During operation of the injection power system, a portion of fuel is mixed into the passing air flow (or directly injected into the cylinders). But in order for the injectors to inject gasoline, it must be under pressure. Fuel is pumped by an electric fuel pump.
In this case, the pressure created inside the fuel system must be within a strictly specified range. And the fuel pressure regulator used in the design of the injection system maintains it at the required value.
The role of the fuel regulator in the car system
At different engine operating modes, it is necessary to create the appropriate fuel pressure in the fuel system. To implement this task in practice, a special pressure regulator is used. It is used in injection engines, where the correct operation of the engine depends on the accuracy of the injection parameters.
When the governor is faulty, the engine runs unevenly, acceleration times are increased, and in some cases power can be significantly reduced. So, for example, if the amount of air coming from the manifold remains unchanged, and there is more fuel than necessary, the air-fuel mixture will not ignite or will not burn completely.
Even if in this mode the electronic control unit shortens the injector opening interval, it will not be possible to completely compensate for the excess fuel pressure. This will lead to interruptions in engine operation and an increase in the amount of unburned fuel in the exhaust, which can prematurely damage the catalytic converter or particulate filter.
Conclusion
The fuel pressure regulator is an important element of recirculating fuel systems, responsible for maintaining pressure in the system and, as a result, the normal operation of the power unit. If this regulator fails, the driver will certainly face the problem of instability of speed, a decrease in the power and environmental performance of the internal combustion engine, a change in the nature of the exhaust and other troubles. Selecting a new RTD is not difficult, and in many cases the driver only needs to choose a universal device. Also, the original regulator can be replaced with a more advanced model if you are tuning your car.
What are the consequences of malfunctions in the operation of RDTs?
Over time, the engine starts more and more poorly. Fuel begins to come out of the cracks, which leads to a strong increase in its consumption. When the pressure changes unevenly, the dynamics of movement are disrupted, surges occur, and the car jerks during acceleration.
Is it possible to repair a failed part? In most cases, no, you have to completely change it. Repair units are almost always non-separable. Some experts suggest repairing the component, but this is dangerous. It is better to buy a new regulator - fortunately, it is inexpensive.
Determining violations in the operation of RTDs is not a very difficult task, which can be handled independently. Remember that this part of the machine needs to be checked periodically. By detecting the problem in time, you will protect important car components from rapid wear.
Fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
Problems in the engine power system can vary. For this reason, during diagnosis it is necessary to look for certain signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator. Most often, the main symptoms are considered to be when the engine does not pick up speed and does not develop full power, and also stalls in different operating modes. In the list of main signs, experts note:
- unstable operation at idle, the unit stalls at idle;
- loss of power, noticeable increase in fuel consumption;
- slow reactions to pressing the gas pedal;
- jerks and dips during acceleration, at the moment of throttling;
- the car does not accelerate, does not gain momentum;
Note that the malfunction of the RTD on gasoline cars is similar in symptoms to common problems with the fuel pump or its strainer. For this reason, when determining faults in the power system, a mandatory check of the fuel pressure regulator is necessary.
In other words, if the car stalls at idle, the engine power is lost, dips appear, the car jerks during acceleration or when changing gears, significant fuel consumption is noted, then the problem may not only be in the fuel pump grid, the motor or its relay, but also in the fuel pressure regulator.
Regulator malfunctions usually come down to the fact that the spring loses the required force, as a result of which the fuel is prematurely drained into the “return”, and the engine simply does not have enough fuel when you press the gas and increase the speed, as well as in transient modes. It turns out that the pressure in the fuel rail when the fuel pressure regulator spring is faulty is low, as a result of which the engine runs unstably, engine power decreases, the ECU is not able to correctly adjust the mixture composition for different operating modes, etc.
It is also worth noting that a decrease in throughput, as well as blockage of the RTD, is also possible. With such a malfunction, the engine stalls regardless of the operating mode of the internal combustion engine. If the regulator is heavily clogged, then the pressure in the system increases and fuel begins to pour out through the sealing elements at the joints. The fact is that car manufacturers always take into account the possibility of a decrease in the performance of the pump and injectors. To solve the problem, the gas pump always pumps fuel “with a reserve”. If draining into the return line is difficult for some reason, then the excess fuel cannot return to the fuel tank, and as a result the pressure increases.
Failures in the operation of the RTD are also possible when the pressure regulator in the fuel rail begins to jam at certain intervals. In such cases, pressure drops occur in the fuel supply system, and the car begins to twitch. Let us add that the most common reasons for regulator failure, which results in signs of malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator on a diesel or gasoline car, also include wear and tear of the materials inside the device, that is, the valve simply wears out its service life over time. The service life and condition of the regulator are affected by the quality of the fuel and the content of various impurities in it, long periods of vehicle downtime without starting the engine, etc.
