Problems that arise with the brakes while traveling are considered critical and must be corrected immediately. The culprit of the malfunction is often the main cylinder, installed in the engine compartment and rigidly connected to the pedal. To find out the cause of the breakdown and repair the unit yourself, you need to know the structure of the brake master cylinder (MBC) and its principle of operation. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to distinguish and filter out problems with other elements of the system.
What is a brake master cylinder and what is it for?
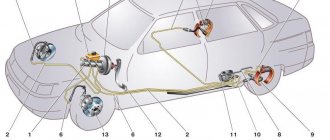
Brake master cylinder and reservoir.
Braking is accomplished by pressing the pads against the disc. This is done by pistons that are driven by a hydraulic system containing brake fluid. However, for brake mechanics to work, pressure must be somehow transmitted by pressing the pedal. For this purpose, a master brake cylinder is needed, which transmits the mechanical action of the driver to the hydraulic system through a booster.
Considering the importance of the part, they try to make it as reliable as possible. But even greater reliability can only be ensured by an additional system, which is why all modern cars have a two-section GTZ. Each section serves an independent circuit, which, in the event of a breakdown of the first, will be duplicated, although with less efficiency.
The circuits can be connected in the following ways:
- Parallel (4+2). One circuit is used for all wheels and has insurance on the front ones.
- Parallel (2+2). One circuit is responsible for the front wheels, the second - for the rear.
- Diagonal (2+2). Each circuit operates on one front and one rear wheel diagonally.
As a rule, a diagonal system is used in front-wheel drive cars, and a parallel 2+2 in rear-wheel drive cars.
About checking the GTZ
Malfunctions of the master cylinder may require repair or complete replacement. It is recommended to start checking the brake cylinder with an external inspection. It is necessary to carefully check it for external defects and leakage of brake fluid. After a visual inspection, you need to check the operation of the brake pedal. To do this, you need to press on it and make sure that it does not jam or fall through.
As for the master cylinder, it can not only wear out, but also become rusty from the inside over time. This often happens due to the fact that the brake fluid contains oxygen and water in certain quantities.
The cylinder is designed in such a way that if brake fluid leaks from the first section, the other will remain in working condition. That is, the first piston will pass through its own section and give movement to the second piston, which in turn will create the necessary level of pressure for the operation of its own section.
If the second section leaks
, then the first trigger will look completely different. When the piston operates in a good section, the piston from the faulty one is drawn into operation. That, in turn, moves forward unhindered and rests against the movement limiter, thereby blocking the outlet. In turn, the pressure in the first section increases, which entails braking of the wheel mechanisms.
As a result, when you press the brake pedal, it falls through. In this case, braking efficiency is observed only at the end of the pedal stroke.
How does a brake master cylinder work?
The structure of the main brake cylinder: 1 - Housing with compensation holes; 2-3 - Circuit drive piston; 4 - Spacer washer; 5. Rod;
To make it easier for the driver to brake comfortably and confidently, in modern cars the pressure on the pedal is transmitted through a brake booster, often a vacuum one. Often the brake master cylinder is mounted on the booster cover, forming a single unit with it. In this case, a compensation tank is located above the cylinder, which contains a reserve of brake fluid, which can be useful in case of minor leaks or natural evaporation.
The rod coming from the vacuum booster rests against the double piston. Since the pistons are located on the same axis, the force of the rod moves them simultaneously, allowing pressure to be created in two circuits at once. At the same time, liquid also enters the compartments expanding behind the working cavities from the tank. This will avoid vacuum in the circuits, which can occur if the pedal is released abruptly. Having removed the force on the rod, the piston is returned by springs to its original position, after which the pressure in the cylinder is equalized.
The operating principle of the GTZ in simple words
The process is activated by pressing the brake pedal. The result of mechanical force is a load inside the cylinder, carried out using a rod. It directs the pistons along the desired path, overcoming the force of the return spring. The movement of the pistons is accompanied by the closure of the compensation channels, which causes the opening of the bypass channel and sealing of the entire circuit.
