ECU
- an abbreviation for the term “electronic engine control unit” in English is Powertrain Control Module, which is one of the main parts of the vehicle’s engine control system.
This block is often called the “brain” of the engine control system. The ECU receives and processes incoming information from most vehicle sensors and, using the collected data, determines the control action on most control systems. photo gallery:
Control unit software modules:
Functional
. Receives and processes signals from sensors, and also exerts a control effect on individual vehicle devices.
Controlling
. Checks and corrects signals. Most Electronic Control Units are a programmed device, so the user can reprogram the device at any time. This function is especially relevant for those who decide to do engine tuning: installing a turbine and hypercooler, making changes to the fuel system, or installing additional equipment to process additional types of fuel.
How input and output signal conditioners work
As already stated, there is no point in an ECU if there are no sensors connected to it. They measure physical parameters, convert the measurement results into an electrical signal and then send it to the control unit. The signal from the sensor passes through a shaper, in which it is amplified or attenuated - this is called level matching. Input drivers also protect the ECU from overvoltage. Shapers work with the following signals:
- Analog;
- Discrete;
- Frequency.
Shapers are divided into subtypes depending on what signals they work with. This is due to the fact that different types of signals have different parameters . For example:
- Analog signals change continuously over time. An example is the signal from the throttle position sensor. Continuously incoming signals pass through processing into the formers, and then go to the analog-to-digital converter and to the processor part of the ECU;
- Discrete signals change abruptly and are intermittent. As an example, we can take the ignition switch signal. Its changes occur abruptly, and the signal itself enters first the converter, and then directly to the processor part of the ECU;
- Frequency signals are the most interesting. They don't just change the frequency - these changes themselves carry information about real changes in the quantities that the sensor measures. Accordingly, the processing of these signals will be difficult. First, they are limited in amplitude and then fed to the timer input.
Spare parts for Nissan primera
Steering rack/mechanism oil seal (see standard sizes)
PRIMERA sedan (P11) (09.96 - 01.02)
Spare parts for Chery beat
Anti-rain BEAT (11-)
Special microcircuits, otherwise called drivers, are responsible for generating output signals. They amplify the power signals and also protect the controller outputs from short circuits and overloads . Drivers are often called “smart” because if they operate abnormally, they inform the central processor that an error has occurred. Output shapers are divided into subtypes according to the power of the signal with which they work.
Functions performed by the electronic engine control unit:
- Optimization, adjustment and control of fuel injection;
- Correction of the damper position at any stroke;
- Optimization of systems responsible for ignition, prevention of problems associated with it;
- Regulation of exhaust gases and management of spent fuel vapor collection systems;
- Advanced regulation of most gas control systems and control of their distribution;
- Controlling the temperature of the cooling fluid.
Electronic engine control unit
connects to all vehicle electronics and works in conjunction with them.
Conclusion
The engine ECU is perhaps the most critical element of a car's on-board electrical system. Thanks to it, the power unit has optimal performance, exhaust composition and high stability. ECU malfunctions occur frequently, but in most cases they are caused by a problem with some electrical or electromechanical element of the car. If the problem lies precisely in the ECU, then often the only way to solve it is... an expensive replacement of the unit. We advise you to contact trusted specialists for diagnostics, and only then make plans for purchasing the necessary spare parts and their further installation.
The main causes of malfunctions in the ECU:
- Interference with electronic systems of a car by an unqualified worker;
- “Lighting up” with the car engine running;
- Incorrect polarity connection of the car battery;
- Removing the battery terminal with the engine running;
- Starting the starter with the power bus disconnected;
- Electrode contact with sensors or wiring during welding work;
- Excessive humidity, which will cause water to enter the ECU;
- Malfunction of parts of the ignition system;
- Short circuit or partial break in the vehicle wiring.
If a malfunction occurs, you should immediately take the car to a service center.
In service conditions, only basic internal fault codes can be determined. The unit cannot be repaired; it must be replaced entirely.
You can independently troubleshoot by following the universal algorithm:
- visual inspection of the electronic engine control unit;
- scanning using special equipment;
- checking the serviceability of the device by replacing it;
- monitoring functions to ensure the operation of the on-board vehicle;
- full check of on-board performance functions.
Before performing a visual inspection or replacement, you must ensure that:
- there is no fuel in the gas tank;
- there is no plug in the exhaust pipe;
- battery terminals are securely tightened;
- the car's electrical wiring is not damaged;
- The ignition key is genuine.
One important point to note is that when you change the control unit, the main work is connecting to the wiring through the appropriate connectors. Connection is often complicated by inaccessibility to the location of the ECU.
It must be remembered that in any case, before connecting the unit, you need to disconnect the terminal from the battery
, otherwise the probability of failure of the electronic unit is very high.
