On injection systems of engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, the controller (ECU, control unit) is a device that coordinates the operation of all sensors and systems included in the ECM. This is a specialized mini computer in which an engine control program is installed. Let's consider the applicability of controllers on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099.
VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 with engine 2111 without converter, with CO potentiometer (device for manual adjustment of CO content in exhaust gases), until 2001 (emission standards R-83):
— BOSH M1.5.4 (2111-1411020);
- January 4.1 (2111-1411020-22).
VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 with engine 2111 without a neutralizer, without a potentiometer, but with the ability to electronically adjust CO using a scanner or a technological, plug-in potentiometer, since 2001 (toxicity standards R-83):
— BOSH M1.5.4 (2111-1411020-70);
— January 5.1 (2111-1411020-71);
- VS 5.1 (2111-1411020-72).
VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 with engine 2111, with neutralizer, one oxygen sensor, gasoline vapor recovery system (EURO-2 standards):
— GM ISFI-2S (2111-1411020-10 (20, 21));
— BOSH MP7.0N (2111-1411020-40);
— BOSH M1.5.4N (2111-1411020-60);
— January 5.1 (2111-1411020-61);
- VS 5.1 (2111-1411020-62).
VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 with engine 2111, with a neutralizer, two oxygen sensors (control and diagnostic), a gasoline vapor recovery system (EURO-3 standards):
— BOSH MP7.0N (2111-1411020-50).
Notes and additions
— Controllers GM ISFI-2S (2111-1411020-10 (20, 21)), January 4.1 (2111-1411020-22), BOSH M1.5.4 (2111-1411020) are currently discontinued.
More articles on the VAZ injector
Front-wheel drive VAZ cars are very popular in Russia due to their high maintainability, relatively low cost of spare parts, and simple design. But due to the large number of modifications, it is not easy for the driver to understand even the instructions where this or that unit (part) is located, in particular, on the VAZ-21099 car the injector.
Before repairing a car, some parts have to be searched for a long time and painstakingly, thus wasting a lot of time. In this article we will help you figure out where this or that device is located on the VAZ model 21099, and we hope that the information will be to some extent useful to car owners who have just bought a car, or to novice drivers.
Differences between control units
ECUs of older models worked with a limited number of sensors, so they could not ensure high-quality engine operation and preparation of the air-fuel mixture. The lack of support for the phase sensor (DPRV) led to the fact that the controller did not determine which cylinder was working at the moment, so it injected fuel not into the combustion chamber but into the air manifold. Devices operating in this mode were called central injection ECUs.
Installing a phase sensor on the engine made it possible to clearly determine the operating order of the cylinders, thanks to which fuel was calculated separately for each combustion chamber. Devices operating in this mode were called distributed injection ECUs. Over time, ECUs got better and better. Support for an oxygen sensor made it possible to more accurately regulate fuel combustion. Support for two oxygen sensors made it possible to move to higher toxicity standards, because in this case it was possible to effectively use the catalytic converter. The appearance of each new ECU model brought with it new functions that reduced fuel consumption, increased engine power or service life, and made driving more comfortable.
The controller is a complex electronic device, a microcomputer, so the breakdown or malfunction of any element leads to disruption of the functioning of the entire computer. In most cases, it is possible to determine an ECU malfunction only by elimination, checking the operation of the entire injector. For information on how to do this, read the article “Injector Diagnostics”.
No weight on the engine
If there is no ground on the engine, it is necessary to check the quality of all electrical system contacts coming directly from the engine housing.
Or you need to check the condition of the stud, because... The manufacturer does not process this type of equipment in any way other than painting, so they are often susceptible to oxidation or corrosion. As a result of using low-quality parts, voltage drops in the system, which is accompanied by a lack of mass on the engine, resulting in problems in the operation of the machine.
Where is the temperature sensor located?
If the temperature sensor does not show on the instrument panel, there is a high risk of overheating the engine, since the instrument panel does not inform the driver about the heating of the internal combustion engine coolant. Of course, the instrument panel or electrical wiring may be faulty, but most often the temperature sensor (DTOZH) on the engine itself refuses to work.
Where is the temperature sensor located on an injection car 099? Of course, you need to look for it in the engine compartment:
- open the hood;
- we find the wiring that is located between the rear of the engine valve cover and the air filter housing;
- where the DTOZH is located can be seen in more detail in the following photos.
Types of ECU (esud, controller). What kind of ECUs are installed on VAZ?
"January-4", "GM-09"
The very first controllers on SAMARA were January-4, GM - 09. They were installed on the first models before the year 2000. These models were produced both with and without a resonant knock sensor.
