To ensure high compression in the engine, and this greatly affects its efficiency and other capabilities in terms of efficiency, ease of starting and specific consumption, the pistons must be installed in the cylinders with a minimum clearance. But it is impossible to reduce it to zero; due to different temperatures of the parts, the engine will jam.
Therefore, the gap is determined by calculation and strictly observed, and the necessary seal is achieved by using spring piston rings as a gas and oil seal.
Why does the gap between the piston and cylinder change?
Car designers strive for engine parts to operate in fluid friction mode.
This is a method of lubricating rubbing surfaces when, due to the strength of the oil film or the supply of oil under pressure and at the required flow rate, direct contact of the parts does not occur even under significant load.
On the subject: How to understand that the cylinder head gasket is broken
This state cannot always be maintained and not in all modes. Several factors influence this:
- oil starvation, the supply of lubricating fluid, as is done in the sliding bearings of the crankshaft and camshaft, under pressure into the area between the piston and cylinder is not carried out, and other lubrication methods do not always give a stable result; special oil nozzles work best, but for various reasons they put them up reluctantly;
- a poorly made or worn honing pattern on the surface of the cylinder, designed to hold the oil film and prevent it from completely disappearing under the force of the piston rings;
- violations of the temperature regime cause the thermal gap to zero, the disappearance of the oil layer and the appearance of scuffing on the pistons and cylinders;
- the use of low-quality oil with deviations in all significant characteristics.
It seems counterintuitive, but the cylinder surface wears more, although it is usually made of cast iron, a solid cast iron block or various dry and wet liners cast into the aluminum of the block.
Even if there is no liner, the surface of the aluminum cylinder is subjected to special treatment, and a layer of a special hard wear-resistant coating is created on it.
This is due to a more stable pressure on the piston, which, in the presence of lubricant, almost does not remove metal from it during movement. But the cylinder is subject to rough operation of spring rings with high specific pressure due to the small contact area.
This is interesting: How to check the camshaft position sensor DPRV
Naturally, the piston also wears out, even if this happens at a slower rate. As a result of the total wear of both friction surfaces, the gap continuously increases, and unevenly.
How to choose piston rings
The selection of piston rings means that the dimensions of the piston rings must necessarily correspond to both the dimensions of the pistons and the dimensions of the cylinders. Let us add that selecting piston rings by size is a little easier compared to selecting the pistons themselves. This is due to the fact that repair piston compression and oil scraper rings for various engine models are more or less interchangeable today. This means that you can purchase both original piston rings and select parts from a third-party manufacturer.
Selection of rings by size
It is necessary to select rings taking into account the following basic parameters:
- piston ring height;
- piston ring diameter;
Any high-quality analogue that has the required dimensions often becomes available without any problems. To be completely sure, it is also necessary to take into account the radial width of the piston rings, or rather, the correspondence of this width to the piston grooves. In other words, the depth of the grooves in some cases may be insufficient.
As for compression rings, such rings are structurally similar, often have the same or almost the same radial width, so problems usually do not arise after installing correctly sized rings from this group. The selection of oil scraper rings, on the contrary, requires increased attention both to the design of the ring itself (box-shaped, stacked oil scraper rings), and additional clarification of their radial width according to special catalogs of the ring manufacturer.
We also recommend reading the article about what to do if the piston rings are stuck. From this article you will learn about the reasons for the occurrence of rings, self-diagnosis of the problem and how to repair this problem yourself.
I would like to add that selecting piston rings for diesel engines is more difficult. Compression rings for diesel engines are molybdenum coated and also have a trapezoidal profile, which can additionally have different angles. Oil scraper rings in diesel engines are usually box-shaped, but this fact must also be checked in catalogs, since there are cases of installation of set rings on a diesel engine.
Please note that it is highly not recommended to install piston rings from a gasoline engine on a diesel engine. At the same time, in some cases, it is possible to install piston rings from a diesel engine to a gasoline engine.
Which piston rings are better
In addition to choosing from the available nominal and repair sizes of rings, you will also need to separately select the material of manufacture. It is quite fair to say that piston rings for a low-power, low-speed engine, which was developed 10-15 years ago (even taking into account their full compliance in size), will be able to function normally and for a long time in a highly accelerated turbocharged power unit.
The fact is that the materials, coating applied and tolerances on the geometry of the rings may well differ. During the selection process, close attention should be paid to these factors, especially in the absence of accurate data in the manufacturer’s catalogs. It should also be added that rings for new engines usually work well in older internal combustion engines, but not vice versa.