And along with it, the consequences will affect the operation of the power supply, transmission, exhaust system and other elements. Since for proper functioning, the electronic unit needs signals from all sensors, it requires normal voltage from the battery, a good connection to ground and the ability to send control pulses and signals to all actuators of the electronic system.
A few words about (firmware) CHIP tuning
Of course, I already have an article about this process, read it . But now I’ll repeat myself a little. CHIP tuning is a software improvement of the standard “firmware” (microprogram), which is installed from the factory. Now there are a lot of companies that do this type of work, but it is worth remembering that the firmware must also be original or adapted for your car. The new program will increase power, improve smoothness, and also make fuel consumption more economical. By the way, the firmware also regulates the operation of your automatic transmission, shifting, etc.
I will say this, with the help of CHIP tuning you can achieve an increase in power of 10% and sometimes even higher, if we say, remove the catalyst .
This is how the article turned out, now watch the short video.
This is where I end, read our AUTOBLOG, it will be interesting.
Similar news
- What is wheel alignment
- Parktronic, what is it?
- What is ESP?
Add a comment Cancel reply
FAQ
What is an ECU?
ECU stands for “electronic control unit”, which is the brain of a modern car and is controlled by electronic sensors. It is a block with data transmission buses between sensors and the control controller.
What's inside the ECU?
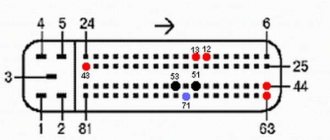
Inside the metal case of the ECU there is a board, also known as a controller, on which the firmware with the operating algorithm is stored. There's nothing else there. The board has a processor and permanent and RAM devices. The housing is equipped with plug pins for inputting information and outputting signals.
How does the electronic control unit work?
The ECU receives data from a huge number of sensors and vehicle systems, processes them according to specified algorithms and, based on the information received, issues signals to the control electronics. In this way, the operation of the engine or other systems is regulated. In the engine, the ECU is responsible, for example, for controlling the injection and ignition system, regulating exhaust gases and other settings.
Where is?
I have already touched a little on the location of this block. BUT now I want to repeat it a little. There are only two main locations:
- Vehicle interior . This could be under the panel; for example, in our VAZs it is located in the area of the heater radiator. Also under the rear seat, on many business class foreign cars it is located there. I also read somewhere on the Internet that it could be in the trunk of a car.
- Under the hood . NOT the best place, because there is mud, snow, water and other delights. Usually located next to the battery (like mine), or next to the fuse box. As a rule, such ECU units are well sealed.
So finding it is not that difficult. Even an ordinary driver will be able to disassemble part of the instrument panel (as a rule, it is not so difficult to remove), or look under the hood of his car. If you see a box with two cables coming from it, this is the ECU. But I don’t advise you to get into it - if you don’t understand anything, it’s better to trust the professionals.
Table of ECM masses in various vehicles
The mass in the ECM is usually the car body. If any of the contacts with ground loses reliability, the electrical circuit is disrupted, and the quality of system operation decreases. For example, the engine begins to randomly change its operating mode, gaining or decreasing speed without driver intervention. To cope with such a problem, you need to know the grounding locations of the ECM.
| Models | Grounding points |
| AvtoVAZ 2108-9 and 13-15 family 1. | The ECM weight is taken from the engine, from the bolts securing the plug on the right side of the cylinder head. In BOSCH 7.9.7 or January 7.2 controllers, the ground is taken from the pin that secures the dashboard center console frame to the floor tunnel (inside the center console, under the ashtray). |
| VAZ 2110-12 family, 1.5L. | From the bolts on the left side of the block head. |
| Family VAZ 2114, 21124 1.6L. | BOSCH controllers 7.9.7 or January 7.2. Weight for four ignition coils from the M6 bolt, weight to the ECM - from the stud on the ECU mounting bracket, on the left. On the stud - from the engine shield. Problems are possible here; you need to tighten the constantly loosening nut. |
| Niva with Bosch MP 7.0 controller. | From the bolts securing the plug in place of the ignition distributor - distributor. |
| Niva with Bosch M 7.9.7 controller. | The mass is taken from the body, from its mounting studs. A common problem is that the terminal is much thicker than necessary to press the castle washer evenly against the body. |
| Chevrolet Niva with Bosch MP 7.0 controller. | The ground is taken from the engine, from the M8 studs in its lower left part, under the ignition module. |
| Priora | C on the ECU mount (on the bracket). |
| Kalina | The ground contact is located on the right side of the engine, on the intake manifold mounting bracket. |
| Model range 2104-07. | Old controllers. The weight is taken from the bolt that attaches the ignition module mounting bracket to the engine. |
| Gazelle with engine 405, 406 | From a welded pin on the platform above the right side member, under the overhang of the engine shield. |
| UAZ Patriot with Mikas 11 E2 | Contact from the body through the welded pin at the bottom of the left mudguard. |