In this article, you will learn where the Kalina fuel pressure regulator is located and how to change it yourself.
The regulator is an important component of the fuel system. It supplies and distributes the quantity and pressure of fuel in the car. In older Lada Kalina car models, the regulator design was somewhat different, and it was located in the engine compartment. In modern models with the advent of injection systems, it has changed and was moved directly to the gas pump itself, immersed in the gas tank. The malfunction of this important component causes significant discomfort to any car enthusiast. The main cause of wear is the weakening of the regulator spring, which results in the return of fuel back to the tank and a general decrease in pressure in the fuel system (rail). Driving with a faulty device is characterized by the following symptoms:
- change in the power component (slow acceleration, poor dynamics);
- the car starts to stall when starting or idling;
- an unreasonable increase in fuel consumption;
- noticeable discomfort in control;
- presence of “floating” engine speeds.
It should be understood that some of the above symptoms may be characteristic of other types of breakdowns and malfunctions. In order to understand that the cause of incorrect engine operation is the fuel pressure regulator, it is necessary to carry out proper diagnostics. We will dwell on it in more detail.
Checking the fuel pressure in the engine supply structure
The basic indicators for determining the suitability of the engine power supply design are the fuel pressure in the fuel rail of the Lada Kalina 2 car
. If the pressure is unsatisfactory, the following failures are possible:
• Unstable engine operation
• Stopping the engine at idle
• Unstable crankshaft speed at zero load
• The motor does not work at full power
• Jerks and dips during engine operation
First, we advise you to make sure that the electrical contacts in the harness blocks of the injection units, which are responsible for the supply of gasoline, are reliable.
The fuel pressure in the power supply structure is checked using a pressure gauge with a breather for connection to the fuel rail.
Note
The fuel pressure was checked using the example of a VAZ-21116 engine. On viburnums with other engines, check in the same way.
1. When you turn on the ignition, you will hear the sound of an electric fuel pump running. If you don't hear anything, check the pump's electrical circuit.
Note
If you turn on the ignition several times without starting the engine and do not hear any operating sounds, this does not indicate a defect. It will turn on when you start the car.
2. Unscrew the protective cap of the fitting for monitoring the fuel pressure at the end of the ramp. Please note that the sealing ring is fixed in the cap. If you notice flaws on the ring, replace it or the cap.
Note
On VAZ-21126 and VAZ-21127 engines, the pressure measuring valve in the fuel rail is located slightly differently.
3. Reduce the pressure in the supply structure.
4. Take the iron protective cap and unscrew the spool
Note
If the breather used during the pressure check has a tip similar in design to the tire pump breather tip, do not unscrew the valve stem.
5. Unscrew the spool valve from the pipe.
Note
Gasoline may leak while unscrewing the spool valve. Remove drips with a cloth.
6. Connect the fitting and breather to the pressure gauge. Secure the breather to the fitting using a tie. Start the car and check the pressure on the pressure gauge. Acceptable pressure should be 360-400 kPa.
7. Stop the motor, reduce the pressure in the power structure.
8. Disconnect the pressure gauge and pressure regulation fitting. Screw the spool valve into the fitting and secure the protective cap to the fitting.
Replacing a faulty valve
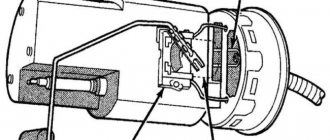
The regulator to be replaced is located in the fuel block, which includes other elements: an electric fuel pump, a coarse filter and a Kalina fuel level sensor.
You will need to remove the entire unit from the tank and then change the regulator. To do this, relieve the pressure, as described above, and then remove the rear seat. The module is located under a hatch covered with a mat and sound insulation, which moves to the side. You need to unscrew the screws and remove the hatch, then disconnect the wires and fuel hoses.
The pressure ring holding the assembly is twisted to the left. You can move it from its place with light blows of a hammer on the protrusion through the adapter. Then the fuel module along with the float is carefully removed from the opening.