The upper ring is the most heavily loaded during the operation of the internal combustion engine. For this reason, such rings are made of alloy cast iron, which is also plasma sprayed with chromium or molybdenum. Chrome has a porous structure, which allows it to effectively retain the required amount of engine oil. Coating with chromium or molybdenum increases the wear resistance of the rings and also provides a low coefficient of friction during contact with the cylinder walls.
Cast iron piston rings are considered to be of sufficient quality. Such parts are made of high-strength cast iron, which has improved properties and actively resists wear. Oil scraper rings are available in chrome plated and also without chrome coating. Steel rings additionally equipped with a spring element are also on sale.
Chrome rings are usually installed on engines with a high compression ratio, which implies more severe loads on the internal combustion engine and CPG. Foreign-made civilian cars often have stainless steel piston oil rings. Such rings are characterized by a long service life, low weight and reasonable cost.
Compliance standards
In its initial state, the cylinder fully corresponds to its name; it is a geometric figure with a constant diameter along the entire height and a circle in any section perpendicular to the axis. However, the piston has a much more complex shape, and it also has heat-setting inserts, as a result of which it expands unevenly during operation.
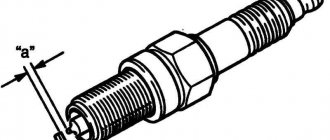
To assess the state of the gap, the difference between the diameters of the piston in the skirt area and the cylinder in its middle part is selected.
Formally, it is generally accepted that the thermal gap should be approximately 3 to 5 hundredths of a millimeter in diameter for new parts, and its maximum value as a result of wear should not exceed 15 hundredths, that is, 0.15 mm.
Of course, these are some average values; there are a great variety of engines and they differ both in different approaches to design and in the geometric dimensions of parts, depending on the working volume.
Repairing engine 21126 VAZ 2170 Priora after timing belt break
Today we brought one of the old clients to the Priora, as it turned out, the jammed pump broke the belt and, as a result, the valves were bent.
But progress at AvtoVAZ does not stand still, and if on the engines of the tenth family the valves were simply bent, then on the Priora 126s the connecting rods also lose alignment and, if they are not changed, there is a high probability that the engine will begin to eat oil and, accordingly, your money. Glory to the designers of AvtoVAZ!
But every cloud has a silver lining, there are sets of pistons for 126 engines with grooves that do not bend the valves. In this article we will describe the procedure for repairing the cylinder head after a broken timing belt, as well as replacing the piston. Removing and installing the timing belt is described in this article, so we will not dwell on it in detail.
To perform this procedure, torque wrenches are required!
I use two keys: 28-210 Nm with a 1/2 square and 5-25 Nm with a 1/4 square.
Result of clearance violation
As the gap increases, and usually it is also associated with a deterioration in the performance of the rings, more and more oil begins to penetrate into the combustion chamber and is wasted.
Theoretically, this should reduce compression, but more often, on the contrary, it increases, due to the abundance of oil on the compression rings, sealing their gaps. But this doesn’t last long, the rings coke, lie down, and compression disappears completely.
Pistons with increased clearances will no longer be able to work normally and begin to knock. The piston knock is clearly audible on the shift, that is, in the upper position, when the lower head of the connecting rod changes the direction of its movement and the piston passes the dead center.
The skirt moves away from one wall of the cylinder and, choosing a gap, hits the opposite wall with force. You can’t drive with such a ringing noise; the piston may collapse, which will lead to a disaster for the entire engine.
How to choose piston rings: protection against counterfeiting
In the process of selecting parts, it is imperative to adhere to a number of rules and tips that will help you avoid purchasing counterfeit parts. Let's start with the fact that replacement parts produced by well-known brands should not be too low in cost compared to original parts.
To produce high-quality products, the manufacturer must use high-quality materials and use modern production technologies. Before searching for non-original replacements, it is recommended that you first familiarize yourself with the cost of similar original spare parts.
Piston rings must be packaged in original packaging. The box itself must be carefully glued together. The inscriptions on the box must have a clear and identical font, stamps, holograms (if it is known that such protection is used on the original packaging). The parts are packaged in small polyethylene bags, stacked in three rings.
The specified package must contain the following designations:
- kit number;
- engine model;
- piston ring size;
An indirect indicator is also the total number of bags with rings. This quantity must correspond to the number of cylinders of the specific engine for which this repair kit is intended to repair.
Additionally, examine the markings of the rings. Piston rings are automatically marked with a special mark at the factory, which indicates the size of the rings and the manufacturer of the part. This marking is located on the ring in a clearly defined location. Counterfeit parts may not be marked or may be marked in a location different from where such markings appear on the original product.
Before purchasing, it is recommended to inspect the expansion springs in detail. These springs must have a variable pitch of turns, and also have a polished surface at the ends and outer diameter. The absence of such signs may indicate either poor manufacturing quality of the parts, which will greatly affect the service life, or a counterfeit.
