December 13, 2020 Lada.Online 14 198 11
Replacement of rear brake pads on Vesta should be done as a set on wheels of the same axle. Installation of brake pads from different manufacturers or different types on wheels of the same axle is not allowed. How to replace the pads with your own hands is described in the technological instructions.
Required
: brake pads (drum brake), article number 440609415R (see other pads).
How does a car's braking system work?
Before discussing the process of replacing elements of a car's brake system, it is necessary to consider how it works. Most mid-class and budget models are equipped with disc brakes at the front and drum brakes at the rear. While the goal is the same—to slow the car—these two types of brakes work slightly differently.
With disc brakes, the main mechanism that slows the wheels is the caliper. Its design, modifications and principle of operation are described here . The brake pads included in its design clamp the brake disc on both sides.
The drum modification is made in the form of a drum mounted on the rear wheel hubs. The brake pads are located inside the structure. When the driver presses the pedal, the pads move to the sides, resting against the sides of the drum.
The brake system line is filled with a special fluid. To activate all elements, the principle of expansion of liquid substances is used. The brake pedal is connected to a vacuum, which increases fluid pressure in the system.
Disassembling the brake mechanisms
The brake mechanism with a hydraulic drive (GAZ-51 car) must be disassembled in the following order:
- disconnect the hoses from the wheel cylinders;
- remove the brake drum;
- remove the tension spring of the pads;
- unscrew the nuts, remove the support pins with eccentric bushings and remove the pads;
- unscrew the bolts and remove the wheel cylinder assembly;
- disassemble the wheel cylinder by removing from it the stop pins 1 of the pads, sealing covers 2, pistons 3, cuffs 8 and spring 7;
- Unscrew the nuts, remove the springs and remove the adjusting eccentrics.
Rice. Wheel cylinder parts: 1 - thrust pins; 2 — sealing covers; 3 - pistons; 4 - valve plug; 5 — air release valve; 6 — cylinder body; 7 - spring; 8 - cuffs.
To disassemble the brake mechanism with a pneumatic drive (ZIS-150 car), you must:
- disconnect the brake chamber rods from the brake levers 6;
- remove the cotter pin and remove the brake lever from the expansion knuckle shaft 3 together with the worm adjusting device 4 and 5;
- remove the brake drum;
- remove tension spring 2 pads;
- unscrew the nuts, remove the locking brackets 14. remove the eccentric support pins 10 and remove the pads;
- remove the shaft with expansion fist 1.
Rice. Brake mechanism of the ZIS-150 car: 1 - expansion fist; 2 — tension spring of pads; 3 — expansion fist shaft; 4 - worm gear; 5 - worm; 6 — brake lever; 7 — air supply hose; 8 — brake lining rivet; 9 — brake pad; 10 — eccentric support finger; 11 — support pin bracket; 12 — protective brake disc; 13 — brake drum; 14 — locking brackets; 15 - plate; 16 — worm stopper; 17 — brake chamber.
Why change brake pads?
The quality of brake pads directly affects the vehicle's slowing efficiency. This process is especially important in emergency situations, for example, when a child runs out onto the road or another car suddenly appears.
The friction lining has a certain thickness. The more often and harder the driver presses the brakes, the faster they will wear out. As the friction layer becomes smaller, the driver needs to exert more effort each time to slow down the car.
The brake system of a car works in such a way that the front pads wear out more than the rear ones. If you do not change them on time, this will lead to loss of controllability of the vehicle at the most inopportune moment. This in many cases leads to an accident.
When to change brake pads?
The car manufacturer indicates this regulation in the technical documentation. If the car was purchased on the secondary market, then most likely these papers are no longer available. In this case, official data about the car published on the Internet on the websites of manufacturers or dealers will help.
Since the pads wear out depending on how actively they are used while driving, the replacement of brake pads is determined not by the time interval, but by the condition of the friction surface. Most pads require replacement when this layer becomes two millimeters thick.
Operating conditions also affect the suitability of the pads. For example, in a car that frequently travels on the highway, the braking system is used less than in the same car, only in active urban conditions. And if we compare the pads of these cars with SUVs that often conquer swampy terrain, then in the second case, due to the presence of abrasive particles, the friction surface wears out faster.
