Many car owners are faced with a situation where, after starting the engine, the on-board computer or one of the devices begins to show that the battery is being recharged.
The consequences of this situation are very different and depend on how much the voltage in the on-board network exceeds the nominal one.
Slightly increased parameters will only negatively affect the battery (boiling of the electrolyte followed by its evaporation), but if the voltage coming from the generator greatly exceeds the norm, then electrical consumers may fail.
In any case, overcharging is a phenomenon that must be eliminated, otherwise it will not have the best effect on the service life of the battery and electrical appliances.
Next we will look at why the generator produces a higher voltage of 16, 17 volts into the car’s on-board network, the reason why U jumps and how to eliminate them.
Which cars are affected by the problem?
Naturally, the probability of the battery receiving an excess charge on new foreign cars is significantly lower than on products with a significant mileage from the domestic automobile industry.
However, there are a number of models where overcharging is considered a common problem. We are talking about classic VAZ cars. Among the “classics”, this malfunction most often occurs on the “six” (VAZ 2106).
Trucks and some UAZ models are equipped with on-board voltage sensors and sometimes these sensors begin to signal an increase in the charging current between the generator and the battery (18V or more). This is not normal and may lead to rapid overcharging. However, often the problem is in the sensors themselves, which show incorrect information.
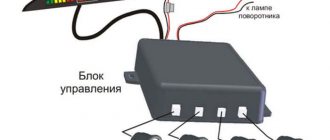
Features of the circuit or why the generator voltage may jump
Above is a general connection diagram, without details, but it is enough to understand how it all works. Now about the features of battery charging.
The generator cannot independently regulate the parameters of the generated electricity, so the output voltage from it varies (jumps) and depends in a significant range on the crankshaft speed and the load in the on-board circuit.
That is, the battery overload is essentially constantly present while the generator is producing energy.
In order for the battery to accept a charge, it is necessary to apply a voltage slightly higher than the nominal value of the battery. On different cars, the input voltage to the battery is different, but in general this figure ranges from 13.9 to 14.5 V.
It is at this voltage that the battery can “take” a charge. If the voltage is lower, the battery will be undercharged, and if the voltage is higher, it will be overcharged. Both situations have a negative impact on the battery.
The generator produces a voltage with a high value, and in order to maintain it in the circuit within the required limits, a relay regulator is included in the circuit.
On some models, this element is included in the design of the generator and is combined with a brush group (the most common design) or represents a separate group (found, for example, on VAZs of the classic family).
After all, the relay-regulator is the only element responsible for ensuring that the voltage in the on-board network corresponds to the norm and that no overloads occur, and for taking into account the load created in the on-board network when switching electrical consumers to.
Is it possible to charge a full battery?
Reasons for discharging the VAZ 2110 battery
Many car enthusiasts know the phenomenon of battery overcharging. It occurs when, for some reason, the voltage regulator starts to work incorrectly, so the voltage at the generator output exceeds 14.5 Volts. The optimal voltage of a fully charged battery is 14 Volts. When the voltage difference between the generator and the battery exceeds one volt, the latter begins to absorb additional energy, which leads to boiling and evaporation of the electrolyte, as well as destruction of the lead plates. As a result, the electrolyte level first decreases, then the battery capacity decreases. After a short time (depending on the generator voltage), the drop in capacity becomes irreversible and cannot be restored by adding distilled water.
If the generator voltage regulator is working normally, then the voltage is maintained at 14 - 14.5 Volts, due to which the battery avoids overcharging. All this fully applies to stationary battery charging, which is carried out using a special charger. If the voltage at the output of the device does not exceed 14.5 Volts, then the battery will take the amount of electricity that is necessary to change the density of the electrolyte. When the voltage of the generator and the charger are equal, the rate of absorption of electricity will drop so much that further charging becomes meaningless. Even if the battery sits on the charger for two days, its capacity and charge will not change. If the voltage at the charger output exceeds 14.5 - 15 Volts, then overcharging will begin, which will lead to a decrease in battery capacity.
If you are using a charger that displays charging current but not voltage, consider the following. The charging current of a fully charged battery should not exceed 1 percent of its capacity. As soon as the charging current has dropped to 1-2 percent, it is necessary to disconnect the battery from the charger to avoid damaging it. Do not charge the battery from a charger without a voltage indicator if the charging current is less than 5 percent of capacity. This will extend the life of the battery and protect it from premature damage.
Battery charging circuit
For a general understanding of the reasons for overcharging, first consider the battery charging circuit diagram. And although it is structurally different on different cars, the general principle of construction is the same.
This circuit includes:
- Generator;
- Rectifier block (diode bridge);
- Relay regulator;
- Fuse box;
- Egnition lock;
- Charge indicator lamp;
- Battery
The recharging system works using the example of the VAZ 2106 and other cars from the VAZ classic series as follows: after starting the power plant, by means of a belt drive, the crankshaft begins to rotate the generator rotor, as a result of which this unit begins to generate electricity.
Car battery malfunctions
Pulse charger for car battery
The service life of a car battery depends on how it is used.
Here are some reasons why a car battery may die:
- battery plates are corroded
- the active coating of the battery plates has become depleted
- battery electrolyte is depleted
If the battery is poorly cared for, a number of malfunctions may also occur, for example the following:
- The battery plates will be coated with lead sulfate.
- The battery will self-discharge quickly.
- A short circuit will occur between the battery plates inside the battery.
- Electrolyte will leak out through cracks in the battery tank.
- The battery poles will oxidize.