It would be a good idea to check the profile and height of the protrusions. If the protrusions are minimal or completely absent, then the rings may not be new, but used. To be on the safe side, use a micrometer to determine the nominal and repair sizes of the rings.
When selecting compression rings, tactilely feel the chamfer, which is located on one or both sides of the outer diameter of the ring. Low quality products do not have these chamfers. On high-quality rings, you can also see the ends, which are lighter in color and have a slightly rounded shape.
Chrome-plated piston rings and rings without such a coating are identical in color, but the version with chrome applied differs from the analogue without chrome by special protrusions. On uncoated rings such protrusions are asymmetrical. The presence of chrome also gives the compression rings a characteristic matte finish, while piston rings without chrome have a steely sheen.
pistons play
The car is not mine, the engine is an SF carb, they removed the head to replace the gasket, but found that the pistons were playing, there was no oil being consumed, is it normal for such play to exist or is it being prepared for serious repairs?
Comments 18
if you are making a car for yourself, it’s better to capitalize as soon as the oil starts to wear out
The car is not mine, the owner decided that it would still drive like this, only he gave the head for capital, it won’t cope with a global repair
ok guys, thank you everyone for responding, we decided that we won’t touch the piston until it looks like this, we just gave the head away for capital)
I also had approximately, while the compression was 14, I consumed a liter and a half of oil from replacement to replacement. the master said that you don’t have to touch anything and it will go on for who knows how long, but it still needs to be done in a good way... now I’m running it in, I’m driving calmly, but even at low speeds it feels like some of the horses have been resurrected =) at the bottom it pulls noticeably Better yet, next week I’ll change the oil and then I’ll see how the car drives overall)
Well, now you will advise))) There is nothing to do with a probe. Take a bore gauge from someone and measure in 2 planes and 3 points vertically. You need to look at the barreliness of the cylinders. You can measure without removing the pistons, that will also work. further look at the manufacturer's tolerances. If wear is within tolerances and compression is normal, then drive on.
And pistons in a cold state always play in the head area. Even completely new ones are normal. During operation, this part of the piston becomes very hot and expands. Due to this, the gap is reduced. In addition, the main load for sealing is borne by compression rings. Most of the time on our engines, it’s enough just to change the rings, overhaul the cylinder head - and the engine is like new, well, the liners can be replaced if they are scuffed and have traces of foreign inclusions.
so don't worry, this play may turn out to be normal.
Yes, we decided to leave it like that, we’ll ride around and see how it goes, now we just gave the head away for capital)
Measure the gap with a feeler gauge. There are tolerances, if within the limits, then continue riding.
reassemble if the compression is normal, then it’s better not to touch it, but while the head is removed, fill the valves with kerasin and check for leaks. I also had a small play, I didn’t sharpen it, but I just changed the rings for about 130 thousand, the flight is normal. They can also bore them, so you’ll have rings every six months meyat. In my field, in the past month, my hands were ground down to the state of foil to tear off such axes.
There should not be such a play, you can assemble it like this, but there will be a loss of power.
When I invested in my ex, it was the same... the new one actually stood up clearly... this didn’t happen and I was much better luck.
well, normal piston wear. But what happened with the compression? In general, it’s good that there is this backlash. but in principle, if you drove normally, you can score, but little by little you can already collect money
I don’t know, he said he didn’t measure the compression, but a year ago he measured it at 12 everywhere, but a lot could have changed in a year
Source
Cylinder head repair
We mark all hydraulic compensators with numbers using an ordinary clerical touch and put them away. An ordinary magnet will help you pull them out. We dry out the valves and remove the oil seals (valve seals), the valves into scrap metal, the oil seals into the trash. We clean all channels. We take the head for grinding, just in case. After washing it again with kerosene after sanding and blowing it with air, we begin to assemble it.
We arrange the recently purchased valves in the sequence in which they will be located in the cylinder head and begin to grind in one by one. Lubricate the valve stem with clean oil and apply lapping paste to the edge.
We insert the valve into place and put a valve grinding tool on the valve stem. The stores sell a device for manual lapping, but since this is the twenty-first century, we are mechanizing the process. We take the old valve and cut off the rod from it, select a rubber tube for it of such a diameter that it fits tightly. The rod is in a reversible drill, one end of the tube is on it, the other is on the valve being ground in. At low speeds we begin to grind the valve, constantly change the direction of rotation and periodically press it to the seat or weaken the force. On average, the valve takes about twenty seconds. We take it out and wipe it.
The valve is considered ground in if a uniform gray strip of at least 1.5 mm wide appears on the chamfer.
The same stripe should appear on the valve seat.