The control system of any modern engine with an injection system consists of a huge number of sensors that depend on one another, and together they report to the electronic control unit about the condition of the engine. Based on this data, the ECU adjusts the main characteristics of fuel formation, the operation of the ignition system, right down to the operation of the transmission. And if one sensor or regulator gives incorrect readings, the engine will not work correctly. The fuel pressure regulator is also an important element for monitoring engine condition.
Fuel pressure regulator - signs of malfunction
The control system of any modern engine with an injection system consists of a huge number of sensors that depend on one another, and together they report to the electronic control unit about the condition of the engine.
Based on this data, the ECU adjusts the main characteristics of fuel formation, the operation of the ignition system, right down to the operation of the transmission. And if one sensor or regulator gives incorrect readings, the engine will not work correctly. The fuel pressure regulator is also an important element for monitoring engine condition. Content:
Injector purpose
Installing an injector in the VAZ 2107 made it possible to significantly improve engine performance. Changing the type of fuel system increases the amount of energy that is produced during the combustion of gasoline. Compared to a carburetor engine, a fuel injection system is more efficient in the initial stages, but over time its performance decreases. What does this depend on?
VAZ 2107 injector plays the role of the final element in the fuel system of the car. The air mixture, together with a cloud of atomized gasoline, creates a huge amount of energy. Over time, this atomization may become less effective, the fuel jets will become weaker, and all due to low-quality gasoline.
The main cause of injector failure is poor fuel. Car fuel consists of many chemical components; in addition, various impurities are added to it, which should improve the overall performance of the engine. This factor cannot be ignored, since such gasoline leaves sediment on the walls of the fuel system. The thinnest channels are in the injectors, and it is these devices that suffer first. VAZ 21074 injector has the same problem. During operation, deposits from fuel only accumulate. What needs to be done to stop this?
Why do you need a fuel pressure regulator?
As mentioned above, this regulator maintains the required fuel pressure necessary for normal operation of the injectors, taking into account one or another operating mode of the power unit. In other words, the RTD affects the amount and intensity of the fuel supply that enters the engine cylinders through the injectors.
Simply put, the amount of fuel supplied to the engine at the time of injection depends on the pressure that is created inside the fuel rail (rail), as well as on the pulse duration for opening the injector and the vacuum in the intake manifold.
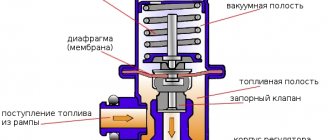
For more accurate dosing and maintaining constant pressure, a diaphragm valve-regulator is used, which experiences fuel pressure on one side, and a spring force on the other. RTD is used in power systems where there is a so-called “return”. The regulator is installed at the fuel rail. Also, this element can be located in the fuel tank, while such systems do not have a return line.
- Let's first look at the common design in which the regulator is located in the fuel rail. The element operates on the following principle: the fuel pump forces fuel from the fuel tank along the line. The resulting fuel pressure acts on the regulator. The device itself has two chambers (a spring chamber and a fuel chamber), which are separated by a membrane. On one side, the membrane is pressed by fuel, which enters the regulator through special inlet holes, and on the other side, there is spring pressure and intake manifold pressure. If the fuel pressure turns out to be stronger than the spring force and the pressure in the inlet, then the regulator opens slightly, resulting in some of the fuel being discharged into the return line. The fuel returns through the return line to the fuel tank.
- In systems without a return line, the regulator is usually located directly in the tank. The advantages include the absence of an additional pipeline. The injectors are supplied with the required amount of fuel directly from the tank, that is, excess fuel does not enter the engine compartment, and there is no need to deliver it back to the tank. This also allows us to talk about less heating of the fuel and provides a number of additional advantages in the form of less intense evaporation.
The fuel pump supplies the injectors with a strictly defined amount of fuel in relation to specific conditions and operating modes of the internal combustion engine. Let us add that in this system there is additionally an excess pressure relief valve, which helps to avoid its increase to a critical level.
