A wheel rim is one of the components of a car wheel. It serves as the basis for mounting the tire, as well as for transmitting torque from the drive shafts to it. Depending on the technology and material used, there are several types of wheel rims, each of which has both advantages and disadvantages. And the parameters of the wheel rims, such as the size of the rims and other indicators, determine the choice in favor of one option or another.
PCD - what is this parameter?
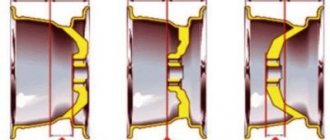
The standard wheel marking looks like this: 7×17/5×108 D63.3 ET50. It includes four components. Let's decrypt it.
The first parameter consists of two numbers: 7×17, where 7 is the width of the disk landing flange, expressed in inches; 17 is the diameter of the annular part of the rim, also measured in inches. The latter must correspond to the tire diameter. The tire marking is usually indicated as 17R.
The second parameter is also two numbers 5x108, and they interest us most. 5 is the number of holes for mounting the disc on the hub. There can be 3, 4, 5 or even 6. There can be as many as 15 on trucks. 108 is the diameter of the circle along all centers of the mounting holes, expressed in millimeters. This is PCD, or Pitch Circle Diameter. This characteristic in tire fitting is also often called drilling or bolt pattern. The PCD must completely match the dimensions of the hub, otherwise installing the wheel on the car will be very problematic, if not completely impossible. Only eccentrics can save you, but you can only ride them temporarily.
Next comes the DIA parameter – D63.3, indicating the diameter of the central (hub) hole in millimeters. On light alloy wheels it is usually closed with a seal.
The ET50 marking is the wheel rim offset in millimeters, i.e. the distance between the mounting plane of the disk and the middle of its width. The offset can be positive, zero or negative. The smaller the offset, the larger the car's track, and the wheels protrude more beyond the car's body.
Auxiliary markings
Some designations on rims are intended only for professionals - for those who sell rims and do tire fitting.
For example, the letter "J" in the marking "6Jx15" indicates the shape of the side flanges. There are other options: “JJ”, “JK”, “K”, “B”, “P”, “D”. The difference between them is in the roundings, sizes and angles of inclination of the side edges of the disk. The symbols “H2” indicate the shape of humps - ring protrusions on the landing flanges of the disk. There are also such options: “H”, “FH”, “FH2”, “CH”, “EH2” and “EH2+”. They differ in design. In most cases, the markings will be “J” and “H2”.
In addition, on the disc you can find the maximum load marking in kilograms or pounds, production date, country of production, brand name, regulatory marks and, for example, model code number.
What happens if the PCD diameter is neglected?
All parameters are important for installation; the installer will center the disk to the hub, which will make tightening the bolts much easier. The more accurately the wheel aligns with the hub, the more fully it will reveal its useful properties of handling and braking.
But if the width, rim diameter and offset can be changed to one degree or another, then the drilling is fixed once and for all by the manufacturer, since the design of the hub is simply not intended for mounting a wheel rim of a different size. For example, your car has a bolt pattern on the hub of 5×114.3, i.e. five bolt holes and 114.3mm circle diameter. And you want to buy a rim with 5×111, i.e. five holes with a circle diameter of 111 mm. The first parameter completely matches, but the second is a failure. It seems that the difference is only three millimeters, but it is fundamental. It is unlikely that even a professional will be able to visually identify a wheel with incorrect drilling if he does not know the numbers.
Violation of the disk parameters will lead to the fact that it cannot be properly centered and tightened. As a result, only one nut will be fully tightened, and the rest will sit, at best, skewed. The consequence of this will be a dynamic imbalance - the wheel will begin to sway imperceptibly from side to side, wear out the suspension and steering mechanism, and provoke body vibration, which sooner or later will lead to breakdown or even an accident.
Before experimenting with diameters, check the manufacturer's recommendations. Otherwise, incorrectly selected parameters can cause deformation of the wheel rim, runout, or even the wheel will simply fall off.
