Correctly set camber and toe angles are one of the key conditions for the normal operation of a car’s suspension. If these parameters deviate from the norm, a number of problems arise: uneven tire wear occurs, the vehicle’s handling and directional stability deteriorate, the steering wheel moves from the zero position when driving in a straight line. The load on shock absorber rods, silent blocks, CV joints, and steering system elements also increases.
Measuring the toe-in and camber angles should be performed at certain intervals, on average 1-2 times a year. Checking the position of wheels in specialized car services is an expensive service, especially when using computer methods. Frequent visits to workshops are expensive, so many car owners are looking for ways to carry out such work in a garage. We invite you to familiarize yourself with a simple, but accurate and effective method for independently determining the alignment and camber parameters.
Advantages of the method
The technology discussed below is widely used by both beginners and experienced motorists. Among its main advantages it is worth highlighting the following:
- High accuracy. According to this criterion, this method is not inferior to the computer method. The technology makes it possible to measure almost all angular and linear indicators, which are determined using electronic equipment. Even the slope of the site on which the machine is located can be taken into account when measuring wheel alignment and camber.
- Body parameters are taken into account. With computer diagnostics, these characteristics are not determined by the equipment; at best, computer stands can calculate the clearance value. The method discussed in the article allows you to see the natural axis of symmetry of the body and determine the location of the chassis relative to it. This will help you understand why, after wheel alignment and camber adjustments, some wheels protrude from the arches more than others.
- Disc failure does not affect the results. The parameters of the wheel rims can be important when adjusting the angles on a computer. Therefore, some craftsmen working in specialized services refuse to carry out work if the car has wheels with different offsets on the front and rear axles. The method under consideration, in turn, makes it possible to measure alignment and camber, even if different disks are on the same axis.
Why do a wheel alignment and how often should it be done?
Some motorists mistakenly believe that wheel alignment in a car needs to be adjusted only in case of repair/replacement of some suspension elements, as well as in case of “inadequate” behavior of the car on the road. In fact, you should adjust the wheel position much more often:
- every 15-20 thousand kilometers, i.e. twice a year (in order not to miss the time for such replacements, experts recommend adjusting the wheel alignment at each seasonal change of tires/wheels);
- in case of uneven and/or too rapid wear (abrasion) of tires;
- immediately after purchasing a new car, because, as practice shows, dealers very often miss this point during pre-sale preparation;
- if the car has different turning radii to the right and left;
- after tuning the suspension - changing the ride height through the use of thicker rubber bands or special stands;
- every time you replace ball joints, steering rods, ends, springs, struts, silent blocks, steering rack/gearbox, pendulum arm;
- when the steering wheel is in a crooked position;
- when the car behaves “incorrectly” on the road - swimming along a rut, belated steering, constantly “moving” to the side;
- when the steering wheel stops returning to a straight position after turning.
If you don’t do this and drive with a broken wheel alignment, you may face the following troubles:
- the edges (external - with positive toe-in or internal - with negative toe-in) of the tires will instantly wear off;
- when cornering, the car will roll, and when accelerating/braking on a straight line, the car will behave unstable, and this is a direct threat to the safety of everyone who drives this car, so you need to approach wheel alignment adjustment responsibly: if it is not possible to carry it out at the service station, do it at least with your own hands - there are many ways to do this, let’s name the simplest of them.
Important clarifications on the procedure for measuring wheel alignment angles
The proposed method only makes it possible to determine wheel alignment angles (AWA) in order to get an idea of the current wheel alignment and camber parameters. Further work on their adjustment can be carried out either with your own hands (if you have the appropriate experience and knowledge) or in a car repair shop.
It is assumed that the measurements are carried out with a working suspension and normal tire pressure. Therefore, the corresponding work related to the diagnosis and repair of the chassis is not considered.
It is also necessary to take into account that this article does not discuss what the toe-off and camber angles should be. We will only talk about the process of their measurements. The results obtained must then be compared with the factory values, which may differ for cars of different brands and models.
