After replacing the brake cylinder, the brakes disappeared
(VAZ 2114) In a car service center, the front end was cracked.
Changed everything. The front brake hoses were also replaced. The brakes were bled. I've been driving with normal brakes for 10 days. I'm going on shift for a month. Upon arrival I discover that there are no brakes. Well, they were only there if you pressed the pedal all the way to the floor (the right front wheel braked to the skid). I took up pumping and pumped it up. The first day everything was fine, the brakes were rough, then they gradually began to disappear again. Result, 2 days passed, the brakes returned to their original non-working state. What could be the reason? Z.Y. Before bleeding, I changed both rear brake cylinders. I checked, there were no leaks and the liquid did not leave, and even now it does not leave. They advised me to change the master brake cylinder, so I did. Still the same nonsense. After a day or two the pedal falls into the floor again ((
Is there air in the system when bleeding?
Yes. There was air. We figured it out. The problem was invisible. When replacing the brake hoses at a car service center, the left one was not tightened properly. Air was sucked in there.
October 2, 2012, 20:39 #5 123
Guys who have encountered a problem: I replaced the brake master cylinder with 2114 and pumped the brakes 3 times, but sometimes the pedal goes to the floor when I press the brake pedal, tell me if anyone has encountered what the problem could be.
- Posts: 21843
- From: Voronezh province
- Daewoo Nexia
October 2, 2012, 20:41 #6 123+ 1
RECARO, October 2, 2012, 20:39, #5
Guys who have encountered a problem: I replaced the brake master cylinder with 2114 and pumped the brakes 3 times, but sometimes the pedal goes to the floor when I press the brake pedal, tell me if anyone has encountered what the problem could be.
Obviously the air is poisoning, maybe the vacuum and the cylinder itself are working.
October 2, 2012, 20:43 #7 123+ 1
RECARO, October 2, 2012, 20:39, #5
Guys who have encountered a problem: I replaced the brake master cylinder with 2114 and pumped the brakes 3 times, but sometimes the pedal goes to the floor when I press the brake pedal, tell me if anyone has encountered what the problem could be.
Such a thought - maybe they bled the brakes incorrectly, due to lack of skill?
October 2, 2012, 20:52 #8 123
Felix, October 2, 2012, 20:41, #6
Obviously the air is poisoning, maybe the vacuum and the cylinder itself are working.
I don’t think it’s poisoning, he understands the fact that I can drive for 3 hours, everything is fine, the pedal is hard, and then it’s rubbish and there is no brake, 2-3 pumping and everything is fine again
October 2, 2012, 20:53 #9 123
actros, October 2, 2012, 20:43, #7
Such a thought - maybe they bled the brakes incorrectly, due to lack of skill?
Well, I’ll say this) my father is a god at car repairs) and they pumped the brakes on his and my car more than once)
It’s just that my gravel brake was leaking and I had to replace it, and these are the troubles that come up
- Posts: 21843
- From: Voronezh province
- Daewoo Nexia
October 2, 2012, 20:54 #10 123+ 1
RECARO, October 2, 2012, 20:52, #8
I don’t think it’s poisoning, he understands the fact that I can drive for 3 hours, everything is fine, the pedal is hard, and then it’s rubbish and there is no brake, 2-3 pumping and everything is fine again
Try to carefully plug the hose from the vacuum and try to see how it wakes you up - know exactly what it will do, but just carefully, otherwise bang.
October 2, 2012, 20:57 #11 123
Felix, I don’t know how to do this, I just don’t understand, I’ll pump the brakes until the brakes grab at the slightest pressure. everything works and then yok and print on the floor) and then everything is fine)
March 23, 2016, 09:52 #12 123
I have a similar situation now. How did it end? What was the reason?
- Posts: 12128
- From: Vladimir
- Oka AvtoVAZ Oka
March 23, 2016, 10:19 #13 123
Dmitry 1974, March 23, 2016, 09:52, #12
I have a similar situation now. How did it end? What was the reason?
Replace. or repair the front and rear brake calipers!
Look. where are the brake puddles under the car?
