 7.2/7.2+, M73
VAZ cars of the 2110, 2114, Kalina, Priora family. It manifests itself in the fact that the car suddenly stalls at full speed after some time of operation. As a result of checking all the actuators, relays, immobilizer, nothing suspicious can be found. In such incomprehensible situations, replacing the ECU with a known good one helps determine the cause. As a rule, we can successfully restore an ECU with such faults!
How to remove the ECU on a Lada Kalina - step-by-step instructions
In order to remove the ECU unit on a Lada Kalina, you must perform the following procedure:
- First you need to unscrew 2 screws, the location of the first is shown by the arrow. The second is at the same level on the engine side. Before doing this, you must remember to remove the terminal from the battery. After unscrewing the screws, do you need to pull the block towards the passenger door? and he must leave from there along the guides. Sometimes it happens that the wires rest against the carpet. Then they need to be corrected.
- In order to remove the connector and disconnect the unit from the wires, you first need to: pull the connector lock to the side. The latch is a bracket. I think you can easily find it on the connector.
Self-diagnosis systems
Like any computer, the Priora ECU has feedback from the user.
The driver learns about problems using signal codes, which can be seen in two ways: using an additional on-board computer connected to the diagnostic connector, and on the instrument panel after performing simple manipulations.
For self-diagnosis, you can install the following devices:
- State X 1 P Priora. A small device that is inserted in place of a standard button. Has an LED display with 3 characters. In addition to the diagnostic function using 30 parameters, it allows you to warm up the spark plugs during cold periods, independently regulate the temperature at which the cooling system fan turns on, and reset engine errors.
- Priora State Matrix. A more serious on-board computer. It is placed in place of the standard clock and has a graphic display of 128 x 32 pixels.
In addition to the functions listed on the previous computer, the device can work with gas equipment, reading gas consumption. The “Afterburner” function allows you not only to reset engine errors, but also to roll back the controller to its factory state, thereby resuscitating it. After activating this option, the “Priors” ECU mode will turn on, which was set at the factory. This bookmaker also has the ability to update the software.
Multitronics C-900. Universal on-board computer. Can be installed in different places. It has enormous capabilities both in diagnostics and adjustments. Suitable for a wide range of cars. It has a 480 x 800 pixel LCD display and the ability to change settings directly from your home PC.
Basic malfunctions of the ignition module 2110
Despite the fact that the ignition module on the 2110 is a fairly reliable device, the element can still fail. The most common causes of breakdowns identified during diagnosis in almost 90% of cases are:
- Using components that do not meet the parameters. These could be high-voltage wires that do not match the parameters of the module, spark plugs that can damage the ignition module itself (a large charge can break the coil), etc.
- Parts with factory defects or poor quality assembly. As a result, failure of other elements of the ignition system.
If the ignition module does not perform its functions, this is reflected in the performance of the vehicle’s internal combustion engine:
- increased fuel consumption;
- the engine stops starting;
- during acceleration (sharp change in speed), dips appear;
- unstable operation of the internal combustion engine (two cylinders do not work);
- After the engine warms up, there is a noticeable drop in power and thrust.
Frequent malfunctions of the VAZ electronic control unit
Considering that the controller is a complex electronic device, failure of the ECU cannot be ruled out. As a rule, the causes of ECU malfunction can be different, ranging from mechanical damage to software failures.
For example, a common cause of breakdowns is overheating or liquid ingress. As practice shows, on the Lada Samara the ECU is located near the heater radiator. It is not difficult to guess that a radiator leak and coolant entering the controller often disables this device.
In this case, the check engine light does not always light up on the panel, but the engine malfunctions. In such a situation, when no other causes have been identified, what is needed is not diagnostics of the engine and systems, but professional diagnostics of the car's ECU, which can only be performed by an experienced specialist. Often, after checking, the unit may need to be replaced, since ECU repair is often not recommended.
What is an ECU (brains)
The ECU - or electronic control unit on the VAZ-2112 - is the main element that is responsible for the entire cycle of transferring fuel to the engine combustion chamber system, as well as controlling its operation as a whole.
The following two tabs change content below.
