AFS (Active Front Steering) is an active steering system, which is essentially an improved classic steering system. The main purpose of AFS is the correct distribution of force between all components of the steering system, and the main goal is to improve the efficiency of driving at various speeds. The driver, if the car has active steering, receives increased comfort and confidence in driving. Let's consider the principle of operation, the AFS device, as well as its differences from the classic steering system.
What is active steering
Active steering is essentially a modified version of conventional steering. The presence of this system on board the car helps to improve dynamic characteristics, better control of the car, and also improves comfort. The AFS (Active Steering) system was first installed in 2003 on top-end BMW models.
In more detail, active steering can change the ratio between the steering wheel and the steering mechanism, depending on the speed of travel. In addition, the system can independently adjust the angle of rotation of the front wheels when entering a turn or braking on a slippery road. In addition, the active steering system can steer the rear wheels, thereby increasing the vehicle's maneuverability.
Corrective Steering
In addition to providing a variable steering ratio, the BMW active steering system is also capable of generating corrective steering actions to enhance vehicle yaw stability. Unlike conventional brake activated stability control, corrective steering actions occur in a continuous manner and its operation is often not perceived by the driver. Furthermore; the elimination of brake intervention allows yaw stability control without loss of forward speed, thus vehicle performance is improved.
In the event of oversteer; the active steering system creates a countersteering action thus reducing the yaw moment and yaw rate. In extreme oversteer cases active steering works in conjunction with conventional brake activated stability control for maximum effect. In the event of understeer, further increasing the front wheel slip angle does not generate additional lateral force at the front axle, therefore active steering is not helpful.
The corrective steering function is de-activated (along with the brake activated stability control system) by pressing a dash mounted switch. This allows the driver full control over the front wheel steer angle and is intended for use in extreme recreational driving (eg on track days). The variable steering ratio remains active.
How the system works
Active Steering is activated when the engine is started. The system works by changing the steering gear ratio depending on the speed and driving conditions.
When performing maneuvers at low speed, the electric motor turns on in accordance with the signal from the steering angle sensor. The electric motor transmits rotation through a worm pair to the epicyclic gear of the planetary gearbox. Rotating the gear in a certain direction at maximum speed provides the smallest steering gear ratio, which reaches a value of 1:10. At the same time, the steering wheel becomes sharp, the number of rotations of the steering wheel from lock to lock is reduced, thereby achieving high driving comfort.
As the driving speed increases, turning is accompanied by a decrease in the rotation speed of the electric motor, and the steering gear ratio increases accordingly. At speeds of 180-200 km/h, the gear ratio reaches the optimal value of 1:18. At the same time, the electric motor stops rotating, and the force from the steering wheel is transmitted directly to the steering mechanism.
With a further increase in speed, the electric motor turns on again, while rotating in the opposite direction. The steering gear ratio can reach 1:20. At this gear ratio, the steering has the least sharpness, the number of rotations of the steering wheel from lock to lock increases, thereby ensuring safe maneuvering at high speeds.
If, when cornering, the car is oversteering (loss of traction of the rear wheels with the road), the AFS system, based on signals from the DSC system sensors, independently corrects the angle of rotation of the front wheels. As a result, the vehicle's directional stability is maintained. In the event that the active steering system cannot fully ensure vehicle stability, the dynamic stabilization system is activated.
Likewise, Active Steering stabilizes the vehicle when braking on slippery surfaces, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the ABS anti-lock braking system and reducing braking distances.
Active Steering is always on and cannot be switched off.
References
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
- Koehn, P., Eckrich, M., 2004. Active Steering – The BMW Approach Towards Modern Steering Technology. SAE World Congress and Exhibition, 03/08/2004 – 03/11/2004. Detroit, Michigan, USA.
Active steering device
The design of the active steering system is not the simplest and at the same time combines several other safety systems. Nevertheless, experts identify the main parts that are responsible for turning the wheels and stabilizing them; other mechanisms are considered auxiliary, including steering the rear wheels. Among the main mechanisms are the steering rack, sensors, control unit, the steering wheel itself and steering rods. Now let’s take a closer look at what function each of the parts performs.
The entire activation process of the active steering mechanism begins with the input sensors. Regardless of the car model, they are designed to measure different parameters. For example, steering angle sensors, electric motor position, total rotation angle sensors, as well as vehicle dynamic stabilization sensors. Although, recently they have stopped using the total rotation sensor, taking information from other sensors of the car.