In order to notice the wear of the pads in time, during the seasonal replacement of tires, you should pay attention to the brake pads, as well as the condition of the discs and drums.
Watch a short video on how to eliminate squeaking brake pads:
⬤ Brake pads will no longer squeak after this video.
How to determine the degree of wear of brake pads?
Wear of brake system consumables, and discs and pads are precisely consumables, because the brakes require dry friction between these elements to operate, can be determined visually. Most modern brake systems are equipped with a special metal plate, which, if the friction layer of the brake pad is severely worn, will scratch the brake disc, producing a strong squeaking noise.
Some types of brake pads are equipped with wear sensors. When the pad is worn out (the remaining thickness is one or two millimeters), the sensor transmits a signal to the control unit, due to which the corresponding icon lights up on the dashboard.
To prevent pad wear from catching the driver by surprise during a long trip, experts recommend checking the thickness of the pads every 10 thousand kilometers, especially if the driver enjoys a sporty driving style with frequent braking.
As for the wear of the brake disc, this can be determined by touch by running your finger in the contact area of the edge of the brake pad. If a deep edge has formed on the disk, it must be replaced. Considering that the disc is an expensive part of the brake system, before replacing it with a new one, you should measure the depth of wear. If the edge is more than 10 millimeters high, then the disk definitely requires replacement.
Brake caliper design
Car enthusiasts are not always good experts in the field of car maintenance and sometimes do not know all the intricacies of the technical standards that are required for the effective operation of cars. Calipers are cleaned annually or every 40,000 km of the vehicle. The frequency and types of work differ significantly from servicing a conventional brake.
The device consists of pads, brackets, pistons and sliding pins that press the pads against the rotors during braking. Over time, the pins consume all the lubricant, and the sliding process is disrupted, after which the following “problems” appear in the car:
- The brakes do not make contact with the rotor, causing the pads to wear unevenly.
- The pad constantly interacts with the rotor, which creates heat that destroys the brakes.
- The brakes become weak due to the fact that the linings do not lie on the entire working surface.
The device is an integral part of the braking system. When the brake pedal is depressed, fluid flows from the master cylinder to the calipers, putting pressure on the piston inside, thereby pushing the pads against the metal discs and stopping the car. The key role is to create friction with the rotors, thereby braking the wheel. There are two types of devices: floating and fixed. Floating - Moves in and out, creating friction with the rotors. Brake grease washes away on wet roads. Metal parts are susceptible to rust, so it is recommended to clean them to improve the performance of your car.
It is advisable to carry out cleaning annually. In expensive cars, brake discs are made of cast iron. Conventional brake systems are very sensitive to corrosion and must be thoroughly cleaned during mandatory equipment lubrication procedures. Rust residue in critical areas can cause brake problems.
Preparing the car for replacing brake pads
Repairing the brake system does not always require a lot of time and effort. To prepare your car for replacing the pads, you first need to take care of safety. To do this, you first need to make sure that the machine does not move during the work. Wheel chocks will help with this.
The wheel on which the pads will be replaced is weakened (the bolts do not completely unscrew). Next, jack up the car and unscrew the bolts to remove the wheel. To prevent the car body from slipping off the jack and damaging important elements when falling, it is important to prevent this situation. To do this, place a safety wooden beam under the hanging part.
Some people put the removed wheel under it, but it will interfere with the process of replacing the pads. In addition, the car owner will be partially under the car when performing work, and in an emergency, the width of the wheel rim may not prevent injury when the car falls from the jack.
In addition to the wheel wrench, wheel chocks and safety bar, other tools will be required to service the brake system.
Rust removal sequence
To keep your brake calipers in tip-top shape, you need to clean the sliding pins regularly. Remove old oil, debris and rust, then add heat-resistant lubricant to the pin and put it back in. The entire process may take about an hour.
