Electric power steering (EPS), like any other power steering, is designed to reduce the force exerted by the driver when acting on the steering wheel, thereby increasing the level of comfort and ease of driving. Additional force is created by an electric drive. The absence of hydraulic elements in the system increases its reliability and creates additional opportunities for implementing functions such as automatic parking. In this article, we will look at what other features the EUR has, find out its structure and operating principle.
Functions and purpose
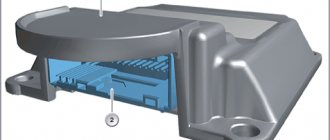
General view of the EPS
The abbreviation EPS (Electric Power Steering) is translated as “electric power steering,” which is an alternative to power steering. The main purpose of the ESD is to reduce the effort exerted by the driver on the steering wheel while driving.
The main advantages of an electric booster compared to a hydraulic booster include:
- high reliability due to the absence of hydraulics: the likelihood of leaks and other malfunctions characteristic of power steering is eliminated;
- higher accuracy and ease of steering control;
- fuel economy due to the fact that the electric power steering only works when the steering wheel is turned.
A variation of the electric power steering system is the adaptive electric power steering system, which works in conjunction with the exchange rate stability system. It offers important safety benefits: it corrects the steering angles of the wheels, increasing vehicle stability, and also compensates for understeer or oversteer.
Rotation methods
Maneuvering by turning the steered wheels is the most common way to turn vehicles. Steering with turning wheels quite fully satisfies the requirements for steering control. In all cases where this is permissible, the number of pairs of steered wheels is sought to be chosen as small as possible. This simplifies the steering design and increases driving stability.
However, if the number of pairs of steered wheels is less than n-1, where n is the total number of axles of the car, then when turning, lateral slip of the unsteered wheels is inevitable. The location of the steered wheels with this method of turning depends on the type and purpose of the vehicle (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Arrangement of steered wheels: NP - direction of rotation
Wheel rolling without lateral slip for a two-axle vehicle is ensured when the front wheels are steered. The rotation of the car (Fig. 1, a) occurs relative to the point O - the center of rotation of the car, located at the intersection of the axis of the rear wheels and the axes of both steered wheels. The steered wheels are rotated at different angles, and the angle of rotation of the inner wheel Θв is greater than the angle of rotation of the outer wheel Θн, Θв>Θн. The required ratio between the angles depends on the distance between the axes of the axles B and the wheelbase of the vehicle L and is determined by the relationship ctg Θн= ctg Θв+B/L.
The vehicle's turning ability is considered to be the minimum turning radius Rmin, equal to Rmin = L/sinΘнmax. For most cars, the value of Θнmax is (30... 35)° and the minimum radius is approximately twice the base of the car. The maximum turning angle of the steered wheels can be increased for off-road vehicles to 45°.
To improve steering ability, both front and rear wheels can be steered (Fig. 1, b). For such a scheme, the minimum turning radius is Rmin = L/(2sinΘнmax), i.e. with the same bases, the turning radius can be halved.
The turning of three-axle vehicles with front steered wheels (Fig. 1, c) is different in that the wheels of the middle and rear axles cannot roll without side sliding. Therefore, they strive to position the wheels of the trolley axles as close to each other as possible, to do this, make the distances L and l as small as possible. For such cars, an additional criterion for turning is the “overall corridor” Br - the width of the lane beyond which the car does not go when turning.
Maneuvering by turning the axles (Fig. 2, a) or bogies (Fig. 2, b) is used in cases where it is difficult to make the wheels rotatable for layout reasons due to their width (pneumatic rollers, wide-profile wheels). Sideways sliding of wheels on the road with this type of turning is inevitable.
Turning by folding the TTM links (Fig. 2, c) provides increased maneuverability and can be used for special or long-wheelbase vehicles. The folding angle can reach 90°.
The onboard turning method (Fig. 2, d) is carried out by disconnecting from the internal combustion engine, using clutches F1, F2, wheel drives of one of the sides of the machine and braking the disconnected drive using brake mechanisms T1 or T2. Thus, the turn is carried out almost on the spot.
Rice. 2. Methods for turning wheeled vehicles
This is the least rational method of turning, but when used, it is possible to significantly simplify the design of the machine. The method is most suitable for short-wheelbase vehicles. On soft ground, turning is accompanied by deformation and shear of the ground, which further increases the resistance to movement.
Advantages of the device
- Reliability.
- Possibility of implementing automatic vehicle control.
- Easy to maintain and silent operation.
- Environmental and technological safety.
- Ability to control the vehicle in the event of system failure.
