Removal and installation of TPS
Removal
1. Turn off the ignition.
2. Disconnect the wire from the negative terminal of the battery (spanner 10).
3. Disconnect the wiring harness connector from the sensor.
4. Unscrew the two screws securing the sensor to the throttle pipe and remove the sensor from the throttle pipe (using a Phillips screwdriver).
Installation
1. Install the sensor on the throttle pipe. In this case, the throttle valve should be in the normally closed position.
2. Tighten the two sensor mounting screws (Phillips screwdriver).
3. Connect the wiring harness block to the sensor.
4. Connect the wire to the negative terminal of the battery (spanner 10).
5. Check the sensor output signal as follows:
- connect the diagnostic tool, select the “Parameters” mode; ADC channels, POL.D.Z.”;
- with the ignition on and the throttle valve closed, the sensor output voltage should be 0.3...0.7 V. Then slowly open the throttle valve - the sensor output voltage should increase to 4.1...5 V. If it is outside the ranges, replace sensor.
How does GTZ work?
The functioning mechanism of a classic brake cylinder is as follows.
- When the car pedal is pressed, both pistons move forward. This allows all fluids to be pushed into the circuit tubes. When pressure is applied, the brake wheel cylinders are activated. They compress the pads on the discs.
- The liquid, or rather some part of it that did not have time to penetrate the tubes, flows into the expansion container through special through holes.
- When the driver releases the pedal, the springs push the pistons out in the reverse order. As a result, they acquire their original position. The liquid coming from the tubes and reservoir again ensures that the cylinder is filled.
- To compensate for the expansion that occurs with the brake fluid, the developers create several additional holes that lead to the expansion tank.
If you need to replace the brake master cylinder, you need to contact our company. We employ highly qualified craftsmen to replace this part, who will carry out the work as cheaply and accurately as possible.
Self-replacement of the GTZ on Lada Kalina
The need to replace the brake master cylinder (MBC) arises when characteristic signs of a malfunction occur. Braking becomes ineffective, the pads are not fully extended, the drums and discs heat up, the pedal sinks or braking occurs only at the end of the pedal stroke.
If you experience any of the above, most likely the GTZ has failed. There is nothing terrible about this, since replacing the master brake cylinder is far from the most difficult task, and almost anyone can do it.
To work you need to have:
- New GTZ;
- Key "13" + head "13" with ratchet, cardan and extension;
- WD-40 (preferably), container for TJ;
- Straight arms and some free time.
Replacing guides and their lubrication
So, the first thing you need to do is remove the wheel bolts. Then lift the car with a jack, and finally unscrew the bolts and remove the front wheel. Then, using a flat-head screwdriver, bend the locking washers of the caliper bolts and unscrew the top bolt, as shown in the photo below.
We disengage the brake hose from the front strut, then use a screwdriver to push the cylinder down a little so that you can then tilt the bracket up without any problems.
And we fold it back, as mentioned above.
Now we have access to the upper caliper pin. With a slight movement of your hand, you can remove it by slightly pulling it to the side, overcoming the force of the boot.
Now that the finger is removed, thoroughly rinse it with cleaner and the boot, if it is intact. If necessary, take a new finger and boot.
Now you can apply new lubricant in small quantities so that excess does not get on the active working surfaces (brake pads and discs). For this procedure, I used MC1600 lubricant, which at one time was actively advertised in videos on YouTube and on third-party Internet sites. But I took it not because of advertising, but because of the lack of more or less normal lubricants in the store at the time of purchase.
According to the stated characteristics, the operating range of this lubricant is from -50 to 1000 °C. By the way, I didn’t expect that the cost of this bag is only 80 rubles. I thought it was several times more. Although, I can’t say that it’s particularly cheap! If you are constantly servicing the brake system while on the road, then of course it is more profitable to buy a large tube. If I'm not mistaken, it costs about 600 rubles per 100 grams.
This same bag will be enough to service the calipers of your Kalina for a year for sure!