Causes of malfunctions
There are not many reasons why the fuel regulator fails. The element cannot be called ultra-reliable; it works, as they say, under wear and tear, and is very dependent on the quality of the fuel.
- Marriage. This is not a common reason, but sometimes you come across defective products from domestic automakers. It is recommended to check the spare part before purchasing.
- Wear. Usually observed after 100-200 thousand kilometers. In the regulator, the membrane becomes less elastic, the pressure control valve gets stuck, and the spring becomes weaker.
- Bad fuel. Gasoline and diesel car engine fuel often contains too much moisture, debris, and foreign toxins. Water in fuel causes rusting of the metal parts of the regulator. Increasing over time, they interfere with its normal functioning and lead to weakening of the spring.
- The fuel filter is clogged. Garbage fractions in the fuel clog the system, including the RTD, and become clogged. This leads to spring wear and valve jamming.
On a note! RTDs are usually not repaired, but replaced with a new one. But, if the cause of the breakdown is clogging, it can be cleaned.
Operating principle of RTD
The valve design and operating principle depend on the type of fuel system of a particular vehicle. There are 3 ways to supply gasoline from the tank to the injectors:
- The pump together with the regulator is installed inside the tank; fuel is supplied to the engine through one line.
- Gasoline is supplied through one tube and returned through another. The fuel system check valve is located on the distribution rail.
- The circuit without a mechanical regulator provides for electronic control of the fuel pump directly. The system contains a special sensor that registers pressure; the pump performance is regulated by the controller.
In the first case, the return flow is very short, since the valve and electric pump are interlocked into a single unit. The RTD, located immediately after the supercharger, dumps excess gasoline into the tank, and the required pressure is maintained throughout the supply line.
Reference. The first scheme with a regulator inside the gas tank has been implemented on all Russian-made VAZ cars.
The second option is used in most foreign cars. A valve built into the fuel rail allows excess fuel to flow into the return line leading to the tank. That is, 2 gasoline pipes are laid to the power unit.
There is no point in considering the third circuit - instead of a regulator, there is a sensor whose functionality is checked using a computer connected to the diagnostic connector.
A simple fuel pressure valve installed in the fuel pump unit consists of the following elements:
- cylindrical body with pipes for connecting the supply and return lines;
- a membrane connected to a locking rod;
- valve seat;
- spring.
The amount of pressure in the supply line depends on the elasticity of the spring . While most of the fuel goes into the cylinders (high load on the engine), it keeps the membrane and valve stem closed. When the crankshaft speed and gasoline consumption decrease, the pressure in the network increases, the spring compresses and the membrane opens the valve. The fuel begins to be discharged into the return line, and from there into the gas tank.
The fuel pressure regulator installed in the rail operates on a similar principle, but reacts faster to changes in load and gasoline consumption. This is facilitated by connecting an additional pipe of the element to the intake manifold. The higher the crankshaft speed and the vacuum on the spring side, the stronger the membrane presses the rod and closes the passage of fuel into the return line. When the load decreases and the speed drops, the vacuum decreases and the rod releases - the return flow opens and excess gasoline begins to be discharged into the tank.
Types of RTD faults
Judging by the appearance of a mechanical fuel pressure regulator, there is nothing to break in it. But still, this is a mechanism consisting of many parts, which during long-term use are subject to wear, corrosion and “fatigue”. There may also be a defect in the manufacture of this device.
The main reasons that lead to malfunction of the regulator:
- The shut-off valve does not maintain the required pressure in the cavity. If we take into account only the regulator, then the cause may be a spring (burst, sagged) that does not provide sufficient force when acting on the valve. As a result, the fuel that should be supplied to the injectors leaks into the “return”, and the engine is difficult to start, does not develop enough power, has poor dynamics, etc.
