- home
- Car electrics
- …
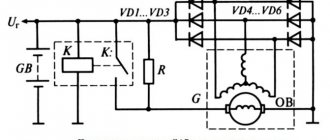
Beginners now no longer know what generators were like (20-30 years ago), their pulleys and belts that made them work. But I remember it very well. It happened that some Zhiguli car would go 15-20 thousand and everything breaks, it needs to be changed (and it’s better to do this in advance). It seems to have been tightened, there is no “sagging”, oil and brake fluid are not leaking, but they don’t move anymore, “even if you crack”! But everything turned out to be banal and simple, slippage occurs constantly - this is how the engine works. Its work is not linear; the inertia of the generated system itself also adds a fly in the ointment. But on modern cars this element can run for a very long time, often up to 100,000 kilometers - how did they achieve this? It’s all just a matter of a tricky clutch, which is called “overrunning”. It was she who extended the service life significantly. Therefore, knowing how it works and what it is needed for is very useful...
Of course, the materials themselves have been updated since those times, and the belts have become completely different, they are now wide and are called poly-V-ribbed (you can also hear rivulet), but this will be a separate article, I just want to note that even such a technically advanced type would not pass 30,000 km, although it would have overtaken the old “single-wedge” modifications.
Why do you need a generator overrunning clutch?
The overrunning clutch is installed on the generator shaft pulley.
The locking rollers take the main load. While the car engine is running, at the moment when the fuel-air mixture ignites in the working chambers of the cylinder, the crankshaft accelerates the outer race of the generator clutch. The locking rollers close and begin to hold the outer and inner races together, thereby transmitting rotational motion to the armature, that is, the generator shaft also begins to unwind.
At the moment the engine is running, when ignition does not occur in the working chambers of the cylinders, but compression occurs, the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine slows down, and the inner race, which is on the generator shaft, begins to overtake the outer race, which is connected by a pulley and belt to the crankshaft. To avoid affecting the rotation of the crankshaft and breaking the generator's wallpaper clutch, the design of the clutch copes with this situation. Namely, when the generator shaft rotates faster than the crankshaft, the locking rollers plunge into special grooves or turn sideways, thereby separating the outer and inner races from each other. In the disconnected state, the cages rotate independently of each other.
This design of the coupling and its principle of operation allows us to avoid the negative effects of inertia. If the clips were not separated in time, the belt would slip, putting a load on the shafts of the internal combustion engine and generator.
What exactly is the problem
When the first front-wheel drive cars appeared, with various power steering and power steering units, air conditioners and other attachments, and they decided to abandon the carburetor in favor of an injector, it only got worse. More energy was required, and accordingly the parts of the generating plant (the hull itself, the anchor, etc.) had to be made larger, the inertia of all these units only increased.
On the other hand, the engine does not run smoothly; torque is transmitted in impulses, namely when combustion occurs in the cylinders (once every two revolutions of the crankshaft). That is, conventionally, combustion occurs - sharp acceleration, the exhaust gas removal cycle has a slight subsidence. I think this is understandable.
However, the remaining parts of the system, which are untwisted using a belt, are not capable of such jumps. Due to the inertia of the shafts or armatures, they either lag behind the crankshaft (when ignition occurs) or overflow (gas removal). It’s worth adding here – starting and stopping the engine, sharp acceleration and braking. This is the main problem - such jumps wear out the belt drive, and at one point it simply breaks.
It is clear that something needs to be done, namely to level (smooth out) these moments of inertia and the impulse work of the power plant. A special and fairly compact mechanism was developed.
Working principle of the coupling
Roller overrunning clutch diagram
Let's look at the principle of operation of a roller freewheel clutch, since this type of this mechanism is most common in the automotive industry.
The freewheel roller clutch is divided into two coupling halves: the first coupling half is rigidly fixed on the drive shaft, the second coupling half is connected to the driven shaft. When the drive shaft rotates clockwise, the clutch rollers, due to the action of friction and springs, roll into the narrow part of the gap between the two coupling halves. After this, jamming occurs, and torque begins to be transmitted from the driving half of the coupling to the driven half.
When the drive coupling half rotates counterclockwise, the rollers roll into the wide part of the gap between the two coupling halves. The drive and driven shafts are disconnected, and torque also ceases to be transmitted.
Based on the principle of operation, we note that the roller freewheel clutch transmits torque in only one direction. When rotating in the other direction, the clutch simply scrolls.