You should not be overzealous, as excess may end up on the working surfaces, which will lead to a decrease in braking efficiency, and you will have to remove the residue with a cleaner or other degreaser.
Now you can put your finger in its place.
The lower finger changes in a similar way, so you are unlikely to encounter any difficulties when carrying out this repair! The effectiveness of the lubricant used can only be judged after long-term use, so we won’t rush to conclusions!
Fault diagnosis: how to do it?
As a rule, if there is a problem with the brake system, a corresponding signal appears on the dashboard. After detecting the indicator, the motorist must visually check the master cylinder body for problems. In this case, you need to inspect it for leaks, and also pay special attention to the places where the pipeline and circuit outlets connect. After completing this activity, you should measure the pressure in the circuits using a pressure gauge. after which the measurement results must be compared with control parameters, which are usually contained in the vehicle operating instructions. If there is a difference in these readings, then this will be a sure sign of a violation. As for the tightness of the device, it can only be checked on a special stand. Therefore, in this case, you will have to seek help from specialists.
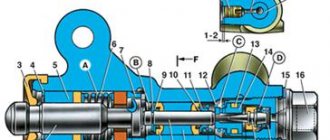
General information
Figure 1 — Steering parts from the vehicle interior:
- steering wheel
- upper steering shaft facing casing assembly
- M8 nut
- steering shaft assembly
- bolt M8x35
- washer 8
- M8 nut
- horn switch
- screw
- ring sealing
- screw 4.3x12.7
- lower steering shaft facing casing
- screw M5x20
- washer 5
- self-tapping screw
The steering is injury-proof, with a height-adjustable steering column, with a damping element on the steering wheel 1, Figure 1, and a rack and pinion steering mechanism.
Figure 2 — Power steering shaft assembly
An electric power amplifier is installed on the steering shaft, Figure 2, which reduces the force on the steering wheel.
Figure 3 — Steering mechanism parts:
- steering gear housing assembly
- right protective cap
- cover slats
- cover clamp
- plate
- locking plate
- steering linkage bolt
- stop insert
- rack stop
- ring sealing
- retaining ring
- spring
- screw
- nut plug
- gear boot
- bolt
- washer
- gear oil seal
- crankcase cover
- ring sealing
- separator assembly
- gear assembly
- steering rack
- left protective cap
- steering linkage support
- rod support bracket
In the lugs of the crankcase 1, Figure 3, of the steering mechanism, a drive gear 22 is installed on roller and ball bearings, which is meshed with a rack 23. The rack is pressed against the gear by a spring 12 through a metal-ceramic stop 9, which is sealed in the crankcase with a rubber ring 10. The spring rests against nut 13 with a locking ring 11, which creates resistance to unscrewing the nut.
There are marks on the steering gear housing and on the boot for correct assembly of the steering mechanism.
A protective cap 24 is put on the steering gear housing 1 on the left side, and a pipe with a longitudinal groove is pressed onto the right side. Through the groove of the pipe and the holes of the protective cover 3, bolts 7 pass, securing the steering linkages to the rack 23. The bolts pass through rubber-metal hinges pressed into the heads of the linkage tips. The bolts are secured with a locking plate 6.
The steering shaft 4, Figure 1, is connected to the drive gear 22, Figure 3.
The upper part of the shaft rests on a radial ball bearing. At the upper end of shaft 4, Figure 1, on splines, through a damping element, steering wheel 1 is secured with nut 9.
Figure 4 - Steering parts from the engine compartment of the car:
- right steering gear mounting bracket
- right support
- washer 8
- M8 nut
- bracket
- M6 nut
- washer 6
- protective casing
- steering mechanism
- shaft seal
- left steering gear mounting bracket
- steering gear support left
The steering drive consists of two horizontal rods and rotary arms of telescopic front suspension struts. The length of each rod is changed by a tubular rod, which is screwed onto the inner tip of the rod with one end, and screwed into the outer tip with the other and tightened with a bolt. The head of the outer tip contains the ball joint parts. The steering arms are welded to the front suspension struts.