Results
Experienced motorists often say that you should never save on two parts of your car - wheels and brakes. What diameter of the central hole of the wheel rim needs to be chosen so that the car drives like clockwork? This parameter is not the main one when choosing a “new thing” for your car. But it is certainly worth considering when purchasing; do not take a size smaller than the diameter of the hub. But if you take a disk with a hole slightly larger than necessary, then nothing bad will happen. The main thing is to contact a trusted tire shop, which will install new wheels with all the additions necessary for your safety.
How to measure the PCD parameter on disks yourself?
On cast models, as a rule, all these indicators are indicated on the packaging or they are extruded on the surface. If there is none, then you can measure the PCD on the disk yourself.
This also makes sense because some manufacturers indicate parameters that are slightly larger than what they actually are. It is better to first check the diameter with the manufacturer, and then check the data yourself. As they say: trust, but verify.
There is nothing complicated in measuring the diameter of a PCD, but you shouldn’t approach this matter carelessly, because between 4x98 and 4x100 the difference only seems modest. Most often, diameter measurements are carried out using a caliper. Let's take a standard five-hole rim and take two measurements:
- From the inside edge of the mounting hole to the near edge of the center hole. For example, we get 20 mm.
- From the outer edge of the mounting hole to the far edge of the center hole. Here it turned out to be 92 mm.
You will get two values that need to be added together to get the PCD diameter we need. 92 mm + 20 mm = 112 mm. As a result, we got a PCD equal to 5x112.
If you don't have a caliper on hand, you can try measuring the wheel with a ruler. Here, the technology for measuring diameter is the same as in the previous case, but it is not always possible to obtain accurate data due to error. The main thing is to make sure that the ruler passes exactly through the middle of the main hole.
You can also try to get by with an ordinary stationery compass, which every schoolchild has. But this method is not particularly accurate, and should be used as a last resort. We place the needle in the core of the disk and draw a circle along the centers of the mounting holes. Then we fix the radius, apply the compass to the ruler twice and get the diameter.
You can often find another way: measure the distance between the centers of the two farthest holes for fasteners and multiply by the coefficient:
- For a rim with three holes, multiply by 1.155;
- Four disks - 1.414;
- Five – 1.701;
- Six – 2.0.
For wheels with three or five bolt holes, this measurement will not be accurate, but it can be easily corrected by simply comparing it with the standard sizes of new wheels. The easiest way to measure the diameter of a disk without a coefficient is if it has four or six holes for fasteners - we simply measure the distance from the extreme point of two opposite holes, and then measure the diameter of the hub hole and add up the results.
If you still have the car's operating instructions, then you don't have to look for a caliper or ruler, but just look at the section with technical specifications. Or find your wheel on the Internet.
Nowadays, many stores have data on PCD diameter and other parameters of cars, and the buyer does not need to worry about making a mistake. Our online store will help you choose a wheel based on the make of your car and other characteristics. All you need to do is enter your details and add your purchase to the cart. Our filter will offer all models that can be installed on a particular car. Note that the only parameter that remains unchanged in either case is PCD.
As a rule, these characteristics are standardized among different car manufacturers. For example, in modern Audi models the diameter of the PCD disc is always 5x112, BMW produces cars with a size of 5x120, Ford has a very small drill hole - 5x108, on domestic VAZs it is even smaller - 4x98. Take these parameters into account and there should be no problems with the selection of wheel rims.
If for some reason you need to install a wheel from another manufacturer, you need to do this with caution, and it is better to check with the manufacturer for information - perhaps wheels for different brands are in principle incompatible.
Hub diameter for different cars
Each car has its own list of permissible wheel diameters. The parameters may change, you can usually find them out by the sticker next to the driver’s seat or from the technical characteristics of the car. The variety of diameters of the central hole sometimes confuses buyers. They sometimes differ by literally 0.1 mm. There are no uniform standards, so some manufacturers indicate data more accurately, while others less so. Some self-respecting disk manufacturers go further and indicate indicators not of 1/20 of a millimeter, but up to as much as 10 microns, i.e. up to 0.01 mm. What standards are accepted for cars of the most popular brands?
