How to change the pressure sensor on a car's fuel rail
The fuel rail sensor, like any part of the fuel system, can malfunction, usually resulting in a rough running engine, ignition problems, or other instances where the check engine light comes on.
The ATC fuel rail pressure sensor is a part that can reduce evaporative emissions by delivering a specific amount of fuel to the engine to keep it running properly. A pressure sensor ensures that excess fuel does not remain in the conductive channel.
The sensor's job is to determine the pressure directly in the fuel rail, thereby determining the exact amount of fuel in the rail. When the sensor detects the presence of fuel, an electrical signal is sent to the fuel pump for further pumping. As soon as the fuel pressure reaches a certain point, the fuel pump receives a signal to stop working. When the pressure decreases, a request is made to renew the fuel supply.
When a pressure sensor malfunctions, it can be determined by some initial signs that will tell you that something is wrong. Usually there are difficulties with ignition: it takes longer than expected to start the starter. In addition, the engine begins to operate unevenly. Sometimes problems with the pressure sensor on the fuel rail even lead to the engine simply stalling during normal operation.
The following are the alarm codes (for machines with a computer system) that correspond to the pressure sensor: P0087, P0088, P0170, P0171, P0172, P0173, P0174, P0175, P0213, P0214, P0190, P0191, P0192, P0193, P0194.
Location and purpose of the fuel pressure regulator
The pressure regulator is a structural part of the vehicle's power system. It is placed on the fuel frame and involves connection to three lines:
- inlet - through it fuel flows to the regulator;
- direct exhaust - directs the flow with adjusted pressure to the internal combustion engine;
- return exhaust - if excess pressure is detected, it returns part of the fuel to the tank.
The fuel pressure entering the regulator is created by a fuel pump, in front of which a filter element is installed. Thus, the task of the part is reduced to monitoring and, if necessary, flexible change in the pressure of pre-purified fuel in accordance with the needs of the engine.
Absorber and its system
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
Some Lada cars have a fuel system with an absorber. An absorber is an indispensable thing nowadays. It serves to reduce emissions of fuel vapors into the environment.
Absorber
The absorber is a flask filled with special carbon that evaporates fuel vapors and supplies them to the car's receiver. Installed in the vehicle's engine panel.
Absorber sensor
The absorber sensor controls the opening and closing of the air supply to the absorber to control vapors. Installed on the engine cover in engine versions with a volume of 1.6 liters, in engine versions with a volume of 1.5 liters it is installed directly on the absorber flask.
Separator
The separator in Lada cars is installed under the rear left wing near the shock absorber strut and serves to expand the fuel vapor formed in the tank due to temperature changes. Externally, the separator looks like a coolant expansion tank.
Tilting valve
This valve is installed next to the separator under the rear left fender of the car. The valve serves to prevent fuel from entering an overturned car during an accident. That is, when the valve is turned over, it shuts off the fuel system, protecting the car involved in an accident from fire.
Symptoms of breakdowns
Knowing the signs of a malfunction of the DT regulator, you can immediately determine the level of the problem - whether the unit, mechanical or electronic, has completely failed or partially. But all the “symptoms” listed below do not differentiate a regulator breakdown from other faults - they may also indicate a breakdown of the fuel pump or a clogged filter.
Signs of RTD failure are the same for gasoline and diesel engines:
- The engine does not start. The starter spins for a long time when the clutch pedal is pressed.
- The engine stalled at idle. To keep it running you have to press the gas pedal all the time. The second option is instability of speed, leading to engine shutdown.
- Power is lost. The car cannot drive up the mountain and cannot cope with the load. Simply put, “it doesn’t work.”
- Fuel is consumed more than normal. Losses depend on the nuances of the malfunction.
- Fuel is leaking from the hoses. Moreover, replacing hoses or clamps, as well as other closely located elements, does not help.
If at least one symptom appears, a diagnosis is needed.
In new cars, the regulator is the fuel pressure sensor in the rail. If it fails, an error occurs in the ECU memory and the LED lights up, signaling a motor failure.
Errors regarding the RTD are listed under numbers p2293 and p0089 - “mechanical fault” and “controller faulty”, respectively.
Failure options
The regulator is a simple device from a technical point of view, so there are few breakdowns that can happen to it. In almost all cases it is recommended to replace the RTD.
What can break:
- Spring. This is the main failure in the RDT. Due to the weakening of the spring, the engine becomes “starved”, there is not enough fuel at high speeds, when the clutch is pressed and during transient conditions.
- Pollution. When clogged, the ability to pass fuel is lost. The engine stops in any operating mode. If the RTD is heavily contaminated, the pressure in the vehicle rises sharply and fuel leaks through the sealing material. The problem is solved by pumping a large amount of fuel into the fuel pump.
- Jammed. The RTD in the ramp may periodically jam. The car twitches.
RTD contamination
Another malfunction of the regulator is its contamination and reduced throughput. In this case, the engine stalls regardless of which specific operating mode is selected. If the regulator is heavily contaminated, the pressure in the system increases sharply, and this can lead to fuel escaping through the sealing parts and joints. Vehicle manufacturers always consider the possibility that injector and fuel pump performance will deteriorate over time. This problem is solved by pumping more fuel into the fuel pump. Excess fuel increases pressure if it cannot return back to the return line.
