Various sensors are responsible for the operation of all systems of a modern car. They take readings and transmit them to the electronic engine control unit (ECU). If the sensor malfunctions, an error is stored in the memory, and in some cases a Check Engine error appears on the instrument panel.
Where are the sensors located?
All modern Lada cars (Granta, Kalina, Priora, Vesta, Largus, Niva or Lada XRAY) are equipped with domestic VAZ engines. The location of the sensors on these motors is the same:
Elements of the electronic engine control system of the VAZ 11186/11189: 1* – controller; 2* – crankshaft position sensor; 3* – control oxygen concentration sensor; 4* – diagnostic block; 5* – diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor; 6 – throttle control unit; 7* – vehicle speed sensor; 8* – adsorber purge valve; 9* – gas pedal module; 10* – brake signal switch; 11* – clutch pedal position sensor; 12 – battery; 13 – mass air flow sensor; 14 – coolant temperature sensor; 15 – ignition coil; 16 – knock sensor; 17 – spark plugs; 18* – nozzles. *The item is not visible in the photo.
Location of ECM elements in the vehicle interior (for clarity, without dashboard): 1 – clutch pedal position sensor; 2 – brake signal switch; 3 – gas pedal module; 4 – controller.
All engine sensors 21116, 21126, 21127
Each sensor is equipped with a connector fixed to its body:
The second contact of the sensor is the housing itself
The smooth operation of the engine is ensured by a set of elements:
- The air flow sensor (AFS) is part of the intake system. Not used on engines 21127. The part is designated as 11180-1130010;
- Two throttle position sensors - variable resistors, built into the throttle pipe;
- The antifreeze temperature sensor is a thermistor with a screw fastening, screwed into the thermostat housing. Catalog number – 21120-3851010;
- The knock sensor is a piezoelectric element with two leads, mounted on the cylinder block body. Catalog number – 21120-3855020;
- Two oxygen sensors (OS), diagnostic and control, are equipped with a screw mount and are screwed into the exhaust pipe housing. 21074-3850010 is the designation of each module;
- The speed sensor is an electronic module, mounted on the top of the gearbox housing. Catalog designation – 21700-3843010;
- The crankshaft position sensor (CPS) is an electronic module mounted on the oil pump housing. Designated as 21120-3847010;
- The phase sensor is an electronic module designated 21120-3706040. 21116 is not used in the engine design;
- Oil pressure sensor - has a screw mount, designated as 11180-3829010.
The element indicated under number “9” will be installed at different points depending on the configuration (see photo). The third figure shows where sensor “8” is attached:
The design of the resonant intake system uses a separate sensor that measures air temperature and pressure. The element is designated as 21800-1413010:
Engine air pressure and temperature sensor 21127
The design of the throttle valve modules was not considered. The bug has been corrected below.
For different Kalina-2 engines, their own module, unique in design, is suitable, containing an electrically driven throttle valve:
- 21126-1148010 – the element is intended for internal combustion engine 21126;
- 21127-1148010 – part of the engine 21127 design;
- 21116-1148010 – part of the intake tract of the 8-valve engine (21116).
The module body is made of light alloys and is equipped with a connector to which the contacts of the sensors and the electric motor are connected.
Engine throttle assembly 21126
If necessary, it is better to replace the module as an assembly rather than try to repair it.
When manipulating electrical equipment, you need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery. The requirement also applies to the operation of replacing sensors.
Coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH)
Designed to measure coolant temperature in the engine cooling system. Based on the indicators, the ECU adjusts the crankshaft speed, the composition of the fuel-air mixture and the ignition timing. The sensor practically does not break, but sometimes it lies. Quite often the wires at the base of the connector fray so much that there is nothing to even solder to. The coolant temperature sensor is installed in the thermostat cover.
See Replacing and checking DTOZH.
Video “Checking DPKV”
In the video below you will learn how to check the performance of the DPKV (the author of the video is IZO)))LENTA).