- Ensuring light and smooth steering.
- Ensuring consistency between the angles of rotation of the steering wheels and steering wheel.
- Ensuring proportionality between the forces of resistance to wheel turning and the force on the steering wheel.
Power steering for Lada Vesta cars
Electric power steering is installed on cars of all trim levels of the Lada Vesta line without exception. To be more precise, it is electromechanical, since transmission mechanisms are used inside the unit. The electric booster itself is a Nissan development, so there is no doubt about the quality of the part. But, like any mechanism, the EUR tends to break. And if the unit refuses to work, then most likely the cause of the breakdown is an electrician (burnt-out electric motor, broken wiring, failed relay or blown fuse). Mechanical damage is practically excluded and, if possible, it occurs only after serious road accidents, as a result of which the steering mechanism is damaged.
EUR device
EUR design
Structurally, the EUR consists of the following elements:
- electric motor (electric motor);
- mechanical transmission (gearbox);
- control system.
Electrical engine
It is the electric motor, which is usually represented by an asynchronous electric motor, that drives the electric power steering. In this case, there are several schemes for installing an electric motor:
- The electric motor transmits force to the steering wheel shaft.
- An electric motor transmits force to the steering rack.
In the first design, the electric power steering is built into the steering column, and the electric motor transmits torque to the steering wheel shaft through a mechanical transmission.
Electric motor installation options
The second option, which is called electromechanical power steering (EMPS), is considered the most popular. Its design options come in the form of twin-pinion power steering or parallel-drive power steering.
In an ESD with two gears, torque is transmitted from the steering wheel to the steering rack by one gear; The torque is transmitted to the other gear using an electric motor.
In an ESD with a parallel drive, the electric motor transmits force to the steering rack through a belt drive or a screw-ball nut transmission.
Control system
Steering device with ESD
The ESD control system consists of:
- input sensors;
- electronic control unit;
- executive device.
Input sensors:
- steering angle sensor;
- torque sensor on the steering wheel.
In addition to these elements, the ESD control system uses information coming from the ABS control unit (wheel speed sensors) and from the engine control unit (engine speed sensor).
The ECU processes sensor signals, on the basis of which it gives a command to the actuator, which is the electric motor of the amplifier, to start working.
Why do you need electric and hydraulic power steering and what is better to choose?
Electric and hydraulic power steering in a car is a device that is needed to make it easier to turn the steering wheel when performing maneuvers.
Its presence allows you to drive the car with greater comfort. The main component of the unit is the spool; its position determines the functioning of the units and elements of the system. Regardless of the type of spool movement, which can be axial or rotary, there are no differences in the principle of operation. When the steering wheel is in the center position, the spool is held in place by centering spring elements. This ensures that oil can move freely throughout all system components. But provided that the distributor is in the correct position.
The pumping device operates in enhanced mode, dispersing the working fluid throughout the system. This unit always works, regardless of whether maneuvers are being performed or not. The main purpose of the pumping device is to pump oil.
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the spool begins to move, as a result of which the drain pipe closes. This leads to the supply of oil to one of the cavities of the cylinder, the injection procedure is carried out under the influence of pressure.
At the same time, the piston components and rod, due to the movement of fluid, rotate the wheels and the distributor housing in the direction where the spool moves. The switchgear housing can overtake the spool only at the moment when it stops moving, this indicates that the maneuver has been performed.
Then the spool element moves to its original state, and the oil drain pipe opens.
Depending on the type of hydraulic booster, its design may vary.
Operating principle of electric power steering
The principle of operation of the electric power steering is as follows: when the driver turns the steering wheel, the torsion shaft twists. The torque sensor transmits this information to the control unit. The ECU processes the data, correlates it with the readings of other sensors and calculates the force that must be applied to help the driver turn the wheels. The electric motor receives a command and acts on the steering column shaft or steering rack.
The following operating modes of the electric amplifier are distinguished:
- turn the car in normal mode;
- turning the car at high speed;
- turning the car at low speed;
- return the wheels to the middle position;
- keeping the wheels in the middle position.
Hydraulic booster
Hydraulic boosters, despite their relative simplicity of design, are efficient, reliable and easy to use. Such a booster includes a reservoir with hydraulic fluid, as well as a pump driven by an engine, which is responsible for pumping the required pressure into the system. The operating principle of such hydraulic amplifiers is extremely simple. The pump used provides pressure in the hydraulic system, which, by acting on the steering rack, significantly simplifies the rotation of the steering wheel.
