string(10) “error stat”
The radiator is a key element in the cooling system of the internal combustion engine. Its task is to transfer excess heat generated during fuel combustion to atmospheric air. Even the earliest cars with internal combustion engines had devices resembling a modern radiator, because in the absence of a special element that ensures cooling of the power units, the operation of the latter, as it was established, was simply impossible. A car radiator ensures that the temperature of a running engine is maintained within certain strictly defined limits, preventing it from overheating and the inevitable jamming in this case.
History of creation
With the invention of internal combustion engines, people began to think about how to cool this engine. The first car to have a cooling radiator installed was the Benz Velo. Benz Velo began selling in 1886. Next, Wilhelm Maybach began to improve the cooling device and came up with a honeycomb design. Such a radiator with honeycombs was installed on a Mercedes 35HP car. Since the time of the first Mercedes 35HP model with a cooling radiator, the design of the radiators has not changed much, except for the geometry and some modifications.
The first samples of water cooling radiators were without a pump. The liquid circulated on its own. Structurally, cooling devices were created in such a way as to create the effect of a thermosyphon (a pipe with liquid in a pipe with a vacuum.
Due to the thermosyphon effect, the cooling liquid entered the radiator. The following physical phenomena occur in a thermosyphon: if water heats up, then its density decreases. Water with reduced density rises. The heated liquid, which rose upward, ended up in the device passing through the upper pipe.
And in the radiator itself, the temperature of the liquid decreased and the density increased. The cool, weighted liquid went down and through the pipe entered the cooling jacket of the internal combustion engine.
The main disadvantage of a radiator with a thermosyphon is that such a device does not cope well with cooling high-power motors. Further, the designers invented a pump to maintain circulation in engines of any power.
What is better: repair or change?
Replacing the engine cooling radiator on a VAZ-2114 with your own hands: removal and replacement
All motorists can be divided into two categories. The first ones believe that the failed part needs to be replaced with a new one. The latter are confident that everything can be repaired. And repairing radiators is a frequent topic of controversy.
The Internet is replete with all kinds of advice on how to fix leaks yourself. Some use special plastic compounds. Others pour products into the system designed to plug cracks. Sometimes some methods help to temporarily extend the life of a part. But in most cases, these methods only clog the cooling system.
It makes sense to repair copper models because they are quite easy to solder. In the case of aluminum analogs, the situation is different. They can be soldered, but this will require expensive welding. Therefore, the cost of repairing a leaking radiator will be almost identical to the price of a new part. It makes sense to agree to this procedure only in the case of an expensive heat exchanger model.
Cooling radiator design
The main function of this device is to remove heat from heated substances. This can be ensured by the design feature of the radiator and the materials from which it is made. Also, to create the best cooling effect, the installation location should be where the device encounters a large air resistance flow. Therefore, on all cars, regardless of the make and model, the cooling system radiator is installed in front of the engine and, therefore, the body elements in front of the radiator are made slotted (radiator grille).
There are cars in which the engine is mounted at the rear. Even with this arrangement of the internal combustion engine, the radiator is placed in front. The only thing is that long lines have to be laid to circulate the liquid. On sports cars you can find a design where the internal combustion engine and radiator are located at the rear, but there are air intakes on the sides of the body.
What does a cooling system radiator consist of?
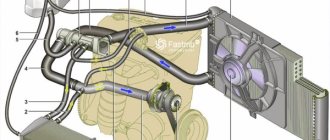
The design of a car radiator can be of several types, but the basic diagram is as shown in the figure.
a — the radiator itself; b - steam valve open; c - air valve in open position.
- Top tank.
- Top pipe.
- Radiator filler cap.
- Steam pipe.
- Aluminum or brass tubes connecting the upper 1 and lower 7 tanks.
- Plates. They are soldered to tubes 5. They serve to increase the surface cooling area.
- Bottom tank.