The following step-by-step instructions will make cleaning easy:
Remove the caliper. This is not possible if the car is at ground level, so you will first need to jack up the car
Once it is raised, loosen all the nuts on the four wheels without removing them completely. Remove the nuts on the front two wheels. Keep the nuts in a safe place. Carefully place the film on the surface and cover the cap. This process ensures that most of the vacuum is properly retained in the brake system. Loosen the line at the point where it meets the caliper. Unscrew it partially and bring the tray to collect the drops. Using a screwdriver, remove the spring clip. Loosen the bolts and remove them, then remove the caliper from the rotor. When it is completely free, you can pull out the pads. After removal, use the rubber vacuum cap and pan to collect the liquid
Place a piece of wood between the piston and the outer flange. Do-it-yourself cleaning of calipers from rust is carried out using brake fluid to remove contaminants and grease. Use a cleaning brush and brake fluid. Spray some of the brake cleaner onto the brush and begin processing. Do not spray cleaner directly onto the calipers. The more carefully this step is performed, the better the cleaning effect will be. When finished, remove the front locking clip and close the drain valve using masking tape. Once it is closed, secure the brake hose fittings as well. Take some stiff cardboard and cut out a piece in the shape of an inverted L. You need to protect all parts of the car with plastic film. If paint gets in, the normal functioning of the braking system will be disrupted. You may need to use duct tape to hold the plastic in place. Spray the paint onto the caliper using a slow and steady motion. Take special care to prevent paint from getting between the brake pad and rotor. Leave the paint to dry before removing the plastic and cardboard. Move to the next wheel and repeat the process. Make sure the paint is completely dry before attaching the wheels. Repeat the process until the caliper is completely clean. Observe safety precautions when performing work. Any dust or dirt in the air can get on wet paint. In addition, the smoke from spray paint is dangerous if the driver inhales it, so it is recommended to wear a dust mask when working. Replace the piston and reattach the brake line, then install the brake caliper into the wheel. Once all four calipers are serviced and the wheels are installed, check the brakes. If any problems are found, contact customer service.
Tools for replacing brake pads
To replace the pads you will need:
- Clamp. It is useful for pressing on the disc brake caliper piston. This will facilitate the subsequent installation of the mechanism in its place. Also, when the device is disconnected from the line (if a decision is made to simultaneously replace the brake fluid), its reservoir contains the remainder of the fluid, which also needs to be drained into a container;
- An open-end wrench suitable for the cross-section of the caliper mounting bolts and brake line fitting;
- Personal protective equipment. These are gloves, a respirator and goggles. They are needed because brake fluid contains substances that are harmful and aggressive to the skin. You need to protect your hands, eyes, and especially your respiratory tract from them. When dismantling boiled metal parts, chips often break off and can get into your eyes. For this reason, safety glasses are especially necessary;
- Although this is not a tool, but a consumable item, new brake pads should also be prepared in advance.
Most motorists have the useful habit of having the necessary tools in the garage or even carrying the necessary tools in the car. This will make it easier to prepare the car for replacing the brake pads.
Types of car brake pads
All brake pads are divided into two types:
- For disc brakes;
- For drum brakes.
They differ from each other in shape, but they work the same way - they rub against the smooth surface of a steel disk or drum.
Based on the material of the friction layer, brake pads are divided into the following types:
- Low metal. The friction layer of such pads contains 10-30 percent metal (copper or steel is used). The remaining binding materials are organic. When using such pads, the brakes make a lot of noise, and due to the large amount of organic substances, they create a large amount of dust that settles on the discs.
- Semi-metallic. Such products consist of metal from 30 to 65 percent, and the binders are organics and graphite. Such pads also create noise when braking, but compared to the previous type they last longer.
- Ceramic. These products are the most expensive, but at the same time they are less noisy, do not wear out brake discs as much and have an increased service life. The composition of such pads contains ceramic fibers and an admixture of non-ferrous metals.
- Asbestos-free or organic. The composition of such pads can be different, for example, Kevlar, glass, carbon, and rubber, various resins and rubber are used to bind the fibers. Brakes equipped with such pads are the softest and most gentle on the discs. But due to their great softness, they quickly wear out and form a large layer of dust.
Video: Which brake pads are better to put on AUTO
Here is a short video review of brake pads for a car:
Which brake pads are best for cars?
Choosing new pads
You understand perfectly well why you should replace your pads after showing signs of wear.
Do not forget to simultaneously check the disks and the condition of the handbrake, even if your car has an electronic handbrake. A failure of the handbrake is also not a problem, so its components will also need to be replaced if they fail.