Having received the necessary information from the sensors, it enters the electronic control unit (ECU). We can say that this is the heart of the entire system and thanks to it, all active steering mechanisms are controlled. The task of the ECU is not difficult: to receive signals, process them and transmit them to actuators. Most of all, the electronic active steering wheel unit interacts with the electric power steering, the engine management system and the vehicle dynamic stabilization system.
After processing the information, the signals are sent to the steering rack, or rather the steering rack electric motor. Due to this, the system can independently decide how much to turn the rack in one direction or another. The electric motor itself rotates the ring gear, as a result of which the gear ratio of the mechanisms changes. As for the steering wheel and tie rods, they perform the same functions as in normal driving.
Steer-By-WireEdit
The aim of steer-by-wire technology is to completely do away with as many mechanical components (steering shaft, column, gear reduction mechanism, etc.) as possible. Completely replacing conventional steering system with steer-by-wire holds several advantages, such as:
- The absence of steering column simplifies the car interior design.
- The absence of steering shaft, column and gear reduction mechanism allows much better space utilization in the engine compartment.
- The steering mechanism can be designed and installed as a modular unit.
- Without mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the road wheel, it is less likely that the impact of a frontal crash will force the steering wheel to intrude into the driver's survival space.
- Steering system characteristics can easily and infinitely be adjusted to optimize the steering response and feel.
Car active steering diagram
Taking into account the complex design of the active steering mechanism, as well as understanding what certain parts are responsible for, we should consider the laughter of the mechanism.
The photo shows a diagram of the car's active steering
- steering angle sensor;
- steering wheel shaft;
- shaft gear;
- steering wheel torque sensor;
- electronic control unit;
- electric motor;
- rack;
- amplifier gear.
We can say that these are the main parts of the active steering system. In addition to the listed elements, the mechanism also includes a reservoir for working fluid, an emergency lock, connecting hoses, a gearbox and a system valve.
Power steering or electric power steering: advantages and disadvantages of power steering
The AFS system design combines a planetary gearbox and a control system.
The planetary gearbox is used to change the speed of rotation of the steering shaft. It is installed on the steering shaft. The planetary gearbox includes a sun gear, a planetary gear unit and a ring (epicyclic) gear. At the input, the steering shaft is connected to the sun gear, at the output - to the satellite block.
The epicyclic gear is rotatable. When the gear is stationary, the gear ratio of the planetary gearbox is equal to one and the steering shaft transmits rotation directly. Rotation of the epicyclic gear in one direction or the other allows you to increase or decrease the gear ratio of the planetary gear, thereby achieving a change in the gear ratio of the steering mechanism. The rotation of the gear is ensured by an electric motor connected to its outer side via a worm gear.
A control system has been created to implement the functions of the active steering system. The electronic control system includes input sensors, an electronic control unit and actuators.
Input sensors are designed to measure system operating parameters and convert them into electrical signals. The AFS system in its work uses sensors for the position of the electric motor, the total angle of rotation, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel, and sensors for the dynamic stabilization system (vehicle rotation speed around the vertical axis and vertical acceleration). The total steering angle sensor may not be installed; in this case, the angle is calculated virtually based on the signals from other sensors.
The electronic control unit receives signals from sensors, processes them and, in accordance with the established algorithm, generates control actions on actuators. The electronic control unit has a connection and interacts with other vehicle systems: Servotronic, DSC dynamic stabilization, engine control, vehicle access.
The electric motor acts as the actuator of the AFS system. It ensures the rotation of the epicyclic gear of the planetary gearbox. The electric motor is equipped with an emergency electromagnetic lock that blocks the worm gear. In the initial position, the transmission is blocked. When current is supplied to the electric motor, the electromagnet is activated, and the latch, overcoming the force of the spring, releases the rotor of the electric motor. If a malfunction occurs in the AFS system, the supply of current to the electric motor is stopped and the latch blocks the worm gear.
The occurrence of malfunctions in the system is accompanied by the activation of a warning light on the instrument panel. A self-diagnosis message appears on the information display.
Integrated Chassis Management (ICM) control unit
Another task of the ICM control unit is to provide the systems in the entire vehicle with the dynamic handling characteristics in the form of signals.
Sensors that used to be installed separately in the DSC sensor are now fitted in the ICM control unit. The ICM control unit uses these sensors to calculate variables that are important for the dynamic handling characteristics of the vehicle at that time:
- Longitudinal acceleration and vehicle inclination in longitudinal direction
- Lateral acceleration and vehicle inclination in transverse direction
- Yaw rate
The ICM control unit is available as a basic version and a high version. The high version features a redundant sensor system for lateral acceleration and yaw rate (safety requirements for active steering).