Welcome! Coolant temperature sensors - if we talk specifically about the Lada Kalina car, then there are only two sensor data in it, one goes to the controller (This is the brains, to put it simply), and the other to the device, that is, one sensor shows what the temperature of the coolant in the car is and displays this is all for the device, and another one (which gives readings to the controller) turns on the cooling system fan when the car is boiling, and also regulates the fuel-air mixture (Simply put, when the car is cold, thanks to this sensor it will warm up faster, because the sensor richens the mixture and the temperature immediately rises), both of these sensors are important and if they fail they will cause quite a lot of trouble, especially for the sensor that gives readings to the device, if it stops working, then you simply will not know the temperature of the coolant and in connection with which you can overheat the engine.
Knock sensor (DS)
Designed to determine the moment of occurrence of high-frequency vibrations of the cylinder block that occur during detonation combustion of fuel. Based on the sensor signal, the electronic engine control unit selects the optimal ignition timing, which allows for the most complete and efficient combustion of the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinders, as well as automatically adjusting the ignition timing for fuels with different octane numbers. The knock sensor is located on the front wall of the cylinder block between the 2nd and 3rd cylinders.
See “Replacing and Inspecting the Knock Sensor.”
Troubleshooting
The sensor that determines the angle of rotation is a variable resistor with 3 terminals. The thermistor, as well as the piezoelectric element, are equipped with two contacts. The crankshaft position sensor consists of a solenoid and a magnet. But speed and phase sensors contain electronics in their design.
Note that failure of the phase sensor does not lead to breakdown or shutdown of the engine. The same can be said about the speed meter.
Each of the two oxygen sensors is a complex electronic device. But the reliability of their circuits can be considered high. Hall effect sensors, used for speed and phase control, fail more often than the oxygen analyzer.
Oxygen sensor for engines 21116, 26, 27
A variable resistor used in any design is duplicated. If the indicators obtained from two “horseshoes” differ, then the Check lamp turns on.
All errors, including breaks and short circuits of sensor contacts, are constantly monitored by the ECU.
Let's say the Check Engine light doesn't come on. If you feel that the power has decreased and the dynamics have deteriorated, try replacing one of the elements:
- Knock sensor;
- Phase sensor;
- One of the DCs.
We wish you success.
Crankshaft position sensor (CPS)
The sensor provides the control unit with information about the speed and angular position of the crankshaft. Based on the sensor signals, the ECU calculates the phase and duration of the control pulses for the injectors and ignition coil. If it malfunctions (no signal), the engine will not start. It is located in the tide hole of the oil pump cover.
See Replacing and checking DPKV.
Smart choice
The Lada Kalina 8 valve has certain differences from the 16 valve engine. However, automotive specialists sometimes install a mechanism with 8 valves to 16, and the engine works correctly.
The main differences between similar system elements:
- form;
- connector size.
The Kalina 8 cl phase sensor may be distinguished by the absence of a special slot required for the signal disk. This product cannot be installed on an engine with sixteen valves. It operates with a pin mounted on the camshaft (at the very end).
To avoid situations of inconsistency, purchase a mechanism according to the characteristics of the engine. No need to pay attention to the manufacturer's markings. The spare part number according to the VAZ catalog (Granta, Largus, Kalina, Priora) will always be the same:
- engine with eight valves - 21110370604000;
- 16-valve – 21120370604000.
Definition of failure
The device is located close to the cylinder head, on the power unit. It is easy to understand the first signs of poor functioning of the mechanism, especially for an experienced car enthusiast.
Here are the main criteria for recognizing a breakdown:
- a light comes on and goes out, designed to constantly monitor the engine while turning the ignition key in the car;
- “Check engine” lights up on the dashboard after the starter makes three to four revolutions and the engine comes into action. The sensor will be triggered if the electronic control unit does not receive the necessary information and has to use data from the DPKV;
- engine dynamics become worse - the vehicle slowly picks up speed (this is easy to notice when driving downhill). In this case, there are three reasons for the problem. The first - the camshaft sensor is broken, the second - the mass air flow sensor is broken, the third - the compression is reduced;
- high fuel consumption - this “symptom” is not very accurate and has a number of possible causes. You shouldn’t take it as a separate criterion for a problem, but you can use it as one of several.