Good afternoon. Now I will outline the essence of the problem, if you have any assumptions, help me solve it. So, the story goes like this. After passing the GTO, a problem with the rear brakes was identified. There were practically none. TRW Lucas rear brake system. It was decided to replace the discs and pads. I bought discs with Skf VKBD1011 bearings (original 4249.34 - disc hub) and TRW pads (original 4252.23).
I didn't take a photo. About the left side: I took off the wheel, unscrewed the guide bolts, moved the cylinder to the side, and pulled out the pads. Then the fun began. The hub fastening nut was rolled in a very original way, we suffered for a long time, in the end the grinder helped)). After this, the caliper bracket mounting bolts could not be unscrewed. They are under Torx 50, the edges were licked off, they could barely unscrew them. They were still seated on the anti-rotation sealant, which was hard. The boot of the brake cylinder was torn, maybe that’s why it didn’t work properly. About the right side: Everything is the same. It was rolled like a human being; I unscrewed the hub nut quickly. But with the caliper bracket mounting bolts on this side it was worse. I had to cut down one bolt. It also didn’t work out (it was drilled crookedly the first time), so I had to go buy another bracket. In a Eurocar, the right rear caliper bracket (original 4404 67) new 1630 rubles, used 770. I took a used one. And I took a repair kit for the brake cylinder, because the boot on the left was torn. There was ERT 400454 for 600 rubles, I took it. I installed the disc, tightened the hub nut, screwed on the bracket, and installed the pads. On the left I replaced the outer boot, on the right I replaced the inner rubber. I did not remove the cylinder from the car, I changed everything on the spot. I squeezed out the cylinder by pressing the brake pedal, and a little brake fluid came out. During the process of replacing the boots, liquid was still pouring out of the cylinder. After installing the anthers, I pressed the cylinder in place using a special tool. BLEEDING: I added fluid to the reservoir with brake fluid, took a bottle with brake fluid poured into it, unscrewed the fitting on the right cylinder, put a hose on it for 8, the other end into the bottle, pressed the brake several times, dirty brake fluid and bubbles came out. I started the car, pressed the brake a little more, and the brake fluid still came out dirty. Tighten the fitting and release the brake pedal. I added fluid to the reservoir and did the same on the left side. I added a total of 1.5 liters of liquid and it came out about the same. Now the PROBLEM: it didn’t pump up. The brakes are sluggish, they start to slow down at the very end, when the car is not running, the pedal sinks to the middle, when you press it, the sound of air escaping (zilch) is made. How to bleed the brakes correctly? I read that the problem could be that air got into the ABS? Maybe due to the fact that when replacing the boots on the cylinders, brake fluid remained between the cylinder body and the cylinder (or should it be there)? Maybe the front brakes also became airy (although I didn’t touch them) when bleeding the rear ones? I'm asking for advice.
Main causes of malfunction
Before starting repairs, the cause of the failure should be determined. It could be:
- Malfunction of the main brake cylinder;
- Unadjusted gap between the pedal and the cylinder piston;
- Poor quality brake fluid or insufficient brake fluid;
- Incorrectly installed brake disc or pads;
- Faulty vacuum pump.
How to diagnose a problem if the brake pedal fails
In order to diagnose the brake pedal for damage, it is necessary to carry out a number of measures. It is recommended to do this at a service station, by the hands of experienced specialists. It can cost up to 5 hours of time and a round sum. However, if financial capabilities do not allow you to go to the service, then, if desired, any car owner can solve the problem on their own:
- Lack of brake fluid. You just need to check for its presence and top up if necessary;
- Checking the brake pedal.
- Checking pads and discs. Pedal failure can occur due to insufficient pressure on them;
- Checking the brake cylinder;
- Checking the integrity of the pumps.
Find out in our material how to change wipers on a car and why many drivers prefer frameless wipers.
How to install HBO and register with the traffic police and how to avoid unnecessary troubles - see here.
Finding out why the brake fails
It is important to fully diagnose the brake system, since one malfunction may be accompanied by another.
Most often, the pedal fails due to the fact that the brake system is serviced with low-quality brake fluid . This fluid can cause the brake lines to swell and begin to disintegrate. In order to check if there is a problem with them, you need to blow out the brake pipes. For comparison, you need to take a new tube and blow it out in the same way to understand how badly the car’s brake hose is clogged.