How is it structured?
Today, two types of such devices operate successfully: friction and ratchet type units. Friction type products are also divided into several varieties. They can be:
- Mechanisms with radial closure;
- Devices with axial closure;
- Belt mechanisms;
- Units with a spring mechanism;
- Wedge overrunning mechanisms.
The last of the listed devices include products with roller overrunning clutches, which are most widespread in the automotive industry. The design of such devices is based on three important parts, these are two cages, outer and internal, as well as two rows of rollers, which act as a connecting link between the clips. One row of rollers moves along a profiled section of the inner races. This allows them to function as locking mechanisms. The second row of rollers plays the role of a needle bearing. The inner race has a rigid connection with the generator shaft, and the generator set pulley is mounted on the outer race.
In addition, the design of roller overrunning clutches contains:
- Contact plate with an oil seal built into it;
- Inside it you can see two bushings, one of them has a normal appearance, the second is made with inclined planes;
- A lid made of plastic;
- Gasket made of high-strength elastomer;
- Profile with slots.
The operating instructions strictly prohibit using this device when the cover is missing. It can be installed only once, installation is easy, and there are no problems.
Overrunning clutch device
How the OAP overrunning clutch works
Interestingly, the generator pulley with and without an overrunning clutch looks almost the same. Because the overrunning clutch is a mechanism built into the pulley. And if a regular pulley is a piece of iron with grooves attached with a nut to the generator shaft, then the design of a pulley with an overrunning clutch is more complicated.
Imagine that an ordinary pulley was cut into two separate “donuts” - external and internal. And a special bearing was inserted between them. Because this is what a pulley with a generator overrunning clutch looks like. It has an outer ring that engages with the belt. And there is an internal race that is threaded onto the generator shaft. And between them there is a bearing with rotating and locking elements. There are seals at the ends of the overrunning clutch that prevent dust and dirt from getting inside.
Device and main components
Let's look at the design and components of the two main types of overrunning clutches - roller and ratchet.
The simplest roller freewheel consists of the following components:
- outer ring with special grooves on the inner surface;
- inner race;
- springs located on the outer ring and designed to push out the rollers;
- rollers that transmit torque due to the friction force when the clutch jams.
Ratchet Overrun Clutch
The ratchet overrun clutch uses teeth instead of grooves on the inner surface of the outer ring that have a stop on one side. In this case, both rings are jammed by a special pawl, which is pressed against the outer ring using a spring.
A little about the operation of the generator
First, it’s worth studying the question of how a car generator works. If you want to seriously understand the structure of this unit, then you should study thematic materials - it’s quite interesting. Now we will look at some aspects of the generator’s operation and try to understand its structure. In general, car generators consist of many elements, but its main components include the following:
- Pulley;
- Frame;
- Rotor (rotating part of the generator);
- Stator (fixed part of the generator);
- Diode module;
- Diode module protection;
- Voltage regulator;
- Brush unit.
Overrunning clutch: definition and functionality
A car owner's interest in an overrunning clutch usually arises only when the vehicle's mileage exceeds 100,000 km. This is due to the wear of the part and the need to replace it. How does an overrunning clutch work? What types of parts are there? Why does the clutch fail? Let's discuss it in this article.
Overrunning clutch: definition and functionality
Overrunning clutch
is a device that ensures smooth running and independent rotation of the shaft and pulley inside the generator mechanism when they move unidirectionally.
Overrunning clutch device
Do not forget that the overrunning clutch is an integral part of the generator pulley. The "improved" and regular pulleys look almost identical. The only difference is that the “stuffed” pulley has an outer rim for installing a belt, while the inner rim is designed to be screwed onto the generator shaft.
As mentioned above, bearings with locking mechanisms and rotation elements are installed between the inner and outer rings of the part. Seals installed on the end sides of the part allow you to protect the metal from dust particles and road dirt.
By comparison, a traditional pulley is a grooved solid metal part connected to the shaft sleeve with a matching nut. The operating principle of a conventional pulley is quite simple, but, as it turned out, it is not effective.
Types of generator overrunning clutches
There are currently two main types of overrunning clutches produced worldwide:
1. Overrunning clutch based on OAP technology (from the English “Overrunning Alternator Pulley”)
is an example of a freewheel mechanism. A clutch of this type ensures unlimited rotation of the generator rotor, provided that the speed of the rotor mechanism exceeds the rotation speed of the generator crankshaft. Otherwise, the generator belt “comes to the rescue” of the spinning rotor. The freewheel was first introduced by INA, and it was its engineers who came up with the idea of creating the part.