You need to remove the wire from the regulator installed in it and pull out the spring retainer with a Phillips screwdriver. After this, the valve can be easily removed and replaced with a new one. Before reinstalling, the O-rings of the new part must be lubricated with fresh engine oil.
When assembling the unit, it is important to monitor the condition of the gaskets and replace them if worn. When installing the fuel module into the opening, you must ensure its orientation; the arrow on the cover should point towards the trunk. At the end, it doesn’t hurt to check the pressure again, and only then you can screw in the spool and start the engine.
To be sure, the Lada Kalina should be tested in motion, making sure that the dynamic properties of the car are restored.
tweet
back The process of replacing the clutch on Kalina
Next Why doesn't the Lada Kalina ECU work?
Tags: replacement, umbrella, valve, fuel pressure regulator, installation
Reduced pressure in the fuel rail - the fuel pump dies
For those blog readers who follow my YouTube channel, the information will not be new, but for the rest I will describe everything here. So over the past few days my Kalina has started having problems. And they were as follows:
- After a long period of inactivity, the engine began to start poorly, often even on the second try.
- the car became very “dull”, and it felt like the loss of power was about 20%
- fuel consumption increased by 10% when the engine was idling, and when driving too
In general, based on all the signs described above, it looked like a dying gas pump. Of course, I checked the mass air flow sensor first, since its operating voltage is also already close to critical. But when it was turned off, nothing changed for the better.
As a result, I began to deal with the fuel system. I’ll say right away so that there are no unnecessary questions:
How to change the coarse mesh
The work package for replacing the first stage filter consists of several stages:
- Buying a new part.
- Preparation of tools and repair site.
- Disassembly, removal of the gasoline pump and replacement of the mesh catcher.
To replace the old dirty mesh, you need to remove the fuel pump
How to choose a Kalina mesh filter is described in the previous section. The location for repair work does not matter, since you do not need a car overpass or inspection ditch - disassembly is carried out from the interior.
Preparatory stage
In warm weather, disassemble the car directly on the street, but in windy weather, find a quiet place, otherwise dust will blow into the interior. In winter, it is more convenient to work in an insulated garage or box.
The tools you need to prepare are:
- a Phillips and flathead screwdriver;
- pliers;
- a small chisel or metal point;
- hammer;
- clean rags.
To disassemble and dismantle the fuel pump you will need a modest set of tools
Before starting work, remove unnecessary objects from the rear row of seats, and then remove the seats themselves. They block access to the technological opening with a hatch leading to the fuel tank. The latter is attached to the bottom of the car from the outside.
Removing the fuel pump and replacing the mesh
The first step is to relieve excess pressure in the fuel line, otherwise when the pipes are removed, a stream of fuel will splash around the trim and the pungent smell of gasoline will “linger” in the cabin for a long time. There are 2 ways to relieve pressure:
- Pull out the 15 A fuse for the fuel pump electrical circuit, located under the cover in the center tunnel. Start the engine and wait until it stalls due to lack of fuel. Repeat the operation 2-3 times.
The fuel pump electrical circuit fuse is located under the cover on the center tunnel.
- Open the hood and locate the injector fuel rail valve. It is located on the right side (in the direction of travel) under the receiver and is a regular spool (the same ones are found in tires). Place a small container and press the valve, after twisting the protective cap.
The pipe with the spool is located behind the engine to the right of the ramp
After removing the rear seat, you will have access to a hatch covered by a fold-down trim flap. Place the cover aside and proceed to disassembly, performing the operations in the following order:
Take a Phillips head screwdriver and remove the 4 screws holding the hatch in place. Remove the cover.
The hatch is screwed to the bottom of the car with 4 screws
Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery, then disconnect the fuel pump power connector.
To disconnect the connector, you need to pry the plastic tab with your finger.