If the mechanism fails, the “Check engine” will light up, and the system will display error “P0340”. Such a moment means a 100% malfunction. If this happens, you need to check the device. After a detailed diagnosis, it is recommended to replace the faulty parts.
Camshaft position sensor (phase sensor)
Designed to generate a signal by which the ECU determines the top dead center of the piston of the first cylinder during the compression stroke. The operating principle of the sensor is based on the Hall effect. If the sensor is faulty, the ECU switches the system to backup mode. The engine may run erratically, stall, or have difficulty starting. DPRV cannot be repaired. If it malfunctions, it is replaced with a new one.
See “Replacing and checking the phase sensor (PPRV) on LADA”.
Method number 1. Visual control
The factory software has settings that provide for a running-in mode for the power plant and its further operation under average conditions. A malfunction of the mass air flow sensor, as noted above, leads to either an over-enrichment or a depletion of the fuel mixture with gasoline or diesel fuel, which negatively affects the functioning of the engine and can lead to serious damage.
DBP and DTV
The absolute pressure sensor (MAP) and the air temperature sensor (ATS) are used on VAZ 21129 and VAZ 21179 engines. They are combined in one housing, which is installed on the receiver of the intake module. They are described in more detail here.
Idle air control (IAC)
The IAC is installed on the throttle body. Structurally, it is similar to a DC motor with a worm gear. At the tip of the sensor there is a cone head that closes or opens the idle passage in the throttle, thereby regulating the air supply to the engine at idle. This sensor is installed only on a mechanical throttle and is involved in operation only at idle.
Signs of malfunction:
- The engine stalls at idle;
- The revolutions are floating;
- When starting, you must press on the gas pedal;
Oxygen sensor (OS) or lambda probe
The oxygen concentration sensor allows you to estimate the amount of remaining unburned fuel or oxygen in the exhaust gases. The signal is used by the control unit to maintain the optimal ratio of air to gasoline in the combustion chamber. Installed in the catalytic collector before the exhaust gas catalytic converter.
Refer to Oxygen Sensor Replacement and Testing.
Lada Kalina high fuel consumption reasons
There are four main models of the Lada Kalina passenger car:
- sedan - has a closed body, with 2-3 rows of seats for the driver and passengers, the trunk is separated from the car interior, there is no lifting door in the rear wall;
- station wagon - has a closed cargo-passenger body, one of the sedan variants, which has an enlarged luggage compartment, is equipped with a lifting door in the rear wall;
- hatchback - has a body with 1-2 rows of driver and passenger seats, with a shortened rear overhang (hence the name - “hatchback” means “short”) and a smaller luggage compartment, equipped with a lift-up door in the rear wall;
- sport - is a sports version, which is equipped with a number of special parts - a bumper, an exhaust pipe tip, sports pedals, alloy wheels, a SAAZ Sport sports suspension, front and rear disc brakes, an original reinforced gearbox.
As you can see, the main difference between each model is its body type. Gasoline consumption (unleaded AI-95) is calculated in liters over a driving cycle, which is 100 kilometers.
In this case, the following parameters of the vehicle itself are taken into account:
- Engine size (Lada Kalina comes in two types - 1.4 l and 1.6 l).
- Number of valves (for Lada Kalina - 8 and 16).
Experts have prepared an information table that shows the factory fuel consumption indicators for each model of the Lada Kalina passenger car, taking into account the mandatory parameters.
Model Lada Kalina
Mass air flow sensor (MAF)
This important sensor is located behind the engine air filter. It is also called an air flow meter. Its purpose is to estimate the amount of air entering the car engine. Based on the information received from the sensor, the electronic control unit (ECU) calculates the required amount of fuel to maintain the stoichiometric fuel-to-air ratio for the given engine operating conditions.