Before measuring the toe-in and camber angles, it is necessary to place the car on a flat, hard surface - for example, on the concrete floor of a garage. When driving onto a work site, keep the steering wheel in the zero position. In this case, the wheels will be as close as possible to the position in which they are when the car is moving on a straight road.
If the car is raised on a jack or lift after stopping, this will lead to unloading of the suspension, then the wheels will not be level enough on the floor. To eliminate such errors, you will need turntables or sliding platforms, which most car owners do not have. Therefore, it is strongly not recommended to lift the body before taking measurements. The car's suspension should be under the usual load.
Measurements should begin by determining the vanishing angles, since these are the parameters that are adjusted on most car models. This characteristic is determined for each of the four wheels, so it is sometimes called “semi-toe.” Individual toe-off is measured relative to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. It can be built in several ways, let's look at it in more detail.
Signs of the need for such work on a car
There are several signs and symptoms that can help you understand that it's time to adjust your wheels.
When driving, the steering wheel is in the central position, and the car leans to the side. The steering wheel is turned to one side, but the car still drives in a straight line. If you just bought a car, be sure to contact a car service for an alignment. Masters at the store's internal service station must carry out the procedure before selling, but in practice this does not always happen. Ideally, it is better to ask about this before purchasing. When changing tires, stop by a service station to check the wheel alignment.
You may not have to do it, but there is a possibility. Also, pay attention to fuel consumption and tire wear rates. If these parameters have increased, perhaps the problem is in the condition of the wheels.
Uneven tire wear is one of the signs that a wheel alignment is needed.
Rear wheel alignment
Is it necessary to perform a rear wheel alignment in a front-wheel drive car? Yes, but you need to keep in mind a small nuance. If the rear wheel is turned outward, the rear axle will be pulled to the side of the road, which will lead to severe skidding when cornering. If the wheel is turned towards the center of the turn, the car will have difficulty turning.
However, a slight reduction of these parts of the car to one another only benefits the driver, since it will be easier to move in a straight line, and the suspension will be able to better “steer” in a certain direction even with strong gusts of side wind, which is a constant help for a novice driver.
So, if the undersides of the rear wheels are slightly turned towards each other, this is normal. But their discrepancy needs to be eliminated.
Chassis problems and setting wheel parameters
Be sure to perform a wheel alignment if the chassis of the vehicle has been repaired
It is especially important to do this when replacing the following parts:
- silent blocks;
- tie rod ends;
- suspension arms.
Theoretically, when replacing upper and lower ball joints, springs and shock absorbers, there is no need to resort to the procedure, but some experts recommend performing it when working with absolutely any chassis component. Just in case.
What should the installation angles be: negative and positive values?
The optimal value for a passenger car is either zero or slightly negative (i.e., the wheels should point slightly outward with their bottoms). Positive values can be set from 0 to 4.5 degrees. Sports cars use a negative value of -0.5 to -5.5 degrees. Thanks to this, a high level of grip is achieved and cornering stability is increased.
Negative angles have disadvantages. So, when driving in a straight line, the inner edge of the tire will wear out faster, and instability may occur during acceleration and braking on a straight path. The best option is to set the indicator at -0.5 degrees.
Positive and negative camber
Three options for constructing the longitudinal axis of a car
There are three different methods to choose from that can be used to create a “baseline” line when calculating individual wheel alignment angles:
- The longitudinal axis can be taken as a horizontal line that passes through the axis of symmetry of the body. It can be easily constructed by marking their midpoints on the front and rear bumpers.
- The second option is the longitudinal axis of the chassis. This line is lined up along points that are located at the centers of the distances between the wheel hubs.
- Quite often, the trust line is used as the longitudinal axis. It is laid strictly in the direction of movement of the rear axle of the car. This vector does not always coincide with the longitudinal lines built along the body or chassis, as in previous versions. A similar phenomenon is typical for cars in which the rear axle is turned slightly to the side. At the same time, the car drives sideways, which is often observed on old Zhiguli, Gazelles, etc.