Squeezing the plastic retainer with your hand, pull the first pipe from the pump fitting. To remove the second tube, bend the metal bracket and plastic latch.
The pipes leading to the pump are held on by plastic latches
The pump housing is held in place by a lock washer. To unscrew it, use a small chisel and lightly use a hammer to turn the washer counterclockwise.
The lock washer is loosened by light blows of a hammer through the adapter
Remove the locking plate and carefully remove the fuel pump from the tank. At the same time, tilt the body to the side so as to pull out and not bend the float
Cover the opened hole with a clean rag to prevent debris from accidentally getting into the tank.
Pull out the pump carefully so as not to damage the float
Disconnect the internal pump connector (located under the cover) and remove it from the glass by bringing together the 4 long plastic latches.
To remove the pump from the glass, you need to press the plastic latches
The old mesh is simply pressed onto the fitting and removed by hand.
The mesh is removed and placed on the pump fitting by hand
It is advisable to remove dust with a vacuum cleaner so that it does not fall into the open tank
The new strainer is installed on the fitting until the latch clicks, after which the assembly can be assembled in the reverse order. Before doing this, look inside the glass where the gas pump is located: if you find dirt at the bottom, remove it with a rag or wash it with a brush soaked in gasoline. Before starting the engine, turn the ignition on and off several times, allowing the fuel pump to raise the pressure in the line to normal.
The above-described procedure for replacing the coarse filter element is performed in the same way on Kalinas with different body types. The same technology is used when repairing a Lada Kalina Sport car.
What should be the pressure in the fuel rail of the Lada Kalina?
So, having bought a fuel pressure gauge, which, by the way, cost me as much as 1,500 rubles, I decided to measure the pressure, which as a result was around 3.4-3.5 kg/cm². From the data obtained we can conclude that this was not enough for normal engine operation.
Moreover, when the speed increased to certain values, the pressure in the ramp dropped to 3 kg/cm², which also should not happen in a working fuel system.
The normal pressure in the system is from 3.8 to 4 kg/cm². Of course, if you are a fan of the “retirement” driving style up to 2000 rpm, then you may not feel any difference in power loss. But when the speed increases to at least 3000, you immediately feel a failure, and overtaking is difficult with such a “stupid” ride.
LADA KALINA. Injector malfunction, which takes out the brain.
Hello. Today I want to continue the series of articles about the symptoms of faulty injection wiring. Using the Lada Kalina car as an example.
In my practice, there were cases of malfunctions in the engine control system, which sometimes baffled me. One of these reasons was on Kalina.
The owner of the car complained about floating speed, increased fuel consumption, loss of dynamics, and an illuminated engine malfunction lamp.
When connecting diagnostic equipment, we see an error on the oxygen sensor: “lean mixture”. At the same time, at idle, the oxygen sensor works: it draws a sine wave. But as soon as the engine cooling fan turns on, its signal shows 0.1-0.2 Volts, which corresponds to a lean mixture. The engine begins to idle unsteadily.
After the fan works, the oxygen sensor also hangs in a lean mixture until you change the gas several times.
After all the checks (measuring fuel pressure, checking for air leaks, timing marks), all that remained was to check the injection wiring. And indeed, when the wiring moves, next to the electronic engine control unit, the oxygen sensor readings return to normal.
We unravel the injection wiring in the car interior and find massive twists. Over time, the copper in them oxidizes and the ADCs of the sensors begin to float.
We also unscrew and clean the ground wire that goes from the engine to the body.
I wrote about this in previous articles, but the symptoms of the malfunction were simply different.
We solder the twists. After this, we are happy that the engine is working properly.
This wiring problem occurs on Lada Kalina cars produced before 2011, with a mechanical throttle cable.
I hope the article will be useful to car enthusiasts.
Result after replacing the fuel pump
So, after replacing the fuel pump, a pressure gauge was immediately connected and when starting the engine, excellent readings of 4 kg/cm² could be observed, and when the speed was set to almost maximum, the pressure did not decrease.