- It happens that the valve, in the given engine operating modes, fits tightly to the hole and does not allow gasoline to flow into the return line. The reason may be low-quality fuel, a long period of idle time of the car, corrosion of the material, which is why the valve is “stuck” to the socket. With such a malfunction, the pressure in the fuel rail increases, the spark plugs may flood, the safety valve is triggered, or leaks appear in the system connections.
- The shut-off valve “wedges” during operation, that is, the pressure in the ramp does not change evenly, with a delay from the specified parameters. The reason is usually poor quality fuel, dirt, corrosion, etc. At this time, the car cannot be accelerated; it begins to twitch. When parked without load, the idle speed “floats”.
How to check the fuel rail? Checking the RTD yourself
Checking the fuel pressure regulator is carried out to identify malfunctions or for prevention.
Such checks are carried out based on the recommendations of the car manufacturer. But still, how to check the pressure in the fuel rail? Basically, the check consists of inspecting and checking the pressure of the fuel system at various engine speeds. Then comparisons are made with indicators that correspond to the norm. It is necessary to carefully inspect the tightness of the connections, the condition of the vacuum hose, as well as the regulator itself. If no damage or defects are found, then the regulator is dismantled by completely disassembling it. If a blockage is detected in this unit, it is washed.
Important: the pressure in the fuel rail should be diagnosed using a pressure gauge. It is connected to a special diagnostic fitting.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator. Fuel pressure regulator diagnostics
You can also check the regulator yourself. To do this, you do not need to use any special tools or have any special auto mechanic skills. You will need to pinch or disconnect the valve and observe the force of the jet. Or for a better check, use a pressure gauge.
To measure the RTD pressure in the engine when turning on idle speed, it is worth connecting a pressure gauge, installing it between the fuel hose and the fitting. Don't forget to disconnect the vacuum hose. Below we will look at what pressure should be in the fuel rail of a VAZ 2110.
When measuring the pressure in the fuel rail with your own hands, the pressure should begin to increase from
0.3 to as much as 0.7 Bar.
If the pressure remains in place, repeat the procedure. It happens that after a number of necessary procedures, the pressure remains the same. This means that the regulator is faulty and cannot be repaired. It needs to be replaced.
How do malfunctions of the fuel pressure regulator affect engine performance?
A faulty regulator valve affects not only operation, but also the very start of the engine.
If the device is working properly, the pressure in the fuel rail does not drop after the engine stops. If the valve has a malfunction, then the pressure in the fuel rail drops when the engine stops. The engine will not start until the sediment has completely filled the system. And only after reaching the desired level, the first engine start signals may appear. Here everything will depend on the power of the battery. Otherwise, the engine will not be able to start. Therefore, if the pressure in the fuel rail does not hold, this indicates a malfunction! In addition to the above, gas failures may occur during acceleration of the car, unstable idling, and a general weakening of engine power will begin to appear.
Damage diagnostics
How to understand that an injector needs to be replaced, checked or repaired? Even without sensors, you can understand that repair of fuel system elements is required if there are 1 of 2 main signs in models 2107, 21074:
- Unstable engine operation. Sometimes it may stall or have difficulty starting.
- A much less obvious sign is loss of power. This effect is noticeable if you mostly drive at medium speeds, but at high speeds it is very noticeable.
- The last sign is recorded only by sensors - the pressure inside the system increases.
The cause of such failures is clogged injectors; even diagnostics are not needed. Cleaning helps restore the engine to its original performance. If the problem has not been resolved after cleaning, it is worth checking the tubes and injectors for damage or breakdowns. In such cases, it is better not to start repairs, but simply replace the damaged parts with new ones.
Sometimes it is impossible to determine on your own where the damage is, and only then will diagnostics at service centers come in handy. A blockage can cause quite serious damage to the VAZ 2107 injector, as well as rupture of channels. The pressure that arises inside the system can easily destroy the most fragile parts. Here you won’t be able to fix the situation with your own hands, even if you have a complete diagram of the car at hand. There is only one conclusion - you need to devote a lot of time and attention to cleaning injectors and do it regularly.