Doesn't show fuel level AT ALL
When the arrow points to “0” with a full tank, then attention should be paid to all contacts and connections:
- First of all, this concerns the bolts located on the back side of the instrument panel, since they are the ones who create contact by fixing on the indicators.
- It is possible that the fuel level needle has lost its position and needs to be adjusted.
- The instrument panel itself may also be faulty. Since its mechanical parts are very susceptible to wear.
- We test all the “negative” wires, especially the one located near the handbrake. Because often it is he who is promoted.
- The float or the FLS itself is jammed.
Having analyzed all of the above, we can come to the conclusion that this whole problem lies entirely in the power supply system and the mechanical part of the fuel level sensor.
Please note that if you have an on-board computer (not older models - approx.), it is possible to control the fuel level electronically. You just need to enter the readings after each refueling of the car and the faulty FLS needle will no longer bother you.
How does the fuel pressure regulator work?
On the one hand, the pressure in the regulator is generated by a spring and this is combined with pressure from the intake manifold. In the opposite direction, the force is generated by the fuel pump. When the spring compression forces and the energy from the intake manifold are exceeded, the diaphragm valve opens. This cycle ensures the intake of fuel in the required volume. Next, the pressure from the supplied fuel decreases and the pressure regulator membrane closes.
Schematically, functionality is ensured due to design features. Fuel is pumped into one of the two chambers. The remaining one has a spring. The cavities are separated by a membrane that opens when there is a difference in pressure.
If there is no valve, its functions are assigned to an electronic special sensor. It measures the voltage in the electric pump that supplies gasoline to the system. Thanks to this solution, it is possible to fix the pressure at the optimal level, as well as remotely regulate the fuel supply. This makes it possible to directly control the pump.
The system, developed on an electrical basis, is very accurate when compared with its mechanical counterpart. However, practice shows that “mechanics” gives more reliability when used in domestic conditions. The block is less exposed to negative external influences.
Where can I buy
Spare parts and other products for the car are easily available for purchase at auto stores in your city. But there is another method that has recently received significant improvements. You no longer need to wait a long time for a parcel from China: the AliExpress online store now offers the opportunity to ship from transshipment warehouses located in various countries. For example, when ordering, you can specify the “Delivery from the Russian Federation” option.
Follow the links and choose:
Signs and Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Fuel Pressure Regulator
- the engine stalls at idle;
- engine power is greatly reduced;
- when accelerating, it is not possible to achieve normal dynamics;
- the car reacts poorly to pressing the gas pedal;
- fuel consumption suddenly increases greatly;
- the amount of carbon dioxide emissions increases;
- the crankshaft rotation speed changes.
All these problems arise due to the fact that the regulator becomes clogged or completely clogged over time. Another common cause of failure is weakening of the spring, leading to a strong decrease in pressure. In the absence of normal pressure, fuel supply decreases, power decreases and controllability deteriorates. Such problems are especially common on Ladas - Kalina and Priora, as well as on cars of the 2110, 2112, 2114, 2115 series.
To check the part, you need to carefully inspect it itself, the vacuum hose and all connections. Any leaks found must be corrected. It is also recommended to check the membrane. Disconnect the tube that goes from the RTD to the receiver and shake it. If no gasoline comes out from inside and there is no strong odor, then the membrane is in order.
RTD in diesel engines
Diesel vehicles running on the Common Rail system are also equipped with a pressure regulator. It fits into the fuel rail or is located on the high pressure fuel pump housing. The principle of operation is approximately the same. A special valve diverts unused fuel into the return line, preventing excessive loading.
In diesel engines, the regulator has a slightly different structure than in gasoline engines. It consists of a solenoid and a rod, which rests against a ball to shut off the return line. The design protects the engine from hydraulic vibrations and, as a result, from rapid wear.
Symptoms of element failure
During the operation of the car, a car owner may encounter two types of RTD failure:
- The pressure drop in the rail is below the permissible level - the regulator directs most of the fuel through the return line to the gas tank.
- Increase in pressure to maximum - the element does not allow fuel to flow into the return line.
Note. As a rule, the first malfunction is accompanied by a rapid drop in pressure in the system after the electric fuel pump is turned off.
It is quite simple to track the signs of the first malfunction - the power unit is sorely lacking fuel for normal operation in all modes. Symptoms appear as follows:
- cold starting is difficult, the engine runs extremely unstable until it warms up;
- “dips” during acceleration and jerks when moving uphill;
- the car often stalls at idle;
- Gasoline consumption per 100 km increases.
The increased fuel consumption is explained by the actions of the driver trying to compensate for the lack of fuel mixture by pressing the accelerator pedal. Driving in this mode is quite difficult - it is better to immediately check the fuel pressure regulator for functionality.
When the valve does not allow excess fuel to flow into the tank, the following consequences are observed:
- Due to too high pressure from the ramp side, the injectors begin to leak and fill the cylinders with pure gasoline, and not with the working air-fuel mixture.
- The engine is bad, it emits black smoke from the exhaust, and sometimes you can hear popping noises in the exhaust manifold. The reason is flashes of unburnt fuel.
- Consumption increases noticeably.
- Leaks may be observed at the joints of the fuel pipes, and a strong gasoline smell may be felt.
Practical experience shows that a lack of fuel mixture occurs more often than an excess. That is, the most common problem with an RTD is the draining of gasoline into the return pipe and tank.