Longitudinal axis and trust line on a car.
The angle between the “trast line” and the central longitudinal axis of the machine should ideally tend to zero. But in some cases, rear suspension defects cannot always be eliminated. Therefore, when diagnosing alignment and camber, measurements are taken based specifically on the “trast line”.
Why adjustment is needed
Based on everything that has been said above, it is not difficult to guess that one of the reasons why you should still monitor the correct alignment is your safety. A car that has the correct wheel alignment angles is maneuverable and obedient, holds the road well, does not skid, it sensitively and - most importantly - reacts correctly to steering movements.
Why do you need wheel camber adjustment?
Also, a correctly set toe and camber angle will allow you to save a little on tires and consumables, as it keeps them in good condition longer, will allow you to get rid of rapid wear, and will protect suspension parts from destruction. And the tire tread, and the bearings in the hubs, and all sorts of rubber parts - everyone will say “thank you” for the good camber.
Volumetric camber adjustment
Measuring individual wheel alignment
To measure the toe-in of each wheel, it is necessary to create a corridor consisting of two parallel lines. To create them, you can use strong threads, fishing elastic bands, and laser beams. The lines must run strictly horizontally; they must be aligned to the height of the wheel centers. A basic corridor can be created in three ways:
- The first is to attach the threads directly to the wheels. This is the simplest, but least accurate method. The wheels may have different offsets relative to the arches, which disrupts the parallelism of the lines.
- The second is fixing the threads on stationary supporting structures. The method is more accurate in comparison with the previous one, but it is inconvenient because during the process of adjustments and rolling the car, the chassis may shift relative to the constructed lines.
- The third is to create a corridor around the car body using rack and pinion fastenings. The slats are fixed in the front and rear of the car, strictly in the centers of the wheels.
There are many examples of such constructions on the English-language Internet. For example, type “BG rasing string lines kit” in the search.
The corridor around the car body is made of river fasteners.
In garage conditions, it is appropriate to use the most budget-friendly and simplest method. To measure alignment and camber, you will need two aluminum slats, which can be purchased at any hardware store. One of them needs to be placed on the floor near the rear or front axle of the car. Next, you need to make marks on the rack at a short distance from the wheels - about 5 cm. Then the distance between the marks is determined, the resulting value will be the width of the measuring corridor. By dividing this parameter in half, you can calculate the location of the midline. Next, you need to attach a second strip to the marked tube and transfer the resulting marks to it.
Setting marks on aluminum tubes.
Two additional marks are applied to the car’s bumper exactly in the center. They are set using a tape measure and marked with a piece of electrical tape or masking tape.
Installing a tag on a car bumper.
Aluminum tubes are fixed using ordinary office clothespins. They are attached to bumpers, mudguards or other body elements, depending on the design features of the car.
Fixing aluminum tubes on a car bumper.
Fixing aluminum tubes on a car bumper.
Next, you need to tighten rubber cords on the slats in the previously marked places, which can be purchased at any fishing store. Instead, you can use non-elastic threads, which can be secured to the tubes with rubber bands for money. This will avoid breaking the threads, ensure the necessary tension and minimize the error in determining the wheel toe angles.
Fastening rubber cords to aluminum tubes.
At the next stage, the measuring corridor is centered along the marks that were previously marked on the bumpers. Next, you need to set the steering wheel to the zero position; for greater accuracy, you can use a building level.
Setting the steering wheel to the zero position.
After the above steps, you can already detect the lateral displacement of the wheels. To do this, measure the distances from the centers of the hubs to the threads of the base corridor and determine the difference between them. This is relevant for drivers in whose cars the wheels extend out of the arches at different distances.
Measuring the distance from the centers of the hubs to the threads of the base corridor.
Now you can start measuring the individual alignment of each wheel. Measurements are carried out by determining the distances from the lines of the base corridor to the symmetrical points of the rim of the discs in front and behind the center of the wheel. The results obtained must be recorded in a notebook or, in the absence of one, written down with chalk on the asphalt in the garage.