Plate sulfation is the formation of a coating of large white lead sulfate crystals, also called sulfate, on battery plates.
Battery plates coated with sulfate cease to participate in the reactions occurring in the battery.
When sulfated plates appear in the battery, then the battery capacity decreases. The battery becomes unusable.
A characteristic sign that partial sulfation of the plates has occurred is the rapid discharge of the battery when the load is on.
The reasons causing sulfation of the plates are as follows:
- Systematic undercharging of the battery.
- The battery was stored in an incompletely charged state or with electrolyte not drained.
- The battery was charged below the permissible limit.
- The battery cells have low electrolyte levels.
- The electrolyte in the battery is of high density.
Any battery has natural self-discharge. Self-discharge occurs for various reasons.
For example, a lattice of plates and the active mass with which it is covered already constitute a galvanic couple and a local current also flows in it.
When the battery is in good condition, self-discharge does not exceed two percent per day of the battery capacity.
Self-discharge of the battery may increase if, when preparing the electrolyte, you use sulfuric acid or water contaminated with impurities (for example, undistilled water).
Additional vapors may also form in the battery when something foreign gets inside.
If the battery self-discharges due to dirty electrolyte, you need to drain it and wash the battery. And fill in a new good electrolyte.
Self-discharge of batteries increases due to high temperature, dirt, water and electrolyte on the lid, and so on.
Self-discharge of the battery can also occur from oxidized pins and terminals.
Oxidized battery terminals and pins must be cleaned.
During the operation of the battery in it, naturally gradually:
- Separators are destroyed.
- The active mass falls out of the plate grids.
- The reason that causes the active mass to fall out of the plates may be prolonged recharging of the battery, vibration, insufficient fastening of the plates, etc.
- As the charging current increases, the battery plates become warped.
The plates warp when there is a short circuit in the circuits, and if the electrolyte level has dropped, and when the starter is turned on for a long time and frequently - at this time the battery is loaded with a high discharge current.
Warping of the plates leads to their contact, that is, to a short circuit inside the battery itself and the operation of the battery stops.
Signs of a generator malfunction
In modern cars, breakdowns of the electrical system are one of the most common. A large number of electronics requires particularly careful monitoring of the operation and condition of the generator and battery, because their failure can immobilize the car. The most common signs of a generator malfunction are:
- battery indicator light on the instrument panel;
- unstable operation of the battery (its boiling over or undercharging);
- different intensity of headlights;
- extraneous sounds from the generator.
If you notice incorrect operation of the car, then perhaps the battery charging current from the generator is insufficient.
All malfunctions of electrical equipment, which includes the vehicle’s energy-generating device, are mechanical (deformation or breakage of fasteners, housing, malfunction of bearings, pressure springs, drive belt, etc.) or electrical (winding breaks, diode bridge malfunctions, burnout or wear of brushes , short circuits between turns, breakdowns, etc.).
Don’t write off a non-working generator: find out if there are repair kits and spare parts. Replace them if possible. If you cannot carry out repair work yourself, then take the generator to a workshop. Many craftsmen will be able to restore the unit at no extra cost and in the shortest possible time.
However, some breakdowns require the purchase of a new device that generates electricity. For example, a failing bearing that is soldered into the generator housing cannot be restored or replaced in most cases.
Remember that failure of this unit can be caused not only by wear and corrosion, but also by poor quality of elements and components; excessive load; external influence of salts, liquids, temperatures.
What can constant overcharging lead to?
- During recharging, the electrolyte boils, and it partially flows out through the gas outlet holes and plugs of the cans. If the process continues long enough, the leaked sulfuric acid solution will end up on the radiator, wires, cooling hoses and body. The acid concentration is not high, but over time it will corrode some of the above.
- With a slight overcharge, the electrolyte falls on the battery case in the form of condensation on the terminals, causing them to oxidize and become covered with a green coating.
- Evaporation of the electrolyte leads to a decrease in its level in the banks, some of the electrodes are exposed, the plates overheat and the active mass falls off from them. This threatens to short circuit the cans and cause the battery to fail completely.
- Recharging at the final stage is accompanied by significant overheating, during which the electrolyte water breaks down into oxygen and hydrogen. The resulting mixture of gases may explode, with acid ending up in the engine compartment.
- Fuses and light bulbs on the dashboard and in the cabin blow out, other on-board electronics stop working (the voltage limit they can withstand does not exceed 17V). In some cases, the on-board network wires may melt and catch fire.
What charger to choose for a car battery, how to use it
AGM batteries are especially sensitive to overcharging. The electrodes of such batteries are separated by matte glass separators. When heated, the electrolyte quickly evaporates from the porous glass fiber, leaving the plates dry. As a result, the active mixture crumbles and the battery becomes unusable.
Gel batteries suffer no less. With constant recharging, the gel can settle, exposing the upper part of the plates, which immediately close. After this, the battery will immediately become unusable.
Repair and troubleshooting
All mechanical problems are eliminated by replacing faulty components and parts (brushes, belt, bearings, etc.) with new or serviceable ones. Older generator models often require grinding of slip rings. Drive belts are replaced due to wear, maximum stretching or expiration of service life. Damaged rotor or stator windings are currently being replaced with new assembled ones. Although rewinding is common among auto repair services, it is becoming less and less common - it is expensive and impractical.