- The diameter of the central hole of the VAZ disk will be 58.6 mm.
- The same figure for Audi is 57.1 mm.
- The diameter of the central hole of the Honda disc is 64.1 mm.
- For BMW, the hub diameter ranges from 74.1 to 72.6 mm.
- In Citroen cars, the indicators also vary - you can find cars with a central hole diameter of 65.1 and 58.1 mm.
- Fords also have a wide range of sizes: 57.1; 63.4 and 64.1 mm.
Basic disk dimensions: where to look and how to determine
Before we present information on the wheel bolt pattern inherent in cars of certain models, let’s understand their dimensions in general. After all, in order to purchase wheels, you need to know their exact parameters, or at least tell the seller the main characteristics of the car: year of manufacture, engine modification, and sometimes the body.
In the store they will select everything as it should be, but if you are going to buy wheels secondhand, you should know where the size is indicated on the rims. True, some parameters need to be measured independently.
Where is the width and diameter of the rim indicated on the disc?
Factory markings: where to look, what it looks like
Usually there is no need to measure all parameters yourself. But how can you find out the rim width of an alloy wheel or the diameter of a car wheel without taking measurements? Car manufacturers indicate the required parameters on original branded wheels. The markings are standard, the same for steel and alloy wheels.
Remove the spare tire from the trunk or remove the wheel from the car. Read the labels, most often on the inside of the disc. As a rule, 3 main parameters are indicated there: diameter, width and offset. For example: 5.5J x 13, where the first value 5.5J is the width of the disk in inches, and the second is the diameter, also in inches. The inscription ET35: the offset value in millimeters is 35. Instead of ET, the designation OFFSET or DEPORT is found - depending on the country of origin.
Markings can also be applied, for example, d54.1, which means DIA - the size of the hole for the hub is 54.1 mm. This inscription answers the question of how to find out the internal diameter of the disk and even how to find out the size of the hub on the disk - look for such markings, this is important.
If numbers are present, say 5x120, then you know the number of landing bolts (5) and PCD - the diameter of their location (120 mm).
Recommendations and Cautions
- Follow the car manufacturer's recommendations when selecting; do not use wheels that are not intended for this modification of the vehicle.
- Use only special nuts and bolts designed for this purpose to secure the wheel. Under no circumstances try to attach the wheel with regular bolts with suitable threads, as this may result in them spontaneously unscrewing while the car is moving and an inevitable accident.
- Do not under any circumstances try to put tires with a smaller diameter on a wheel of a larger diameter; they simply will not fit on the rim.
- Be extremely careful when determining the PCD, because the mounting holes of all wheel rims have a larger tolerance, and if the difference is only a few millimeters, it is quite easy to make a mistake. In the event of such an error, it will be impossible to tighten the mounting bolts and center the wheel, because when tightening the first bolt, it will “lead away”. The result may be strong beating when moving, disk distortion and spontaneous unscrewing of the mounting bolts.
- Never try to drill or counterbore mounting holes on a disc. This is unacceptable and leads to imbalance and damage to the wheel.
- Do not use wheels on a vehicle with a disc offset not specified by the manufacturer. The disc offset value is very important when selecting car rims. If the offset value is too small, the wheel may cling to the car's fender, and the load on the bearings and suspension parts of the car will also greatly increase. If the offset of the car disc is too large, then the disc will cling to the wheel hub when installed on the car or will not be installed at all.
- Use plastic centering rings; they are less durable than metal ones, but they do not “stick” to the hub.
Before purchasing rims for your car, we recommend that you seek advice from our company’s specialists. This will help you avoid annoying misunderstandings and make the correct selection of tires and wheels.
If you still have questions, call and our specialists will be happy to help you.