Determination of distances from the lines of the base corridor to the symmetrical points of the rim of the disks.
Then you need to roll the car forward or backward half a revolution of the wheel without changing the position of the lines of the measuring corridor. It is important that the steering wheel remains in the same position. Next, you need to take repeated measurements of the individual wheel alignment several times. If there are no significant differences between two measurements, they can be accepted as true. If the difference is significant, you should roll the car a few tens of centimeters more and find “crooked” wheels. This way we calculate the wheel curves. To compensate for wheel runout during calculations, we find the most frequently repeated values of individual toe-in alignments.
To convert millimeters to degrees and minutes, we use the table below.
Table for converting millimeters of individual wheel toe into degrees and minutes.
When all half-toe angles have been determined with sufficient accuracy, the steering angle of the rear axle can be calculated. The presence of such an angle may be indicated by differences in the parameters of the semi-convergence of the rear wheels relative to the center line.
If adjustment of the rear wheels is not planned, you can reorient the base corridor along the trust line laid through the rear axle. To do this, you need to move the fixed slats so that the semi-convergence of the rear wheels is aligned with the new position of the corridor. Then you will need to adjust the position of the front wheels according to it, fixing the car’s steering wheel strictly in the center. Thus, the car will drive slightly sideways, but the driver will not notice it.
When determining the parameters of semi-toe-in, it is necessary to take into account the total toe-in of the wheels on the axles (on the front and rear axles), which consists of individual angles taking into account their signs. It is this indicator that determines whether the tires will wear out evenly and how controllable the car will be while driving. To find out the optimal value of overall toe for a specific car model, you should study reference materials that contain the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Anti-roll bar
Modern sports cars have a fairly low suspension height and a low center of gravity. Accordingly, their body roll is usually barely noticeable. However, even in low-slung cars, body roll remains a problem because drivers like to corner without body roll, at high speeds, and with full vehicle control. As a first approximation, stiffer suspension springs are installed to reduce body roll. There is really no reason to use additional stabilizers, since the car is usually quite light and roll can only be dealt with by the correct choice of springs. The main argument against installing stabilizers is the partial loss of independent wheel suspension properties, and the stiffer the stabilizer, the greater the loss.
If the car is structurally equipped with a stabilizer bar (often due to the fact that the donor car has such a suspension design), there is no need to add stiffness to the stabilizer; select the stiffness of the suspension springs. On eco-vehicles with a high center of gravity, there is often no alternative to a stabilizer or other devices that reduce body roll.
When installing the stabilizer, you can use relatively soft suspension springs. However, you need to stay within the limits of good roll control when driving at high speed on winding roads. The stabilizer is made of spring steel and works like a torsion spring: the greater the car roll, the stronger the resistance of the stabilizer (naturally, within the strength of the material). Typically, the stabilizer is activated when the body rolls more than 3-4 degrees and prevents further growth of the roll, while the stabilizer only works when driving in corners and on uneven roads. In other words, in the absence of a stabilizer, due to the installation of medium or low stiffness springs, body roll can reach 7 degrees or more.
On cars with a low center of gravity, you can install relatively soft suspension springs and a lightweight stabilizer, but when braking, the front of the car will “dive” unless a special anti-dive suspension design is used. Remember, the front suspension springs should always be stiff enough to prevent excessive body dive when braking.
When installing a stabilizer, you need to ensure its rigidity so that it is minimally necessary to prevent body roll, or at least the roll is within acceptable limits (the stiffer the stabilizer, the more independence of the wheel suspension is lost).
Loose or worn stabilizer mounts will reduce the effectiveness of the stabilizer.