But all electrical problems with the generator need to be solved by checking both other elements of the circuit (in particular the battery), and directly its parts and output voltage. One of the common problems that car owners have to deal with is overcharging , or, conversely, low voltage of the generator . Checking and replacing the voltage regulator or diode bridge will help eliminate the first malfunction, but low voltage output will be a little more difficult to deal with. There may be several reasons why the generator produces low voltage:
- increased load on the on-board network by consumers;
- breakdown of one of the diodes on the diode bridge;
- failure of the voltage regulator;
- slipping of the poly V-belt (due to low tension)
- poor contact of the ground wire on the generator;
- short circuit;
- drained battery.
Greetings, forum members! The problem is this: at idle the charge is 13.6-14 V. At 16 V, the high beams, heaters, and music are on. After dropping the speed, the voltage at idle remains 15.8 V. The diode bridge is intact, I have already changed two generators, before installing them on the car, I checked them on a stand, both produced 14.3 V. They are obviously both in good working order. I installed a 3-level voltage regulator from a VAZ-2110. The situation has changed: at idle it consistently produces 13.6 V (on the regulator it was set to 13.6 V), but at speed it now produces 15.2 V with all consumers turned on. Why Is the tension rising?
First maintenance is an important point for the battery.
Many car battery malfunctions are the result of improper maintenance, and in particular the very first one. To prevent battery malfunctions from causing constant stress and additional material costs, the first maintenance must be performed correctly:
- Cleaning the battery case from dirt, oil, electrolyte.
- Checking and tightening the battery fasteners in the engine compartment.
- Gently but thoroughly clean the gas outlet holes in the plugs. To do this, it is convenient to use a toothpick or a thick needle.
- Checking the condition of the wire tips going to the battery terminals, assessing the reliability of their fastening. If signs of oxidation are detected on the terminals, they are thoroughly cleaned with a wire brush and sandpaper.
- The electrolyte level is controlled using a glass tube. If topping is necessary, use only distilled water.
Important! During the second and subsequent checks, the above is added to the measurement of electrolyte density and its correction.
What is the danger of battery overcharging and how to prevent it
Motorists will rightly support the statement that when using a high-quality battery and using it wisely, the battery does not create any special problems during its entire service life. Some batteries last as long as the car, meaning they don't need to be replaced as often.
But sometimes the battery is under the influence of increased loads and is operated in extreme conditions. Overcharging is considered one of the most dangerous phenomena.
Not all car enthusiasts know what it is and what the real threat is. This gap in knowledge must be filled by further understanding how to act correctly when such a situation arises.
Recharge - battery
Overcharging of the battery (signs: increased gas formation, cell voltages above 2 35 - 2 4 V) or undercharging (decrease in density by 0 01 - 0 02 and cell voltages below 2 1 V) should not be allowed.
The battery can be recharged directly after a normal full charge once every three months.
The battery is specially recharged with a weak current equal to 1/10 of the maximum charging current (or 0 25/10) until intense gas formation occurs on the plates of both polarities and normal density is achieved.
To avoid overcharging the battery (main elements), a current equal to the load current should be selected for recharging additional elements. In addition, to maintain constant voltage on the buses, it is necessary to reduce the number of elements by moving the lever of the double element switch to the appropriate position.
The main reason for overcharging the battery is the high voltage maintained by the relay regulator in the vehicle's electrical system. Along with periodic checks of the regulated voltage, when signs of overcharging appear, it is necessary to carry out an extraordinary check and, if necessary, adjust the relay regulator.
Therefore, in order to avoid overcharging the battery, it is necessary to reduce the regulated voltage of the generator.
Premature destruction of the plates occurs when the battery is overcharged for a long time, the density of the electrolyte is increased, the battery is poorly secured to the car, or the water in the electrolyte freezes.
Destruction of the active mass of the plates occurs due to overcharging of the battery or due to charging it with too much current, as well as as a result of freezing of the electrolyte in the battery. Battery performance is restored by replacing the plates.
An excessively rapid decrease in electrolyte level is a sign of overcharging of the battery due to increased generator voltage. When recharging, electrolyte is also observed to splash onto the surface of the battery. Overcharging is harmful to batteries as it reduces their service life. At the first sign of overcharging, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the generator set.
Due to the lower strength of the active mass of the positive plates, when the battery is recharged, it is destroyed by gases faster than the active mass of the negative plates.
Due to lower mechanical strength, the active mass of the positive plates, when the battery is recharged, is destroyed by gases much faster than the active mass of the negative plates.
| Charge current and capacity of SP type batteries (SPK. |
Equalizing charges of a battery with armored plates are carried out in the same cases as recharges of a battery with surface plates.
Constantly maintaining the battery in a state of full charge requires increased regulated voltage values, which in a number of operating modes leads to overcharging of the battery and shortening its service life. The time to fully charge the battery depends on the initial temperature of the electrolyte, the ambient temperature, the value of the regulated voltage, the adjustment of the current limiter, and the load current.
A short circuit in a battery cell is caused by the following reasons: warping of the plates, damage to the separators, the formation of dendrites (growths) on the plates, overflow of the active mass falling off the plates into the grooves at the bottom of the battery tank and for this reason the formation of conductive bridges between the plates of different polarities. Sometimes, when recharging a battery, abundant gas formation in the electrolyte causes crumbled particles of the active mass to float to the surface, which form conductive bridges.
Other causes of low voltage
A small potential difference in the system is not always associated with a breakdown of the generator or a bad battery. If the diagnosis of these elements does not reveal any problems, then you should pay attention to the following:
- condition of the battery terminals - connection density and oxidation;
- electrical wiring problems - oxidation, violation of its integrity;
- output contacts to electrical appliances;
- correctly selected energy consumers.