About the expert:
Fan-auto
All my life I have been surrounded by cars! First, in the village, already in the first grade, I was rushing around on a tractor through the fields, then there was JAVA, then a penny. Now I am a third-year student at the Polytechnic Faculty of Automotive Engineering. I work part-time as a car mechanic and help repair cars for all my friends.
Below we will tell you how to find this part in the car and replace it.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, by analogy with various foreign cars, VAZ injection engines of different generations are also equipped with controllers of various types. Early versions have simple solutions that are responsible for simple mixture formation and work with a small number of sensors.
At the same time, more modern control units are distinguished by support for distributed injection, more flexible control of the ignition system, as well as the ability to interact with oxygen sensors, etc.
Only after all the nuances have been taken into account can you expect that the engine under ECU control will operate correctly and without failures, and the owner himself will receive stable operation of the power unit and systems, environmental friendliness and maximum efficiency from the engine in different operating modes of the car’s engine.
Significant features of Lada Priora engine tuning
The main feature of chip tuning for a Lada Priora car is that it can be used to improve certain engine characteristics without the need to disassemble it.
Engine chip tuning can only be done if the car has a special electronic control unit that controls the operation of the engine system. It looks like a kind of automobile-type computer that controls the operation of the engine. The main tasks of the control unit are to provide signals to turbocharging systems, fuel injection devices and ignition systems. The computer receives this information from special sensors that determine fuel consumption, speed and other parameters.
This device has a special chip with a microcircuit on it containing programs that control the motor system. Some changes may be made to the microcircuit regarding operating parameters: marking ignition timing, amount of fuel in the cylinders, controlling the level of exhaust toxicity, etc.
Connection to diagnostic motor
The chip tuning process is carried out in two ways. The first involves dismantling an existing chip and reprogramming it after removal. After this, the chip is installed in its original place. The second way is to replace the standard microcircuit with a new one with different software.
To improve some technical characteristics of the engine, there are several methods for modifying it. For example, it is possible to increase the power ratings of an atmospheric turbocharged or gasoline power unit. The microcircuit can provide the car with economical characteristics that significantly reduce fuel consumption.
Most of the programs used by Russian manufacturers for the Lada Priora do not meet all the requirements and are rather imperfect. Therefore, individual chip tuning helps eliminate all the shortcomings present in the factory version. The new version of the program has improved algorithms for calculating the fuel mixture and the ignition timing. In addition, improvements have been made to cold start calibration and idle speed control.
Recently, it has been possible to install special systems in a car, with the help of which you can select programs for working with the engine. Their convenience is that the driver can switch the engine system to sport or economical quiet mode at any time.
Engine chip tuning is very useful for the Lada Priora car. It will be appreciated even by those car enthusiasts who do not like a sporty driving style and high speeds. It provides high-quality speed and traction performance, the ability to carry out sharp accelerations of the car when overtaking, and guarantees ease of movement even when the vehicle is heavily loaded.
Among the reasons are:
- Mechanical damage (cracks, impacts, etc.);
- Exposure to moisture (“drowned people”, as well as cases where the car was stored improperly);
- Outside interference (reprogramming, incorrect firmware, etc.);
- Overheating or hypothermia;
- Voltage drops in the on-board network, as well as a short circuit (due to incorrect connection of the battery terminals, as well as attempts to “light” and other violations of the rules for operating the on-board network);
- Corrosion or oxidation of some areas of the board or other important elements of the ECU.
ECU interchangeability on Lada Kalina
I will give a table of interchangeability of Kalina ECU
. This data was not verified by me personally, but by one authoritative master. The interchangeability of these blocks applies only to blocks with factory firmware (that is, after installation there is no need to reflash the block for your engine and sensors). So, in each line there is a block marking, firmware version and toxicity class.
- Bosch 21114-1411020-40 with software B104CR01(02) Euro3 (in my cases it was this one) can be replaced with:
- Bosch 21114-1411020-40 with software B102СQ05(CR06) Euro3;
- Bosch 11183-1411020-02 with software B101CR01(02) Euro2.
All of the above Bosch blocks can be replaced with domestic Janvr7.2 and 7.2+ blocks.