Here you can see information on replacing the fuel pump, which was done in this case. As for the result specifically in terms of the operation of the motor and its power characteristics, everything is excellent here too. Now the car drives very quickly, there are no dips or slowdowns when pressing the gas pedal. As surprising as it may sound, fuel consumption also returned to normal both at idle and when driving.
Operating principle of the element
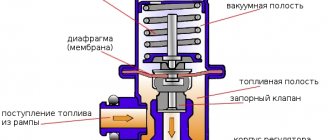
The regulator (RDT) is a conventional diaphragm valve, whose task is to maintain constant gasoline pressure in the line running from the tank to the fuel rail. Whatever mode the engine is operating in, its value should be in the range from 3.7 to 3.9 bar.
When the upper pressure threshold is exceeded, the valve begins to dump excess fuel directly into the internal volume of the tank. If the fuel pressure is insufficient, the regulator is not able to increase it, but if it breaks down, it can itself cause a decrease in pressure. How Kalina’s power system works is well reflected in the diagram above.
To correctly diagnose a diaphragm valve malfunction, you need to understand the algorithm by which the fuel system operates:
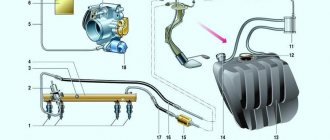
- When the ignition of the Lada Kalina car is turned on, the fuel pump (item 6) starts working, creating the necessary pressure in the fuel rail (item 2). If after a few seconds the starter is not started, the controller will automatically turn off the pump.
- Gasoline passes through coarse and fine filters (item 7) and enters the RTD, and from there along the line (item 4) to the ramp and injectors (item 3).
- After starting, the engine begins to consume fuel to varying degrees, depending on the driving style.
- At idle speed, the fuel pressure regulator dumps most of the fuel back into the tank (item 5), since its consumption is low, and the fuel pump constantly operates in one mode.
- At high speeds, the engine needs a lot of gasoline and the valve resets almost nothing.
There are 2 types of regulator malfunctions, characterized by a decrease in fuel pressure or, conversely, its excessive increase. The element cannot be repaired and must be replaced if broken.
Signs and malfunctions of the fuel pressure regulator
Welcome to the DIY car repair website. A reliable car is not one that looks beautiful, but one that rarely breaks down. Unfortunately, VAZ cars do not always please their owners, forcing them to pay a lot of attention to repairs or restoration work.
Fuel pressure control
So, one of the weakest links is the fuel pressure regulator. Due to the low quality of gasoline, it often fails, forcing you to check the VAZ fuel pressure regulator and replace it. All that remains is to find out how to diagnose the malfunction and check the functionality of the device.
The purpose of this small device
The car's system is designed in such a way that fuel flows through the injectors to the intake manifold. It is very important that the pressure does not change. In turn, the regulator makes an accurate calculation of the volume of gasoline supplied.
As a result, the device controls the pressure parameter inside two elements - the intake manifold and the fuel rail. In this case, the regulator’s task is to maintain the pressure difference at the same level. In addition, the regulator controls the pressure parameters at the injector and in the intake manifold.
A decrease in power, malfunctions of the power unit, an increase in consumption - all these are signs of a malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator (we’ll talk about this in more detail below). At the same time, the task of the car owner is to diagnose the problem in time and accurately determine whether the fuel pressure regulator is faulty or the problem lies elsewhere.
Operating principle of the element
The regulator (RDT) is a conventional diaphragm valve, whose task is to maintain constant gasoline pressure in the line running from the tank to the fuel rail. Whatever mode the engine is operating in, its value should be in the range from 3.7 to 3.9 bar.
When the upper pressure threshold is exceeded, the valve begins to dump excess fuel directly into the internal volume of the tank. If the fuel pressure is insufficient, the regulator is not able to increase it, but if it breaks down, it can itself cause a decrease in pressure. How Kalina’s power system works is well reflected in the diagram above.