See “How to check the mass air flow sensor on LADA cars”
Location of sensors on viburnum 8 valves
This data serves to uniquely install spare parts during a certain production period, as manufacturers are constantly upgrading cars off the assembly line.
Modern cars are complex units, replete with a large number of electronic modules. Sensitive sensors transmit information about the state of the blocks in real time, which allows the ECU to properly control the processes occurring in the motor.
Despite sufficient reliability, Lada Kalina sensors can fail, thereby disrupting the performance of the entire power plant. Therefore, to repair or replace them, you will need to know where they are.
The Lada Kalina air flow sensor is located in the drain manifold, directly behind the air filter. The sensor is also sometimes called an oxygen flow meter. The device is responsible for measuring and transmitting information about the amount of air entering the engine.
However, it should be taken into account that, on individual vehicles, the location of the sensor may differ.
Some motorists ask questions about where the antifreeze temperature sensor is located on the Lada Kalina. The question is quite rare - the sensor does not fail often. The insert is responsible for transmitting information about the state of the cooler, which helps the ECU correctly distribute the load.
The manufacturer installed the sensor itself on the thermostat housing.
DD – knock sensor
The next sensitive element is part of the engine protection system against detonation of the fuel mixture. The part picks up vibrations and transmits information to the BC.
The element is located in the engine block housing, between cylinders 2 and 3.
When asking where the Lada Kalina idle speed sensor is located, just look into the throttle valve, where the required part is installed in the bypass channel.
The element itself protects the engine from overflowing gasoline at idle and regulates the amount of gasoline. If a part fails, the power plant does not operate stably, sneezes, coughs or stalls.
You will also need diagnostics when the car does not behave correctly:
- engine speed fluctuates;
- the stability of the power plant is disrupted;
- After starting the engine immediately stalls.
The gas pedal will tell you that the DXH may be the cause of the trouble. For example, the engine has started and the driver holds the pedal down - everything is fine. As soon as you release the lever, the power plant begins to act up, sneeze or stall.
The next sensor that often breaks is the speed sensor or speedometer. The insert is located on the clutch housing and looks like a connector screwed on with two bolts.
It is quite simple to determine whether a part is broken - if the speedometer on your car stops working, you should check it.
The oil pressure sensor is responsible for the correct lubrication of the crankcase compartment and the condition of its ventilation system. If there is a leak in the device, the sensor transmits information to the computer.
The part is located next to the timing belt casing and can be changed using key No. 13.
Intake duct length control sensor
The Lada Kalina is equipped with a throttle with adjustable channel length. The specific design allows for maximum engine efficiency at different loads and crankshaft speeds.
The corresponding sensor is responsible for reducing or increasing the channels themselves. The part is located above the camshaft pulleys and looks like a black plastic fitting.
There are also a large number of other sensors in the car that are responsible for the main or auxiliary systems. A complete list of sensitive elements can be found in the vehicle's service manual.
Vehicle speed sensor (VS)
Serves to measure vehicle speed and transmit this information to the ECU. Its failure is directly related to a non-functioning speedometer. The vehicle speed sensor is installed on top of the clutch housing, above the right front wheel drive inner joint housing. Replacing it is very simple.
Replacing the device
Installing a new device is actually quite simple. To do this you will need a minimal set of tools and very little time:
- disconnect the battery;
- compress the spring clamp of the device;
- remove the cable block from the sensor;
- unscrew the fastening screws;
- remove the sensor, install a new one and do all the same manipulations in reverse order.
This is how the rough road sensor is changed on most domestic cars; on foreign cars this process may look a little different.
Intake system channel length control valve
AVTOVAZ began installing an intake manifold with variable geometry starting with the VAZ-21127 engine. This design allows for maximum torque at low speeds and maximum power at high speeds. The length of the intake manifold is adjusted (switching from one length to another) using a valve that is part of the engine management system.
See how to replace and test the sensor.