An air lock in the brake system can also cause pedal failure. The air that gets into the brake pipes begins to compress. This happens due to wear on the lines or improper replacement of the brake fluid. Pressing the brake pedal does not perform the braking process, but compresses the air. In this case, the pads are practically motionless. Braking is ineffective or completely absent.
Problems with the master brake cylinder (pictured). Its rubber seals may swell and delaminate. This usually occurs when using low quality brake fluid and due to tire wear. All this leads to the fact that the system is susceptible to depressurization and leakage of liquid. This problem can be solved by replacing the rubber seals. After this, you need to bleed the system to eliminate air congestion. Replacing the master brake cylinder will be necessary in case of excessive wear on the working surfaces.
How to check the brake pedal
Checking the brake pedal is that when pressed there should be no play in different directions, no extraneous sounds and no failure. The pedal may become rusty over time and may not be fully functional. The solution to the problem is to replace it with a new one. In addition, you should determine whether the distance between the brake pedal and the piston is adjusted correctly. To do this, the pedal is pressed by hand, released and monitored. If the pedal pauses at a certain stage of returning to its original position, then the problem is in adjusting the gap.
If the gap between the pedal and the piston is insufficient, the brake fluid will stagnate, causing the pedal to not return all the way, but to remain lower.
Why does this problem occur on domestic cars?
The problem of the brake pedal sinking is often found on domestic cars, in particular on the 10th VAZ family.
Often on domestic cars this problem manifests itself when replacing brake pads. The “ten” on new pads may behave inappropriately and twitch. When returning, the brake pedal bounces back to its original position with force. This problem can be solved by adding brake fluid. After this, the pedal will become hard, as necessary for normal operation of the car. After running in, which is at least 500 km, the entire brake system will function properly without failures.
Problems with the vacuum pump when you press the brake pedal are accompanied by a loud sound that resembles a hissing sound. This indicates damage to the pump. Rubber seals or valves responsible for maintaining the required pressure for normal operation may fail. Cracks that form on the pump allow excess air to get inside. The vacuum booster can be repaired by replacing the seals and boots.
How to troubleshoot the brake pedal - watch this video:
Finding the cause of pedal failure
The most common reason, which accounts for up to 70% of cases of brake pedal failure while the engine is running, is airing of the system, that is, atmospheric air entering the pipelines and lines through which the brake fluid moves. This, in turn, may be caused by the following factors:
- Low fluid level in the compensating tank - when the brake fluid level drops below the minimum mark, the vacuum created by the system elements begins to draw air in.
- Severe mechanical wear of the pads and working surfaces when the fluid level is close to the minimum - in combination, these phenomena lead to airing due to the pistons traveling too deep in the brake cylinders.
- Incorrect choice of brake fluid - a discrepancy between the fluid class, operating conditions and design features of the system can cause destruction of seals and cuffs, and the formation of viscous clots - “thrombi”.
- Boiling of the liquid - occurs when the system is severely overheated, for example, during prolonged aggressive driving in the hot season. Causes sudden and severe pedal failure due to changes in the physical properties of the substance.
- Depressurization is the occurrence of breakdowns, breaks, leaks in system elements and places and contacts through which brake fluid flows out and air gets in.
In addition, pedal failure is often associated with a rupture of the vacuum booster diaphragm. This type of malfunction is easy to diagnose - it only appears when the internal combustion engine is running, and the brake fluid level does not change while the pedal is depressed. This is explained by the fact that a torn diaphragm is not able to create the required vacuum in the amplifier chamber even with full pedal travel.
If the pedal does not fall completely, but moves jerkily, going through some areas easily, and others with considerable effort, we can conclude that the pads or caliper are not installed correctly or are poorly secured. However, do not forget that the first two to three hundred kilometers after their installation may also be due to the natural break-in of parts.
Why does the brake pedal fail?
One of the elements of the described hydraulic system is a special composition circulating through tubes and other cavities. The main feature of brake fluid is that it cannot be compressed. As a result, the force from pressing the pedal is transferred “unchanged” to the pads, which stop the rotation of the wheel. “Sinking” indicates that the line has become larger in volume or has depressurized. The main causes of the problem are discussed below.