No pressure in the fuel rail, reasons
The presence of a certain pressure in the fuel rail of an injection engine is one of the conditions for its operation.
Using the example of the fuel rail of the fuel injection system 2111 of the VAZ 21093 (21083, 21099) car, we will consider the signs and reasons for the disappearance or decrease in gasoline pressure in it.
Signs that there is no pressure in the fuel rail
Car engine does not start
The starter turns, but there are no or infrequent sparks in the cylinders.
The car engine starts and immediately stalls
After starting, the engine makes a few revolutions and stalls.
Unstable engine speed at idle
The engine jerks, shakes, and tries to stall when idling.
Dips, jerking and jerking after pressing the gas pedal
When pressing the gas pedal, instead of the expected increase in speed and pickup while the car is moving, the driver feels that the engine is trying to stop and stall - failure or several such attempts extended over time - jerking and jerking.
Reduced power and throttle response of a car engine
The car's former agility and engine traction have disappeared somewhere; the car can barely pull.
Causes of the “no pressure in the fuel rail” fault
Fuel pump faulty
The electric fuel pump cannot create the required pressure in the fuel system due to its malfunction or a malfunction of the electrical switching circuit. If the pump fails completely, then there can be no question of any pressure in the fuel rail.
Fuel filter clogged
When the fuel filter of the fuel injection system becomes clogged, its throughput decreases (in some cases it disappears altogether). As a result, gasoline cannot be pumped into the fuel rail by the gasoline pump with sufficient pressure, or maintaining the required pressure at different engine operating modes becomes impossible. See “Signs of a clogged fuel filter in the fuel injection system.”
Checking, replacing, price of VAZ fuel regulator
You can judge the condition of the regulator only after checking it, since we have already said that these symptoms may also indicate other malfunctions. The nominal pressure in the fuel rail of VAZ cars with an injection power system is from 0.3 to 0.7 bar. This is exactly the parameter that the pressure gauge should show when connecting it to the ramp. At lower pressure, the fuel will go back into the tank, and the next time you start it, you will have to turn the engine with the starter for quite a long time to start it.
Replacing the fuel pressure regulator will cost from 600 to 800 rubles, depending on the manufacturer. The old regulator is not treated and is disposed of, and a new one, after releasing the pressure, is installed in its place. Check your blood pressure more often and have a good trip everyone!
Source
Device
The VAZ 2107 injector consists of the following elements:
- Computer;
- Sensors;
- Fuel pipes and hoses;
- Fuel and air filter;
- Actuators;
- Gas tank;
- Wiring.
The injector power system contains the main element - a computer or ECU. Its permanent memory contains a program (algorithm) in accordance with which the control of actuators is implemented, these include:
- Fuel pump;
- Injectors;
- Idle air control;
- Canister valve.
Each of the above elements performs its own function.
Gasoline pump
Turned on by the ECU output signal through a relay. Has a strainer and fuel level sensor. The gasoline from it passes through the fuel filter. The pump is located in the tank and to remove it, you need to remove the back seat, remove the hatch and unscrew the fastener.
Nozzle
It is a sprayer equipped with a solenoid valve. Triggered by an ECU impulse. Accordingly, the duration of valve opening (the amount of gasoline supplied) depends on the time the pulse is applied. It is installed on a ramp common to all injectors, a constant pressure in which is maintained by a valve. If it is exceeded, the valve opens and gasoline returns back to the tank. The injector enters the intake manifold. The air flow, passing through the intake manifold, carries away a portion of gasoline ejected by the nozzle.
The structure of the VAZ 2107 fuel system
Idle speed control
The fuel system maintains engine idle speed using a regulator. It is a stepper motor connected to a conical shaped control body. Its approach reduces the air flow entering the intake manifold; its removal, on the contrary, increases it.
Canister valve
It is needed to turn on the ventilation of the adsorber, which accumulates gasoline vapors and releases them into the intake manifold at the right moment.