Each contact must be tightly adjacent and intact, that is, there must be no formations (for example, sulfation) that will disrupt the flow of current. Incorrect connection of contacts leads to accelerated battery discharge even when the car is not running.
Common battery problems
As a rule, motorists encounter the following battery malfunctions:
- damage to the plates (chemical or mechanical);
- short circuit of the battery plates or electrodes;
- damage to the battery case, due to which the battery banks lose their seal;
- chemical oxidation of the terminals at the battery terminal.
In most cases, battery malfunctions occur for the following reasons:
- Incorrect use of the battery.
- End of battery life.
- Manufacturing defects.
It's time to move directly to the car's alternator. Generator breakdowns are much more common, which is caused by the more complex design of this element. And it can be much more difficult to detect problems.
Specialists often deal with the following generator malfunctions:
- voltage regulator failure;
- damage to the diode bridge (aka rectifier);
- wear of current collecting brushes;
- defects in the charging circuit wires;
- damage or operational wear of the pulley;
- wear of slip rings or commutator;
- short circuit of individual turns on the stator winding;
- bearing failure.
Every self-respecting car enthusiast should understand what causes generator malfunctions most often and how they can be dealt with. It is also necessary not to forget that timely prevention helps to avoid serious problems. Towards the end of the article, we will look at some tips that will help you learn how to test the generator yourself. But let's first learn about the internal structure of the node.
There are DC and AC generators. Nowadays, passenger cars are equipped with AC devices with an integrated rectifier, which is also called a diode bridge. It is this part that ensures the conversion of alternating current into direct current, which is necessary for the functioning of electrical devices in the car. In most cases, the diode bridge is located in the housing or cover of the generator. Typically, it is built into one of these parts.
The electrical equipment of a modern car can only operate within a given voltage range. Very often, a voltage from 13.8 to 14.7 Volts is considered working. Since the generator is connected to the engine crankshaft using a special belt, its operation directly depends on the speed of the vehicle and the current engine speed.
In order to smooth out the resulting current, a voltage regulator relay is used. Essentially, it is used as a stabilizer and helps to equalize the operating voltage, in which there should be no dips or surges. Many automobile generators are equipped with integral-type voltage regulators, which motorists call “pills” or “chocolate bars.”
Why is the battery being recharged?
Overcharging the battery from the charger is a consequence of incorrect selection of charging time, voltage and current in manual mode or a malfunction of the charging unit itself. A short-term recharge from a charger is less dangerous than from a generator, since it usually does not have time to lead to irreversible consequences.
The reasons for overcharging the car battery on board are 90% due to a faulty generator. Therefore, it is this that needs to be inspected and checked first. Less commonly, the cause of battery overcharging lies in wiring faults. Specific causes of increased voltage and their consequences are listed in the table.
Table of reasons for overcharging a car battery:
| Causes | What causes overcharging? |
| Generator relay problems | The relay is not working correctly, the voltage in the on-board network is too high or voltage surges are observed. |
| Faulty generator | The generator, due to a short circuit in the windings, a breakdown in the diode bridge or for other reasons, cannot maintain the operating voltage. |
| Regulator relay failure | The voltage regulator relay (“tablet”, “chocolate bar”) does not function, which is why the output voltage significantly exceeds the permissible value. |
| Weak contact of the relay-regulator terminal | Due to the lack of contact, the relay receives an undervoltage, as a result of which a compensating effect is not generated. |
| Consequences of generator tuning | To increase the voltage on older models (for example, VAZ 2108-099), craftsmen install a diode between the terminal and the relay regulator, which lowers the voltage by 0.5–1 V in order to deceive the regulator. If the diode was initially selected incorrectly or the drop increased due to its degradation, the voltage in the network increases beyond the permissible limit. |
| Weak contact in wiring | When the contacts on the connecting blocks oxidize and move away, the voltage on them drops, the regulator regards this as a drawdown and increases the output voltage. |
In some vehicles, battery overcharging from the alternator is a common problem caused by design flaws. The table below will help you find out which models are overcharging the battery and what is the reason for it.
A table with the causes of “congenital defects” in some cars, which lead to overcharging of the battery:
| car model | Reason for recharging the battery from the generator |
| UAZ | Overcharging often occurs due to poor contact of the regulator relay. It often occurs on “loaves”, but it also happens on Patriots. At the same time, the original voltmeter is not yet an indicator of overcharge, since it can go off scale for no reason. You need to check the recharge only with a known accurate device! |
| VAZ 2103/06/7 (classic) | Poor contact in the contact group of the lock (terminals 30/1 and 15), on the contacts of the relay-regulator, and also due to poor ground contact between the regulator and the car body. Therefore, before replacing the “chocolate”, you need to clean all these contacts. |
| Hyundai and Kia | On Hyundai Accent, Elantra and other models, as well as on some KIAs, the voltage regulator unit on the generator (catalog number 37370-22650) often fails. |
| Gazelle, Sable, Volga | Poor contact in the ignition switch and/or fuse box connector. |
| Lada Priora | Voltage drop at generator contact L or 61. If it is lower by more than 0.5 V than at the battery, you need to check the wiring and look for the place of the drawdown. |
| Ford Focus (1,2,3) | Voltage drop at the generator regulator connector (red wire). Often the regulator itself fails. |
| Mitsubishi Lancer (9, 10) | Oxidation or breakage in the generator chip of contact S (usually orange, sometimes blue), due to which the RR produces increased voltage. |
| Chevrolet Cruze | A mains voltage slightly higher than 15 V is normal! The ECU analyzes the condition of the battery and, using PWM, regulates the voltage supplied to it in the range of 11–16 V. |
| Daewoo Lanos and Nexia | On Daewoo Lanos (with GM engines), Nexia and other GM cars with “related” engines, the reason for overcharging almost always lies in a malfunction of the regulator. The problem of replacing it is complicated by the difficulty of dismantling the generator for repairs. |
Checking the generator yourself
The simplest option for those who do not know how to test the generator is to inspect the fuse. If the element works, we move on to the generator itself. It is necessary to make sure that the belt is not torn, the rotor rotates freely, and the housing is not damaged. Next, the slip rings and brushes are diagnosed. Brushes need to be changed periodically. If you notice excessive sparking, this indicates the need to purchase new generator brushes. Sometimes autogenerator malfunctions are caused by stator failure.