The technical condition of the car, including its braking system, can be checked using a car diagnostic scanner. A similar device costs around 2,000 rubles, which will pay for itself in 1-2 trips to the service station. Of those on the market, we can recommend Scan Tool Pro Black Edition
This car scanner is compatible with most old and new cars, easy to use and has wide functionality. The advantages of this model include not only engine diagnostics, but also other vehicle systems. Connection is made using bluetooth or wi-fi. All information about the condition of your car and a description of existing faults is displayed on the screen of your phone or tablet in Russian.
Low quality brake fluid
The composition circulating in the system is quite aggressive. Gradually, bad brake fluid begins to corrode rubber and even metal parts, hoses, and tubes through which it moves. The walls of the latter become thinner to such an extent that they swell when pressure is created. Because of this:
- an excess volume is created into which the brake fluid goes;
- when you add it, the pressure is restored, but the tubes may not be able to withstand it: microcracks form through which the liquid gradually leaves and air enters instead (when the pedal moves in the opposite direction, it is literally sucked in). In the worst situation, the hoses may burst.
Air in the brake system
Its entry into the line is a consequence of depressurization of components and parts of the brake system. A plug may also form due to the fact that the fluid level in the tank has dropped below the existing MIN mark. Another reason is improper bleeding of the brakes when replacing the circulating compound. The danger with air in the system is that, unlike liquid, it is compressed. As a result, the force applied to the pedal goes to waste - in the literal sense of the word.
Master cylinder malfunction
Its main problem is most often related to depressurization. This occurs due to deformation and rupture of seals - cuffs. Their destruction is caused by poor-quality brake fluid or natural aging of the elements. The main brake cylinder becomes leaky even if scratches or wear appear on its walls.
This occurs due to the appearance of foreign particles in the line. They can get inside if the system is carelessly and inaccurately filled. Sometimes “extra” elements are wear and tear products if the car has been in use for a long time.
Repairing a brake cylinder is a difficult task. If you do not have the relevant experience and do not have special tools or devices, it is better to take the part to a workshop or buy a new one.
Problems with the vacuum booster
If it is faulty, then most often this can be determined by the characteristic hissing sound that occurs when you press the brake pedal. This situation may indicate depressurization of the vacuum pump. The reason may lie in a ruptured diaphragm, seals, or a broken equalizing valve. To solve the problem, purchase a repair kit and replace all rubber parts. Air can also enter the vacuum booster due to cracks in the underwater pipes: tighten the clamps on them or, if damaged, replace them (in a carburetor car, such a hose fits at the bottom of it).
Incorrect clearances
We are talking about the presence of a gap between the main brake cylinder (its rod) and the pedal. The latter in this case fails and remains in this position. If the clearance is correct, the pedal will initially move smoothly, but at a certain period of travel it will become stiff. If the distance to the GTZ rod is large, resistance to pressing will be felt only at the very end of the stroke.
Unprofessional repair
The reason when the brake pedal fails may lie in the caliper, the fastenings of which are not tightened well enough. Then its vertical axis will be shifted in relation to the brake disc and the pads will not be able to get used to function properly. Also, any unprofessional actions (poor tightening, lack of spring washers where needed, etc.) when repairing or bleeding the brake system will lead to its ineffective operation.
Corrosion
The metal that makes up some of the brake system elements can simply rust. In such cases, the pedal goes down and freezes there, from where it has to be “picked out” with a pry bar or other improvised tool. Corrosion usually succumbs to traction, which just needs to be sanded off.
Brake pad wear
In this situation, an increased gap appears between the disc and the pads. As a result, the pressure created in the system is not enough to brake the wheel. The solution is obvious: replacing the pads.
Solution
If your car has such a breakdown, the main thing is to solve it comprehensively. It happens that malfunctions are associated with several reasons at once. If the problem is that the pedal is simply rusty, it needs to be replaced. It is easy to correct the situation by replacing the brake fluid with a higher quality one. By the way, you will have to update the fluid in any case - in order to “update” the entire system. Otherwise, over time, the pedal will definitely begin to fail when pressed.
