Selection of pistons for block cylinders
For new engines, the gap between the piston and cylinder is 0.025-0.045 mm and is set by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinder class.
To do the job you will need a bore gauge.
1. We prepare the car for work (see “Preparing the car for maintenance and repair”).
2. Remove the pistons from the cylinder block (see “Piston rings and connecting rod bearings - replacement”).
How to use the caliper, see the attached instructions or special literature.
3. Using a bore gauge, we check the wear of the cylinder walls.
We carry out measurements in four zones (5, 12, 62 and 112 mm from the upper edge of the cylinder) in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the engine. The cylinder does not wear out in the upper belt. Based on the difference in bore gauge readings in different belts, we determine the degree of wear of each cylinder.
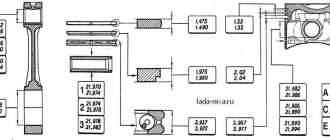
Engine cylinder diameters are divided into five size classes (see Table 8.4). The class of each cylinder is stamped on the lower mating surface of the cylinder block.
Table 8.4. Cylinder diameter classes
Small uniform wear of the cylinder (within 0.05 mm) can be compensated by installing a piston of a different class with a larger diameter.
If the maximum wear is 0.15 mm or more, boring the cylinders and installing repair size pistons is required.
The cylinders are bored by 0.4 mm and 0.8 mm to fit the dimensions of the repair pistons.
4. There are markings on the piston bottom, where:
2 — piston pin hole class; C - piston class; ← - mark that should be directed towards the front end of the crankshaft; G - piston mass group.
Based on the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) every 0.004 mm.
According to the outer diameter, pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) every 0.01 mm (measured in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 55 mm from the piston bottom).
In terms of size, pistons come in nominal and two repair sizes. Pistons of nominal size are not marked. Pistons of the first repair size are manufactured with a diameter increased by 0.4 mm and are marked with the symbol “Δ”. Pistons of the second repair size have a diameter increased by 0.8 mm and are marked with the symbol “□”.
All pistons on the engine must be of the same mass group. Pistons of the nominal group are designated by the symbol “G”. Pistons with increased and decreased mass by 5 g are designated “+” and “-”, respectively.
The class of the finger is marked with paint on its end.
According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three classes (blue, green and red), every 0.004 mm.
To make it easier to select a finger for the piston hole, the required class of the finger is indicated with paint on its inside.
The required pin class is indicated on the connecting rod cover (number 2). Depending on the weight of the heads, connecting rods are divided into classes. The marking is applied on the connecting rod cover with the letter “M”.
Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine (see Table 8.5).
Source
Video - How to measure the piston correctly
In addition to the size of the pistons, their mass is also a very important indicator. The weight of the pistons can be normal, or with a change of plus (minus) 5 grams. In addition, it is necessary to select the correct oil scraper rings for the pistons, which must be of repair sizes.
After the pistons have been selected and installed, it is necessary to check the size of the gaps again. If it is within normal limits, then you can begin reassembling the engine. The cylinder head is installed, then the gas distribution mechanism drive. After this, the cylinder head cover with a new gasket and all the attachments are screwed on. Don't forget to add oil, coolant and adjust the gas distribution mechanism. After this, most likely, you will have to set the ignition timing. The car is now completely ready for use.
This completes checking the gap between the piston and cylinder. No matter how simple this complex procedure may seem to you, it is still recommended to perform it only in specialized service stations, since assembling a cylinder block is a responsible task and it is better to entrust it to professionals. Good luck on the roads!
Piston markings
Calculator for calculating the working volume of an internal combustion engine
Calculator for calculating the cylinder displacement of a car engine
The marking of pistons allows us to judge not only their geometric dimensions, but also the material of manufacture, production technology, permissible installation gap, manufacturer's trademark, installation direction and much more. Due to the fact that there are both domestic and imported pistons on sale, car owners sometimes face the problem of deciphering certain designations. This material contains as much information as possible, allowing you to obtain information about the markings on the piston and understand what the numbers, letters and arrows mean.
1
— Designation of the brand under which the piston is manufactured.
2
— Product serial number.
3
- The diameter is increased by 0.5 mm, that is, in this case it is a repair piston.
4
— Value of the outer diameter of the piston, in mm.
5
— Thermal gap value.
In this case it is equal to 0.05 mm. 6
- Arrow indicating the direction of installation of the piston in the direction of movement of the machine.