To correctly diagnose a diaphragm valve malfunction, you need to understand the algorithm by which the fuel system operates:
- When the ignition of the Lada Kalina car is turned on, the fuel pump (item 6) starts working, creating the necessary pressure in the fuel rail (item 2). If after a few seconds the starter is not started, the controller will automatically turn off the pump.
- Gasoline passes through coarse and fine filters (item 7) and enters the RTD, and from there along the line (item 4) to the ramp and injectors (item 3).
- After starting, the engine begins to consume fuel to varying degrees, depending on the driving style.
- At idle speed, the fuel pressure regulator dumps most of the fuel back into the tank (item 5), since its consumption is low, and the fuel pump constantly operates in one mode.
- At high speeds, the engine needs a lot of gasoline and the valve resets almost nothing.
There are 2 types of regulator malfunctions, characterized by a decrease in fuel pressure or, conversely, its excessive increase. The element cannot be repaired and must be replaced if broken.
Signs and malfunctions of the fuel pressure regulator
The main sign of a problem is the appearance of malfunctions in the car. So, the following symptoms of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can be identified:
- Problems starting the engine. The starter rotates, but the engine does not “support” its efforts;
- power has decreased significantly. As a rule, this is immediately noticeable when accelerating a vehicle or when driving downhill;
- The engine is unstable at idle speed. At the same time, it may stall from time to time (for example, at an intersection);
- fuel consumption increases.
There may be two reasons:
- Valve failure;
- the valve just doesn't hold.
The regulator valve has failed. In this case, excess fuel is not poured into the tank, but an increased pressure of 2.5 kg/cm2 or more is created. This problem invariably affects the amount of fuel injected into the combustion chamber. As a result, fuel consumption increases, and the gasoline itself does not burn completely.
The valve doesn't hold. In this case, there is a constant “staggering” of fuel throughout the system. As a result, the pressure decreases, and with an increase in engine speed, a clear fuel shortage occurs.
In such a situation, the power and throttle response of the power unit drops significantly. In addition, during starting, you need to turn the starter for a long time to create the necessary pressure.
Basic malfunctions of the injection engine power system
All modern cars with gasoline engines use a fuel injection system, since it is more advanced than a carburetor, despite the fact that it is structurally more complex.
The injection engine is not new, but it became widespread only after the development of electronic technologies. This is because it was very difficult to mechanically organize control of a system with high operating accuracy. But with the advent of microprocessors this became quite possible.
The injection system differs in that gasoline is supplied in strictly specified portions forcibly into the manifold (cylinder).
The main advantage of the injection power system is compliance with the optimal proportions of the constituent elements of the combustible mixture at different operating modes of the power plant. Thanks to this, better power output and economical gasoline consumption are achieved.
Features of checking the fuel regulator
To solve the problem, it is important to know how to check the fuel regulator. This can be done using a regular pressure gauge. Everything is simple here. The device is mounted in the space between the fitting and the fuel pipe. To take measurements, the vacuum hose must be disconnected.
In this case, measurements should be made in four different modes:
- When the ignition is turned on. The nominal parameter is “three” atmospheres;
- when measured at idle – 2.5 atmospheres;
- in case of squeezing of the return flow hose - 7 atmospheres;
- with the hose removed from the pressure regulator - 3.3 atmospheres.
If the measured parameter does not correspond to the specified data or does not increase at all, then the device is faulty. In such a situation, it is enough to figure out how to change the fuel pressure regulator and perform the replacement.
Be attentive to your car, promptly respond to problems that arise, carry out diagnostics and make repairs. This is the only way to extend the life of your VAZ car and protect yourself from high costs in the future. Good luck on the roads and of course no breakdowns.
How to repair an RTD?
As part of component repair, the following work must be performed:
- Look under the hood of the car where there is a fitting plug designed to control fuel pressure. Unscrew it, then using a special protective metal cap, carefully unscrew the spool inside the fitting.