Diagnostics
There are a number of methods to diagnose the condition. All of them are simple, even a novice car enthusiast can handle them.
Test methods:
- Visually. This is an option for carburetor engines. Pinch the valve or disconnect it. The fault can be determined by how intense the fuel flow is. The method is simple, but inaccurate.
- Pressure gauge. Install the device between the fitting and the hose, temporarily disconnecting the vacuum hose. The reading on the pressure gauge should rise to 0.7 bar.
- By pinching the hose. Check the RTD by clamping the return line. The pressure gauge should respond immediately. If the engine does not rev up, the governor is faulty. Start the engine by clamping the return line. Watch the speed and listen to his work. If its operation is uniform, the adjustment valve is faulty - it must be replaced.
The procedure for checking the performance of an RTD depends on its type - mechanical and electrical components are checked differently.
How to check a mechanical regulator:
- locate the fuel return hose under the hood;
- start the engine - let it run for a minute to warm up a little;
- using pliers - very carefully, pinch the return hose;
- if after clamping the engine begins to work well, then the problem is a broken RTD.
It is forbidden to pinch the hoses for a long time - this creates additional stress on the pump, which leads to its breakdown in the future.
In injection engines, fuel hoses are made of metal rather than rubber to increase reliability. Electrical sensors in such systems are made on the basis of strain gauges. To determine if the RTD on the injector is faulty, check the voltage at the sensor output.
In diesel engines, RTDs are checked by measuring the resistance of the sensor inductor. Usually the normal value is around 8 ohms. If the resistance is noticeably higher, or vice versa, much lower than stated, the regulator is broken. Detailed diagnostics are carried out only in the service center - at special stands where sensors and the entire fuel supply system are checked.
Design and principle of operation
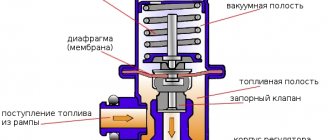
Fuel pressure regulator in closed (a) and open (b) positions.
The fuel regulator consists of the following elements:
- Frame. It is made of metal and has a high tightness necessary to prevent fuel leakage and loss of pressure.
- Membrane (diaphragm). Reacts to excess pressure and opens the drain line.
- Check valve. Located at the entrance.
- Spring. Places additional pressure on the valve diaphragm.
- Fittings for fastening fuel inlet and drain lines.
- Seals. Ensure the tightness of the system at the inlet and outlet.
The operating principle of a mechanical fuel volume regulator is simple. The membrane divides the internal space of the housing into two chambers (fuel and air). The first is supplied with fuel using a pump, which exerts some pressure on the membrane. The check valve prevents fuel from returning to the intake manifold, which allows the pressure necessary for engine operation to be created.
The classic valve design is a mechanical unit whose operation is based on pressure differences. In common rail systems, instead of a fuel regulator, a solenoid valve controlled by the engine ECU can be used.
On the reverse side of the membrane (in the second chamber) there is a spring that locks the regulator. This chamber is connected with a hose to the intake manifold, in which, under various modes, a certain level of air rarefaction is formed, which also affects the diaphragm. At the moment when the fuel pressure exceeds the total effect of the spring and vacuum in the intake manifold, the valve opens, dumping part of the fuel.
Thus, the lower the vacuum in the intake manifold, the greater the pressure of the fuel supplied to the fuel injectors. The control mode of the fuel regulator is engine idling, when the vacuum is minimal and the pressure is maximum.
Data from this mode are usually recorded on the outside of the housing, which simplifies the process of diagnosing and repairing the engine power system. When the engine stops, the valve closes completely, which maintains constant high pressure in the fuel rail (rail) and simplifies restarting.
Installation locations
On cars, the injection system is equipped with a separate line for draining excess gasoline, which goes from the fuel rail to the gas tank (fuel recirculation). In such injectors, the regulator is installed directly on the fuel rail (or connected to it), so the unit quickly “reacts” to changes in engine operating conditions and adjusts the pressure in the rail. In this design of the power system, a mechanical type RTD is used.
There is another version of the injector - without gasoline recirculation. In this system there is no “return” at all, and regulation is carried out at the output of their fuel pump. A feature of such a system is the location of the regulator - in the tank or near it. An RTD is already used here, the operation of which is controlled by the ECU - the control unit, through a sensor installed in the ramp, monitors the necessary parameters and corrects them by sending signals to the regulator.
Power systems with electronic regulators are used less frequently than mechanical ones due to their complex design and, accordingly, lower reliability.