Helpful information:
You can get professional advice when selecting a product and detailed information on all your questions by calling (calls within Russia are free).
Let's find out what could be causing your brake master cylinder to fail. First of all, its breakdown occurs due to the fact that the brake fluid is unevenly distributed inside the mechanism.
The cylinder itself consists of two working sections, each of which is responsible for braking one of the front wheels, as well as the rear one, located on the opposite side. You should know that in rear-wheel drive cars the picture is completely different: the sections are responsible for the operation of the brakes, which are located along the axes.
The work of the GTZ itself begins from the moment the pedal is pressed. If a vacuum booster is provided in the design of the car, then the brake cylinder contains 3 chambers, one of which converts pressing the brake into pressure, which makes it lighter. By pressing the pedal, a certain load is transferred to the piston section, which forces the brake fluid to press on the caliper. This, in turn, compresses the brake discs through the pads.
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
How to fill brake fluid correctly
First of all, it is worth noting that spoiled brake fluid can be identified due to its darkened color and thickened consistency. To replace, you will need the following materials and tools:
- New brake fluid.
- Syringe for removing old fluid.
- Dry cloth.
- Container for draining old fluid.
- A rubber hose, the hole of which must fit the bleed fittings on the wheels of the car.
- Brake wrench 8 by 10 mm.
Procedure for replacing the brake master cylinder repair kit
Clutch diagram of the VAZ 2107 master cylinder. Signs of a malfunction of the master brake cylinder and the need for its repair are the following:
Brake fluid leaks onto the brake booster housing, where the joint with the master cylinder is located. This indicates that the low pressure cuff is worn out and needs to be replaced.
The brake pedal is too soft. This may indicate air getting into the brake system, wear on the inner surface of the master cylinder, or wear on the seals on its pistons.
Brake pedal jamming. This is a clear sign that the compensation hole in the cylinder body is blocked or clogged.
Brake pedal sticking when braking. This may be caused by jamming of the pistons inside the master cylinder due to dirt getting in there. This is due to the increased hygroscopicity of the brake fluid, which absorbs not only additional moisture but also small particles of debris.
Failure to return the brake pedal to its original position. This is a sign of broken or worn master cylinder return springs. Or the brake pedal is faulty. Replacing the brake master cylinder repair kit consists of the following steps:
1. Determine where the fault is located and make sure that it is the master brake cylinder that is faulty.
If, when you press the brake pedal, the system does not respond to the first press, but responds to the second, then the reason lies in a decrease in pressure in the brake system. A drop in pressure can be caused by:
Brake fluid leaks and air enters the system.
Wear of seals in working cylinders.
Wear of the components of the main brake cylinder.
A clear sign of wear on the brake master cylinder elements is the leakage of brake fluid into the vehicle interior through the boot. You can find out about this by looking at the pedal assembly, moving away the rug and other obstacles.
2. Prepare your workspace.
Before replacing the brake master cylinder repair kit, you should prepare everything you need. To replace you will need:
The table where the replacement procedure will be carried out.
Vise.
A set of wrenches that can be used to tighten nuts up to 36 mm in diameter.
A rag for wiping brake fluid from the main brake cylinder elements.
3. Remove the brake master cylinder.
First you need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery and the terminals from the brake fluid reservoir. All brake fluid from the reservoir must be removed with a syringe or bulb.
The master brake cylinder is mounted on the vacuum booster and secured with two studs. To remove the master cylinder, you will need to unscrew the studs, remove the hoses going to the rear brake circuits and to the brake fluid reservoir
The tightening torque of the nuts of all elements is very high, so the removal procedure must be carried out extremely carefully and with suitable wrenches so as not to “lick the edges” of the nuts
4. Disassemble the main brake cylinder.
To disassemble, it is necessary to secure the master brake cylinder in a vice and unscrew the plug nut in the central part of the device. Here you need to be extremely careful, since the many springs inside the cylinder can cause injury. It is also worth remembering exactly the order of arrangement of all elements inside the cylinder, since violating this order during assembly will render the device unusable. Wash and dry all elements of the device.