If cracks appear in the pumps, the brake may also begin to fail. Moreover, even microdamages can be the cause of such a breakdown. So if you want the brake to function and not fail in the middle of the road, you will have to replace everything that has stopped working. It turned out to be enough for me to make one replacement. At this point, the question of why the brake pedal failed was closed. To be convinced, it was enough to just start the engine. No extraneous sounds. And if before the return after pressing was too slow, now everything works perfectly.
When not to panic
- If you got behind the wheel, decided to start the engine after a long period of inactivity, pressed the brake and started the engine, and at that moment the pedal “went away,” then there is no need to look for a malfunction: the phenomenon is normal. The fact is that when the car starts, the hydraulic vacuum booster begins to work: the process involves installing the mechanisms of the unit into the working position. It’s just that there is a difference between the force transmitted to the pedal when the engine is turned off and when the engine is running.
- If the brake fails after completing repair work to replace the pads, it also does not always indicate problems. In this case, the pedal begins to “go away” after bleeding the system, but then functions normally. This is due to the pistons of the working brake cylinders - they “search” for some time for the optimal gap between the disc and the pads.
The brake failed at full speed: what to do?
First, try pressing the pedal sharply several times: perhaps its functionality will be partially restored. Next, assess the situation and identify a place where you can gradually turn. Then tighten the handbrake (don't do it too hard) and start shifting (if you have a manual transmission) to a lower gear. At the same time, when the lever is in “neutral”, press the accelerator (perform “re-throw”) to “prepare” the gearbox gears for emergency operation. As a last resort, choose the lesser of two “evils” - it is better to run into some obstacle near the road (roadside bushes are a good option) than to collide with a car.
How to operate the pedals
Despite the fact that most young motorists buy cars equipped with an automatic transmission, experienced drivers still drive a manual transmission. Such a vehicle has three pedals - gas, brake and clutch. The right foot should be responsible for the brake and gas, and the left foot should be responsible for the clutch. In order to learn how to properly control two pedals at once, move only the toe of your foot, and not your entire foot at once.
You should also remember the “raw egg” rule. You can slow down smoothly or start moving only when you press the pedals as if you don’t want to crush an egg, that is, very carefully. The left foot is constantly on the clutch pedal; we release it when completing the trip or changing gear.
If you bought a new iron horse and don’t know where the gas and brake are on an automatic transmission, then on the right is the gas, on the left is the brake. In this case, control is performed with one foot, and we place the second on the stand located on the left. Holding both is extremely dangerous, because it is then that inertia can be applied to both pedals at once.
Vacuum booster - symptoms of malfunction
Almost all cars have a vacuum booster. It reduces the force applied by the driver to the pedal, while at the same time increasing the force transmitted by the fluid. It only works after the engine is started. Poor performance is often caused by wear or damage to the vacuum seal diaphragm. In this case, no vacuum is created in the chamber. We need to look at the fuel fluid level: if it is normal, we check the operation of the amplifier. If the vacuum tank is not topped up in a timely manner, it first malfunctions, then the diaphragm is damaged.
First, we check with the engine not running: depress the pedal and hold it pressed. If it begins to gradually fail, the reason is in the gas turbine engine: the cuffs are leaking or the working surface of the cylinder is worn out. Without releasing the pedal, we start the engine. It should fall smoothly and slightly and stop. If everything is exactly like this, then the vacuum seal is in order. If the pedal falls while the engine is running, the reason is in the amplifier, the GTZ is to blame. When driving with a damaged diaphragm, the speed during braking practically does not decrease. You need to immediately replace the diaphragm with a new one.
When the vacuum seal dies, when braking, the car, especially in cold weather, tends to stall, and the noise of escaping air is clearly audible.
Are adjustments done differently on different brands of cars?
The above procedures are universal and can be performed on machines from any manufacturer. The essence of the procedure is always the same - to reduce or increase the pedal stroke by tensioning or loosening the cable, or adjusting the hydraulic pusher.
But when adjusting the clutch in cars of different brands, there may be some differences. For example:
- normal pedal amplitude or clutch clearance;
- procedure for accessing the clutch adjusting and control nuts. So, in a VAZ-2114, 2115 you will have to remove the battery before starting work, and in a Lada Kalina you will have to unscrew the air filter.
Before starting work on adjusting the clutch, read the technical information about your vehicle, the operating instructions and the repair manual. This will allow you to complete the procedure correctly.