- Introduction
- Chapter 1. Chassis
- Chapter 2. Suspension height
- Chapter 3. Suspension geometry
- Chapter 4. Suspension springs and shock absorbers
- Chapter 5. Camber, longitudinal and transverse angle of inclination of the steering axis
- Chapter 6. Ackermann angles, wheel toe, “shock control” and anti-roll bars
- Chapter 7. Rear suspension
- Chapter 8. Brakes
- Chapter 9. Vehicle Settings
- Chapter 10. Testing and adjusting the vehicle
Measuring camber angles
To determine these parameters, the base corridor is not needed; it can be removed. Camber angles can be determined in several ways: using a plumb line, bubble level, digital inclinometer or other inclinometer.
Before you start measuring camber angles, you need to make sure that the car is standing on a level surface. If the camber is measured using a digital inclinometer, then it is enough to calibrate the device by the slope of the surface on which the car is located. To do this, apply a square to the surface and check the position of the protractor with the position of its vertical edge.
Place two vertical marks on the wheel rim with a marker or chalk. We apply the cord with a plumb line to the wing, and along the marks with a ruler or caliper we measure the distance from the rim to the cord at the top mark, and then at the bottom. The difference should be within +-2mm. We roll the car a quarter turn of the wheel (90 degrees) and make two more vertical marks. Again we measure the distance from the plumb line to the wheel rim, thereby leveling out the measurement error associated with the runout of the wheel disk.
Determination of the camber angle.
For front-wheel drive vehicles, the average values of camber angles are considered to be 0 ± 1 mm; for rear-wheel drive vehicles, the normal range is +1 ± 3 mm. For wheels of sizes 13 and 14 inches, 1 millimeter of camber is equal to approximately 10 minutes of arc. It is best to find out the exact wheel camber tolerance for a specific car from the recommendations of the car manufacturer.
Measuring the camber angle using a bubble level.
The camber angle can also be measured using a bubble level or a phone with an angle measuring program installed.
What operations can you do yourself?
The only operation that cannot be done correctly on your own is fine adjustment of the castor. If the accident has not changed the geometry of the body, then symptomatic adjustment of the castor can be done. When the car does not listen well to the steering wheel, turns unsteadily and with a delay, you just need to increase the caster for 20–40 minutes. If, during sharp acceleration, the steering wheel begins to be pulled out of your hands, the castor needs to be reduced. It must be remembered that an increase in castor leads to an increase in wheel camber. You can also adjust the wheel alignment yourself. If the body is damaged as a result of an accident, which led to a violation of its geometry, then any adjustment of the suspension is pointless. You will spend a lot of time, and the result will be extremely doubtful. Therefore, after even a minor accident, be sure to check the body geometry on a special stand.
Measuring the longitudinal and transverse angle of inclination of the axis of rotation
Of greatest interest is the measurement of the tilt parameters of the rotary axes. Their position is determined by two key characteristics: lateral inclination and longitudinal (caster).
A short video (2 min) about what a caster is
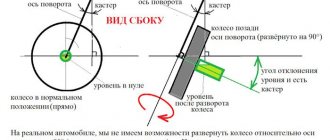
If the wheels of a car could turn 90 degrees and stand across the body, these parameters could be easily calculated using an inclinometer. But in real conditions this is impossible to do, so you need to limit yourself to a rotation of 20 degrees in both directions relative to the zero position. The difference in the obtained angles must be multiplied by an additional factor of 1.5 - this is necessary to compensate for errors that are allowed during the measurement process.
To measure caster, the bubble level bulb must be mounted perpendicular to the plane of the wheel.
To determine caster, you first need to turn each wheel 20 degrees in front of the steering axis: right to left, and left to right. In this case, you need to set the inclinometer to zero or write down the results. Next, the wheels are turned behind the turning axis: right to the right, left to the left. If the angle measured behind the steering axis is greater than the angle measured in front of the steering axis, then the caster is positive. If it's the other way around, then the caster is negative. The protractor should show a slight difference of a few degrees. This difference should be multiplied by the same factor of 1.5. For example, if the protractor showed a value of +2 degrees, then the caster value should be taken as +3 degrees.
The transverse inclination is calculated in a similar way, but the protractor is installed in a slightly different position. For additional convenience, you can use a smartphone, on which you should install in advance an application that simulates two mutually perpendicular bubble levels. An ordinary building level, preferably with a rotating bubble, will also work for these purposes.