5. Replace the master brake cylinder repair kit.
Replace all rubber seals and cuffs. If necessary (if they are very worn out or become unusable), replace the springs and pistons of the main brake cylinder.
You also need to make sure that the inner surface of the cylinder is intact. Any scratches on it are a reason to completely replace the unit, since replacing its elements will not give the desired result.
6. Assemble the brake master cylinder.
All elements should be assembled in the reverse order of disassembling the unit. When all the elements are inserted into the body, the central plug is screwed in (when screwing in, you will have to overcome some force from the springs.
7. Install the brake master cylinder in its original place in the car and check its operation.
When installing the master cylinder back into the car's brake system, you need to correctly and firmly secure all the hoses, screwing the nuts exactly along the threads. After this, bleed the brake system and make a test drive to check the quality of the work done.
Thus, replacing the brake master cylinder repair kit is a simple procedure and is within the capabilities of most motorists.
Common GTZ malfunctions
Like any other mechanism, the GTZ has its own characteristic problems. One such problem is excessive pad wear and brake fluid leakage. As a result, the liquid level drops. If such a violation occurs, operation of the vehicle is prohibited until the problem is completely eliminated. In such a situation, you should definitely check the working and master cylinders, hoses and brake pipes, as well as the brake calipers for leaks. If a leaking part is found, it must be replaced. If the violation concerns the automatic drum brake adjustment system, this may be accompanied by a low brake pedal. In this case, you will need to restore the pedal travel manually. To completely eliminate the problem, you will need to completely clean the automatic adjustment system. Also, the problem can often be caused by depressurization of the brakes.
FakeHeader
Comments 110
Hello. What about technical inspection? They won't cower.
The car has been out of production for a long time... its receiver 2114... was not available. and there was this one. I installed it, the bolt fit... That’s the whole answer. But in fact, they know the weight of how they are doing maintenance right now
Did I understand correctly, the GTZ Kalina has a different thread than on the 99 tubes? (in my case 2108) And the diagram is as follows: Front - Inlet - adapter - tube - adapter - regulator - adapter - tee And the same thing back. Did I understand correctly?
something cleverly written hurts
So, it’s all the same... I’m starting my journey through the hemorrhoids... please tell me, have you ever thought about screwing the 3/40 into the GTZ right away? If I understood everything correctly, then in the state there are 10x1, and the regulator is 15x1. Maybe it’s easier to give the GTZ to a turner so that he can cut 15x1, of course I didn’t look at it, maybe they won’t let the shirts stretch so much in diameter... well, and the adapter right away. For some reason I already broke my head (after work, my brain doesn’t cook anymore) And with the front contour, leave the same tube just re-roll the end under 10x1.25. And if I understand correctly, the result is 4 adapters (elements)?
1 in the Nexia GTZ they look down, but in ours they look to the side, it will come out painfully grammatically 2 but the GTZ body won’t allow it to be sharpened like that 3 the front contour will go through the tee
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
Rear brake pressure regulator
Removal
Place the car on a two-post lift, apply the parking brake and turn off the ignition (electro-hydraulic lift, type PV-3-T-SP, with a lifting capacity of 3 tons).
Disconnect brake pipes 1, Figure 1, from brake pressure regulator 2 and install plugs on them (wrench 67.7812-9525 for brake pipe fittings, technological plugs).
Figure 1 — Removing the rear brake pressure regulator:
- brake pipes
- rear brake pressure regulator
- pressure regulator drive lever
- Pressure regulator bracket mounting nuts
Remove the retaining ring and washer from the pin securing lever 3 to the rear suspension arm and disconnect the lever.
Unscrew the nuts 4 securing the bracket to the body and remove the regulator 2 as an assembly with the bracket and lever 3 of the pressure regulator drive (wrench 13).
Installation
Tighten nuts 4 securing the bracket to the body and install regulator 2 assembled with the bracket and lever 3 of the pressure regulator drive (wrench 13).