Video
Problems with the RTD: it doesn’t drive well, it doesn’t accelerate, it jerks.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator. Example on a BMW E34 (BMW E34).
How to measure the pressure in the fuel system on a VAZ 2110 car.
Violation of the integrity of the body
Poor quality fuel, the presence of foreign impurities in it and other negative factors contribute to the destruction of the hull. The device stops working normally. Detecting a small fluid leak is quite difficult. This is due to the fact that gasoline evaporates quickly. Smudges and stains form at the installation site.
If a violation of the integrity of the housing is detected, the product should be replaced immediately. A leak may cause a fire.
Design and operation of RTD
The fuel pressure regulator is a device designed to maintain pressure in the injectors at different operating intensities. Essentially, this regulator is a diaphragm valve, on which fuel presses on one side and the intake manifold spring on the other. This device consists of a fuel tank, a fuel drive with a pump, injectors, a fuel filter, a switch and an electronic control unit pump.
I think many car enthusiasts know what factors determine the amount of fuel injected. Absolutely right, it depends on its pressure inside the fuel rail, the vacuum process taking place in the manifold and on the duration of the injector operation.
To more accurately calculate the amount of fuel injected, taking these three factors into account, an appropriate regulator is used (only in systems with fuel recirculation).
The regulator is located on the fuel rail, and the principle of its operation includes the following points: at the initial stage of pump operation, the fuel mixture leaves the tank and is cleaned in the filter; then enters the regulator, where the system maintains its uniform pressure all the time.
If there is no recirculation in the system, then such a part must be placed directly in the tank, while the function of maintaining pressure remains the same. True, in this case the difference between the pressure in the intake manifold and the fuel pressure will not be constant, so it is taken into account based on the injection duration.
Let's now take a closer look at the principle of operation of the device in a system with fuel recirculation. In such conditions, the regulator looks like two chambers separated by a membrane: fuel and spring. The condition of the membrane is influenced by different types of pressure: from the top, the spring pressure and the pressure of the intake manifold, and from the bottom, the fuel pressure entering the chamber through the intake ports. If the fuel pressure exceeds the spring force, the valve opens slightly and allows fuel to flow into the return line.
In systems with unintended recirculation, where the pressure regulator is most often located directly in the fuel tank, there is no need for a return pipeline, so it is not provided for in the design. The calculated amount of fuel is immediately supplied to the injectors, and its excess is returned to the tank without entering the engine compartment, unlike the previous system. As a result, the fuel heats up less, which means the amount of evaporation is much less.
Also, at present, there is an automatic fuel control system that does not provide a mechanical fuel pressure regulator. Control of its parameters and the required amount of supply is regulated by a special module that measures the voltage on the electric pump.
This system allows you to reduce fuel heating to the optimal value, and the fuel pump supplies only the amount of combustible mixture that the engine needs in a specific time period, which significantly increases fuel economy. As an addition, a relief valve is installed in the automatic system to prevent pressure build-up.
Replacing the sensor
There is a new common rail injection system for diesel engines. It is also used for gasoline injection engines. The difference between this system and the classic version is that fuel is supplied to the injectors not from the fuel pump, but from a ramp, which acts as a general storage tank. This element has the appearance of a cylindrical vessel with thick walls and can withstand increased pressure. The fuel pump and RTD maintain optimal pressure, the ramp is connected to the injectors by separate fuel lines.
The Common Rail system reduces fuel consumption and toxic emissions. The noise of the diesel engine is also reduced and its dynamic performance is increased.
The fuel supply is regulated by an electronic unit, which allows for a wide range of system operation settings.
It is quite possible to replace the sensor yourself in the garage. The process of removing and installing an element for a VAZ 2110 or a fuel pressure regulator for a Priora, like many other similar cars, is not particularly different and includes the following steps:
- The pressure in the motor power supply system is released.
- The nut securing the fuel pipe is unscrewed.
- The bolts holding the regulator to the rack are removed.
- The fuel pipe is disconnected.
- The fitting is carefully removed from the niche in the rail.
- The new element is installed on the system in the reverse order.
- The performance of the system is checked with a pressure gauge.
When installing a new regulator or replacing some elements, it is necessary to lubricate the O-rings with gasoline to extend their service life and reduce wear.
You can easily check the functionality of the fuel pressure regulator and replace it, following the correct sequence of actions and being careful. Timely detection of the problem and regular checking of system elements for wear will ensure optimal and high-performance engine operation.
The fuel pressure regulator is an element of the injection engine power system, which allows you to maintain the required fuel pressure in the fuel injectors at different operating modes of the internal combustion engine. In other words, the overall performance of the injectors and the stability of the engine depend on the serviceability of the fuel pressure regulator (FPR).
Considering that the pressure regulator is actually a diaphragm valve, failure of this element can greatly affect the operation of the engine. In this article we will look at the principle of operation of the regulator, highlight the main signs of its malfunction, and also talk about how to check the fuel pressure regulator.
Read in this article
Diagnostics
There are a number of methods to diagnose the condition. All of them are simple, even a novice car enthusiast can handle them.
Test methods:
- Visually. This is an option for carburetor engines. Pinch the valve or disconnect it. The fault can be determined by how intense the fuel flow is. The method is simple, but inaccurate.
- Pressure gauge. Install the device between the fitting and the hose, temporarily disconnecting the vacuum hose. The reading on the pressure gauge should rise to 0.7 bar.
