The thermostat is one of the most important elements that is installed in the liquid cooling system of a gasoline or diesel power unit. In its standard version, this small device has a diameter of about five centimeters and is located between the engine and the radiator. The main task of the thermostat is to control the flow of coolant that circulates through the engine jacket and cooling radiator. The result of the device’s operation is the ability to quickly and effectively warm up the internal combustion engine during a cold start and further maintain optimal temperature balance in all operating modes and under any engine loads.
Appearance and modernization of the device
One of the first thermostats is considered to be the appearance of a mercury device for maintaining optimal temperature balance in a chicken incubator, which was invented in 1620 by Mr. Cornelius Drebbel from Great Britain.
The thermostat has been actively used in the liquid cooling system of internal combustion engines since 1922, when the first and relatively powerful units with large heat release during operation appeared. Early on, there were several unsuccessful attempts to use the device in a cooling system. Further, the design was improved, engineers selected optimal manufacturing materials and achieved such characteristics and reliability that the thermostat became a widely used element in the liquid cooling system of an internal combustion engine.
We also recommend reading the article about the design of a centrifugal pump for an internal combustion engine liquid cooling system. From this article you can learn about the design features of the pump, its functions in the cooling system, features of operation and repair of the pump.
There are two types of thermostats used in car cooling systems. There are solutions with solid or liquid filler. The gel thermostat for automobile liquid engine cooling systems was invented by a Frenchman named Serge Vernier in 1963. The Vernet company specializes in the production of thermostats today, and the products of this brand enjoy well-deserved authority in the auto parts market for various brands of cars around the world.
Thermostat filler
The thermostat can have various types of filler at the core of its design. We have already mentioned that there is a liquid filler and a solid filler. The operating principle and design of these solutions are almost the same. The differences lie only in the increased sealing of the liquid structure, as well as in the individual physical properties of the filler itself and its sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, depending on the composition.
Modern engines have received this type of device, which is based on a solid filler. By such a filler we mean the main thermoelement, which is initially in a solid physical state inside the thermostat.
Functions and location
Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, it becomes necessary to maintain this indicator within strict limits until the very moment the engine stops, and in some cases, for some time after the engine stops operating. The main task of the device is to control and distribute the flow of heated cooling liquid inside the system to remove heat from the engine.
The thermostat can be located in different places, depending on the engine layout in the engine compartment, and the location of its installation directly depends on the model of the power unit. Also, the installation location of the device is influenced by the design features of the implementation of the cooling liquid system itself. In most cases, the thermostat is located where the coolant exits the cylinder head. The second most common location for its installation is the inlet of the centrifugal coolant pump (pump).
How to avoid equipment damage
The thermostat has a maximum switching frequency, or turns heating and cooling on and off at temperatures on either side of the set point. This reduces the risk of equipment damage due to frequent switching. You should know that you cannot set the temperature higher than the temperature range of the thermostat. The manufacturer calibrates the temperature controllers so that the values in the testing laboratory correspond to the actual room temperature. This means that the room temperature will remain around the thermostat, but can also be about 5 degrees higher or lower at any time.
Manufacturers recommend installing thermostats in living rooms. Installation in kitchen areas, corridors, and boiler rooms leads to disorientation of the device and false alarms. It is advisable to install in the coldest room or in a room where there are the most people.
There should be no heat sources near the thermostat, for example, radiators or heaters. Exposing the device to direct sunlight is also highly discouraged. Installation with close electrical devices that emit thermal noise is not recommended.
Before turning on a mechanical temperature controller, it is important to read the instructions on the device information letter. The data sheet has a separate section about connecting the device
Types of temperature control devices in a car
Let's talk in more detail about the different types of autothermostats, taking into account the features of their design. The engine can be equipped with various thermostat options, including:
- thermostat with one valve (single valve);
- two-stage thermostat;
- device with two valves (two-valve thermostat);
- electronically controlled thermostat;
Single valve, two valve and two stage thermostat
The single valve solution is characterized by its simplicity of design and associated reliability. Automakers around the world prefer this type of design and equip most of their cars with this type of device.
A separate type of thermostat with one valve is the two-stage design. The installation of such a solution is due to the fact that some cooling systems create very high coolant pressure during operation. It is difficult for the thermostat valve to overcome this pressure. For this reason, the design of a two-stage thermostat received a solution that implies the presence of two valve plates, which are called small and large. The first to open in the thermostat is the small plate, which requires noticeably less force to overcome the pressure created in the system. The small plate opens easier, and when it opens, it interacts with the large plate and simply pulls it along with it. Opening the large (main) thermostat plate all the way opens the coolant passage.