Install a retaining ring and a washer on the pin securing lever 3 to the rear suspension lever and attach lever 3.
Remove the plugs and attach brake pipes 1, Figure 1, to brake pressure regulator 2 (wrench 67.7812-9525 for brake pipe fittings, technological plugs).
Check the brake fluid level in the hydraulic brake reservoir and, if necessary, bring it up to normal. The brake fluid level in the reservoir should reach the “max” mark when the reservoir cap is removed.
Loosen the wheel bolts (replaceable head 17 or 19, wrench and extension).
Hang the car up, unscrew the wheel bolts and remove the wheels (replaceable head 17 or 19, wrench).
Raise the car, disconnect the elastic brake pressure regulator drive lever from the shackle on the rear suspension arm bracket and fix the lever in the upper position (flat-head screwdriver, pliers, utility hook).
Clean the bleeder fittings from dust and dirt (wiping rags).
Place the car at a height of no more than 0.5 m and bleed the rear right brake cylinder, to do this:
About checking the GTZ
Malfunctions of the master cylinder may require repair or complete replacement. It is recommended to start checking the brake cylinder with an external inspection. It is necessary to carefully check it for external defects and leakage of brake fluid. After a visual inspection, you need to check the operation of the brake pedal. To do this, you need to press on it and make sure that it does not jam or fall through.
As for the master cylinder, it can not only wear out, but also become rusty from the inside over time. This often happens due to the fact that the brake fluid contains oxygen and water in certain quantities.
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
Bleeding the brakes
After repairing the GTZ or RTC, as well as replacing the fluid, brake hoses or pipes, the brakes need to be bled. The essence of the event is to remove air from the braking system. For this procedure you will need:
- 8 (10) mm key;
- silicone transparent tube according to the diameter of the fitting;
- capacity;
- brake fluid.
All classic Zhiguli models use DOT-3 or DOT-4 brake fluid. Its volume in the “penny” hydraulic drive system is 0.66 liters. It is more convenient to bleed the system with a partner.
You need to start pumping the brakes from the right rear wheel. The process consists of the following steps:
- We install the machine on an overpass or inspection hole.
- Unscrew the filler plug of the expansion tank and check the fluid level. If necessary, bring it to the mark on the tank.
If the brakes are pumped correctly and there is no air left in the system, the pedal should feel tight when pressed and braking should be effective.
Video: how to bleed the brake system on a “classic”
I have repeatedly had to bleed the brakes alone, because there is not always an assistant available, for example, if a breakdown occurred on the road. For such situations, I always carry an expansion tank cap with a valve from a tubeless tire in stock. To make such a simple device, just drill a hole in the lid and insert a valve into it. When it becomes necessary to bleed the brakes, I screw this cap onto the reservoir. Using a piece of hose, I connect the valve to the spare wheel, having first unscrewed the valve valve from it. This creates pressure in the tank. Then I bleed the brakes according to the above scheme, ensuring that all air leaves the system, not forgetting to control the fluid level. I bleed the clutch in a similar way.
If there is a problem with the master brake cylinder, as evidenced by characteristic signs, the part needs to be diagnosed and subsequently repaired. If the unit has severe wear, then the problem can only be solved by completely replacing it. To carry out repair work, it is not necessary to visit a service station. It is enough to prepare the necessary list of tools and materials, read the step-by-step instructions and follow them during the work.
voice
Article rating
Symptoms of a GTZ malfunction
The GTZ, or master brake cylinder, is one of the most important elements of the braking system, since it is thanks to it that the car slows down after the driver presses the brake pedal.
Modern cars are usually equipped with two-section gas turbine engines, which form two circuits that operate independently. This system allows the brake system to remain operational even if one of the circuits fails or loses its seal.
The operation of the GTZ varies depending on the location of the drive. On front-wheel drive vehicles, the first circuit controls the operation of the front right and rear left brake pads, the second - the front left and rear right. On rear-wheel drive cars, the first circuit controls the operation of the front brake pads, and the second circuit controls the operation of the rear brake pads.