You can determine what type of alternator pulley is installed on your car yourself. A more modern generator design, which has a number of advantages, has a dark cover that acts as a boot. At the same time, the presence of a stopper nut indicates that your vehicle model is equipped with a conventional pulley, which is known for its shortcomings. Unfortunately, the location of the assembly does not allow the nut to be clearly seen, therefore, most often, pulleys are distinguished by the cover.
Operating principle of the generator overrunning clutch
Possible faults
A malfunction of the overrunning clutch can occur for the following reasons:
● Contamination and water ingress into the part. As a result, rapid wear of the material from which the bearings and reversing rollers are made occurs.
● Jamming is the most common failure of an overrunning clutch. The failure of the bearings and inner race occurs due to abrasion of the surfaces of the parts. Thus, the system operates like a regular pulley without an overrunning clutch.
● Separate rotation of the inner and outer races. This problem occurs for the same reason as wear of the elements inside the pulley. Repair will be required immediately, because the generator will simply stop charging.
● Destruction of the overrunning clutch. Rupture of the cage can occur due to jamming of the roller components. If the crankshaft significantly overtakes the generator rotor, or vice versa, a breakdown often occurs. “Side effects” of this failure may include serious deformation of the generator shaft, as well as mechanical damage to the drive unit.
Overrunning clutch diagnostics
A mandatory check of the functioning of the pulley with an overrunning clutch is carried out if:
Car headlights began to shine dimly or the battery fault icon lit up on the dashboard. (the battery is probably not charging enough). At low speeds, an uncharacteristic noise and vibration, noticeable when pressing the brake pedal, appeared, accompanied by strong jerks, noticeable when driving the car. (such signs are characteristic of jamming)
Typically, an inspection of the overrunning clutch is carried out by specialists by dismantling the entire generator structure using a special key. At the same time, the operation of the automatic transmission, the condition of the transmission, as well as the starter and clutch are diagnosed. Self-inspection of the system is not recommended, as it requires special skills and experience.
If you find problems with the generator, contact the official service centers of FAVORIT MOTORS Group of Companies. Highly qualified service technicians will thoroughly check and repair all significant vehicle systems using modern equipment and original spare parts. We offer affordable prices and high quality service to each client.
To neutralize this negative fact, an overrunning clutch was created, which was simply built into the generator pulley. It has two clips:
Advantages and disadvantages
The overrunning clutch has the following advantages:
- automatic switching on and off of the mechanism (the clutch does not require control drives);
- with the help of freewheel mechanisms, the design of machine components and assemblies is simplified;
- simplicity of design.
Operating principle of an overrunning clutch
Note that an overrunning clutch with a ratcheting mechanism is more reliable than a device with rollers. At the same time, the ratchet mechanism is repairable, unlike the mechanism with rollers. Trying to repair a roller overrunning clutch is a waste of time, since it is a non-separable unit. Usually, when it breaks, a new similar part is installed. When installing a new roller clutch, do not use impact tools, as the mechanism may jam.
The overrunning clutch is not without its drawbacks. The disadvantages of the roller freewheel mechanism are as follows:
- inability to regulate;
- strict alignment of shafts;
- increased manufacturing accuracy.
An overrunning clutch with a ratcheting mechanism has the following disadvantages:
- The main disadvantage is the impact when the pawl engages the teeth. Because of this, this type of freewheel mechanism cannot be used in units operating at high speeds, or in cases where a high frequency of switching is required.
- The ratchet mechanism rotates with a characteristic noise. Note that there are now mechanisms in which the pawl, when moving clockwise, does not touch the ratchet wheel and, accordingly, does not make noise.
- Due to heavy loads, the teeth of the ratchet wheel are worn out, after which the overrunning clutch fails.
Lego Educational Ratchet Mechanism
With the help of educational construction kits, you can assemble models with a ratchet mechanism.
In this example, the ratchet is assembled from a standard gear and pawl, which consists of three parts (pin, red retainer and short axle). The gear wheel is driven by a handle. It is important to select such an angle of the pawl relative to the gear wheel so that reliable engagement occurs during reverse rotation.