- Pipe for connecting the radiator and pump. Some modifications have a drain valve on the pipe.
- Fastening elements.
Plates 6 are the core of the radiator. The main element of the heat exchange process. The main part of the cores are seamless tubes with a thickness of 0.15 mm. There is copper or aluminum tape around the tube. The hot liquid passes through the pipes and cools.
The advantage of aluminum as a material for the manufacture of a radiator is only its low weight, compared to radiators made of other metals. Otherwise, an aluminum radiator is inferior in durability and wears out faster.
Classification by core type:
- Radiators with tubular cores.
- Radiators with plate cores.
- Radiators with tubular-ribbon cores.
Tanks materials:
- plastic;
- metal.
Design of steam 11 and air 12 radiator valves:
- 10-spring. Spring elasticity is from 1250 to 2000 grams. A valve and spring with such elasticity allows you to increase the pressure in the cooling circulation system and increase the boiling threshold of the liquid to 110-120 degrees. In this way, the volume of coolant is not that large in modern engines.
- The air valve spring has an elasticity of 50 to 100 grams.
The function of the air valve is to allow air inside the radiator if the coolant (water, antifreeze, antifreeze) boils and cools down, and condensation appears.
Excessive pressure and vaporization occur in the system when the liquid is heated. The lid with the valve itself discharges the pressure, regardless of the atmospheric pressure outside. Since there is low atmospheric pressure in the mountains, the cooling liquid boils faster than on the plain. The air valve protects the radiator from destruction, which can occur from the difference in pressure in the radiator itself and outside.
There are valves on the plug. When the coolant boils, the outlet valve on the cap opens. The steam is removed through the steam pipe. When the liquid in the radiator cools, the pressure drops and, if the pressure in the radiator drops below atmospheric pressure of 1 Atm (kilogram per 1 square centimeter), the inlet valve opens and lets in air so that a vacuum is not created.
If the radiator has a valve cover, then this system is called a closed-type cooling system, since it does not depend on external atmospheric pressure outside.
To drain coolant from a closed cooling system, you need to unscrew the drain bolt or open the tap and open the cover. To completely drain the liquid from the engine cooling system, there is a special drain bolt with a wrench size of 13 (VAZ) on the cylinder block.
If the radiator has a cap without valves, then the cooling system is called open type. In such a system, water, as it should be according to the laws of physics, boils at +100 degrees.
conclusions
An engine cooling system is present on every vehicle. The main purpose of the cooling system is to maintain the optimal temperature of the car engine.
The basic parts of the engine cooling system are the radiator, thermostat, temperature sensor and fan. The system consists of several circuits that are responsible for the correct functioning of the entire system.
The design of the radiator is quite complex, since the design consists of a large number of small channels through which heated liquid flows. Timely inspection ensures normal operation of the power plant as a whole.
Principle of operation
The driving force in an automobile cooling system is the pump. The pump pump constantly moves fluid through the system. There is a small circle of circulation, and there is a large one. While the coolant is not hot, the VAZ thermostat is closed and it circulates in a small circle (engine cooling jacket). When heating, the thermostat opens the valve and a large circle (radiator) opens. The hot surfaces of the internal combustion engine (cylinder head, cylinders) transfer heat to the fluid, which goes into the radiator and transfers heat to the atmosphere.
Is it possible to mix antifreeze and antifreeze or add water to them?
What is the best way to seal a leaking cooling radiator: operating rules and tips for the technician
As you know, antifreeze is the name given to engine coolant. There are many different antifreeze compositions that, in addition to differences in color and price, also have different temperature conditions.
Antifreeze is also a type of antifreeze. But it is not recommended to pour antifreeze into foreign-made cars, since antifreeze, being an extremely caustic liquid, can damage not only hoses, but also pipes and plastic sensors installed in the cooling systems of foreign cars.