The steering angle sensor also transmits its signal via a Private-CAN to the ICM control unit.
| Item | Explanation | Item | Explanation |
| 1 | Integrated chassis management (ICM) | 2 | Plug connection (54‐pin) |
Cost of repairs and parts for AFS
Today, the AFS system can be found not only on BMW cars. Most premium cars are equipped with this mechanism or offered as an option. For example, on Lexus cars the active steering system can be found most often.
As practice and reviews from car owners show, car body position sensors most often fail. No wonder, since the roads leave much to be desired and frequent body roll is simply inevitable. On average, the cost of replacing a sensor is about 150-175 dollars per 1 piece. Depending on the car model, there are at least 4 of them and more often they fail in pairs. The sensor itself will cost about $100-120, so 50% of the cost is the repair itself. The AFS electronic control unit will cost about 10,000 rubles. Repairing the steering rack will cost the most, on average about $1000.
Some car owners manage to replace the sensors themselves. We can say that this is the simplest thing in this mechanism and does not require special skills or tools. In addition, there are many tips and similar situations that are described in detail.
The active steering system, although a complex mechanism, without it, modern cars would not be as comfortable, and safety would be much lower. If it is possible to order the AFS system as an option, paying extra for it, then this will not be superfluous, and the difference in control will be noticeable from the first kilometers.
Planetary gearbox with overriding function with servomotor and servomotor lock
The overriding gear of the active steering is located on the steering box. The planetary gearbox with override function is installed in the split steering shaft. The overriding gear is a planetary gear train with 2 inputs and one output. The steering first input is formed by the bottom shaft of the steering column. The second input shaft is a worm gear on the planetary gear train. The servomotor (actuated by the AL control unit) drives the worm gear of the planetary gear train. The gear ratio from the worm to the worm wheel is 20.5:1. For possible failures, the worm gear is designed as self-inhibiting. The worm gear pair overrides the steering angle of the direct drive-through from the steering shaft. The total steering angle at the steering pinion comprises:
- Steering angle, applied at the steering wheel
- Steering angle applied by the electric servomotor
| Item | Explanation | Item | Explanation |
| 1 | Servomotor, active steering | 2 | two-pin plug connection |
| 3 | Servotronic valve (connected at the Servotronic control unit) | 4 | Electric servomotor lock |
| 5 | two-pin plug connection | 6 | three-pin plug connection |
| 7 | Rotor position sensor | 8 | 4-pin plug connection |
The electric servomotor on the planetary gearbox with override function receives its voltage supply from three phases (= wires) (U, V, W). In the event of a short circuit, the electric servomotor can turn a maximum of 120°. This prevents inadvertent start-up movements of the servomotor in the event of a short circuit. A temperature sensor in the control unit for active steering (AL) monitors the output stage for the servomotor.
The electric servomotor lock blocks the electric servomotor:
- in the event of faults to prevent it from rotating due to external forces
- when the vehicle is at a standstill and the engine is switched off (not when the vehicle is at a standstill and the engine is running)
If the engine is switched off by the automatic engine start-stop function, the electric servomotor lock remains applied.
Active car steering: what is the highlight of the BMW brand?
But, on the other hand, few people know that today there are several types of amplifiers, each of which has its own characteristics.
What is power steering for? Its task is not only to reduce the driver’s energy consumption when turning the steering wheel. This system makes the car more maneuverable, the impacts of the wheels on uneven roads are not transmitted to the driver’s hands in the same way, and, in the event of a tire puncture, it becomes easier to keep the car on the road.
So, today there are three main types of power steering - electric, electrohydraulic and hydraulic. The first cars had “hydraulics”, and it has not lost its relevance to this day. Over time, electro-hydraulic power steering appeared, and more recently, electric power steering.
Which one is more reliable? Which is better to give preference to? Let's look at each type in more detail.
Smart Connect on a TP-Link router
TP-Link decided to come up with its own name for Band Steering - Smart Connect. Which, by and large, does not change the essence of the matter. In the same way, the router automatically selects which network - 2.4 or 5 GHz - will be optimal for a particular client to connect to at a given time. This setting is located in the “Wireless Mode” section
But what positively distinguishes the Smart Connect function on TP-Link from the Band Steering implementation in Keenetic is that there is no need to first register the same parameters for each of the networks, and only then enable the mode. On TP-Link everything is set automatically after activating the “Smart Connect” checkbox.
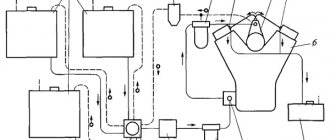
Power steering
The power steering consists of several parts - pump, oil, hydraulic cylinder, connecting pipes and distributor. The main element of the system is a hydraulic cylinder, which is activated by a pump. At the same time, the necessary oil pressure is created in the hydraulic system, which exerts its effect on the steering rack piston and makes rotation of the steering wheel easier.