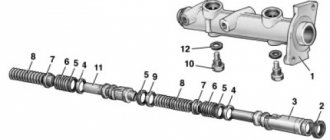
The master brake cylinder has failed
The main brake cylinder, if you remove the valve system and the division into circuits, operates on the principle of a conventional hydraulic drive. Almost like a syringe. We press on the rod - the piston pushes the liquid and supplies it under pressure into the system. If the piston cuffs are worn out, fluid will leak into the cavity behind it. And this will lead to a sinking pedal and almost no brakes. In this case, the liquid in the tank will remain in place.
There is only one way out of this situation: repair or replacement of the brake cylinder. Repairing this element of the system is now very rarely practiced and is not available for all cars. In addition, the repair kits from the cuff set do not always solve the problem. Sometimes the surface of the cylinder is damaged by corrosion, which eliminates the possibility of repair.
VAZ 2114 brakes poorly and weakly
The car brakes poorly. At speed you have to press the brakes with all your might. The car brakes very lazily, smoothly, and not sharply, as it should be when you press the brake hard. The vacuum cleaner is working. The brakes are normal. The brake discs are good. Where to look?
Is there a difference between pressing when the engine is off and when the engine is running? Pump it 5 times and press and start the engine the pedal should go away a little, which means the vacuum is pumping
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, yes, I did that, the pedal fails, the vacuum cleaner works
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, urgently check that all the wheels are skidding. Maybe the butt is completely silent
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, what is use? type check if all wheels are braking? But as?
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, at least on dusty asphalt, brake to the floor and see if there are tracks left by all the wheels or not.
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, I'll try. And if it turns out that everyone is slowing down, then where to dig further? What other reasons could there be? When I brake, the car brakes evenly, the steering wheel does not move.
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, perhaps air
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Alexey, I also thought about this. Does it make sense to pump them up?
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Bleed the brakes. The rear cylinder may still be leaking.
0 0 Answer rating: 0
Pump the brakes or check the cylinders
0 0 Answer rating: 0
pump air there. start from the farthest one, I pump up the rear left-right, then the front right-left. (And for those wise guys who say that this is not correct cross to cross and something like that, it’s your decision) another important point needs to be pumped in the pit and not by jacking it up (for those who say that this is nonsense, go to hell...) because there is a type of load sensor there, I don’t know what it’s called according to the textbook
0 0 Answer rating: 0
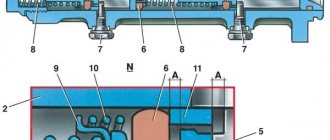
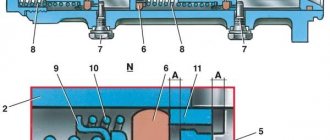
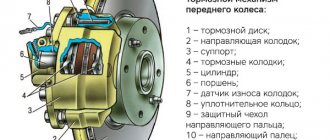
Brake system design
Before you begin to consider the problem, you need to understand the basics of the design and operation of the braking system. Most modern cars are equipped with drum and/or disc brakes with a hydraulic drive, which consists of:
- brake pedal - a control body that transmits the driver’s command to the system;
- vacuum booster - necessary to increase braking efficiency by increasing the pressure in the system;
- master brake cylinder – ensures separation of brake circuits and direction of forces to each wheel;
- working wheel cylinders - act directly on mechanical elements (caliper or expansion fist), providing wheel braking;
- pipelines and highways - connect all elements together and serve as guides for the movement of brake fluid.
The role of the working body directly responsible for braking is the pads acting on the brake disc or drum.
Diagnostics – what does it include?
If the problem is not yet too obvious: something seems to be wrong, but the braking function is working, you can start with self-diagnosis. Very often, failure occurs due to the fact that insufficient pressure is applied to the pads and discs. This may be due to interruptions in the supply of brake fluid. Start the engine, press the pedals and listen - extraneous sounds are the most obvious sign.
The most important thing is not only to notice in time that the brake pedal has failed. The second important aspect is conducting competent diagnostics. I advise you to contact only proven service stations and not skimp on full diagnostics.