At the same time, pressure is created that drives the caliper. Part of the liquid flows into the pipelines, activating the vehicle, the other pushes the second piston, which, when moving, performs the same functions.
The calipers compress the brake discs with the help of the pads, and the car stops. The pistons return through the compensation hole to the initial position after depressing the brake pedal. The initial mode of the pistons inside the circuits is established by the action of springs. Having returned to their original position, the pistons again open the compensation channels, thereby equalizing the pressure in the vehicle. The waste liquid slowly flows back into its reservoir.
Signs of a faulty master cylinder
Cars are often equipped with pressure sensors that can detect a drop in pressure in the circuit. They will notify the driver of problems on the dashboard. Still, it would be useful to find out the symptoms of certain brake system malfunctions, since the causes may be different.
First, let's look at the symptoms that do not indicate a broken cylinder:
- Pull to the side when braking;
- Creaks when braking;
- Heating the pads on a specific wheel.
All this may indicate problems with the wheels, circuits, or jammed pads. Leaks from the working cylinders may also occur, there may be problems in the vacuum booster, or the integrity of the compensation tank may be compromised. Increased pedal travel may indicate pad wear.
As for the GTZ, its main problems are:
- wear of cuffs, gaskets and seals;
- using low-quality brake fluid;
- small particles such as shavings or grains of sand getting into the hydraulics;
- leakage from connecting joints.
Signs of a faulty brake cylinder include the following:
- Slow braking. This may indicate a loss of sealing of the cuffs.
- Great force when pressing the pedal. Often caused by swelling of the rubber in the piston seals.
- Short brake pedal travel. It speaks of a clogged compensation hole due to which the fluid in the cylinder has nowhere to go. Sometimes the hole is blocked by swollen seals.
- The pedal falls towards the end of its stroke. This indicates wear on the cuffs, which leads to fluid flowing behind the piston.
- The pads continue to hold the discs. There may be a piston wedge or a blockage in the bypass hole.
And yet, some signs are not always a consequence of failure of the gas turbine engine. Pedal dips can occur when the tubes are filled with air, and weak braking can indicate a breakdown of the brake booster. Be that as it may, any symptoms of deterioration in braking require immediate diagnosis of not only the cylinder, but the entire system.
Failure of the gas turbine engine and its replacement
One of the common reasons why the brake master cylinder fails is its depressurization. In practice, this is noticeable to the naked eye: the brake cylinder will constantly leak, leaving a characteristic mark and a specific smell. The level of brake fluid in the reservoir will continuously decrease. All these signs indicate the need to repair the gas turbine engine and prevent irreparable consequences.
Depressurization of the brake cylinder
is a good reason to replace it with a new mechanism. Malfunctions of the master brake cylinder such as damage and severe wear of the piston seals, inlet collar, piston return spring, as well as scuffing and severe wear of the mechanism mirror indicate mandatory repair or complete replacement of the turbocharger.
Your life and safety depend on the proper operation of the braking system. Therefore, when the above symptoms appear, it is necessary to urgently eliminate the malfunction so that there is no sudden brake failure on the road.
How to check the brake master cylinder
Car maintenance and diagnostics include checking the brake fluid level every week: if it drops sharply, you can judge about leaks. In addition, it is important to change it in a timely manner, since over time the quality of the fluid deteriorates, which leads to premature wear of parts. It is also worth paying attention to compatibility with the cuffs, as some auto chemicals can damage them. And, of course, you should promptly change all rubber seals, paying attention to the service life declared by the manufacturer. It would be optimal to resort to a repair kit with all rubber bands every 100 thousand km, and it is better not to skimp on the quality of components.
If symptoms of a gas turbine engine malfunction appear, it is advisable to check it, and you need to start with a visual inspection. If, when inspecting the housing, drops of brake fluid are found, the hydraulic cylinder should be removed to look for a leak problem. Also common problems include fluid flowing through the seals, which is easy to check: if gurgling is heard from the reservoir when you press the pedal, the seals must be replaced. And, of course, special attention should be paid to the behavior of the pedal: as already noted, a short stroke or dips may indicate the need to clean the cylinder and replace all rubber elements. The best way to judge their condition is by dismantling the part and disassembling it: sometimes, in addition to minor damage to the gaskets, you can also find a crack in the cylinder itself. In this case, the entire part will have to be replaced.