Domestic blocks are all Euro 2, with the exception of M73 blocks - they are Euro3. January 7.2 and 7.2+ blocks manufactured by Avtel or Itelma (Euro2) for Kalina 1.6l 8V: 7.2 11183-1411020-21(22) with software A(I) 201CO56(57)(58); 7.2+ 11183-1411020-21(22) with software A(I)201CP57. These blocks do not support air conditioning, as I understand it. And, in fact, the M73 blocks, which are suitable for Kalina. These units are all Euro 3: M73 21114-1411020-41 with software A303CE05(CF06) Euro3 (support air conditioning); M73 21114-1411020-42 with software I303CE05(CF06) Euro3 (support air conditioning).
Thus, all of the listed ECUs with Euro3 toxicity class can be changed and can be changed among themselves without hesitation (only if they have factory firmware). It is also possible to replace a block with Euro 3 class with a block with Euro 2 class, but vice versa is not possible. All markings are located on a white plate glued to the ECU cover. Next, I consider it necessary to consider the option of replacing the unit with a used one that was installed on a car with an activated immobilizer, since in this case there is one unpleasant feature.
Error P0504
This malfunction is associated with an incorrect signal from the brake pedal switches. Most often, the cause of such a failure is a malfunction of the brake pedal position sensor, lack of proper adjustment, or a broken spring that is installed in this device. Procedure for checking and troubleshooting:
- We remove the sensor;
- Move the rod lock to the right position using a screwdriver;
- We use a multimeter with an ohmmeter function;
- On Largus, Vesta and Xray cars, contacts 3-4 should be closed and have a resistance close to zero. Contacts 1-2 are open and their resistance should tend to infinity.
- When you press the rod on contacts 3-4, the circuit opens, and on contacts 1-2 it closes. If this is not the case, then the sensor must be replaced.
- On Priora, Kalina, Granta, Niva cars, contacts 1-4 should be closed, and 2-3 open. When you press the rod, the situation is the opposite.
- Before reinstalling the sensor, move the rod to the left position.
Sensor locations in video:
Adjusting the brake pedal position sensor:
Any driver can carry out this procedure at home without a trip to a service station. The part has two nuts in its design. One of them is on top, and the second is on the bottom. The upper nut adjusts the pressure of the rod. First you need to release the lower one, and then tighten the upper one, thereby changing the gap of the element. You need to ensure that the rod is fully pressed and not partially pressed. After this, start the car and let it run for about 10 minutes to check if the error appears.
Instructions for removing and replacing the computer
The need to dismantle the ECM unit 16 of the ten valve engine arises if repairs are necessary when faults are identified. The repair process itself will depend on what exactly happened in the operation of the ECU. For example, if the contacts on the module connector have oxidized, the unit must be dismantled to clean or replace them. If the reason lies in damage to the housing, then the device must be removed for replacement; if water has gotten inside, then the module should be removed in order to dry it. Only after you have dried the block can it be tested.
If the problem lies in the performance of the board and some burnt-out elements, then you can try to repair it yourself by re-soldering some components. But we would still recommend turning to specialists for help, especially if you have never encountered such a problem before (the author of the video about repairing the control controller is Vyacheslav Chistov).
Work sequence
Before dismantling the device, you should disconnect the negative terminal from the car battery:
Do not repair the control unit if you have never had to deal with such a task before!
Checking the functionality of the idle speed sensor
You must identify the breakdown manually - there is no self-diagnosis. The idle speed regulator of the VAZ 2110 is located in the intake after the valve (throttle body).
First, analyze the electrical part with a multimeter:
- The pinout of the IAC VAZ 2110 is being studied (available in the product instructions or on the Internet).
- They check whether the sensor is powered normally, for which it is disconnected and the block is removed.
- They take measurements of the two outer terminals on block A and D: Turn on the ignition, turn the multimeter to “continuity”, the black probe to ground (on the body itself) of the internal combustion engine, touch the positive (red) contacts one by one. A value within 12 V is normal. If not, the circuit is broken, the ECU is broken, the battery is discharged. This means we check the integrity (contacts, wires), the ECU (at pins 4 and 54 the norm is also 12 V), and the battery. If they are working properly, the problem is in the valve;