The injector power system contains sensors for measuring, converting and transmitting the signal to the computer.
The following sensors are installed on the VAZ 2107:
- Crankshaft position;
- Mass air flow;
- Throttle position;
- Coolant temperature;
- Speed;
- Oxygen content in exhaust gases.
Fuel system VAZ 2107 injector
With the introduction of mandatory European environmental standards EURO-2 in the Russian Federation in 2006, the Volzhsky Automobile Plant was forced to convert the fuel system of the “seven” from a carburetor to an injector. The new car model became known as VAZ 21074. However, neither the body nor the engine underwent any changes. It was still the same popular “seven”, only much faster and more economical. It was thanks to these qualities that she received a new life.
Power system tasks
The fuel system of a car's power unit serves to supply fuel from the tank to the main line, clean it, prepare a high-quality mixture of air and gasoline, and also timely inject it into the cylinders. The slightest malfunction in its operation leads to the loss of the motor’s power qualities or completely disables it.
The difference between a carburetor fuel system and an injection system
In the carburetor VAZ 2107, the power supply system of the power plant included exclusively mechanical components. The diaphragm-type fuel pump was driven by the camshaft, and the carburetor was controlled by the driver himself, adjusting the position of the air damper. In addition, he himself had to set the quality of the combustible mixture supplied to the cylinders and its quantity. The list of mandatory procedures also included adjusting the ignition timing, which owners of carburetor cars had to do almost every time the quality of the fuel poured into the tank changed. In injection machines, you don’t need to do any of this. All these processes are controlled by the “brain” of the car - the electronic control unit (ECU).
But this is not the main thing. In carburetor engines, gasoline is supplied to the intake manifold in a single stream. There it somehow mixes with air and is sucked into the cylinders through the valve openings. In injection power units, thanks to nozzles, fuel is supplied not in liquid form, but almost in gaseous form, which allows it to mix better and faster with air. Moreover, fuel is supplied not just to the manifold, but to its channels connected to the cylinders. It turns out that each cylinder has its own injector. Therefore, such a power system is called a distributed injection system.
Advantages and disadvantages of the injector
The power supply system of a power plant with distributed injection has its advantages and disadvantages. The latter include the difficulty of self-diagnosis and high prices for individual elements of the system. As for the advantages, there are much more of them:
- no need to adjust the carburetor and ignition timing;
- simplified starting of a cold engine;
- noticeable improvement in engine power characteristics during start-up and acceleration;
- significant fuel savings;
- the presence of a driver information system when errors occur in the system.
Design of the VAZ 21074 power system
The fuel system of the “seven” with distributed injection includes the following elements:
- gas tank;
- fuel pump with primary filter and fuel level sensor;
- fuel line (hoses, tubes);
- secondary filter;
- ramp with pressure regulator;
- four nozzles;
- air filter with air ducts;
- throttle module;
- adsorber;
- sensors (idle speed, air flow, throttle position, oxygen concentration).
The operation of the system is controlled by the ECU
Let's look at what they are and what they are intended for.
Fuel tank
The container is used to store gasoline. It has a welded structure consisting of two halves. The tank is located on the lower right side of the car's luggage compartment. Its neck is placed in a special niche, which is located on the right rear wing. The capacity of the VAZ 2107 tank is 39 liters.
Tank capacity - 39 liters
Fuel pump and fuel level sensor
The pump is needed to select and supply fuel from the tank to the fuel line, creating a certain pressure in the system. Structurally, this is a conventional electric motor with blades on the front of the shaft. They are the ones who pump gasoline into the system. There is a coarse fuel filter (mesh) located at the inlet pipe of the pump housing. It holds large dirt particles, preventing them from entering the fuel line. The fuel pump is combined into one design with a fuel level sensor, allowing the driver to see the amount of gasoline remaining. This unit is located inside the tank.