Diagnostic features
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the readings on the dashboard. As a rule, they react to a malfunction earlier than you are able to diagnose it during operation. So, if there are problems in the brake system, then the corresponding lamp should light up on the dashboard.
When the first signals of a malfunction appear in the brake system, the first thing you need to pay attention to is inspecting the brake cylinder (there should be no obvious signs of leakage on it).
In addition, pay attention to each of the brake circuit outputs, joints, and so on. After an external inspection, check the pressure in the brake system (this can be done using a special pressure gauge).
The pressure obtained during the measurement process is compared with what the car manufacturer recommends. If the measurements show a serious difference, then we can talk about the failure of one of the circuits. It is also worth checking the tightness of the circuit, but this work can only be done with special equipment.
As practice shows, one of the main reasons for the breakdown of the gas turbine engine is its depressurization. This is easy to notice by the appearance of a leak and a characteristic odor. Damage to the housing, failure of the return spring, wear of the cuffs (sealing and inlet) or the assembly mirror - all this is a reason to replace the master cylinder.
Knowing how to identify a faulty brake master cylinder can help you identify the problem early, fix it, and eliminate any risk to life. Good luck on the roads and of course no breakdowns.
Prevention Tips
If you follow these simple recommendations, you will extend the life of your brakes:
Change the fluid promptly;
Select the working solution (PP) in accordance with the vehicle passport;
Check your PP level weekly;
Before each trip, inspect all elements of the system for leaks;
After problems with the system, do not forget to adjust the pedal;
The following need constant monitoring:
To fix serious problems, be sure to contact professional auto mechanics.
You can find a workshop suitable for location, list and cost of services on the aggregator website Uremont.com.
Try our service station selection service
Creating an application is absolutely free and will take you no more than 5 minutes
Vehicles include a large number of elements that ensure full operation. Needless to say, among such systems there are no insignificant ones. Especially when it comes to the braking system, which directly ensures driver safety.
The main brake cylinder can easily be called a key part in the brake hydraulic drive circuit. Therefore, they try to make the GTZ as reliable as possible. And yet, malfunctions can only be prevented by timely prevention, since without maintenance, sooner or later any system in a car stops working.
Video on the topic
Problems that arise with the brakes while traveling are considered critical and must be corrected immediately. The culprit of the malfunction is often the main cylinder, installed in the engine compartment and rigidly connected to the pedal.
To find out the cause of the breakdown and repair the unit yourself, you need to know the structure of the brake master cylinder (MBC) and its principle of operation. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to distinguish and filter out problems with other elements of the system.
| The content of the article: |
Pneumatics
hydraulic (for example, in Toyota Corolla or Rav 4);
pneumatic (trucks, tractors and other heavy vehicles).
In the first case, oil acts as the “working fluid”, in the second – gas.
How to check the air brake system? It is important here to ensure tightness, paying close attention to the connections. You can detect a compressed air leak by ear or with a soap solution.
Corrected by replacing or tightening damaged elements.
When checking you must:
drive pressure 0.6 MPa;
turn on compressed air consumers;
When the level drops below 0.05 MPa for half an hour in the free position of the controls (or 15 minutes when operating).
The parking brake is checked in the off state, the leak is determined by ear. If it is, the root of the problem is in the cylinder seals.
The spring chambers are checked if there is compressed air in the drive circuits of the handbrake and the brakes of the rear cart.
If there are problems with tightness, the vehicle cannot be used.
What parameters of the brake system are checked on the stand?
There are two types of brake diagnostics: road and bench.
Road is used to calculate:
braking distance length;
car stability when braking;
brake response speed;
the maximum possible slope of the road on which the car can stand.
The bench method is used to calculate:
specific braking force;
coefficient of uneven braking capabilities of wheels.
The work is that sensors record reactive moments. Thanks to the recorded data, you receive accurate information about the condition of each vehicle element.