The table contains two columns: 1st column – ECU number, second column – brand of “brains”, firmware version, toxicity standard, distinctive features.
| 2111-1411020-22 | January-4, without DC, RSO (resistor), 1st ser. version |
| 2111-1411020-22 | January-4, without recreation center, RSO, 2nd ser. version |
| 2111-1411020-22 | January-4, without recreation center, RSO, 3rd ser. version |
| 2111-1411020-22 | January-4, without recreation center, RSO, 4th ser. version |
| 2111-1411020-20 | GM,GM EFI-4,2111,with DC,USA-83 |
| 2111-1411020-21 | GM, GM EFI-4, 2111, with DC, EURO-2 |
| 2111-1411020-10 | GM,GM EFI-4 2111,with DC |
| 2111-1411020-20 h | GM, RSO |
VAZ 2113-2115 from 2003 are equipped with the following types of ECUs:
"January 5.1.x"
The following types of hardware implementation are distinguished:
- simultaneous injection;
- in pairs - parallel injection;
- phased injection.
Interchangeable with “VS (Itelma) 5.1”, “Bosch M1.5.4”
| 2111-1411020-71 | January-5.1.1, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-71 | January-5.1.1, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-71 | January-5.1.1, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-71 | January-5.1.1, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-71 | January-5.1.1, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-72 | Itelma, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-72 | Itelma, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-72 | Itelma, without dk, with |
| 2111-1411020-72 | Itelma, without dk, with |
"Bosch M1.5.4"
The following types of hardware implementation are distinguished:
- simultaneous injection;
- in pairs - parallel injection;
- phased injection.
Interchangeable with “VS 5.1”, “January 5.1.x”.
| 2111-1411020 | without dk, rso |
| 2111-1411020 | without DC, with (adjustable with scanner) |
| 2111-1411020-70 | BOSCH, without dc, with |
| 2111-1411020-70 | BOSCH, without dc, with |
"Bosch MP7.0"
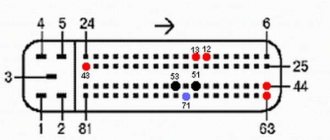
As a rule, this type of controller is released onto the market and installed at the factory in a single volume. Has a standard 55-pin connector. Capable of working with recrossing on other types of ECM.
"Bosch M7.9.7"
These brains began to be part of the car at the end of 2003. This controller has its own connector, which is incompatible with connectors produced before this model. This type of ECU is installed on VAZ with EURO-2 and EURO-3 toxicity standards. This ECM is lighter weight and smaller in size than previous models. There is also a more reliable connector with increased reliability. They include a switch, which will generally increase the reliability of the controller.
How to determine the condition of VAZ electronic units
On VAZ 2108 - 2115 cars, the ECU is located in the front right side of the cabin, just below the glove compartment drawer. To determine the state of the ECU, as well as read the error logs in its memory, you need to connect to the diagnostic connector, which is installed in different places on different models. After all, the “check engine” signal informs about the presence of an engine malfunction, but does not indicate which one. And the error code that is displayed on the dashboard of modern VAZ cars is not very informative.
Diagnostic connectors are located:
- on VAZ 2108 - 21099 with a low panel next to the ECU, under the glove compartment;
- on VAZ 2108 - 21099 with a high panel and 2113 - 2115 inside the center console;
- on VAZ 2108 - 2115 with a Europanel on the panel next to the passenger door.
To determine the state of the ECU and read the error log, you need to connect a diagnostic scanner to the connector. Despite the fact that the cost of inexpensive scanner models is 2–4 thousand rubles, it is advisable to entrust this work to a specialist with professional equipment. After all, it is not enough to extract the error log from memory and decipher it using the reference book. It is necessary to determine what caused the engine to malfunction. Only an experienced diagnostician who is well versed in the repair of injection engines and fuel systems can correctly interpret the scanner readings.
Which mass air flow sensor should I install instead of the faulty one?
The Bosch 116 mass air flow sensor or mass air flow sensor is a regulator designed to control the volume of air that enters the engine. This controller is one of the elements of electronic engine control systems with fuel injection. In this article we will try to answer the question of how models 116 and 037 differ.
Characteristic
On VAZ cars, the mass air flow sensor is mounted between the air filter element and the throttle hose. Today, products from the manufacturer Bosch are very popular among compatriots. Regardless of whether it is a universal Bosch sensor or, for example, spark plugs, quality from a German manufacturer can always give a head start to domestic products. Let's look at the main characteristics of regulators models 116 and 037.
DMRV 116 is designed to control and convert the air flow that enters the motor into voltage. The data transmitted by the regulator makes it possible to determine the operating mode of the power unit and calculate the cyclic filling of the cylinders with air flow. This filling is carried out in steady-state operating modes of the motor, which last no more than 0.1 seconds.
Let's look at the technical features that Bosch 0 280 218 116 has:
- the regulator operates on the principle of measuring air flow;
- the device provides accurate data, which ensures optimal fuel consumption;
- operating range varies from 8 to 550 kg/h;
- the output pulse level when measuring the range from 0 to 100% will be about 0.05-5 volts;
- As for power supply, the controller is powered from the vehicle’s electrical network, that is, 12 volts is enough for it;
- current consumption is about 0.5 ampere;
- the regulator can function normally in the operating range from 45 degrees below zero to 120 degrees;
- The service life of the Bosch 116 mass air flow sensor is about 3 thousand hours.