Advantages of hydraulic boosters:
1. Precise control.
2. Safety in case of power steering failure.
3. Shock absorption and complete protection of the steering column from damage.
4. Simplification of maneuvering at low speed.
However, such hydraulic amplifiers still have disadvantages. It is the unreliability of hydraulic tubes that leads to leaks and the need for repairs. Also, a constantly running hydraulic booster motor leads to increased fuel consumption.
Advantages and disadvantages of electric power steering
The main advantages of EUR include:
- fuel economy - the electric motor eliminates the need to take part of the power from the engine;
- reliability due to the absence of a hydraulic system;
- providing a better connection between the driver and the road;
- compactness and ease of maintenance;
- ease of adjustment of steering characteristics;
- possibility of implementing automatic control.
The disadvantages of the device include:
- the impossibility of using the device on heavy trucks due to its low power;
- insufficient moisture protection;
- high price.
Electric power steering
The electric hydraulic booster is devoid of most of the disadvantages of “pure” hydraulics. Such devices are installed, for example, on the second generation Ford Focus. The design of an electro-hydraulic booster is similar to a hydraulic one, but only the pressure in it is created by a pump driven not by the machine’s engine, but by its own electric motor. His work is controlled by electronics. Sometimes the driver can even choose the operating mode himself. For example, “city” (the steering wheel is lighter) or “highway driving” (the steering wheel becomes “heavier”, which increases control accuracy at high speeds). The performance of the electric hydraulic booster does not depend on engine speed; its power is lost only to drive the generator, but the weight of the system as a whole and its complexity remain at the same level. Thus, the electric hydraulic booster is a transitional option from hydraulics to electric booster.
EPS malfunction
EPS malfunction pictogram
If the warning lamp on the instrument panel (an icon with a steering wheel with an exclamation mark) lights up, this indicates an EPS malfunction. The appearance of an error indicates that the electric amplifier does not undergo self-diagnosis when the ignition is turned on. The cause of the malfunction can be many factors, for example, the failure of any of the sensors included in the EPS control system. Although you can drive a car without an electric booster, you should not do this. It's better to turn to specialists.
Pneumatic power steering
Since the brakes were powered by compressed air, the solution was obvious - to make the booster pneumatic . Such devices were simple and cheap, but very noisy. At the same time, only a very experienced driver could accurately predict how much the steering wheel needs to be turned in order to fit into a turn. The fact is that the pneumatics worked according to the “on-off” principle - if you turn the steering wheel a little, the amplifier did not work, but at large angles the “steering wheel” no longer resisted rotation, but itself tore itself out of the hands and the wheels instantly turned out completely. And if there was a hole or pothole on the road, the wheels, due to the high elasticity of the air, could turn wherever they wanted.
Cost of parts and repair of electric amplifier
As already said, the electric booster is not fancy, but still what should you expect, when this or that part of the mechanism comes out, how much such a repair will cost and approximately how much the parts will be pulled out of your pocket. First, let's look at the cost of electric amplifier parts, since most repairs can be done independently.
It would seem that the control unit should cost the most, but as practice shows, only 1% of 100% of breakdowns occur in the ECU, while the rest of the problems occur with the steering rack, electric motor or other little things. Considering the condition of the road and unpredictable situations, the main shocks and vibrations fall on the electric motor, and the design of this element itself is not simple.
Accordingly, hence the high cost; the more expensive and higher class the car is, the more expensive the electric power amplifier parts are. If, for some reason, it is not possible to repair it yourself at home, let’s consider how much such repairs will cost at a service station.
The cost of repairs is not the cheapest, but also not as high as for a hydraulic booster. The most difficult thing will be with the electric motor, since the device is precise and requires practice to repair such elements. As for the electric booster as a whole, the system not only improved driver comfort and vehicle safety as a whole, but also made it possible to install many additional auxiliary systems. In addition, there is an unlimited flight of imagination for the implementation of new systems, which in the future can completely replace the driver or significantly facilitate control.
Electric booster failures and their symptoms
A special symbol - a steering wheel with an exclamation mark - can signal a malfunction of the EUR. If this symbol lights up on the dashboard, it means the amplifier is unable to diagnose its own system. It is possible to continue driving the car, but it is still better to urgently send the car to a service center. If the warning light (light on the panel) comes on, turn off the fuse.
The main faults are: voltage below normal; lack of signals from speed sensors; increase in engine speed. The sensors and cables through which the current passes may be faulty. The first ones do not work correctly due to moisture getting on them. Repairs must be carried out immediately. There is also simple contact wear. Another possible system failure is a blown fuse. And in the event of an accident, the operation of the electric motor may be disrupted.