- By pinching the hose. Check the RTD by clamping the return line. The pressure gauge should respond immediately. If the engine does not rev up, the governor is faulty. Start the engine by clamping the return line. Watch the speed and listen to his work. If its operation is uniform, the adjustment valve is faulty - it must be replaced.
The procedure for checking the performance of an RTD depends on its type - mechanical and electrical components are checked differently.
How to check a mechanical regulator:
- locate the fuel return hose under the hood;
- start the engine - let it run for a minute to warm up a little;
- using pliers - very carefully, pinch the return hose;
- if after clamping the engine begins to work well, then the problem is a broken RTD.
It is forbidden to pinch the hoses for a long time - this creates additional stress on the pump, which leads to its breakdown in the future.
In injection engines, fuel hoses are made of metal rather than rubber to increase reliability. Electrical sensors in such systems are made on the basis of strain gauges. To determine if the RTD on the injector is faulty, check the voltage at the sensor output.
In diesel engines, RTDs are checked by measuring the resistance of the sensor inductor. Usually the normal value is around 8 ohms. If the resistance is noticeably higher, or vice versa, much lower than stated, the regulator is broken. Detailed diagnostics are carried out only in the service center - at special stands where sensors and the entire fuel supply system are checked.
Checking an element
In most cases, if problems are detected, it is better to completely replace the fuel pressure regulator. Changing individual elements, cleaning and other manipulations cannot always restore the required performance to the device. The affordable price of the RTD also contributes to the decision to completely replace the component.
The easiest, most accessible and effective way to check the regulator is to measure the indicators using a tire pressure gauge. To determine the idle pressure, the device is connected between the fitting and the fuel system hose. The measurements must indicate pressure within a certain range. The vacuum hose is then disconnected.
As the pressure increases, the indicator should be between 0.3−0.7 Bar. If the value is outside this range, install a new vacuum hose and repeat the test in the following order:
- The fuel pressure on the end area of the ramp is determined after unscrewing the fitting plug. It is also necessary to check the O-ring for integrity and elasticity. If there are defects, then the element or the entire plug must be replaced.
- The umbrella is unscrewed from the fitting; for this you can use a metal valve cap. A hose with a pressure gauge is connected to the part and secured with clamps. After this, the engine is started and measurements are taken. Indicators within the normal range are 2.9−3.3 kgf per square meter. cm.
- The hose is disconnected from the regulator. You need to check the pressure gauge readings; the pressure should increase to 20−70 kPa. If the value remains low or zero, the device must be replaced.
Causes of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
RDT may fail for several reasons. For example, defective parts are found on Russian-made cars. There are significantly fewer defects on foreign models, but you can purchase a defective RTD by purchasing a non-original spare part.
Mostly the check valve breaks down due to natural aging. Let's say this can happen after a hundred thousand mileage or more. It should be noted that check valve failures are not common. Most often, in an RTD, the membrane dries out over time, less often the valve jams, and even less often the spring breaks or weakens.
Sensor failure may occur due to low-quality gasoline. For example, in winter, fuel was filled with water, and water got into the regulator. If the fuel filter is not replaced on time, dirt gets into the parts of the power system, including the regulator. In this case, the RTD valve most often jams. It’s hard to imagine what could happen to the spring, but apparently, it still breaks sometimes.
How to clean an RTD
The regulator cannot be repaired; if it malfunctions, it is replaced with a new one; the price of the part is low. But sometimes it is possible to restore functionality by cleaning the built-in mesh filter. To do this, the regulator is dismantled and washed with carburetor cleaner, followed by purging.
The operation can be repeated for better results. It is also possible to use an ultrasonic bath with a solvent, which is used to clean injectors, where similar problems arise due to dirty fuel.
There is no particular point in these procedures, especially if the part has already served a lot. The cost of time and money is quite comparable to the price of a new RTD, despite the fact that the valve in the old one is already worn out, the diaphragm is aged, and caustic cleaning compounds can cause final failure.
Signs of RTD malfunction
The mechanical regulator is a reliable element due to its simplicity of design. But it also breaks. A malfunction of the RTD is manifested by a number of symptoms:
- Difficulty starting the engine.
- Instability and “swimming” of revolutions.
- Reduced power and dynamic performance of the car.
- Spontaneous stop of the unit at idle.
- Jerks and jerking of the car when changing the engine operating mode.
Malfunctions of other components of the injection system also give the same symptoms, which makes it difficult to identify the cause of incorrect operation of the power unit.
At the same time, when searching for a problem, car owners do not even pay attention to the RTD, believing that there is nothing to break in it
Regulator malfunctions:
- reduction in spring stiffness;
- valve jamming (RDT functions spontaneously and haphazardly);
- valve jamming;
- clogged channels;
The pressure regulator is considered maintenance-free, and if a malfunction is detected, it is replaced.
Something else useful for you:
- Why does the engine pick up speed, but does not pull when driving?
- IAC (idle air control): what is it and what is it for?
- How to replace the idle air regulator on a VAZ 2108, 2109, 2114?
Signs of sensor failure
Signs of a malfunction include:
- Activation of the Check Engine warning light on the dashboard. When scanning for errors with the scan tool, one or more errors with numbers P0190, P0191, P0192, P0193, P0194 will be displayed. All of them indicate problems in the fuel pressure sensor control circuit.