As for the mass air flow sensor 037 from Bosch, the technical features will be similar. The controller consists of two main elements - working and control, as well as a heating resistor device. The air that enters the engine cools one of the controllers, while the electronic module converts the temperature differences between the controllers. In the event that sensor 280 218 037 fails, its options will be performed by TPS.
As mentioned above, the technical features of the models are the same:
- the operating range for normal operation varies in the region of 8-550 kg/h;
- when operating correctly, the controller will provide accurate data, making it possible to achieve optimal gas mileage (of course, if the engine is running in normal mode);
- since the element is used in a car, it is logical that it should be powered by 12 volts;
- the controller consumes about 0.5 ampere of current;
- the part can operate normally both at 45 degrees below zero and at 120 degrees of heat, this is its operating range;
- service life is at least 3 thousand hours;
- unlike model 116, the new mass air flow sensor 037 during calculations can produce an error of 2.5 percent (both downward and upward).
What is the difference between sensors 037 and 116?
How can the regulators of these models differ from each other and is it possible to install 116 instead of 037? There are differences between these controllers, and the point is not in the MAF pinout. After all, if these models were the same, what would be the point of giving them different names?
Weight between engine and body
Line “31”, popularly called “ground”, “minus” or “negative circuit”, is very important for a car. And not only for electrical equipment, but also for many other systems, including the engine or automatic transmission.
Almost all cars have a single-wire on-board network system and the role of the “minus” in this circuit is played by the metal parts of the body. This greatly reduces the number of wires and reduces the cost of the car.
It turns out that all participants in this chain have their own connection to the body - instrument panel, headlights, ECU, engine, etc.
Despite the visual integrity of these connections, over time, due to oxidation and corrosion, the contact slowly and imperceptibly deteriorates, which leads to voltage drops when powerful consumers are turned on or disruption of the system.
I would divide the mass connections into main and local. Let's say that the connection of the head light masses is local and if this connection is disrupted, only the head light will suffer. But if the ground contact from the battery to the body is broken, the entire on-board network will suffer, and this may cause problems in the operation of the engine and other important components and assemblies.
This is how the voltage of the on-board network with problematic masses looks like on the diagnostic graphs
And here is the graph after mass prevention of battery - engine - body
Where is the fan relay VAZ-21099 injector
Quite often a problem arises with the Ninety-Nine when the engine fan does not turn on and the coolant begins to boil. If such a malfunction occurs, first of all they check the functionality of the fan itself by applying voltage directly to it from the battery, but there may be other problems.
In order to check the entire circuit, it is important to find where the VAZ-21099 injector fan relay is located, since it is responsible for turning on the airflow. We find this part in the front of the car, on the passenger side, it is installed under the glove compartment, at the passenger’s feet.
The required relay in the picture is indicated by an orange circle, and here you will also find a fuse that blows when the cooling fan is short-circuited.
Operating principle of the controller (ECU)
Throughout the entire operation of the engine, the electronic engine control unit receives, processes, and controls systems and sensors that affect both engine operation and secondary engine elements (exhaust system). The controller uses data from the following sensors:
- DPKV (Crankshaft Position Sensor).
- DF (Phase sensor).
- MAF (instant air flow sensor).
- DTOZH (Coolant temperature sensor).
- TPS (Throttle Position Sensor).
- DK (oxygen sensor).
- DD (Knock Sensor).
- DS (Speed Sensor).
- And other sensors.
Receiving data from the sources listed above, the ECU controls the operation of the following sensors and systems:
- Fuel system (Fuel pump, pressure regulator, injectors).
- Ignition system.
- Idle speed regulator (IAC, IAC).
- Adsorber.
- Radiator fan.
- Self-diagnosis system.
Also, the ECM (ecu) has three types of memory:
- Programmable read-only memory (PROM); Contains the so-called firmware, i.e. a program containing the main calibration readings and engine control algorithm. This memory is not erased when the power is turned off and is permanent. Amenable to reprogramming and chip tuning.
- Random Access Memory (RAM); It is a temporary memory in which system errors and measured parameters are stored. This memory is erased when the power is turned off.
- Electrically reprogrammable memory device (EPROM). This type of memory can be said to be the protection of the car. It temporarily stores codes and passwords for the vehicle's anti-theft system. The immobilizer and EEPROM are compared with data, after which the engine can be started.
One thought on “Location of components and parts on the injection car VAZ-21099”
I have a fan relay on a 2109 injector, located to the left of the one marked in the photo
The Electronic Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the “computer” that controls the entire vehicle system. The ECU affects both the operation of an individual sensor and the entire vehicle. Therefore, the electronic engine control unit is very important in a modern car.
The ECU is most often replaced by the following terms: Electronic engine control system (ECM), controller, brains, firmware. Therefore, if you hear one of these terms, then know that we are talking about the “brains”, the main processor of your car. In other words, ECM, ECU, CONTROLLER are one and the same.