Experts note that the most common mechanical components of a generator that fail are bearings. Their wear can be determined by the characteristic whistling sound during generator operation. Worn bearings must be replaced without fail. Sometimes the generator does not work efficiently because the drive belt tension is too weak. Very often such a whistle appears during acceleration of a car.
Diagnostics of the rotor field winding is performed using a multimeter. On the device, select the resistance determination mode and connect it to the slip rings of the unit. The resistance should be between 1.8-5 Ohms. If you see lower readings, there is a short circuit in the turns. If the indicators are higher than the mentioned values, a winding break has occurred.
To check the generator stator windings for ground fault, disconnect them from the rectifier unit. If the multimeter displays resistance readings with infinitely large parameters, there is no normal contact of the windings with the body (i.e., “ground”).
The diodes in the rectifier block are also tested using a multimeter (we first disconnect them from the stator windings). Select the “diode test” operating mode. The red probe should be connected to the “+” or “-” of the rectifier, but the black probe (negative) is connected to the phase output.
Then the probes should be swapped. If, when performing this procedure, the instrument readings differ significantly from the previous ones, the diode is working normally. If there are no differences, the diode has failed. The malfunction of the diode bridge of the generator is also confirmed by oxidation of the contacts as a result of overheating of the radiator.
Generator repair and troubleshooting
Mechanical breakdowns are “treated” by simply replacing inoperative components with new or working ones. On old generators, slip rings are often ground. Alternator drive belts should be replaced if they are broken, overstretched, or have visible defects. It is recommended to replace rotors and stators whose windings are damaged, since almost no one does rewinding anymore.
How to check the operation of the generator
The battery in a car is an important element of the system, which is responsible for providing the car’s on-board network with electricity. The generator is used to charge the battery while it is active. Unstable operation of a device generating electricity causes a voltage drop in the network and failure to restore the capacity of the power source.
Normal generator performance means timely and complete replenishment of the battery charge level, which decreases under load. Checking the battery charge level from the generator is simple and can be done by the car owner himself.
Diagnostics of an automotive energy-generating device includes a visual inspection of the unit, its elements and related parts, as well as voltage and current measurements. At least twice a year, you should check the tension of the drive belt, excessive weakening of which leads to a decrease in the performance of the generator, and sometimes can lead to breakdown of the device. Once a year, you can check equipment elements - fasteners, diode bridge, voltage regulator and others. Timely maintenance of the battery will also guarantee the absence of problems - cleaning the terminals, adding distilled water.
Diagnostics of indicators such as voltage, current, resistance are also necessary twice a year. To carry it out, you will need special devices - a voltmeter, multimeter or load fork.
Checking the electrolyte level in the battery.
The next step, after checking and eliminating the self-discharge of the car battery, is to check the electrolyte level in it. Of course, this only applies to serviceable batteries.
The electrolyte level is checked using a special glass level tube, and the electrolyte level should be within 10-12 mm above the battery plates.
A level tube is an ordinary glass tube with divisions in millimeters marked on it. In order to measure the electrolyte level, you need to place the tube in the battery filler hole until it comes into contact with the separator mesh, pinch the upper end of the tube with your finger and pull out the tube. The upper electrolyte level in the level tube will correspond to the electrolyte level in the battery.
Basically, a low level is a consequence of the electrolyte “boiling away”; in this case, the electrolyte level is adjusted by adding distilled water.
Topping up the battery directly with electrolyte is done only when you are sure that the drop in level was due to a spill of electrolyte from the battery.
Before proceeding with further testing of the battery, it is necessary to assess the degree of its charge and carry out further testing of the battery after it is fully charged.
The degree of charge can be determined in two ways: either measure the density of the electrolyte in the battery, or measure the voltage on the battery.
What generator is installed on the VAZ 2114?
Having figured out what voltage the generator on the VAZ 2114 should produce, it’s worth understanding what kind of device produces it. This domestic hatchback is equipped with a three-phase generator type 94.3701 from the factory. It consists of a stationary winding or stator, a rotor, rotor bearings, an impeller, and a pulley for putting on a belt. It also has a diode bridge or rectifier, a voltage regulator and a housing.
Russian-made devices of the KZATE brand were installed on the car from the factory. Also, on some cars of recent years of production you can find standard German Bosch. Despite the fact that domestic generators, with proper care, can be used for a relatively long time, foreign-made parts are considered more reliable. Therefore, when replacing, many owners buy products from this or another foreign brand. In addition, sometimes more powerful generators are installed. They are purchased, for example, by car audio enthusiasts, since the factory ones are not designed for such a heavy load.Recharge - battery
Overcharging batteries is accompanied by an increase in voltage above 2 02 - 2 1 V and leads to a reduction in battery life, so it is not recommended.