The design of the fuel pump module includes a filter and a fuel level sensor
Fuel line
The line ensures the unhindered movement of gasoline from the tank to the injectors. Its main part is metal tubes connected to each other by fittings and flexible rubber hoses. The line is located under the bottom of the car and in the engine compartment.
The line includes metal tubes and rubber hoses
Secondary filter
The filter is used to clean gasoline from the smallest particles of dirt, corrosion products, and water. The basis of its design is a paper filter element in the form of a corrugation. The filter is located in the engine compartment of the car. It is mounted on a special bracket to the partition between the passenger compartment and the engine compartment. The device body is non-separable.
The filter design is based on a paper filter element
Rail and pressure regulator
The “seven” fuel rail is a hollow aluminum strip, thanks to which gasoline from the fuel line flows to the injectors installed on it. The ramp is attached to the intake manifold with two screws. In addition to the injectors, it contains a fuel pressure regulator that maintains the operating pressure in the system within 2.8–3.2 bar.
Gasoline enters the injectors through the ramp.
Injectors
Now we come to the main parts of the injection power system - the injectors. The word “injector” itself comes from the French word “injecteur”, which means injection mechanism. In our case, it is an injector, of which there are only four: one for each cylinder.
Injectors are actuators of the fuel system that supply fuel to the engine intake manifold. Fuel is injected not into the combustion chambers themselves, as in diesel engines, but into the manifold channels, where it is mixed with air in the required proportion.
The number of injectors corresponds to the number of cylinders
The basis of the injector design is an electromagnetic valve that is activated when an electric current pulse is applied to its contacts. It is at the moment the valve opens that fuel is injected into the manifold channels. The pulse duration is controlled by the ECU. The longer the current is supplied to the injector, the greater the amount of fuel is injected into the manifold.
Air filter
The role of this filter is to clean the air entering the collector from dust, dirt and moisture. The device housing is located to the right of the engine in the engine compartment. It has a collapsible design, inside of which there is a replaceable filter element made of special porous paper. Rubber hoses (sleeves) fit into the filter housing. One of them is the air intake through which air flows to the filter element. The other sleeve is designed to supply air to the throttle assembly.
The filter housing has a collapsible design
Throttle assembly
The throttle assembly includes a damper, its drive mechanism and fittings for the supply (discharge) of coolant. It is designed to regulate the volume of air supplied to the intake manifold. The damper itself is driven by a cable mechanism from the car's accelerator pedal. The damper body has a special channel through which coolant circulates, supplied to the fittings via rubber hoses. This is necessary to ensure that the drive mechanism and damper do not freeze during the cold season.
The main element of the unit is the flap, which is actuated by a cable from the gas pedal.
Adsorber
The adsorber is an optional element of the power system. The engine can work perfectly without it, but in order for the car to meet EURO-2 requirements, it must be equipped with a fuel vapor recovery mechanism. It includes an adsorber, a purge valve, as well as a safety and bypass valve.
The adsorber itself is a sealed plastic container filled with crushed activated carbon. It has three fittings for pipes. Through one of them, gasoline vapors enter the container and are held there with the help of coal. The device is connected to the atmosphere through the second fitting. This is necessary to equalize the pressure inside the adsorber. The third fitting is connected through a purge valve to the throttle assembly by a hose. At the command of the electronic control unit, the valve opens, and gasoline vapor enters the damper body, and from it into the manifold. Thus, the vapors that accumulate in the tank of the car are not released into the atmosphere, but are consumed as fuel.
The adsorber catches gasoline vapors
Sensors
Sensors are used to collect information about engine operating modes and transmit it to the ECU. Each of them has its own purpose. The idle speed sensor (regulator) monitors and regulates the flow of air into the manifold through a special channel, opening and closing its hole by the amount specified by the ECU when the power unit is running without load. The regulator is built into the throttle module.
The regulator serves to regulate the additional air flow into the throttle assembly when the engine is running without load.
The mass air flow sensor is used to collect information about the volume of air passing through the air filter. Analyzing the data received from it, the ECU calculates the amount of gasoline required to form the fuel mixture in optimal proportions. The device is installed in the air filter housing.