7
— Manufacturer’s technical information (necessary when processing the engine).
How does the gap between the piston and cylinder change during operation?
The reduction in clearance occurs due to natural wear of the working parts of the piston and cylinder. This change in the shape of the metal is associated with its ability to be influenced by temperature changes.
In addition, a decrease in the gap can also occur if the engine is assembled incorrectly. For example, the installation of the connecting rods is incorrect or the cylinders are misaligned. Overheating of the engine is also an issue, since high temperatures tend to expand materials. This is especially true for aluminum, which, unlike cast iron, has a high expansion coefficient.
Like any other defect, a violation of the gap between the piston and the cylinder has a negative impact on engine performance. The contact of the piston and cylinder at the wrong angle leads to dry friction, which occurs without lubricant and increases the temperature of the parts. The consequence of such friction in almost all cases is the appearance of various scratches on the working surfaces of the cylinders.
After this, any engine will definitely undergo repair. To carry out diagnostics, it is necessary to completely remove the cylinder head and as soon as the piston group is visible, you can begin the corresponding measurements. During the measurement process, you will need a micrometer to show the piston clearance and a bore gauge to determine the cylinder diameter.
Information on the piston surface
Discussing the question of what markings on pistons mean, it is worth starting with what information the manufacturer puts on the product.
- Piston size . In some cases, in the markings on the bottom of the piston you can find numbers indicating its size, expressed in hundredths of a millimeter. Example - 83.93. This information means that the diameter does not exceed the specified value, taking into account the tolerance (tolerance groups will be discussed below; they differ for different brands of cars). Measurement is carried out at a temperature of +20°C.
- Installation gap . Its other name is temperature (since it can change along with changes in the temperature regime in the engine). Designated as Sp. It is given in fractional numbers, meaning millimeters. For example, the marking on the SP0.03 piston indicates that the gap in this case should be 0.03 mm, taking into account the tolerance range.
- Trademark . Or an emblem. In this way, manufacturers not only identify themselves, but also provide information to craftsmen about whose documentation (product catalogs) should be used when selecting a new piston.
- Installation direction . This information answers the question - what does the arrow on the piston point to? It “tells” how the piston should be mounted, in particular, the arrow is drawn in the direction of forward movement of the car. On cars where the engine is located at the rear, instead of an arrow, a symbolic crankshaft with a flywheel is often depicted.
- Casting number . These are numbers and letters that schematically indicate the geometric dimensions of the piston. Typically, such designations can be found on European machines, for which the piston group elements are manufactured by companies such as MAHLE, Kolbenschmidt, AE, Nural and others. To be fair, it is worth noting that casting is now used less and less. However, if you need to identify the piston using this information, then you need to use a paper or electronic catalog of a specific manufacturer.
What happens to the clearance between the piston and cylinder
During proper operation of the engine, a natural process occurs and the gap between the piston and cylinder narrows. This occurs based on the conditions of constant operation in high temperature conditions of parts.
In addition, the reason for the narrowing of the gap between the piston and the cylinder may be improper adjustment of moving parts, temperature overload or misalignment of the cylinders. It should not be forgotten that cylinder blocks are increasingly made of aluminum materials, which have double the expansion coefficient compared to alloy cast iron.
The reduced clearance between the piston and cylinder leads to semi-dry friction and, as a result, the temperature of the cylinder block parts increases. Gradually, lubrication stops altogether and the disappearance of the gap results in the first scuff marks on the piston.
Almost always, the result of diagnosing the condition of the cylinder block is the repair of the cylinders and elements of the engine piston group. It is possible to fully determine the extent of defects in pistons, liners and other parts only after disassembling the cylinder head.
Having reached the piston group, we begin to troubleshoot the cylinders and pistons. The main measuring instruments for measuring diameters are: a micrometer - for pistons and a bore gauge (indicating gauge) for measuring the diameter of the cylinder.
VAZ pistons marking
According to statistics, owners or engine repair technicians of VAZ cars are most often interested in the marking of repair pistons. Below we provide information on various pistons.
VAZ 2110
For example, let's take the engine of a VAZ-2110 car. Most often, this model uses pistons marked 1004015. The product is produced directly at AvtoVAZ OJSC. Brief technical information:
- nominal piston diameter - 82.0 mm;
- piston diameter after first repair - 82.4 mm;
- piston diameter after the second repair - 82.8 mm;
- piston height - 65.9;
- compression height - 37.9 mm;
- The recommended clearance in the cylinder is 0.025...0.045 mm.