- Connect the hose with the pressure gauge and secure it to the fitting using a clamp. After starting the engine, check that the pressure reading on the measuring device does not exceed 3.25 Bar.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the RTD. This operation should be accompanied by an increase in pressure. If nothing happens, repairing the fuel pressure regulator is useless; you will have to replace the element with a new one.
If the part cannot be repaired, we proceed to install a new device.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose. The pressure will begin to increase. Having reduced the pressure in the power system, proceed to remove the vacuum hose. You will need to unscrew the securing nut on the fuel drain pipe, where diesel or gasoline flows through the fuel filter to the RTD.
- After unscrewing the two bolts securing the device to the fuel rail, you can safely remove the regulator from the fuel discharge tube itself. The ring remaining in the ramp can be easily removed by hand and placed on the regulator before installation.
- Install a new regulator and perform all previous steps in reverse order. Make sure the new device is in working order, only then proceed with complete assembly. Upon completion of installation, perform a control check of the operation and serviceability of the device.
VAZ fuel pressure regulator: causes of malfunctions and ways to solve them
An important element of the fuel system of any car is the fuel pressure regulator. The performance of the fuel system depends on how stable the fuel pressure regulator is.
The fuel pressure regulator in VAZ cars is a valve-membrane against which the regulator spring rests on the intake manifold side, and the fuel pressure on the other. After stopping the engine, it is the RTD that maintains pressure in the fuel system. If the pressure regulator is worn out, restarting the engine will require some time and manipulation of the ignition key.
The RTD is located either in the fuel tank itself, or, if the fuel system has a recirculation system (increasingly popular), then it moves to the fuel rail. The main task of the RTD is to maintain the difference between the pressure in the tank and the combustion chamber, the injector and the intake manifold. It is thanks to the operation of the fuel pressure regulator that control over the operation of the fuel injectors, the level of pressure in the fuel system is ensured, and excess volumes of fuel are returned to the tank through the return system.
Video review of a dying fuel pump on Kalina
If you don’t want to read everything written above, then you can watch this video, in which everything was clearly demonstrated.
If you have any questions, ask them below in the comments or discuss them on the channel under the video.
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm valve. Fuel presses against it at one end, and the intake manifold spring presses against it at the other. At lower speeds, the valve opens, accompanied by the draining of residual fuel from the engine into the tank.
If this component breaks down, the engine power of the machine drops and uneven operation of the engine is felt. To protect yourself from this, you need to systematically check the regulator and promptly respond to symptoms of damage to the device.
The first sign of RTD malfunction
The first sign of a faulty fuel pressure regulator is increased fuel consumption. The reason for this is simple - due to problems with the RTD, excess gasoline or diesel fuel from the internal combustion chamber does not return to the tank. This leads to an increase in pressure throughout the entire fuel system; Moreover, this increase can be significant - twice or even three times higher than the norm. If the norm is 2 kilograms per square centimeter, then with a faulty RTD this figure can reach 5 and 6 kilograms per square centimeter. This situation cannot take place for a long time, since all the “weak points” of the fuel system are very quickly discovered, and one or another breakdown occurs. In turn, a malfunction in the fuel system is fraught, firstly, with breakdowns, which, in turn, will require major repairs or even a complete replacement of the engine, and, secondly, with serious situations on the road, which are no longer fraught with costs, but with a threat to health and the lives of you and your loved ones.
It should be noted that malfunctions of the VAZ 2110 RTD after five years of operation are a regularity. It is necessary to begin monitoring the condition of the regulator after three to four years of active operation. If your car is already of advanced age, and at about the same age, the fuel pressure regulator should be monitored especially carefully for signs of malfunction.
If the power decreases and the dynamics of the engine deteriorate, the turbocharger may have stopped working altogether. This means that the fuel is not supplied to the internal combustion chamber under pressure, but gets there naturally, so to speak, by gravity. In this case, the engine at high speeds cannot cope with the fuel shortage, which can lead to rapid breakdowns.