When the pedal fails, the brakes squeak, make noise, overheat and after several braking stop responding normally to the pedal, things are bad. Cars with ABS are extremely dependent on the condition of the entire braking system. Therefore, extraneous vibration, wear of friction linings and problems with discs can lead to loss of control, decreased pedal response and emergency situations.
It's one thing to choose brakes on a bike and change them. Working on a car is something completely different. Therefore, I would advise you to contact a trusted car service center. They are well aware of the procedure for replacing pads. The cost is not that high. How much a replacement costs depends on several components.
You can buy yourself a new set of pads yourself. I suggest you find out what pads are currently produced and how to choose them wisely.
Let's start with two main criteria.
- Operating temperatures. For a regular passenger car, this parameter is selected at approximately 300-350 degrees Celsius. If we are talking about fans of sporty and aggressive driving, as well as owners of powerful fast cars, then you will need more durable pads - about 800 degrees.
- Friction coefficient. Until the pads reach operating temperature, which is about 200 degrees Celsius, the coefficient remains low, which is why the pads will wear out quickly. Experts recommend focusing on an indicator of 0.3-0.5. The higher the coefficient number, the better the car can brake.
The next point is the material from which the block is made. There are several of them, and they have their own characteristics.
- Semi-metallic. More than 40% of the composition is high quality metal. Use iron, copper or graphite. Inorganic components are also added to ensure excellent heat transfer and long service life. But at sub-zero air temperatures they brake poorly and wear out faster.
- Organic. Consist of glass, resin, rubber, Kevlar and carbon. Soft, effective, silent. But they don’t like moisture and create a lot of dust when braking.
- Low metal. The composition resembles organic ones, but with the addition of steel or copper. They wear out quite quickly and are expensive.
- Ceramic. The most effective, but also the most expensive. They brake perfectly, are not afraid of temperature and moisture, and are made of metals and ceramic fibers.
If you notice the first signs of wear, do not delay with replacement. When the price for work at a service station confuses you, you can try changing the pads yourself. Photos and videos are kindly offered by YouTube users, as well as various sites where there are similar photo reports and video tutorials.
What kind of pads are on your car and how often do you change them? Write about it in the comments, ask questions. Subscribe, don’t forget to tell your friends about us and expect a lot of new, interesting and useful materials.
(No ratings yet)
Did you like the article?
Subscribe to updates and receive articles by email!
We guarantee: no spam, only new articles once a week!
Any car owner can change the front brake pads themselves in a garage or in the field. This step-by-step instruction will help you change brake pads correctly and without errors. Even those who first decided to swing the pads with their own hands will be surprised how simple and quick the procedure is.
Replacement of front brake pads (disc brakes)
Here is the sequence in which the front brake pads are replaced:
- Under the hood, the cap of the master cylinder expander is unscrewed - this will make it easier to press the piston into the seat;
- The steering wheel is turned so that there is free access to the brake caliper fasteners;
- The caliper guides are removed. In order not to drain fluid from the system and not damage the hoses during repairs, it is worth using a wire to secure the caliper to the shock absorber so that it does not hang on the hose;
- The piston is pressed into the seat with a clamp;
- Use a flat screwdriver to remove old pads and anti-squeak plates;
- The plates and brackets are lubricated with lubricant so that they do not wear out during system operation;
- Before installation, the caliper body must be cleaned of dirt;
- Lubricant is applied to the mounting areas of the brake pads;
- The pads are installed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions;
- If there are grease residues, they must be removed with a rag;
- The piston can also be lubricated;
- The caliper is installed in place (you need to be careful so that the guides are not damaged);
- Lubricant is also applied to the caliper guides, after which they are clamped.
An identical procedure is carried out on the second wheel. As soon as the work is completed, you need to close the lid of the GTZ tank. Finally, the tightness of the system is checked. To do this, press the brake pedal several times. If there are no fluid leaks, it means that the work was completed without damaging the line.
Replacing the caliper repair kit
The most difficult and responsible operation when repairing calipers is replacing the caliper repair kit. During this operation, all seals and rubber parts of the caliper are changed.
To begin with, you must purchase a repair kit for the caliper of your car. To do this, in a car store you will have to tell the seller the make and model of your car, the year of its manufacture and other information that the seller asks.