- Decrease in engine power. At the same time, the car loses its dynamic characteristics (accelerates poorly) and does not pull, especially if it is loaded. The reason for this is the fact that the electronic control unit, when receiving incorrect information from the sensor (or lack of a signal from it), simply substitutes standard quantitative values of fuel and air. Because of this, a fuel-air mixture with suboptimal parameters is obtained.
- Excessive fuel consumption. This value also changes depending on the engine power.
- The car is bad even when cold.
- When the engine operates at high speeds, so-called “dips” may occur, when the speed changes sharply and the car does not obey the accelerator pedal.
In general, it is not advisable to drive a car with a faulty fuel pressure regulator. And this is expressed not only in the fact that the car has lost its dynamic characteristics, but also in the fact that the fuel pump will work, which is called “wear and tear”, since it cannot maintain significant pressure for a long time. And this naturally leads to a decrease in its service life and possible premature failure.
It also makes sense to check the fuel pressure sensor in diesel engines if error P1181 was detected using a diagnostic tool, indicating that the system cannot ensure tightness in the fuel rail. One of the reasons for this could be a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
How to change RTD
The RTD is usually replaced with a new one, but you can try to repair it. You can buy the required unit at any auto store or on one of the online sites that sell spare parts.
- Locate the pressure control plug under the hood. After unscrewing it, unscrew the spool.
- Connect the hose and pressure gauge. Use a clamp. Maximum pressure – 3.2 Bar.
- Unfasten the hose from the RTD. With this procedure, the pressure increases from 20 to 70 kPa. Otherwise, the repair turns out to be unnecessary, you need to install another unit.
If the RTD is not repairable, replace it with a new part:
- Unfasten the vacuum line. The pressure will increase. First lower it and then remove the hose. Unscrew the nut on the drain pipe through which gasoline or diesel fuel flows to the regulator through the filter.
- Unscrew the fastenings of the unit to the ramp. Remove the unit from the line through which fuel is discharged. Remove the ring remaining in the ramp to fit it onto the RTD before mounting.
- Install a new RTD and perform the above steps in the mirror sequence. Check if the new unit is working properly and complete the assembly. After installation, check the quality of operation of the new device.
RTD is a miniature but extremely important part of the car. By regularly checking its readiness for work and changing it on time, it is possible to prevent many problems that car owners often encounter.
Source
Repair and replacement of RTD
If your vehicle exhibits any number of symptoms of fuel regulator malfunction, diagnosing the fuel regulator is the only step toward returning it to proper operating parameters. In the event that a check indicates that the device is out of order, the following must be done.
Step 1. Remove the fitting plug to be able to control the pressure of the flammable liquid at its end.
Step 2. Using a special metal protective cap, carefully remove the spool from the inner cavity of the fitting.
Step 3. Reduce the pressure in the power system, and then carefully remove the vacuum hose from the device.
Step 4. Remove the nut used to secure the fuel supply tube.
Step 5. After the two bolts that secure the module to the fuel frame are unscrewed, you need to smoothly remove the fitting from their holes.
Step 6. Carefully remove the RTD.
As a rule, the removed device cannot be repaired, and it is replaced with a new, more functional one. You can purchase a module with delivery either in any specialized store or via the Internet.
Purpose of the regulator
The sensor maintains the optimal pressure in the fuel rail, necessary for the correct operation of the injectors in different operating modes of the unit. The RTD determines the intensity of fuel supply and its quantity. Fuel enters the engine cylinders through the injectors.
Dosing accuracy and maintaining the required pressure is ensured by a membrane control valve, onto which springs press at one end and fuel at the other. There are two options for placing an element:
- The RTD is used in power systems with a check valve and is mounted on the fuel rail.
- In designs without “return”, the sensor is installed on the fuel tank.
In the first case, the fuel pump pumps fuel through the line from the tank. The resulting pressure affects the regulator. The device contains two chambers: fuel and spring, which are delimited by a membrane.
Fuel enters through the intake hole and presses on the jumper. On the other hand, it is pressed by a spring and the pressure force of the collector. If the fuel pressure is stronger than the spring compression, the sensor opens slightly and dumps excess fuel into the check valve.
When the regulator is located in the tank, additional installation of the pipeline is not required. Excess fuel does not go into the space under the hood and does not need to be returned to the fuel compartment. It also heats up less and evaporates less.
There is another way to regulate the pressure - using an electronic circuit that does not have a mechanical sensor. In this case, control is provided by an electric fuel pump. Electronic sensors record voltage readings and regulate the flow of fuel. This solution saves fuel and reduces its heating.
Repair of fuel level sensor VAZ 2110
Sequencing:
- It is necessary to disable the button that is responsible for sending the minus command to the battery. If it is missing, you need to reset the terminal from the battery.
- Open the door, unfasten the rear seat and remove it. Remove it from the interior and put it aside.
- Move aside the sound insulation to provide convenient access to the inspection hatch in the body.
- Using a Phillips screwdriver, unscrew the screws that secure the hatch. Remove its cover.
Preparing to dismantle the fuel pump
Disconnecting the pump electrical connector
Disconnecting the pump from the fuel line
Removing the pump from the tank
Checking the fuel level sensor
Installing the fuel pump into the tank
Installation locations
On cars, the injection system is equipped with a separate line for draining excess gasoline, which goes from the fuel rail to the gas tank (fuel recirculation). In such injectors, the regulator is installed directly on the fuel rail (or connected to it), so the unit quickly “reacts” to changes in engine operating conditions and adjusts the pressure in the rail. In this design of the power system, a mechanical type RTD is used.