Malfunctions in the fuel system - Replacing the air flow sensor
Any injector consists of a mechanical executive part and an electronic control part, and problems can arise in both of them, which will lead to a drop in power. sport is a sports version, which is equipped with a number of special parts: a bumper, an exhaust pipe tip, sports pedal pads, alloy wheels, a SAAZ Sport sports suspension, front and rear disc brakes, and an original reinforced gearbox.
| Modification | Consumption city, l/100 km | Route, l/100 km | Combined cycle consumption, l/100 km | Acceleration, sec up to 100 km/h |
| VAZ-11180, 5-speed Manual transmission | 9,8 | 6,1 | 7,8 | 13 |
| VAZ-21126, 5-speed Manual transmission | 9,4 | 5,8 | 7,2 | 12 |
| VAZ-21126, 4-st. Automatic transmission | 9,9 | 6,1 | 7,6 | 12,5 |
| VAZ-21127, 5-st. Manual transmission | 8,6 | 5,6 | 6,7 | 11 |
| VAZ-21127, 5-st. Automatic transmission (robot) | 8,6 | 5,6 | 6,7 | 11,2 |
Clutch and brake sensors
Based on the signals from the clutch pedal position sensor and the brake light switch, the controller distinguishes between pressed and unpressed pedal positions. When the clutch pedal is pressed, the controller disables engine load regulation. Both sensors are located on the pedal assembly.
See "Replacing and Inspecting the Clutch Pedal Sensor" and "Replacing and Inspecting the Brake Pedal Sensor."
Some vehicle versions use an electronic throttle valve drive (E-gas). Let us remind you that in order to understand what errors are recorded in the ECU, you need to decipher them.
Keywords: Lada Granta sensors | Lada Kalina sensors | Lada Priora sensors | Lada Granta engine | Lada Kalina engine | Lada Priora engine | Lada Vesta sensors | Lada Largus sensors | 4x4 sensors | lada xray sensors | lada xray engine | Lada Vesta engine | Lada Largus engine | 4x4 engine | ECM Lada Vesta | ECM Lada XRAY | ECM Lada Largus | ECM Lada Granta | ECM Lada Kalina | ECM Lada Priora | ECM 4x4 | Niva sensors | Niva engine | esud niva | universal article
2 0 0 0 0 0
Share on social networks:
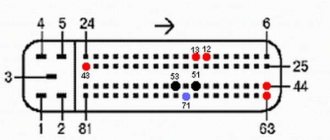
Connection diagram of sensors to the ECU
Let's look at the ECU module connector to understand exactly how the pins are numbered in it:
ECU M74: module with different firmware suitable for different internal combustion engines
The purpose of the terminals of section “1” is given below:
Modern motors are equipped with such a useful element of the on-board control system as a phase sensor. It is located on the left side of the Lada Kalina engine head with 16 valves and is designed to determine the angle of rotation of the camshaft at a given moment. Information from the sensor is sent to the ECU, where it is processed, after which the controller performs control or corrective actions. Without the presence of such a sensor, it is almost impossible to achieve proper operation of the engine in the Lada Kalina 16 valves, because the valve timing will not be correctly adjusted.
After receiving information from the sensor, the control function of the ECU is reduced to setting the correct ignition timing and timely supply of the required volume of fuel to each cylinder individually in Lada Kalina 16 valves. All this functionality ensures smooth, stable operation of the engine at different speeds and when using fuel of different quality.
Driving style and operating conditions. First generation
inoperative, that when the control controller is turned off, the unit begins to operate in emergency mode, fuel consumption, and accordingly, fuel can be increased. Video by the author about demonstrating a failed regulator in Sandro’s garage. Terrain type Lada Kalina, 1.4 l Lada Kalina, 1.6 l Fuel consumption l 100 km Average l 100 km Fuel consumption l 100 km Average l 100 km Urban 6.8-11.5 8.47 7.0 -12 9.5 Road 5.0-8.5 6.18 5.6-9 6.8 Mixed 6.5-8.3 7.29 7.0-9.0 8.0.