Additional information can be printed directly on the piston body. For example:
- “21” and “10” in the area of the hole for the finger - designation of the product model (other options - “213” indicates the VAZ 21213 engine, and for example, “23” - VAZ 2123);
- “VAZ” on the inside of the skirt is the manufacturer’s designation;
- letters and numbers on the inside of the skirt are a specific designation of foundry equipment (you can decipher it using the manufacturer’s documentation, but in most cases this information is useless);
- “AL34” on the inner side of the skirt is the designation of the cast alloy.
The main marking symbols applied to the piston crown:
- The arrow is an orientation marker indicating the direction towards the camshaft drive. On the so-called “classic” VAZ models, sometimes instead of an arrow you can see the letter “P”, which means “in front”. Likewise, the edge where the letter is depicted should be directed towards the direction of movement of the car.
- One of the following symbols is A, B, C, D, E. These are diameter class markers that show the deviation in the outside diameter value. Below is a table with specific values.
- Piston mass group markers. “G” is normal weight, “+” is weight increased by 5 grams, “-” is weight decreased by 5 grams.
- One of the numbers is 1, 2, 3. This is a piston pin hole class marker that determines the deviation in the diameter of the piston pin hole. In addition to this, there is a color designation for this parameter. So, the paint is applied to the inside of the bottom. Blue color - 1st grade, green - 2nd grade, red - 3rd grade. The following provides additional information.
For VAZ repair pistons there are also two separate designations:
- triangle - first repair (diameter increased by 0.4 mm from the nominal size);
- square - second repair (diameter increased by 0.8 mm from the nominal size).
Please note that for different brands of cars (including for different engines), the difference between repair pistons should be found in the reference information.
VAZ 21083
Another popular VAZ piston is 21083-1004015. It is also produced at OJSC AvtoVAZ. Its technical dimensions and parameters:
- nominal diameter - 82 mm;
- diameter after first repair - 82.4 mm;
- diameter after the second repair - 82.8 mm;
- piston pin diameter - 22 mm.
Marking of ZMZ pistons
Another category of car owners interested in piston markings have ZMZ brand motors at their disposal. They are installed on GAZ cars - Volga, Gazelle, Sobol and others. Let's look at the symbols on their bodies.
The designation “406” means that the piston is intended for installation in the ZMZ-406 engine. There are two markings stamped on the piston crown. According to the letter painted on the new block, the piston is matched to the cylinder. When repairing with cylinder boring, the required clearances are made during the process of boring and honing for pre-purchased pistons with the required size.
The Roman numeral on the piston indicates the correct piston pin group. The diameters of the holes in the piston bosses, the connecting rod head, as well as the outer diameters of the piston pin are divided into four groups, marked with paint: I - white, II - green, III - yellow, IV - red. On the fingers, the group number is also marked with paint on the inner surface or on the ends. It must match the group indicated on the piston.
The group number should similarly be marked with paint directly on the connecting rod. In this case, the mentioned number must either coincide or be next to the number of the finger group. This selection ensures a situation where the lubricated pin moves with little effort in the connecting rod head, but does not fall out of it. Unlike VAZ pistons, where the direction is indicated by an arrow, on ZMZ pistons the manufacturer directly writes the word “FRONT” or simply puts the letter “P”. During assembly, the protrusion on the lower head of the connecting rod must coincide with this inscription (be on the same side).
There are five groups, with a pitch of 0.012 mm, which are designated by the letters A, B, C, D, D. These size groups are selected according to the outer diameter of the skirt. They correspond to:
The value of the piston group is stamped on its bottom. So, there are four size groups, which are marked with paint on the piston bosses:
- 1 - white (22.0000...21.9975 mm);
- 2 - green (21.9975...21.9950 mm);
- 3 - yellow (21.9950...21.9925 mm);
- 4 - red (21.9925...21.9900 mm).
Pin hole group marks can also be applied to the piston bottom in Roman numerals, with each digit corresponding to its own color (I - white, II - green, III - yellow, IV - red). The size groups of the selected pistons and piston pins must match.