To reduce the overcharge of TN-450 batteries, the voltage of the auxiliary generator is set to 2 - 3 V lower. The same applies to the TPZhN-250 and TPZhN-550 batteries, the recharging of which is accompanied by boiling off of the electrolyte, an increase in temperature, and leaching of the active mass.
The oxidation of cellophane takes on a completely different meaning if the battery is overcharged, when the voltage at the terminals exceeds 2 05 - 2 1 V. In this case, the transition of silver into the solution intensifies, a noticeable release of oxygen begins at the electrode, cellophane quickly loses its strength, tears and holes form, and the battery fails. Overcharging is also dangerous from the point of view of enhancing the germination of zinc dendrites. While the solution in the pores of the zinc electrode is saturated with zincate, zinc crystallization during charging occurs mainly inside the pores.
The ratio Q3 / Qp 1 (in %) characterizes the percentage of battery recharge.
The ratio Qa / Qp 1 (in %) characterizes the percentage of battery recharge.
| Box plate.| Armored (tubular plate. |
The battery is closed with a cover with holes for current output pins and for removable ventilation plugs. The ventilation plug ensures the release of gases during self-discharge and slight overcharging of the battery and ensures the safety (non-spillability) of the electrolyte at slight inclinations during operation. The plug hole is used when adding electrolyte, measuring its level and concentration; it also serves to release gases at the end of the charge.
Oxygen interacts with the negative plate cadmium and cannot cause a dangerous increase in battery pressure. At the same time, the oxidation of cadmium with oxygen eliminates the possibility of hydrogen evolution on it even when the battery is recharged.
Other gases are absent under normal conditions. However, if there are certain harmful impurities in the electrolyte, other gases may also be released. Haring and Compton discovered, in particular, small amounts of antimonous hydrogen released when the battery is recharged.
An indicating device is connected to the measuring diagonal of the bridge in series with a variable resistor. When a gas-air mixture sample is burned on the sensitive element, the measuring bridge becomes unbalanced and a direct current voltage appears in its diagonal, proportional to the concentration of the controlled substances. If the light guide does not light up when you press the button, the indicator must be sent to recharge the battery.
Which generator is better to put an injector on a VAZ-2114
Every motorist who is interested in the design of his iron horse knows that the main source of electricity in the electrical equipment of any car is a power plant, which includes a battery, a generator and a relay regulator. The battery is the main one in this trio. It powers the entire on-board network of the car, and the generator with a relay regulator, to the extent possible and necessary, feeds the battery and ensures that the on-board network of the car does not exceed the specified voltage (for cars with 12-volt equipment, this voltage is 14-14 .6 V, and for 24-volt - 27-28.8 V). And although generators in a car are long-lasting items, they sometimes fail. Let's see what the Russian market offers us to replace a failed generator, and at the same time test the proposed models in our testing laboratory.
To begin with, a small educational program. The generator is necessary for uninterrupted charging of the constantly discharged battery by electrical appliances included in the vehicle’s on-board network. Modern cars are equipped with alternating current generators. They best meet the requirements for one of the most important power components of a car.
The generator converts mechanical energy received from the engine into electrical energy. The voltage regulator (in the vast majority of modern cars is an integral part of the generator, with rare exceptions when the regulator is “remote”, that is, placed in the engine compartment, separately from the generator) maintains the voltage of the vehicle’s on-board network within specified limits when the electrical load and rotation speed change generator rotor and ambient temperature.
Overcharge
Overcharging causes corrosion of the positive plate grids and excessive gas formation, which destroys the active material of the plates. Overcharging increases the temperature of the electrolyte, which becomes destructive to the plates and separators. Occasional overcharging is beneficial, but when it becomes routine, battery life is reduced.
Overcharging causes corrosion of the positive plate grids and excessive gas formation, which destroys the active material of the plates. Overcharging also increases the temperature of the electrolyte, which becomes destructive to the plates and separators. Occasional recharging is beneficial, but when it becomes routine, it reduces battery life.
Overcharging causes corrosion of the positive plate grids and excessive gas formation, which destroys the active material of the plates. Overcharging increases the temperature of the electrolyte, which becomes destructive to the plates and separators. Occasional overcharging is beneficial, but when it becomes routine, battery life is reduced.
Recharging serves to eliminate lead sulfate inside the active mass of the plates and on their surface.
Recharges are carried out with a ten-hour current. Prolonged recharges will shorten battery life and should be used only occasionally and avoided if possible.
Overcharging causes corrosion of the positive plate grids and excessive gas formation, which destroys the active material of the plates, especially the positive ones.
Overcharging also increases the temperature of the battery, which can rise to such an extent that it becomes destructive to both the plates and separators. Some cases of warping of plates can also be attributed to overcharging, although the latter is not the only cause of warping.
Overcharging, accompanied by excessive gas release, causes unnecessary loss of water, requiring constant monitoring to ensure that the electrolyte in the cell is maintained at the proper level.
Overcharging is not harmful for alkaline batteries. An indicator of the end of charging is the presence of a certain voltage at the battery terminals. For an iron-nickel battery it is 1 8 - 1 9 V, and for a cadmium-nickel battery 1 75 - 1 85 V. At low temperatures this voltage may be higher than specified.
Overcharges, accompanied by increased gas emission and heating of the elements, are also undesirable.
A training recharge is carried out once a month, and an equalizing recharge is carried out once every 3 months.