Remember how much time has passed since the brake began to noticeably go down, the last time the fluid was changed. Perhaps it is no longer enough - try adding more. If this does not help, you will have to find out at the service station why the brake pedal failed. Otherwise, such a brake may simply fail at one moment. A quality diagnostic will include a full check of the entire brake system. Particular attention should be paid to the master brake cylinder - if the problem is there, alas, replacement will be required. A good technician will also check the tightness of the pumps, the pressure in the system, the condition of the discs and pads. High-quality diagnostics will take at least 5-6 hours and will cost money: but whatever, the braking system in the car must be at its best.
The liquid turned into soda
The working fluid of brake hydraulics is capable of transmitting force only if it retains its incompressibility. Liquids and solids have this property, but not gases. The appearance of any of them inside the system ensures its failure. The reasons why the brake pedal fails can be different.
- The system seals are made of a material that blocks the path of both liquids and gases. But at a certain stage of their aging, a stage is possible when they still hold liquid with difficulty, but air begins to pass almost unhindered . As a result, during any braking, the moving parts are likened to a pump, pumping outside air into the hydraulic area. It accumulates and partially dissolves in the liquid. The incompressibility of the working fluid disappears, the stroke of the working cylinder rod increases.
- In addition to the external penetration of parasitic gas, it can also form from the liquid itself. It has the property of hygroscopicity, that is, it is capable of dissolving water vapor from the atmosphere well. The boiling point of water is significantly lower than that of the original composition, which engineers specially worked on, increasing its temperature threshold. The resulting water vapor is a gas, so the phenomena already described above occur. Moreover, this will happen at a critical moment, when the brakes work intensively, which is accompanied by heating.
- More prosaic reasons for airing the brakes are also possible. These are errors in their repair and poor pumping. This is what will appear the first time you try to brake urgently.
Treatment of the situation comes down to following basic brake care rules. The fluid must be changed on time, as specified in the instructions for the car, and not use cheap substitutes. Inexperienced personnel who have little understanding of the technological process should not be allowed to repair brakes.
How to bleed brakes on VAZ cars
This is a procedure performed after repairs, replacement of individual system elements, or when replacing fluid. Pumping needs to be done by two people. But first, check the car's operating instructions, which should indicate the order of actions with the wheels. If there is no such point, start pumping from the rear right and left, then do the same with the front ones. You will also need to prepare:
- a thin hose or plastic tube with a diameter suitable for the bleeder fitting;
- a suitable small transparent container 0.5-1 l;
- key for unscrewing the fitting.
Next, place the car on an inspection hole so that you can get to each wheel from the inside. Have an assistant sit behind the wheel. Further actions:
- Fill the brake fluid reservoir to the maximum level.
- Clean the fitting, put a spanner on it and insert a tube, one end of which is lowered into a container containing brake fluid.
- Have an assistant press the pedal several times and keep it pressed.
- Unscrew the fitting and, holding it with a key, watch the nature of the liquid pouring out. If there are bubbles, tighten the fitting and instruct an assistant to repeat the operation.
- Pumping should be carried out until bubbles stop coming out.
How to bleed the brakes without an assistant is shown in the video below.
If air comes out despite repeating the procedure many times, the reason should be sought in depressurization of the system.
Do-it-yourself brake bleeding
The failure of the brake pedal in VAZ cars can be overcome by carrying out the process of bleeding the system.
Before you start bleeding the brake system, you need to study the car's instructions, which contain a clear bleeding scheme. If there is no such scheme, then the wheels are pumped from right to left (rear right and left, then the front ones in the same way).
You also need to prepare the following necessary elements: a hose and any plastic or glass container.
The work progresses like this:
- Brake fluid is poured into the master cylinder;
- The brake pipe fittings are cleaned;
- Brake fluid is added to the container, into which one end of the hose is inserted. The other end is inserted into the fitting;
- An assistant is brought in to press the brake pedal several times and hold it down. At this time, you need to unscrew the fitting and check the liquid that leaks out. When the system is aired, air bubbles may be noticeable;
- Next, the fitting is tightened and bleeding continues with three wheels, which should be pumped according to this scheme.
Drivers must pay close attention to their “iron horse” and periodically carry out diagnostics and quality maintenance. First of all, this concerns the braking system. Checking it regularly will make it possible to avoid such troubles as the brake pedal sinking.