The ZMZ-405 engine is installed on the GAZ-3302 “Gazelle Business” and GAZ-2752 “Sobol” vehicles. The calculated gap between the piston skirt and the cylinder (for new parts) should be 0.024...0.048 mm. It is defined as the difference between the minimum cylinder diameter and the maximum piston skirt diameter. There are five groups, with a pitch of 0.012 mm, which are designated by the letters A, B, C, D, D. These size groups are selected according to the outer diameter of the skirt. They correspond to:
- A - 95.488...95.500 mm;
- B - 95.500...95.512 mm;
- B - 95.512...95.524 mm;
- G - 95.524...95.536 mm;
- D - 95.536...95.548 mm.
The value of the piston group is stamped on its bottom. So, there are four size groups, which are marked with paint on the piston bosses:
- 1 - white (22.0000...21.9975 mm);
- 2 - green (21.9975...21.9950 mm);
- 3 - yellow (21.9950...21.9925 mm);
- 4 - red (21.9925...21.9900 mm).
Thus, if, for example, the letter B is written on the piston of a GAZ engine, this means that the engine has been overhauled twice.
How to measure piston ring clearance
At the first stage, you just need to visually inspect the part. It should not have cracks or any other defects. If you notice even minor mechanical damage, the element must be replaced with a new one.
Some preventive procedures will also help
The piston head must be cleaned of carbon deposits, and special attention must be paid to the grooves that are located under the rings. Only after these procedures can you begin to inspect the gap. Since there are only three rings in the device
Each has its own parameters:
Since there are only three rings in the device. Each has its own parameters:
- Upper compression 1-0.04-0.075 mm.
- Lower compression 2-0.03-0.065 mm.
- Oil scraper 3-0.02-0.055 mm.
Be extremely careful when taking measurements. Each ring has its own optimal gap size. For greater accuracy, use a micrometer. This is a device that allows you to measure all the parameters you need with extreme accuracy. For this purpose, there are special probes that allow you to easily and quickly take readings from the grooves.
Toyota pistons markings
The pistons on Toyota engines also have their own designations and sizes. For example, on the popular Land Cruiser, the pistons are designated by the English letters A, B and C, as well as numbers from 1 to 3. Accordingly, the letters indicate the size of the hole for the piston pin, and the numbers indicate the size of the piston diameter in the “skirt” area. The repair piston has +0.5 mm compared to the standard diameter. That is, only the letter designations change for repair shops.
Please note that when purchasing a used piston, it is necessary to measure the thermal gap between the piston skirt and the cylinder wall. It should be within 0.04...0.06 mm. Otherwise, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics of the engine and, if necessary, carry out repairs.
Decarbonization of piston rings
If the engine starts to smoke, there is a possibility that there are rings stuck in the piston grooves. Nowadays, there are many different modern means for decarbonizing piston rings, and many drivers use them to restore engine performance. Among the most popular compositions are:
- Nitrox Power;
- LAVR ML-202;
- Titanium;
- LIQUI MOLY;
- WYNN'S.
Motorists believe that if the engine starts smoking, you need to use a decarbonizer, and the engine will work as before, without oil consumption and without smoke. Indeed, sometimes these remedies help, but only in cases where the motor has stood motionless for a long time (for example, after winter), and moisture has accumulated in it. If the car is subject to long-term preservation (put in a garage for winter storage), you should remove the spark plugs and pour oil into the cylinders, and plug the spark plug holes with plugs. With such prevention, the spark plugs will not become damp and rust will not accumulate on the sleeves.
But if, after all, a forgetful car owner has not taken preventive measures, you can use a decarbonizer. We get rid of rust in cylinders as follows:
- pull off high-voltage wires;
- unscrew all spark plugs;
- rotate the crankshaft so that all pistons are in the middle position;
- pour 45 ml of liquid into each cylinder, install spark plugs;
- leave the cylinders to “soak” for 6-7 hours;
- why do we turn out the spark plugs, turn the starter a few revolutions so that all the dirt flies out of the engine;
- We put the removed parts back in place and start the engine. At first it may smoke a lot, but then the smoke will go away.
Car owners should remember that decarbonization is not a panacea for all ills, and if the piston rings are worn out, then only replacing them will help.
As a rule, in Zhiguli cars with an age of more than 150,000, the wear on the piston group is already quite significant, and if you are also the owner of, to put it mildly, a little used “penny” that is being repaired by someone unknown and when, then in 90% of cases you will have to replace the piston with a VAZ 2101.