How to diagnose a malfunction?
Among the first signs indicating that the fuel system is faulty is a sluggish engine response to pressing the gas pedal, as well as difficulty starting. If there is a decrease in pressure, then the Lada Kalina engine does not have enough fuel for normal operation. This confirms the weak speed gain during acceleration. When the pressure is excessive, the car behaves confidently while driving, but the LADA Kalina engine is not able to start stably. This is explained by fuel overflows, which is pronounced in the summer.
The first step is to measure the fuel pressure. To do this, you will need to equip yourself with a pressure gauge, which is equipped with a spool nozzle. A similar device measures the pressure inside wheel tires.
We act in accordance with the algorithm below.
- With the LADA Kalina engine cooled down, open the hood and remove the plastic cap located at the end of the fuel rail (item 1 in the diagram).
- Place a suitable container under the fitting. We press the spool to relieve pressure, and then unscrew it (see photo).
- We put the pressure gauge hose on the designated fitting.
- To start the unit, you will need a wire that connects the positive terminal of the battery to the contact present on the diagnostic connector. It is marked "11". The ignition must remain on. The time to check is about 10 seconds.
Problems and their causes
- Fuel consumption has increased. The cause may be excess pressure in the fuel system due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
- The engine power has decreased, the dynamic performance of the car has deteriorated and continues to deteriorate. The reason is often that the RTD has stopped holding pressure (for example, due to a high level of spring wear).
- Problems with starting the engine: in order to start the engine, you have to repeatedly “torment” the starter. The reason is difficulty in the movement of fuel in the fuel system due to a faulty (for example, jammed) fuel pressure regulator.
- The car periodically stalls, and unexpected and unmotivated jerks are possible while driving. The reason is the jamming (permanent or periodic) of the fuel pressure regulator. It is to pressure surges in the network that you owe all of the above “joys”. Such manifestations are extremely dangerous, especially when driving around the city, with a minimum distance between vehicles.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator
If you have any suspicions about the RDT, its performance should be checked as soon as possible. It’s quite easy to do this even at home, just follow a few simple instructions.
We unscrew the fitting responsible for the fuel pressure and inspect the o-ring. Its condition is of great importance, so if this element is old or damaged, you will have to purchase a new ring. The next step is to unscrew the spool valve from the fitting.
At this point you will need a pressure gauge to measure the pressure while the engine is running. And if the pressure is less than what is specified by the manufacturer for the VAZ model you own and the installed engine, the fuel pressure regulator needs to be changed. Moreover, it is inexpensive, the operation itself is very simple, and you can evaluate the result on your first trip.
- karemat
- buy toys for boys
- sewing store
- engine oil liqui moly
Selecting new filter elements
To purchase fuel purification system parts for VAZ 1117-19 models, you need to know what they look like:
- The coarse filter is a flat mesh bag made of chemically resistant plastic that captures large particles of 80-100 microns. In the center of the element there is a plastic fitting that fits onto the counterpart of the gasoline pump.
The mesh element is equipped with a pipe that fits onto the fuel pump fitting - The fine filter is made in the form of a cylinder with two fittings at the ends. The body is made of metal or special plastic - polyamide, and there is filter paper inside it. It traps particles measuring 15-50 microns. The pipes are equipped with clamps for fastening fuel hoses.
The element is equipped with clamps for fastening fuel line connections
All modifications of the Lada Kalina, including the second generation, are equipped with absolutely identical filter elements - a “barrel” and a mesh catcher. The dimensions of the spare parts are also identical.
There are no tricks in choosing a coarse mesh - the parts are made according to a single sample and cost from 30 to 45 rubles. The only caution: in order not to purchase a low-quality product or a fake, contact well-established stores.
In operation, the plastic case is not inferior to the metal one in terms of reliability.