There is another version of the injector - without gasoline recirculation. In this system there is no “return” at all, and regulation is carried out at the output of their fuel pump. A feature of such a system is the location of the regulator - in the tank or near it. An RTD is already used here, the operation of which is controlled by the ECU - the control unit, through a sensor installed in the ramp, monitors the necessary parameters and corrects them by sending signals to the regulator.
Power systems with electronic regulators are used less frequently than mechanical ones due to their complex design and, accordingly, lower reliability.
Regulator design
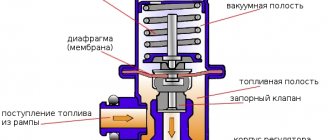
The design of the mechanical fuel pressure regulator is simple. It consists of a body, which is internally divided by a membrane into two chambers. One of them is called the fuel chamber, the second is called the vacuum chamber (or simply vacuum). Each of the chambers is connected to the system components by fittings and channels. The fuel chamber is connected through channels to the fuel rail, and a fitting for the line for draining excess gasoline (“return”) also comes from it. The vacuum chamber also has a fitting, which is designed to connect to the intake manifold.
A needle valve is fixed to the membrane, the seat for which is the channel of the drain line fitting. This valve is constantly in the closed position, and a spring installed in the vacuum chamber presses it to the seat.
RTD device
While the engine is running, the pump constantly supplies fuel under pressure from the gas tank through the line through filters into the fuel rail. From there, through the connection, gasoline fills the fuel cavity of the regulator and acts on the membrane. From the side of the vacuum cavity, the membrane partition is acted upon by a total pressure consisting of the spring pressure and the pressure (vacuum) inside the suction manifold. If the pressure inside the fuel chamber is higher than the pressure in the vacuum chamber, the bypass valve opens and discharges part of the fuel into the return line. Thereby, regulating the portion of fuel to the injectors at a given moment in the operation of the power unit.
Operating principle of RTD
The valve design and operating principle depend on the type of fuel system of a particular vehicle. There are 3 ways to supply gasoline from the tank to the injectors:
- The pump together with the regulator is installed inside the tank; fuel is supplied to the engine through one line.
- Gasoline is supplied through one tube and returned through another. The fuel system check valve is located on the distribution rail.
- The circuit without a mechanical regulator provides for electronic control of the fuel pump directly. The system contains a special sensor that registers pressure; the pump performance is regulated by the controller.
In the first case, the return flow is very short, since the valve and electric pump are interlocked into a single unit. The RTD, located immediately after the supercharger, dumps excess gasoline into the tank, and the required pressure is maintained throughout the supply line.
The second option is used in most foreign cars. A valve built into the fuel rail allows excess fuel to flow into the return line leading to the tank. That is, 2 gasoline pipes are laid to the power unit.
There is no point in considering the third circuit - instead of a regulator, there is a sensor whose functionality is checked using a computer connected to the diagnostic connector.
A simple fuel pressure valve installed in the fuel pump unit consists of the following elements:
- cylindrical body with pipes for connecting the supply and return lines;
- a membrane connected to a locking rod;
- valve seat;
- spring.
The amount of pressure in the supply line depends on the elasticity of the spring . While most of the fuel goes into the cylinders (high load on the engine), it keeps the membrane and valve stem closed. When the crankshaft speed and gasoline consumption decrease, the pressure in the network increases, the spring compresses and the membrane opens the valve. The fuel begins to be discharged into the return line, and from there into the gas tank.
The fuel pressure regulator installed in the rail operates on a similar principle, but reacts faster to changes in load and gasoline consumption. This is facilitated by connecting an additional pipe of the element to the intake manifold. The higher the crankshaft speed and the vacuum on the spring side, the stronger the membrane presses the rod and closes the passage of fuel into the return line. When the load decreases and the speed drops, the vacuum decreases and the rod releases - the return flow opens and excess gasoline begins to be discharged into the tank.
Causes of malfunctions
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PEMmSVodwLU
There are not many reasons why the fuel regulator fails. The element cannot be called ultra-reliable; it works, as they say, under wear and tear, and is very dependent on the quality of the fuel.
- Marriage. This is not a common reason, but sometimes you come across defective products from domestic automakers. It is recommended to check the spare part before purchasing.
- Wear. Usually observed after 100-200 thousand kilometers. In the regulator, the membrane becomes less elastic, the pressure control valve gets stuck, and the spring becomes weaker.
- Bad fuel. Gasoline and diesel car engine fuel often contains too much moisture, debris, and foreign toxins. Water in fuel causes rusting of the metal parts of the regulator. Increasing over time, they interfere with its normal functioning and lead to weakening of the spring.
- The fuel filter is clogged. Garbage fractions in the fuel clog the system, including the RTD, and become clogged. This leads to spring wear and valve jamming.
RTDs are usually not repaired, but replaced with a new one. But, if the cause of the breakdown is clogging, it can be cleaned.
Cleaning the fuel regulator
Before replacing it with a new similar element, you can try to clean it, since this procedure is simple and accessible to almost every car owner in a garage. Often, special carburetor cleaners or carb cleaners are used for this (some car enthusiasts use the well-known WD-40 for similar purposes).