To carry out repairs using a repair kit, you first need to dismantle the caliper. After that, transfer it to the workbench and completely disassemble it
A very important note - the place where the caliper is disassembled must be as clean as possible. Even the smallest grain of sand getting inside the caliper threatens its early failure
When disassembling the caliper, it is recommended to write down or photograph the places and methods of installing certain parts.
In most cases, you will need to replace the following rubber products:
- Brake cylinder seal;
- Brake piston boot;
- Guide boots;
- Guide seals;
- O-ring of the bleeder fitting.
If there is deep corrosion on the working surface of the brake piston (with the formation of cavities), then the piston must also be replaced.
Reassemble the caliper in the reverse order of disassembly. After this, the caliper must be installed on the car, the guides lubricated and the brakes bled. As you already know, you will need an assistant or a special device for this.
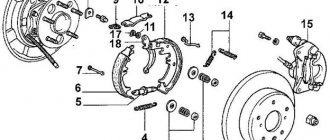
Replacing rear brake pads (drum brakes)
Replacing rear brake pads is done a little differently. First, the car must be prepared in the same way as when working on the front end. The vehicle is removed from the handbrake, since it activates the rear pads.
Then, given that the rear pads are located inside the drum, it is necessary to completely remove the entire assembly. Next, change the pads in the following sequence:
- The drum mounting bolts are unscrewed;
- Often the drum can be removed with some effort. In this case, you can tap it a little with a hammer while simultaneously removing it from the hub;
- The rear brake mechanism consists of many springs, rods and latches, so it would be best to photograph the location of each of them;
- The handbrake cable is disconnected;
- To remove the old pads, you will have to completely disassemble the assembly;
- A new pair of pads is installed in accordance with the photograph taken in advance;
- The handbrake cable is connected and the drum is installed back.
As with the front brakes, you need to test the system by pressing the brake pedal several times.
If during the process of replacing the pads you also need to change the brake fluid, then a separate article will tell you how to do it correctly.
When replacement is required
To begin with, let me remind you that the block consists of two main components. This is the lining (aka friction) and the body itself. It is the friction element that performs the most important function, that is, it brakes the brake disc. Therefore, it gradually wears out naturally. Replacing the pad is only a matter of time. Previously, they only changed the linings themselves, but now they simply dismantle the entire block and put a new one in its place.
When exactly it will be necessary to replace disc brakes or change the drum, no one can say for sure. Wear and performance depend on a number of factors:
If we talk about the pads on the front wheels of a car, they can last approximately 10-15 thousand kilometers. This is a completely normal indicator for an average car in our conditions (road quality, weather, etc.).
And the pads installed on the rear wheels last longer, since the load on them is slightly less. This is if the main load in the car falls on the front brakes, and not the rear. They usually live 30-60 thousand kilometers, and sometimes more.
Installing rear disc brakes is a popular modification for a car because they are more efficient and reliable. Some cars are already equipped with disc brakes. Therefore, when buying a Ford Focus, Renault Logan, Hyundai Solaris, Volkswagen Polo or Passat, Kia or Audi cars, pay attention to how the brake system is designed on them and what it consists of.
There is one general rule for everyone. Brake pads should not be worn more than 1.5 millimeters from their original size. If wear exceeds one and a half millimeters, this will negatively affect the quality of braking, and you risk damaging other components of the system. Plus, the car will start making unpleasant sounds that will literally irritate you every time you press the brake pedal. There is no need to think about what to lubricate or where to turn the wrenches, as long as the creaking goes away. An unusual sound is a clear sign of wear. You will lubricate new components of the brake system during the replacement process.
Now there are so-called smart pads. Their peculiarity is that they have a wear indicator. When the time for replacement comes, that is, the block is ground down to the maximum permissible value, a characteristic squeak appears. From it, the driver easily understands that it is time to change this device, otherwise trouble will not be avoided.
Characteristic signs of wear
Yes, you can periodically send your car to a car service center, of which there are a huge number in the cities of St. Petersburg, Moscow and many others. But before going to the service station, you should understand why such measures and diagnostics were needed in the first place.