If in the first case the thermostat has one valve with two plates, then the two-valve regulator received two separate valves, which are located in a single housing. The first valve is the main one and serves to shut off a large circle during the movement of coolant in the system. The second valve is a bypass valve and is responsible for circulating liquid in a small circle. The operation of the valves is synchronized. When one of them blocks the coolant channel, the other opens the desired circuit. This thermostat design has found wide application in the design of passenger cars and trucks, which are products of the auto industry from the CIS countries.
Electronically controlled device
The most advanced and relatively complex in design, but at the same time the most accurate and efficient, is a thermostat equipped with electronic control. The main advantage of such a device is the provision of different temperature indicators to achieve the optimal temperature in relation to the dynamically changing operating conditions of the engine during its operation.
The design of the device resembles a conventional thermostat with a single valve, but an additional heating resistance is added to its thermocouple. The heating of the specified resistance is controlled by the electronic engine control unit (ECU). Thanks to this design, it becomes possible to implement a flexible temperature regime. The indicator is maintained at 95-110°C at light loads on the motor and 85-95°C at maximum load. The main achievement from the use of an electronic device is a noticeable reduction in fuel consumption, as well as a slight increase in power at the “lower” range due to better cooling of the intake air.
There are also engines that have two thermostats in the liquid cooling system. Such systems are called dual-circuit. One thermostat in such a system controls the temperature in the cylinder head circuit and is responsible for maintaining the indicator at 87°C. The second thermostat is located in the cylinder block circuit.
The temperature threshold in the BC region is higher and is at around 105°C. This implementation of temperature control in the cooling system has found application in the design of high-performance turbo engines and provides a resulting increase in power of the power unit due to improved air cooling.
Mechanical floor thermostats
This device is designed to regulate floor heating systems and other heating devices. The equipment allows you to save electricity by adjusting the temperature and heating period.
Mechanical, operating principle
The principle is simple - the mechanism determines the sensor readings and regulates turning the system on or off, maintaining the set temperature. The temperature regulator contains a thermostatic element. It helps regulate temperature and can be located in the middle or outside of the device.
The temperature sensor is installed in an area that is not exposed to the heating device to avoid false readings. Having analyzed the data received from this device, the mechanical thermostat controls and regulates the heating system. Some models react to other heat sources and take their effects into account.
Mechanical thermostat, installation advantages
This equipment helps you not to worry about the system overheating, because it will turn on or stop heating in time. In an empty room, without people, the device will maintain a normal temperature so that the heating does not freeze, and will save energy. Because of its uniqueness, a mechanical thermostat can be used in everyday life and at work to regulate large heating areas. The device automatically turns on after a power failure. The equipment also has a remote control for programming.
Mechanical thermostat, types
There are several criteria by which equipment is classified. Devices are assembled with various sensors, have different mounting methods, applications, and functionality.
Depending on the type of application, the equipment can be built-in or overhead. Overhead equipment is used when hidden wiring is installed and the temperature sensor is attached to the wall. The built-in sensor is equipped with a special box to protect it.
When installing mechanical equipment, the thermal system heats up to a certain temperature and turns off; they are usually used in industrial premises. Electronic (programmable) thermostats are installed in homes and offices, as they have the ability to set the degree of heating and temperature conditions. They are programmed to reduce heat at night and turn on automatically in the morning.
Solid-state thermostat design
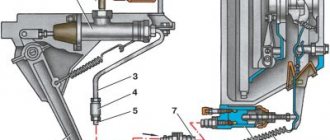
Modern internal combustion engine liquid cooling systems have received the most common version with a single valve, as well as a two-valve thermostat with a solid filler in the vast majority of cases. This element of the internal combustion engine cooling system is a heat-sensitive valve, which is enclosed in a brass frame. The valve also has a plate that is attached to the body. The body itself is a kind of cylinder. A special rod is inserted into this cylinder. The specified rod has one end resting on the upper part of the thermostat frame, and the other end rests on a rubber cavity in the device body. The body and rubber cavity are separated by a heat-sensitive element.
To put it simply, a common two-valve thermostat has a housing, two inlet pipes, an outlet pipe, a main and an additional valve, as well as a coolant temperature-sensitive element. The device is often installed in front of the point where the working fluid enters the centrifugal pump housing and is connected to it with a special outlet pipe. One inlet pipe connects the thermostat to the cylinder head, and the other makes a connection to the lower radiator tank.
The heat-sensitive coolant element consists of a copper cylinder, a rubber diaphragm and a rod. The solid filler is located between the diaphragm and the wall of the balloon. The element is a mixture of copper and granulated wax.
The main requirement for the material is a high coefficient of volumetric expansion. To perform the required functions, fine-crystalline wax or a mixture of copper powder and ceresin is excellent.
Wax was used in the design due to its ability to expand significantly under the influence of heat and change from solid to liquid and back. This wax or paraffin, which is used in the construction of car thermostats, is artificial and differs from the material we are used to. This wax has a number of specific properties that it acquires after undergoing the distillation process.