The most common (and most accessible) thing is to clean the filter mesh, which is located on the outlet fitting of the fuel pressure regulator. Through it, fuel is supplied directly to the fuel rail. Over time, it becomes clogged (especially if low-quality fuel with mechanical impurities and debris is regularly poured into the car tank), which leads to a decrease in the capacity of both the regulator in particular and the entire fuel system as a whole.
Accordingly, in order to clean it, it is necessary to dismantle the fuel pressure regulator, disassemble it, and use a cleaner to get rid of deposits both on the mesh and inside the regulator body (if possible).
Dirty fuel regulator mesh
After cleaning the mesh and the regulator body, it is advisable to force them to dry using an air compressor before installation. If there is no compressor, place them in a well-ventilated, warm room for a time sufficient to completely evaporate moisture from their external and internal surfaces.
Another exotic cleaning option is the use of an ultrasonic unit at a car service center. In particular, they are used for high-quality cleaning of injectors. Ultrasound can be used to “wash” small, stubborn dirt. However, here it is worth weighing the cost of the cleaning procedure and the price of a new mesh or fuel pressure regulator as a whole.
Source
Possible faults
Failures in the power system can occur for various reasons
Therefore, when diagnosing, you need to take into account some features of a regulator failure and symptoms of low fuel pressure. The main features include:
- reduced power, high fuel costs;
- dips and jerks during acceleration and throttle change;
- unstable operation and engine shutdown at idle;
- slow car response when adding gas;
- The car does not pick up speed and does not accelerate.
Signs of low pressure in the RTD on gasoline cars are similar to symptoms of a malfunction in the fuel pump or a broken fuel filter. The system stops working correctly due to loss of spring force. In this case, the fuel does not reach the required level and goes into the check valve. As a result, the engine does not have enough fuel to accelerate and increase speed. Low pressure in the sensor reduces engine power. The electronic control system cannot optimally adjust the fuel for different modes.
In this case, the engine stalls in any operating mode. A clogged regulator can lead to an excessive increase in pressure and fuel overflow through the connections of the sealing elements.
The fuel pump always takes in fuel with some reserve to prevent a possible decrease in the performance of the injectors and sensor. Therefore, if it is difficult to drain fuel into the return valve, the pressure in the system increases.
The car begins to move jerkily, pressure drops occur in the sensor. The cause of the breakdown may also be wear of the valve inside the device. Its service life can be shortened by low-quality fuel with impurities, or by keeping the machine idle for a long time without starting the engine.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PEMmSVodwLU
Everything about repair, tuning, design, operation of a car, tips, auto news, auto facts
Repairing the fuel level sensor is an important process. Even if the operation of this unit does not directly affect driving safety, its incorrect data can cause accidents on the road.
Based on the information provided by the meter, you can plan trips or refuel your car. Therefore, it is not recommended to delay, but to repair or replace sensors on time. In order to prevent troubles on the road, you need to know what the system of this device is, how to check and adjust it. An example is the VAZ 2110 model.
How to repair a fuel level sensor
Functions
RTD is an element of the fuel system (hereinafter referred to as TS), which is responsible for the level of fuel pressure determined by the operating mode of the automobile engine. RTDs are used in injection-type engines, for which the accuracy of parameters during fuel injection is important.
The purpose of the unit is to maintain fuel pressure by regulating the fuel supply to the cylinders, which ensures optimal operation of the injectors.
If the RTD is faulty, the acceleration time increases and even the motor power decreases. If the volume of air from the manifold remains stable, and the amount of fuel increases, then the fuel-air mixture either does not ignite or does not burn 100%.
The role of the fuel regulator in the car system
At different engine operating modes, it is necessary to create the appropriate fuel pressure in the fuel system. To implement this task in practice, a special pressure regulator is used. It is used in injection engines, where the correct operation of the engine depends on the accuracy of the injection parameters.
When the governor is faulty, the engine runs unevenly, acceleration times are increased, and in some cases power can be significantly reduced. So, for example, if the amount of air coming from the manifold remains unchanged, and there is more fuel than necessary, the air-fuel mixture will not ignite or will not burn completely.
Even if in this mode the electronic control unit shortens the injector opening interval, it will not be possible to completely compensate for the excess fuel pressure. This will lead to interruptions in engine operation and an increase in the amount of unburned fuel in the exhaust, which can prematurely damage the catalytic converter or particulate filter.
Why is a control valve needed?
The fuel supply system of most passenger cars requires continuous operation of an electric fuel pump. It constantly pumps gasoline into the fuel line and ramp, raising the pressure to the maximum (5–7 Bar depending on the brand of car). But such performance is needed only under increased load on the engine, when it develops high speeds and consumes a lot of fuel mixture. In normal mode, a fuel pressure at the injectors of 3–3.5 bar is sufficient.
The fuel pressure diaphragm valve, installed in the engine power system after the fuel pump, performs 3 main functions:
- Limits the fuel pressure in the line at low engine loads, dumping excess fuel back into the tank through a separate tube.
- When the gasoline consumption of the power unit increases, the return flow is partially or completely blocked by the regulator. In this way, the valve maintains the minimum pressure required for normal operation of the motor.
- Maintaining pressure for a long time after stopping the power unit.
Without an RTD, the pump would “push through” the locking mechanisms of the injectors and gasoline would flow into the cylinders uncontrollably. In addition, the regulator protects the line from leaks at the connections, which will inevitably appear under the influence of strong pressure.