Some evaluate the current state of the elements with their own hands. Moreover, self-diagnosis looks quite simple:
- the front wheels are removed one by one and the condition of the pads is checked;
- if the thickness is below the acceptable level, it’s time to change;
- on the rear wheels, the drum is additionally removed to measure the thickness of the pad;
- the disk is cleaned of dust and dirt;
- measurements are taken using a caliper;
- The thickness of the brake disc must be at least 10.8 mm;
- If the pad is worn out only on the left or right, it still needs to be replaced in pairs.
Signs of front and rear pad wear
The brake system consists of many components that can fail. The main problem is wear of the brake pads. Here are a few signs that may indicate other problems with the system.
Signal from wear sensor
Some modern cars have a pad wear sensor in the brake system. There are two types of driver wear alert:
- There is a signal layer on the block itself. When the friction part is used up, the signal layer begins to make a characteristic sound (squeaking) when braking;
- Electronic sensor. When the pad wears to the appropriate degree, a signal appears on the instrument panel.
Brake fluid level
As brake pads wear, more fluid is required to effectively slow the vehicle. This is explained by the fact that the stroke of the brake caliper piston increases. Since wear of the friction part occurs almost imperceptibly, the fluid level in the expansion tank will also decrease slowly.
Increasing the brake pedal travel
The situation is similar with the brake pedal travel. The thinner the friction layer, the greater the pedal stroke. This sign also does not change dramatically. However, by increasing the driver's efforts when braking, it can be determined that the braking system needs the attention of a specialist.
Mechanical damage
If chips or other damage to the brake pads are noticed, they need to be replaced urgently. In addition to replacement, it is necessary to find out why this situation occurred. This may occur due to poor quality parts or damage to the brake disc.
Uneven pad wear
If on one of the wheels it was noticed that the pad was worn out more than on the others, then in addition to replacing it, it is necessary to repair or replace the brake caliper. Otherwise, the brakes will operate unevenly, and this will negatively affect the safety of the vehicle.
Increased braking distance
The pads also need to be replaced if the braking distance of the car has noticeably increased. A particularly alarming signal is when this indicator has changed dramatically. This indicates either a faulty caliper or excessive pad wear. It also doesn’t hurt to check the condition of the fluid – its quantity and the need for scheduled replacement.
Loss of straightness during braking
If the car pulls to the side when you press the brake, this may indicate uneven wear on the pads on different wheels. This happens when the calipers or brake lines are not working correctly (impaired performance of the brake cylinders).
The appearance of wheel runout when braking
If during braking you can clearly feel the beating of the wheels (or one wheel), this indicates the destruction of the brake pad. For example, due to a manufacturing defect or expired service life, the friction layer cracked and began to fall out.
If the caliper rattles when the car is moving, then the reason for this may be severe wear of the pad. In a fairly worn pad, braking will be carried out due to the metal base. This will certainly lead to damage to the brake disc, and in some cases to sudden blocking of the wheel during braking.
The appearance of creaks and rattles
Most modern brake pads have a large amount of metal shavings in the friction layer at the minimum wear level. When the pad wears down to this layer, metal shavings scratch the brake rotor, causing a loud squeak or squeal when braking. When this sound occurs, the pads must be replaced so that they do not scratch the discs.
The appearance of dark deposits or dust on the rims
This effect is natural for most types of brake pads in the budget segment. Graphite dust occurs due to wear of the friction layer, which partly consists of various kinds of resins and graphite, which sinter during braking and form soot dust that settles on the car’s wheel rims. If metal shavings are clearly visible in the graphite dust (a characteristic “metallic” tint), this indicates wear on the brake disc. It is better to replace the pads with a higher quality analogue.
Brake caliper piston - device, purpose
If the brake system breaks down, the car owner immediately checks the brake caliper piston and adjacent components. This is justified because this device affects the safety of vehicle operation and ultimately the preservation of people’s health and lives. But what else do we know about calipers and their operation?
Brake caliper piston and other system elements
If we consider the brake caliper design as a whole, we should remember that this is a unit that, with the help of pistons, ensures uniform pressing of the pads.
The very design of disc brakes requires them to operate in critical temperature conditions.
Between the pad and the disc, as a result of friction, the surfaces of the parts are heated to a temperature of 500-600 degrees Celsius.