You can add water to antifreeze and antifreeze (especially if it is in the form of a concentrate). The main thing is to ensure the required ratio of components, which depends on how low the air temperature is “overboard”. In the summer heat, H2O gradually evaporates from antifreeze, so a small addition of distilled water is useful to reduce the concentration of the active substance to a normal value. In winter, highly diluted antifreeze can freeze even at five degrees below zero. In this case, you always need to add antifreeze to antifreeze, and antifreeze to antifreeze, and the color of the added liquid must match the color of the liquid already poured into the cooling system.
So, if you sometimes experience overheating or even boiling of the engine, or you simply want your engine to never “stall” for “unexplained reasons,” then, first of all, study the internal combustion engine cooling system and the design of the car’s radiator. And then you won’t find yourself in a situation where your car’s engine fails at the most inopportune moment.
Source
DIY repair
The main, easy diagnosis is checking the fluid level in the tank.
If you do not change the coolant for a long time (the higher the quality, the less often it can be changed), plaque appears on the inner walls of the channels.
Dirty channels reduce the cross-sectional area and impede circulation.
Procedure for flushing the radiator:
- Disconnect the lower pipe.
- Pour regular water through the neck. It is advisable to supply water under high pressure.
- Some people disconnect the radiator, unsolder the upper and lower radiator tanks, and then clean them mechanically.
Safety precautions! If the engine is hot, do not open the radiator cap, as you may get burned by boiling water or steam.
What is better to fill in in winter: antifreeze or antifreeze?
Experts never tire of saying that almost half of all car engine breakdowns are associated with problems in the cooling system. Using good technical fluids, timely maintenance and monitoring the tightness and quality of cooling will make engine operation much more convenient.
In Russia, drivers have a certain choice among technical fluids: antifreeze or antifreeze. By the way, except for the CIS countries, such a division does not exist anywhere else. However, it is worth determining the difference between these two liquids and understanding what is best to pour into your car in winter to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Why is it needed in the car?
A car engine works due to the combustion process of fuel in the cylinders. As a result, all parts become very hot. When the temperature of metal elements increases, they expand. If they are not cooled, this will lead to various problems in the power unit, for example, cracks in the cylinder head, in the cooling jacket, cylinder head deformation, excessive thermal expansion of the pistons, and so on. Ignoring such problems will lead to expensive engine repairs.
To stabilize the temperature, all internal combustion engines are designed with a cooling jacket through which liquid circulates using a pump. The heated antifreeze flows through the line into the car radiator. In it, the liquid is cooled and then returned to the engine. This process allows you to maintain the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine.
If there were no radiator in the design of the cooling system, the liquid in it would quickly boil. In a car, this part is installed in the front part of the engine compartment. This is necessary so that more cold air enters its plane.
The efficiency of heat exchangers depends on the following factors:
- number of tubes - the more there are, the better the antifreeze will cool;
- tube cross-section - oval shape increases the area of contact with air, which increases heat transfer;
- forced airflow - especially useful in city driving;
- cleanliness - the more debris there is between the fins of the heat exchanger, the more difficult it will be for fresh air to get to the hot tubes.
Purpose and varieties
Heat removal is far from the only purpose of an engine cooling system. She is additionally responsible for performing a number of other tasks:
- heating the air mass for heating the vehicle interior;
- reducing the waiting time required to bring the engine to operating temperature;
- reducing the temperature of lubricants used for internal combustion engines;
- if recirculation is used, the temperature of the exhaust gases from the internal combustion engine decreases;
- if there is an automatic transmission, the lubricant located inside is cooled.
The design of the engine cooling system directly depends on its mode of operation and operating principle. Accordingly, it is customary to classify a node into several categories:
- liquid - heat is removed due to the constant circulation of the technical fluid;
- air - when using the considered scheme of engine cooling systems, heat will be removed by circulated air;
- combined - includes the use of the 1st and 2nd options simultaneously.
Practice shows that the combined option is the most effective, ensuring stable operation of the motor as a whole.