Frequent recharging of batteries is harmful, as the active mass of the plates is destroyed.
The overcharge will be in saturation, and diode D2 is closed by the voltage drop across the resistor Rz, which is higher than the supply voltage. When the voltage across capacitor C decreases to almost zero, the voltage drop across R2 becomes less than the supply voltage, diode D2 opens and the base current of transistor T3 decreases sharply, causing it to turn off. The recharge time constant of the capacitor C, equal to ( R Rz) C, is usually much greater than the charge constant RSC and is selected so that the time from the beginning of the capacitor charge to the moment the transistor T3 closes is greater than the maximum repetition period of the input pulses. Since the capacitor is charged regeneratively, each subsequent pulse, the amplitude of which exceeds the relay threshold, regardless of its shape and duration, leads to a complete restoration of the voltage on the capacitor by the beginning of the recharge. Therefore, the relay output always produces a constant signal without gaps. The relay releases only when the input pulses decrease below the operating threshold.
| Interference in a branched circuit due to overcharging of parasitic capacitances. |
To prevent overcharging Cn from occurring at the leading and falling edge of the pulse, it is necessary to follow a certain order of closing the keys: first close Kb. The order of opening must be reversed.
The engine does not pull: the main reasons for the decrease in engine power
So, if no other symptoms other than loss of traction are detected, then you immediately need to pay attention to the quality of the fuel, the proper functioning of the ignition and power systems. As practice shows, more than half of the cases of reduced efficiency from internal combustion engines are associated with fuel
The engine does not turn on due to the fact that the tank may be filled with low-quality or unsuitable fuel for this type of engine (for example, 92-grade gasoline instead of 95-grade gasoline)
As practice shows, more than half of the cases of reduced efficiency from internal combustion engines are associated with fuel. The engine does not turn on due to the fact that the tank may be filled with low-quality or unsuitable fuel for this type of engine (for example, 92-grade gasoline instead of 95-grade gasoline).
Typically, such manipulations are necessary when, parallel to the loss of traction, unstable operation of the internal combustion engine is noted, the speed jumps or floats at idle and under load, the engine does not start easily, the “check” light is on the panel, etc.
Also, owners of gasoline engines can independently determine the quality of gasoline by the spark plugs and their appearance. To check the spark plugs you need to unscrew them from the engine. A disruption in the combustion process of the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders, as well as the presence of impurities in the fuel, can be identified by soot on the spark plugs and its color.
For example, if the fuel contains a lot of third-party metal-containing additives and additives, then the skirt and electrodes may become covered with reddish soot (brick-colored). Black soot will indicate that the fuel is not burning properly, etc. In any case, malfunctions in the combustion process of the working mixture lead to the fact that the engine stops pulling.
The next step in diagnosis is checking the spark plugs. A decrease in the efficiency of these elements is also accompanied by a decrease in the power of the power unit.
This is especially noticeable during sharp accelerations, and when the car is already moving at high speed. In other words, the motor has no “reserve” left for further acceleration.
The candles may be dirty, and it is also possible that their life has come to an end. To fix this problem, you can clean the spark plugs or immediately replace the entire set with a new one.
If everything is in order with the spark plugs, then you need to check the condition of the fuel and air filters. In the first case, insufficient throughput can lead to the fact that the required amount of fuel is not supplied to the cylinders to prepare the so-called “power” mixture.
Consequences
As I already wrote above, they discharged deeply several times and that’s it! The battery can be thrown away! The positive plates will be completely covered with salts, the density of the electrolyte will drop and will not increase. Even if you replace the electrolyte with a new one of the required density, it will not wash away the formed salts.
As many battery manufacturers assure, the maximum threshold value is 15 - 20 cycles. But I know from experience that after 10 cycles, such a battery cannot cope with its duties in winter; it will still work in summer.
The moral of the story is - do not allow such deep discharge parameters. This really kills your battery, each time you take away about 3% of the capacity.
Main reasons with engines of other cars
Next, we will go through other cars, and we will indicate the most frequently occurring problems that lead to a drop in power.
So, on a Mitsubishi Lancer 9, the problem most often arises with the exhaust gas exhaust system. This car uses a double catalyst, which becomes clogged with carbon deposits relatively quickly.
Therefore, many owners of this car, when the power drops, recommend first of all paying attention to this system. But in the ZMZ-406 and 405 engines, which are equipped with GAZelle and Volga cars, a drop in power often occurs due to:
But in the ZMZ-406 and 405 engines, which are equipped with GAZelle and Volga cars, a drop in power often occurs due to:
- Ignition coil malfunctions;
- Losses in high-voltage wires;
- Non-working spark plugs;
- Failure of sensors (primarily DPKV).
But do not forget about the other above-mentioned elements of the power supply, ignition, as well as timing and CPG systems.
In Ford Focus cars, in general, problems with loss of traction arise due to malfunctions of sensors, as well as elements of the power system - especially the fuel module, which includes both a fuel pump and a filter, combined into a single structure.
Much the same applies to a car like the Renault Megane. In this machine, power loss may occur due to:
- Wear of the distributor cover;
- Faulty spark plugs and high voltage wires;
- Weak exhaust system capacity;
- Worn fuel pump and dirty filter elements;
- Damaged injector sensors.
In general, first of all, you should look for the cause in the power and ignition systems, and only then move on to the timing belt and CPG.
Charging the battery
But if the battery still fails you, then the first thing you need to do is charge it before running to the store for a new one. Usually, even a completely tired battery after charging can go for another week or two without problems and turn your starter several dozen times.