It is worth noting that constant operation of the hydraulic cylinder leads to an increase in vehicle fuel consumption. The weakest link in the entire system is the hydraulic tubes, which are often damaged.
Advantages of power steering:
- The action of the hydraulic booster leads to a decrease in the steering gear ratio, as well as to easier maneuvers;
- The force of impacts transmitted through the steering wheel to the driver’s hands is reduced;
- In unexpected circumstances, it becomes much easier to hold the steering wheel. The steering wheel does not break out of your hands, and controllability remains at a high level;
- Even if the hydraulic booster fails, you can be confident in driving safety;
- The management process is more informative and accurate.
Of the shortcomings, only one can be highlighted - increased fuel consumption.
What is Band Steering and Smart Connect technology on a router?
The “Band Steering” operating mode, also known as “Smart Connect,” owes its birth to the emergence of dual-band routers that support both 2.4 and 5 GHz. The main advantages of the latter are higher speed and less congestion of wifi channels. Therefore, for those devices that can also connect to both of these bands, it is preferable to choose 5 GHz.
Now let's imagine the situation. There is a wifi router that distributes a signal with the same name (SSID), but at the same time at different frequencies. This feature is often found in modern routers today. And this is convenient, because it is simply easier to set up a network. There is no point in creating two different ones if you can make one, but in different ranges.
So, in this case, your laptop or smartphone will randomly choose which one to connect to - 2.4G or 5G. The load on the router is distributed unevenly. There can be 5 clients on one frequency, and 1 on the other. Although they all support both bands.
The Band Steering and Smart Connect mechanisms are designed to streamline this phenomenon and distribute the load evenly. At the same time, it analyzes the capabilities and distance of each of the connecting devices. And he chooses the network that is most preferable for him at the moment.
For example, if you are near a wifi source, it is better to connect to 5 GHz. When you delete and lose signal quality, the router records this and automatically reconnects your gadget to 2.4 GHz. Since it is more resistant to overcoming obstacles in the form of walls and doors. It also has a long range of wireless signal propagation. In this case, you won’t even notice any delays.
But also to force the release of the 2.4 GHz band, Band Steering on the router can be configured so that it switches all clients with 5 GHz support to it.
Electric power steering
This system consists of an electric motor, mechanical transmission and control system. A special feature of the device is the creation of additional force when turning the steering wheel using a special electric drive. Many modern cars have just such an amplifier installed.
The principle of operation is based on the operation of a number of sensors that monitor the position of the steering wheel and the force exerted by the driver of the vehicle. When a certain signal is received from the system, the sensor transmits it to the control unit, where the signal is processed and transmitted to the electric motor placed in the steering wheel rack.
The peculiarity of electric power steering is that it ensures perfect vehicle control when driving at any speed, sharply returning the wheels to the center position or holding them in this place.
Advantages of an electric amplifier:
are compact, fuel saving, easy to set up and adjustable, minimal energy consumption, and the absence of hydraulic lines.
The disadvantages include:
probable failure or shutdown of the system in the event of emergency situations. Such problems are quite likely in the event of serious malfunctions in the operation of the control units, poor contact connections, or a decrease in voltage in the on-board network of the machine. If a malfunction occurs, the corresponding lamp on the dashboard should light up indicating the existing malfunction.
EUR design
ESD for compact cars ESD on the steering column
On light cars, a lot of force from the electric power steering is not required, so both the electric motor and the servo drive are so compact that they easily fit under the steering wheel in the car. At the same time, sensors are also located there. Thus, the entire structure is reliably protected from dust, dirt and high temperatures in the engine compartment, which has a beneficial effect on reliability.
ESD for middle class cars ESD drive with two gears
On mid-size cars, an EUR with two gears is installed. Through one gear, the force from the steering wheel is transmitted to the rack, and through the other, auxiliary force from the electric motor.
To create a large additional force, an EUR of a parallel-axis design is used. To convert the rotational movement of the electric motor into linear movement of the steering rack, a toothed belt drive and a “screw-nut on circulating balls” mechanism are used. A nut rotated by a toothed belt moves the rack axis through the balls. The balls circulate along the thread, returning through a special channel in the nut.
ESD for SUVs and minivans Parallel axle drive device
With any design, in the event of a breakdown, the driver can continue to safely drive the vehicle due to the presence of a mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the steered wheels.
- increase comfort;
- make driving easier;
- improve overall driving safety.