Sensors for diesel systems COMMON RAIL type BOSCH
Bosch COMMON RAIL performance direct fuel injection systems have gained great popularity due to their efficiency, reduced fuel consumption and reliability. There are three types of fuel supply systems, each of which is equipped with a fuel injection pump of a certain class and level:
- with control valve on the high pressure rail;
- adjusting the fuel on the high pressure pipe when exiting to the injection pump;
- “double control” type, with two RTDs on the high and low pressure lines.
You can determine exactly where the regulator is located after studying the fuel supply system of a particular engine. It is recommended to carry out initial diagnostics with a multimeter. Original Bosch sensors for COMMON RAIL have a service life of 10 years and are the last to fail, so in case of any disturbances in the operating mode of a diesel engine, diagnostics begin with checking the injectors, injection pump, and diesel quality.
You can change the RTD yourself in 15 minutes in the garage; the procedure is quite simple. But in order to change the element, you need to completely make sure that the incorrect operation of the internal combustion engine is associated with a failure of the regulator.
Location of the RTD in the fuel rail of the vehicle
The use of a special regulator for the fuel system is associated with the need to reduce or increase the pressure of fuel supply to the engine when it operates at different speeds. For example, idling requires a very small amount of fuel, while as the speed increases, the intensity of its injection should increase.
In order to equalize this difference on all injectors, the device is installed at the end of the fuel rail. As standard, it is mounted in the fuel rail. Very often, its location can be changed - for example, the RTD is placed in a return hose or even in a tank.
Placement in the gas tank makes it possible to avoid the need to install additional fuel lines, and the check valve blocks excess fuel from entering the system. Regardless of the location, the RTD performs the same function, which is to support the fuel pressure required and safe for the vehicle engine.
This is interesting: How to change the thermostat on the engine
For systems without fuel recirculation, the RTD is located in the fuel tank and is designed to maintain the same fluid pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. The specificity of this arrangement is that the differences between the fuel pressures in the tank and in the intake manifold will not be constant, which is ultimately taken into account in the duration of injection of the working fluid.
Location in the vehicle structure
In modern cars, two layouts of the fuel pressure regulator are used. In systems with a return line, it is installed on the fuel rail, and in designs without a “return” - directly inside the fuel tank (in the pump). The diagram located on the fuel rail involves connecting the regulator to two lines of the system:
Layout of the fuel pressure regulator in the system
- inlet - the supply channel from the fuel tank to the power system;
- return exhaust – channel for draining excess fuel (pressure relief).
In such a system, when the regulator opens, excess fuel enters the return line and then into the fuel tank. This scheme has some disadvantages:
- complexity of the design and the need to install an additional pipeline;
- heating of excess fuel when it enters the ramp, which increases the vapors generated in the tank.
Each fuel regulator has its own factory settings and is suitable for a given car model. There are also universal designs for injection systems, which are equipped with pressure gauges and the ability to manually adjust. They are installed instead of the standard regulator exclusively in the fuel rail.
When the fuel pressure regulator is placed directly in the tank, the required amount of working fluid with a given compression level immediately enters the engine without the use of an additional line. In this case, the excess is also discharged directly into the tank, but it does not enter the engine compartment, which eliminates its heating.
In this case, a constant pressure difference is established relative to atmospheric pressure, and the amount of vacuum in the intake manifold is taken into account by changing the injection duration.
Preparatory work
- Take a tire pressure gauge and wrap flax or fum tape around the tip, this will prevent fuel spills and air leakage.
- Prepare a hose with a maximum internal diameter of 9 millimeters, and you will also need clamps for fastening. It is necessary to fix the hose on the pressure gauge and tighten everything with clamps.
- Place the prepared tool on the engine so that the hose and pressure gauge fixed on it do not roll off the surface. This will avoid fuel spilling on the engine.
- We unscrew the nipple spool on the ramp (fuel splashing is possible due to residual pressure).
- We put a hose with a pressure gauge on the ramp connections and secure everything with a clamp.
- Homemade pressure gauge for measuring pressure in the rail assembly.
Operating principle and design
The fuel pressure regulator (hereinafter referred to as the FPR) is mounted on a ramp; for diesel engines with fuel supply using the COMMON RAIL system, and for gasoline internal combustion engines, the location of the sensor is different. The only connection principle remains - a pipe from the pump or installation on a fuel rail. If the system involves fuel recirculation, typical of gasoline injection engines, the regulator is installed on the ramp. If the system does not involve discharging fuel from the ramp, the sensor is mounted immediately after the fuel pump.
Structurally, the RTD consists of a metal membrane that bends under fuel pressure and is tuned to a certain range of operation and an electrical control part. The electrical unit is represented by four strain gauges, which change the resistance of the element during the mechanical action of the fuel on the membrane.
Some cars have two RTDs, on both high and low pressure lines. Before checking the quality of the fuel mixture, both parts are diagnosed by measuring the output voltage. Based on the electrical pulse from the adjustment sensors, the ECU generates a signal to open/close the fuel valve.
Gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines have the same output voltage at the DDT of about 1.3 V, but the parameters of the fuel pressure supplied to the injectors differ.
| Sensor output voltage, V | Pressure for diesel, bar | Gasoline pressure, bar |
| 1.3 | 45–59 | 45–59 |
| 4.5 | 2200–2500 | 200 |