The sensor is installed in the air filter housing
Thanks to the throttle position sensor installed on the device body, the ECU “sees” how much it is slightly open. The data obtained is also used to accurately calculate the composition of the fuel mixture. The design of the device is based on a variable resistor, the moving contact of which is connected to the damper axis.
The sensor working element is connected to the damper axis
An oxygen sensor (lambda probe) is needed so that the “brain” of the car receives information about the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This data, as in previous cases, is needed to form a high-quality combustible mixture. The lambda probe in the VAZ 2107 is installed on the exhaust pipe of the exhaust manifold.
The sensor is located on the exhaust pipe
Withdrawal procedure
- The first step is to remove the fuel module.
- Then you need to lift the fuel module cover and disconnect the wire from the fuel pressure regulator.
Using a screwdriver, pry up and remove the spring clamp of the pressure regulator.
We take the regulator out of the cover.
Installation locations
On cars, the injection system is equipped with a separate line for draining excess gasoline, which goes from the fuel rail to the gas tank (fuel recirculation). In such injectors, the regulator is installed directly on the fuel rail (or connected to it), so the unit quickly “reacts” to changes in engine operating conditions and adjusts the pressure in the rail. In this design of the power system, a mechanical type RTD is used.
There is another version of the injector - without gasoline recirculation. In this system there is no “return” at all, and regulation is carried out at the output of their fuel pump. A feature of such a system is the location of the regulator - in the tank or near it. An RTD is already used here, the operation of which is controlled by the ECU - the control unit, through a sensor installed in the ramp, monitors the necessary parameters and corrects them by sending signals to the regulator.
Power systems with electronic regulators are used less frequently than mechanical ones due to their complex design and, accordingly, lower reliability.
Main elements of the fuel system of an injection engine
The injector is a complex mechanism for supplying fuel to the cylinders. The entire fuel supply process is controlled by the engine's electronic control unit (ECU). The fuel supply system also uses a parallel air supply.
Fuel pump glass
The fuel pump cup is a collection of the main elements of the fuel system assembled on one site.
The fuel pump glass includes:
- Gasoline pump
- Coarse filter
- Fuel level sensor
- Fuel pressure regulator (only in 1.6 liter engine versions)
Gasoline pump
It is one of the main elements of the fuel system. Serves to supply fuel to the cylinder block under pressure. A fuel pump is a kind of electric motor. Its operation is based on the principle of centrifugal force. Under the influence of the magnetic field formed in the stator of an electric motor, its armature is given rotation. A pump volute is installed on the anchor shaft, which directly pumps pressure into the fuel system.
The gasoline pump is very capricious and picky about the purity of the fuel consumed. Most often, the fuel pump fails due to low-quality fuel or its lack in the tank. In order for the gas pump to last as long as possible, it is necessary to refuel at proven gas stations and keep at least 25% of the tank volume in the car’s tank. If you drive with the fuel light on, the fuel pump will most likely fail much faster, since if there are bumps, the gasoline in the tank will squish from side to side and the fuel pump will suck in air.
Injectors and fuel rail
The fuel rail serves as a kind of case for the injectors; it is in it that they are installed.
The injectors of an injection engine are also one of the most important elements of the fuel system. Designed to supply fuel to the engine cylinder block under pressure. The injector sprays fuel into small droplets for better and easier ignition in the cylinder.
Characteristic symptoms of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
By what signs can you determine that an RDT is not working:
- the engine is very difficult to start, you need to turn the starter for a long time and at the same time keep the gas pedal pressed in order for the engine to start;
- The engine idles unsteadily or the speed is very low, the engine often stalls. At the same time, it does not gain power at all; when trying to accelerate, it results in a deep failure;
- The spam engine changes speed sharply, this is especially noticeable at idle:
- Fuel is leaking from the fuel hoses. Attempts to tighten and replace clamps and replace hoses do not help.