The main mistakes car owners make when charging the battery Very often, even experienced drivers forget about some important points when charging, although hundreds of articles have already been written and said about this and even everything is reflected in detail in the battery operating instructions.
Carrying out this procedure in a house or apartment.
It is prohibited to charge the battery in a room that is not ventilated, and a living room is not the best place for this. Firstly, it is not so easy to create drafts here, and secondly, cases of battery explosion cannot be ruled out, although this does not happen so often.
2. Smoking or using open fire near the battery.
If, when electrolyte vapors are released, there is an open fire or even a spark from a cigarette near the battery, you risk exploding the battery. Remember this important point and never smoke or use fire nearby.
Connecting the battery to the device is live.
Very often, beginners make similar mistakes and can pay with their health. Remember: connect the charger to the terminals only when the device is disconnected from the network. Why? This may cause arcing when connecting to the terminals. And about the consequences of sparks, read the previous paragraph and everything will become clear.
Leave the caps in the jars closed.
If you have a serviceable battery, then each bank has its own plug, or they are all covered with one common one. They must be opened, and if this is not done, then at a sufficiently high charging current, the battery case may be damaged as a result of an explosion of electrolyte vapors. If the battery is maintenance-free, then it has one plug in the ventilation channel; we also remove it while charging.
Set the charging current too high.
You should not do this, since in such modes the battery will exhaust its life much faster and you will have to buy a new battery much more often if you neglect this rule - set the charge current to 10% of its capacity. That is, if you have a battery with a capacity of 60 Ampere-hour, then you need to charge it with a maximum current of 6 Amperes.
It would seem that these are quite simple rules, but nevertheless, a considerable number of car enthusiasts make mistakes, which were described above. So, remember them, and try not to repeat them. published econet.ru
If you have any questions on this topic, ask them to the experts and readers of our project here.
What kind of charging should go to the battery from the generator?
It is traditionally believed that 13.5-14.5V should be supplied by the generator to the battery and this is absolutely enough to replenish the battery costs.
It is worth considering that using a battery with a higher power in a car than the manufacturer recommends also requires the installation of a more productive generating device.
It is necessary to take into account the load that the generator must withstand - it is calculated based on the maximum indicators of all electrical appliances and car systems.
Do not forget that the charging current from the energy-generating device will allow you to start the car in the cold season. In order to avoid problems with starting the car, we recommend purchasing generating equipment, the charge current of which will be approximately 10% of the capacity of the power source. That is, a battery of 100 A/h requires a generator that can produce 10A. Please note that for many cars, 100 amp equipment will operate at its maximum capacity, because the power consumption of the automotive system is in the region of 80 amps. Therefore, the choice of a source generating energy must take into account both the battery capacity and network consumption.
Causes and solutions
Excessive battery charge occurs for the following reasons:
- Faulty generator shaft. We are talking about a situation where the regulator is working, but does not perform its functions correctly. The generator snout does not allow the onboard voltage to exceed 14.5V. A defective or faulty device supplies slightly higher currents to the vehicle network, which leads to a stable but not critical overcharge, since the voltage, as a rule, is slightly higher than the standard one.
- Inoperative generator. In such cases, electricity is supplied to the battery directly from the generator without any restrictions, and the voltage can exceed 24V, which as a result causes a significant overcharging of the battery.
- Faulty generator. If the diode bridge is damaged, the winding or armature breaks down on the housing, part of the current will flow past the snout, leading to overcharging.
- Poor contact in the circuit. A working relay perceives the resistance created by a poor contact as an increased load on the vehicle network. Trying to compensate, the regulator passes more voltage into the network, as a result the battery is recharged.
- Incorrect charging from the charger. Some older chargers are manually configured. An incorrectly selected mode leads to overcharging.
The battery is sometimes deliberately overcharged in an attempt to restore functionality. This is done to increase the density of the electrolyte. Under high voltage, the temperature rises, boiling begins, water evaporates and the concentration of sulfuric acid increases.
Most frequently asked questions
Will the battery be recharged if a higher power generator is installed?
No, because regardless of the power of the generator, the voltage at its output is limited by the relay regulator to the maximum permissible for the battery.
Does the diameter of the power wires affect recharge?
The increased diameter of the power wires in itself cannot cause the battery to overcharge. However, replacing damaged or poorly connected wiring may increase the charging voltage if the alternator is faulty.
How to properly connect the second (gel) battery so that there is no overcharging?
To prevent overcharging of the gel battery, it must be connected through an isolation device. To prevent overvoltage, it is advisable to use a limiter terminal or another voltage controller (for example, voltage control relay 362.3787-04).
The generator recharges the battery, is it possible to drive home with the battery removed?
If the relay regulator is broken, you cannot disconnect the battery at all. Reducing the load will raise the already high voltage from the generator, which can cause lamps and on-board electronics to fail. Therefore, when recharging the car instead of the battery, turn off the generator.
Do I need to change the electrolyte after recharging the battery for a long time?
The electrolyte in the battery is changed only after the battery has been refurbished. Replacing the electrolyte that has become cloudy due to crumbling plates by itself does not solve the problem. If the electrolyte is clean, but its level is low, you need to add distilled water.
How long can a battery be charged to increase the density of the electrolyte (evaporate water)?
Time limits are individual and depend on the initial density. The main thing is not to exceed the charge current of 1–2 A and wait until the electrolyte density reaches 1.25–1.28 g/cm³.