Principle of operation
When the engine starts, the thermostat is in a closed state at this moment and blocks the access of coolant to the large circle. The coolant circulates along a route that causes it to leave the cylinder block and return immediately. This feature of the cooling system ensures the most efficient heating of the power unit and its subsequent reaching the optimal temperature for its operation under load in the shortest possible time.
When the heating of the coolant reaches a temperature threshold of 80-90°C, then the thermostat begins to open. This happens because the solid element in the device body begins to melt at this temperature. There is a natural increase in the volume of the thermoelement. An increase in volume initiates movement of the thermostat housing along the rod. The rod itself is not capable of moving, since it is rigidly fixed structurally to the upper frame. The valve disc overcomes the force of the return spring and begins to open. This allows the coolant to pass through a fully or partially open valve and begin circulating through the radiator. The cooling efficiency of the coolant in the radiator increases significantly.
At the maximum permissible increase in coolant temperature, the thermostat is fully open, allowing the coolant to pass through the radiator in full. The thermostat opens fully at a temperature of about 95-105°C. When a car engine operates in various modes that are constantly changing, there is a constant change in the degree of opening of the thermostat.
If we consider the operating principle of a two-valve thermostat, taking into account the more familiar concepts of coolant movement in a “large” and “small” circle, then we get the following. Let's imagine that the temperature of the coolant in the system has exceeded 80 degrees Celsius. The solid filler of the thermostat begins to melt and increases in volume, then presses on the rod, which comes out of the cylinder. The balloon begins to move upward, thereby closing the additional valve of the device. The access of coolant to the small circle is closed.
When the coolant reaches a temperature of about 94 degrees, the additional valve will close completely. The main valve still remains open and the coolant circulates freely in a large circle, which implies its movement through the cooling radiator channels.
In the event that there is a decrease in coolant temperature below 80 degrees, the volume of the filler is reduced, and the main thermostat valve begins to gradually close. The fluid flow in the radiator decreases. At the same time, an additional valve begins to open in parallel, which allows the coolant to circulate in a small circle.
The ability to open fully or partially allows you to most efficiently and flexibly maintain optimal temperature indicators for the operation of the internal combustion engine in various load modes. Additionally, the thermostat allows you to reduce the physical wear of parts and components of the power unit, as well as reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases. The most common and high-quality manufacturers of thermostats are Gates, Wahler and Vernet.
How to install the device
First of all, preparatory measures are carried out, which may involve creating a niche in the wall like a rosette. Next, the cabling is laid
It is important to consider that, in addition to connecting the main power line, the device must be interfaced with the equipment. Another thing is that the same wiring can be avoided by purchasing a wireless model
For example, modern convectors with a mechanical thermostat are already equipped with radio devices in basic configurations, relieving the user of unnecessary hassle with installation. But not all units support the wireless principle of interaction with control equipment, and this nuance must be taken into account in advance. The same applies to the method of installing the remote sensor, which will also require careful preparation of a special point for fixation. Another thing is that the sensor will not require intervention in the wall. For it, it is enough to prepare a mounting bracket on which a small case will be mounted. All necessary fittings of this kind are usually included in basic thermostat kits.
Common faults
The main and most common cause of device malfunction is impaired mobility of the thermostat valves. The reasons are different, but in most cases this phenomenon is a consequence of contamination of the thermostat with scale, as well as the formation of corrosion.
The thermostat fails especially quickly due to the fact that many drivers neglect to regularly replace the coolant in the system and use the coolant much longer than it should be. Many people use low-quality and cheapest products from unknown manufacturers, dilute the coolant concentrate with ordinary water instead of distilled water, skip the most important step of flushing the cooling system before the next scheduled coolant replacement, etc.
Car enthusiasts are very familiar with the expression “the thermostat is stuck.” The result of contamination of the thermostat is that the valves of the device may simply freeze in a certain position. Most often this happens in an open or slightly open position. The second common cause of thermostat failure is the loss of its most important physicochemical properties by the solid filler. If the coefficient of expansion of a solid filler decreases, this will mean that in the expanded state its final volume will also change.
Consequently, the thermostat filler will not exert the required pressure on the rod. The structure will partially or completely fail to move, one or both valves will stop functioning properly. If the thermostat malfunctions, the coolant in the system will either overheat or remain constantly cold, and intermediate temperatures deviating from the calculated norm are also possible.
Diagnosis of failure
Serious problems in the cooling system will be indicated to you by a clear deviation from the normal readings of the coolant temperature indicator on the instrument panel in the cabin. With normal operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system and the air temperature outside is about zero degrees Celsius, the power unit should reach operating temperature under load while driving in 5–10 minutes.