Considering the design of a disc brake with a floating caliper, one should note its characteristic features.
Its movement relative to the disk during braking occurs in such a way that it can quite easily provoke various malfunctions in the form of critical accumulations of dirt, corrosion, and jamming.
In such situations, the pads wear out quickly and fuel consumption increases. A more reliable design is considered to be a fixed version of the caliper, where there is no movement of it relative to the disc.
Front and rear brake calipers
The design and design of the front brake caliper is an open unit, allowing it to be effectively cooled while driving.
It consists of a disc mounted on the wheel hub and the caliper itself. The sockets house cylinders that are installed in a certain position using special clamps.
Inside the cylinders there are pistons sealed with rubber rings.
In order to protect the internal cavity from dust and dirt, a brake caliper guide boot is installed. The outer cylinder contains a special valve that removes excess air.
The rear brake caliper has a more complex design due to the presence of an additional handbrake mechanism. Thus, the braking system of the rear wheels can operate from two drives - conventional hydraulic and mechanical, which provides additional operation of the parking brake.
The integrity of the brake caliper protection is the key to safety.
A preventative repair that your brakes may need to prevent serious problems is replacing the brake caliper boot, which protects the exposed parts from the penetration of moisture, dust and dirt particles, and other chemically active substances. If this small part is not maintained in good condition, then any dirt that gets inside will ruin your complex structure.
However, before removing the boot, you must disconnect the rear brake caliper piston. To remove it from the body, it must be unscrewed from the rod, which is an integral part of the handbrake. The front part of the brakes will be a little simpler.
Many car enthusiasts repair brake calipers with their own hands. However, in modern cars, the design of this system is a rather complex mechanism, the repair of which most often requires the help of qualified specialists.
Replacing the boot - we try to do it ourselves
In what order should I get to the boot and replace it? Remove the cap from the caliper that protects the guide head (also called the “finger”). We take a suitable hexagon, turn it out and take it out. Now we have access to the boot itself, we remove it too.
If there is dirt underneath, it needs to be washed thoroughly, preferably not only from the visible part of the caliper surface. If possible, press in the piston; usually a special tool is used for this.
This will prevent damage to the system inside, where sand will scratch the inner surface of the caliper and the outer piston.
When you have washed everything well, you can return the piston to its usual place and check its progress. If it now moves smoothly and there is no sand grinding inside, then you have achieved your goal, you can install the boot and assemble the system.
But once you are under the car and look into the caliper, you can remove it and check it completely for defects.
What results from untimely replacement of pads?
First of all, worn brake pads will squeak heavily when braking. But even if the driver has nerves of steel and is not bothered by extraneous noise, untimely replacement of the pads can lead to serious damage.
Here are the consequences that can result from failure to comply with the regulations for replacing brake pads:
- Strong creaking sound;
- Premature wear of brake discs;
- Brake calipers will fail faster because when the pads are worn out, the caliper piston extends further to apply the brakes. Because of this, it can warp and jam, which will lead to braking of one wheel even when the pedal is released;
- Critical wear of the brake disc can lead to a wedge of the pad on the disc burr. At best, the brake system assembly will fly apart. In the worst case scenario, a locked wheel can cause a serious accident, especially if the car was traveling at high speed.
Repair
Having figured out the main reasons why the car may not slow down, you can begin repairs. Specifically, in this article we will look at repairing car calipers with our own hands. If everything is clear with the first case, for repairs you just need to clean the calipers from dirt, and everything will be operational again, then in the second case you will have to work.
You can solve the problem with the second breakdown only after searching for information specifically for your car, because there is no universal way to fix this problem.
Unfortunately, these are not the only problems that may cause your car to fail to slow down. Another reason why the wheel may not brake or, on the contrary, may not release, is considered to be a faulty cuff. The cuff is installed as a spring, which returns the brake piston to its place. Over time, the cuff loses its elastic properties and ceases to return the piston, which presses the pads to the brake disc. In this case, the disc will begin to overheat, which will lead to dire consequences on the road. You can check that the cuff does not return the piston only after raising the car.