To measure the lateral inclination of the steering axis, the bubble level flask must be fixed parallel to the plane of the wheel.
Measuring the level of lateral inclination of the axis of rotation.
If the task is not to measure specific numerical values of slopes, but only to compare them (they are not adjustable on most cars anyway), then the results do not need to be multiplied by a correction factor of 1.5. The main thing is to make sure that the angles are equal on both axes (right and left).
In the process of self-measurements, it is not necessary to strictly observe the rotation of the wheels exactly 20 degrees, especially when there are no appropriate tools to determine these angles (for example, graduated turntables). You can turn the steering wheel about 3/4 of a turn. It is necessary to ensure that when turning left and right, the steering wheel is locked in symmetrical positions. To do this, you can put some marks on the bottom of the steering wheel. When the steering wheel is in zero position, the line connecting the marks must run strictly horizontally.
Another way to get accurate results is to draw corners on the asphalt near the wheels using a protractor. If you don't have this tool, you can use a square sheet of paper with equal sides. Folding it diagonally, we get an angle of 45 degrees. Then one corner is folded in half again, resulting in an angle of about 22.5 degrees, which is close to the standard 20. Next, you need to attach the sheet to the wheel and outline its edge with chalk, thereby creating the necessary marks on the asphalt.
Marking the corners for turning the wheel
What is better - manual or computer adjustment?
This question worries every novice motorist, and I can’t count how many disputes there are in garages and services on this topic! After consulting with experts, we answer it. So, manual adjustment is much better and more accurate. The fact is that the stand will provide the opportunity to get the ideal option only if it is perfectly adjusted and configured itself. And this is not so easy to do. Thus, adjusting wheel alignment by hand will be faster, more efficient and more reliable than using a computer.
Computer or manual wheel alignment
However, if you do not want to do it yourself, then it is important to find a good specialist in this field with extensive experience and good recommendations.
Sign 2: Uneven tread wear
Uneven tire wear is a sign of improper alignment in three out of five cases. With positive camber, the outer side of the tread is “eaten up”; with negative camber, the inner side is “eaten up”. This is due to the fact that the load on the tires is distributed unevenly - the wheels are tilted on one side, the tread wears off more actively on the road.
Other possible causes of the problem:
- transportation of heavy loads - in this case, one-sided uneven wear appears, that is, only one side is worn on all wheels;
- damaged suspension bushings, springs, ball joints.
What to do: have your wheel alignment adjusted at a service station. Replace damaged tires - uneven wear affects handling. If you think the problem is damaged bushings, springs, or hinges, check them and replace them if necessary.
Secondly
Depending on the condition of the roads in your region, where you generally drive and the intensity of your trips, the period for performing wheel alignment work may vary.
As a rule, it can vary from one month to six months. And some drivers generally visit the service station only once a year.
If a driver has to visit a service station once every 1–3 months, then these are significant expenses and here many should think about saving money.
Of course, if you have an expensive foreign car, then you will have to put up with such expenses, but if you have a domestic car, then you can do the wheel alignment of the car yourself without any problems.
Firstly
No matter what modern equipment is in a car service center, without a good specialist it is a pile of scrap metal. And here problems can arise:
- How much do you trust this specialist;
- How accurately will the work be carried out (when the equipment was checked for compliance with metrological standards) and whether such accuracy is worth the money;
- What guarantees will you be given for the work performed?
Also read - What is better: mechanical wheel locking or electronic locking?
Numbers you need to know
To set the wheels at the correct angles, you need to know these angles, everything is logical.
Definitions for front wheels
What is CASTER.
The standard value is 6 degrees.
Thanks to this angle, wheel alignment is ensured due to speed.
The CAMBER angle (aka CAMBER) determines the correct lateral inclination of the wheel.
Thanks to the correctly set CAMBER angle, the wheels are aligned due to the weight of the vehicle.
It’s useful to know how to do wheel balancing yourself.