The only condition is the serviceability of the temperature sensor itself, the indicator on the instrument panel and the cooling system. If the tightness of the system and the functionality of other elements are not impaired, the coolant level in the expansion tank is at the required level, then obvious signs of a thermostat malfunction are:
- long engine warm-up;
- inability of the internal combustion engine to reach operating temperature under load;
- lack of warm air from the heater;
- constant overheating of the engine regardless of the ambient outside temperature;
- periodic occurrence of these symptoms and their subsequent disappearance;
Identifying a thermostat malfunction is quite simple. After starting a cold engine, the upper radiator hose should be cold and remain so for a certain period of time. If everything is normal, then the coolant circulates only through the “cooling jacket” of the engine (small circle) and access to the radiator during warm-up mode is blocked by the thermostat valve.
When the upper pipe warms up almost immediately, then there is impaired circulation. This means that the main valve of the device is open and the coolant immediately flows in a large circle. As a result, the internal combustion engine is not able to warm up to the optimal operating temperature. This phenomenon means that there is accelerated wear of power plant parts. The rubbing pairs of the unit do not receive adequate lubrication, since an unheated motor has thermal clearances that are different from the norm. The oil also remains too thick and loses its properties, which leads to increased fuel consumption and premature wear of the internal combustion engine.
If the thermostat valve is constantly in the closed position, then overheating and subsequent boiling of the coolant naturally occur. Drivers conventionally say that the engine has “boiled.” This threatens not only a strong increase in pressure in the cooling system and breakdown of its individual functional elements, but also failure of the engine itself.
It also happens when the thermostat valves stick only periodically. The malfunction disappears on its own, then appears again. In such cases, they say that the thermostat is “stuck.” This breakdown is more insidious, since a malfunction with such symptoms is more difficult to identify. You should check the condition of the cooling system and perform a preventative replacement of the thermostat. You shouldn't wait for the situation to worsen.
There is another way to check the functionality of the thermostat, but this solution is extremely rarely used. We are talking about dismantling and then checking the thermostat under conditions close to actual operation. To do this, place the thermostat in a container of water and begin to heat it. When the water temperature reaches the opening threshold of the thermostat valve, then a working device will respond properly. The filler will expand and open the valve approximately 20mm. If this did not happen at all, the valve opened only partially or did not return to its original state after cooling, then we can talk about a malfunction of the device.
Maintenance, prevention and repair
An important criterion when choosing a new thermostat is the temperature at which it operates and when the valve begins to open. This point must be taken into account and the thermostat must be selected in relation to a specific engine. The fact is that devices from different manufacturers have their own temperature “threshold”. If you set a thermostat that is different from the recommended threshold, then the internal combustion engine may overheat. Early operation will mean the engine is unable to reach operating temperature.
The most common recommendation from most specialists and auto mechanics is to periodically replace the thermostat at intervals of 2 to 5 years (mileage from 50 to 100,000 km). In this case, it is not at all necessary to wait for the device to break down, and the replacement itself is combined with a planned replacement of the pump and/or coolant.
Part cost
Numerous types of thermostats have a number of individual advantages and disadvantages. The price of certain devices can also vary greatly. A domestically produced thermostat often turns out to be noticeably cheaper compared to imported analogues. German devices are considered to be the highest quality and most expensive. There are both universal thermostats that can be installed on most different engines, and models that are specifically designed for a specific internal combustion engine or a limited group of power units.
Often the thermostat is not an expensive part and is easy to replace. The final cost of replacement will directly depend on the design features of the internal combustion engine and the location of the device, as well as on the make and model of the car. The thermostat is usually not repaired. The price of a thermostat for cars of the VAZ family can start from 3 USD. For the latest AvtoVAZ models and most foreign-made cars, the minimum price of the device starts at approximately $9 and above.
Description and operating diagrams for VAZ 2106, 2107, 2109, 2114
In VAZ cars, the cooling system has a number of features. In particular, a special 2-valve thermostat (additional and main) with a solid (wax) filler is mounted in front of the pump.
While the engine has not yet warmed up, most of the coolant will flow in a small circle, that is, covering the system pump, the cooling jacket of the power unit and cylinders, as well as the thermostat.
The liquid then returns to the pump. At the same time, coolant circulates through the jacket of the intake pipe and the mixing chamber in the carburetor.
If the cabin heater valve is open, then the liquid passes through its radiator.
In the case when the engine is not completely warmed up, that is, the coolant temperature has not yet reached the desired level (90 degrees Celsius), the main valve partially opens, the other (bypass or bypass) partially closes, and part of the hot liquid goes to the main radiator.
This allows the power unit to warm up faster. As soon as the temperature reaches 90 degrees Celsius, the valve opens completely, allowing all flow to be directed through the radiator.
The main metals from which the thermostat elements are made are copper and brass.
The principle of operation is similar to what was already discussed above.