On a fully functional car, the wheel spins without difficulty, even if you rotate it by hand
Particular attention will need to be paid to ensure that the wheel rotates completely immediately after the brake pedal is released. Fortunately, this problem can and even needs to be fixed with your own hands.
The main advantage of fixing all problems yourself is budget savings and personal experience in car repairs. So, if something happens on your car that the cuff does not return the piston to its place, then you need to look for the reason. Most often it is hidden in the boot of the brake piston. The first thing you need to look at is the brake disc and pads. The brake disc should not show signs of overheating or signs of severe rubbing. If the disc is heavily worn, it will need to be replaced immediately with a new one. After inspecting the disc, you can begin to inspect the pads.
After the discs and pads have been inspected, we proceed to inspect the caliper piston. This can be done by just looking under the boot. There should be no marks, scratches, or even rust on the piston body; if any of these are present, then you need to disassemble the caliper. In stores that sell car parts, you can find a repair kit for car calipers. Most often, it only includes elastic bands and gaskets. In fact, a piston for a caliper is not so easy to find, so it is best to use an analogue from other cars, which will be similar in diameter and other parameters.
How often are brake pads changed?
Since the wear of brake pads is influenced by a large number of various factors, from the material from which they are made to the driving style, it is impossible to set an exact interval for replacing these consumables. For one motorist they don’t last even 10 thousand, while another will drive on the same pads for more than 40 thousand.
If we take average indicators, then with low or average quality materials, the front pads will need to be changed after approximately 10 thousand kilometers, and the rear ones after 25,000.
When installing better materials at the front, the pads will need to be changed after approximately 15,000 km, and at the rear - after about 50,000 km.
If the car has a combined brake system (discs in front and drums in the rear), then the pads in the drums wear out more slowly and can be replaced after 80-100 thousand.
Tips for use
Car care includes periodic inspection of important components and mechanisms of the vehicle. The brake system is one of the most important; its inspection for wear and possible malfunctions is mandatory.
Every 20 thousand km you should check the pads, springs, levers, etc., measure the brake fluid level, check the condition of the cylinders, seals and pipes for integrity and possible leaks.
When installing new pads, experts advise “rolling in” them:
- Find an empty section of road.
- Accelerate to the permitted city speed and slow down to 10 km/h, repeat the acceleration and reduce the speed at least 10 times. At the end of the procedure, drive another 5 km at a calm pace.
What factors can affect pad wear?
Considering that brake pads are a consumable item, they need to be changed depending on the degree of wear or after a certain mileage. It is impossible to create a strict rule at what interval to change this consumable, because this is influenced by many factors. This is what affects the schedule for replacing pads.
Car model and make
A subcompact car, an SUV, a premium car or a sports car. The braking system of each type of vehicle operates with different efficiency. In addition, cars have different dimensions and weight, which also affects pad wear during braking.
Conditions in which the vehicle is operated
Since all kinds of dirt on the road get on the pads while driving, foreign particles will certainly cause premature wear of the pads.
Driving style
If the driver often uses a sporty driving style (fast driving over short distances with frequent braking), then the friction material of the pads will wear out many times faster. To extend the life of your brakes, slow down your vehicle earlier and avoid using emergency braking. You can slow down the car, for example, by using the engine brake (release the gas pedal and switch to a lower gear at the appropriate engine speed).
The quality of the material used in the manufacture of the pad
This factor plays a key role in the life of the pads. Manufacturers of such consumables use different materials that provide maximum adhesion to the brake disc or drum. Each of these materials has its own resistance to mechanical and thermal overloads.
How to reduce brake pad wear
Regardless of a motorist's driving style, brake pads will still wear out and will need to be replaced. The following factors influence this:
- Vehicle operating conditions – poor road surface, frequent driving on mud and sand;
- Driving style;
- Quality of replacement parts.
Despite such factors, the driver can extend the life of the brake pads. Here's what he can do for this:
- Brake smoothly, and to do this you should maintain a safe distance;
- During the braking distance, do not hold the pedal, but perform several presses;
- To slow down the car, the engine braking method should be used in conjunction with the brakes;
- The brake pads of some cars freeze if you leave the car in the cold for a long time with the handbrake raised.
These are simple actions that any driver can perform. Safety on the road depends on the effectiveness of the braking system, so due attention should be paid to its serviceability.