The following example uses a reversible dog in a mechanical fan model made from a Lego Education EV3 set. When lifting the load, the ratchet mechanism prevents the thread from accidentally unwinding. Next, the dog is transferred to the other side so as not to interfere with the operation of the fan.
Mechanical fan from Lego EV3
In the catapult example, there is a long lever at the opposite end of the pawl. Under the weight of the long end of the lever, the pawl rests on the gear wheel and blocks the rotation of the axle. The catapult cannot fire. As soon as you push the long lever up, the pawl will disengage, unlocking the drive axle.
Mechanical catapult from Lego EV3
The instructions for the catapult can be downloaded from this link.
Application of coupling
Freewheel mechanisms have found wide application in vehicle components of various manufacturers. So, the overrunning clutch is present in:
- internal combustion engine (ICE) starting systems: here the freewheel device is part of the starter. At the moment when the engine starts and reaches operating speed, the clutch disconnects the starter from it. Without the clutch, the engine crankshaft could damage the starter;
- Automatic transmissions of the classic type: in them the freewheel mechanism is part of the torque converter - a device that is responsible for transmitting and changing torque from the internal combustion engine to the gearbox;
- generators - here the coupling acts as a protective component, limiting the transmission of torsional vibrations from the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine. The clutch also neutralizes vibrations on the generator belt and reduces the noise of the belt drive. In general, the freewheel mechanism here significantly extends the service life of the generator.
Some types of overrunning clutches
Overrunning clutches, as a rule, have a simple design. To turn the clutch on/off, no additional actuators are required.
The simplest overrunning clutches can be considered roller and cracker clutches. The roller clutch is widely used in technology due to its simplicity, quiet operation and high reliability:
Overrunning roller clutch
The coupling consists of two rings - internal and external. In the recesses of the inner ring, which is the drive shaft, rollers are installed, which, under the action of springs, are pressed against the grooves on the outer ring, thereby limiting its independent rotation, as a result of which the outer ring begins to rotate synchronously with the inner one. When the outer ring reaches a greater angular speed than that of the drive shaft, the rollers, under the influence of centrifugal force, compress the springs, as a result of which they disengage with the outer ring, which, without transferring force to the drive shaft, can develop a much higher angular speed without damaging it due to possible overloads the entire mechanism (transmission).
The most obvious is the use of overrunning clutches on bicycles - it is thanks to these simple devices that cyclists are spared the need to pedal all the time. In the absence of an overrunning clutch on the drive wheel, the rigid connection of the driven sprocket and the wheel hub would force the pedals to spin all the time.
However, using a “living example” it is possible to more clearly explain and describe the principle of operation of overrunning clutches, using other examples of the use of clutches as examples, and at the same time considering some variants of their devices and the purpose in the operation of a particular mechanism.
Overrunning clutch structure:
- External clip. The outer race engages with the pulley.
- The clip is internal. The inner race is connected to the armature - the generator shaft.
- Rollers in two rows. They are the connecting elements of the outer and inner races. The first row of rollers are needle bearings. The second row consists of specially profiled figures that roll freely in the cage and act as a stopper.
- Contact plate with an oil seal installed in it.
- The bushing is cylindrical.
- Bushing with inclined planes.
- The cover is plastic.
- Gasket made of elastomer material.
- Profile with slots.
Attention! Do not operate the alternator overrunning clutch without a cover.
Types, classification and purpose: briefly about the main thing
The difference between roller type couplings and those with a ratcheting mechanism is only in the mechanism for engaging the outer and inner coupling halves. In a ratchet-type coupling, in the outer ring, instead of engagement grooves, there are teeth with emphasis on one side - with the help of a friction spring, both coupling halves engage with each other due to the teeth, which ensures the blocking of the unit.
The design purpose and advantages of using both types of couplings in transmissions are similar - among the advantages of the coupling connection, the following stand out:
- Simplicity of the device and ease of maintenance.
- Simplification of the design of the transmission unit.
- Autonomous operation of the unit and no need to use control drives.
Moreover, each type of coupling has its own set of disadvantages. The main disadvantages of a roller type coupling include:
- High labor costs during production.
- Requirements for the alignment of coupling halves during installation.
- Lack of adjustment options.
Among the disadvantages of a unit with a ratcheting mechanism, it is customary to highlight:
- Accelerated wear and greater load on the part when engaged.
- Increased noise level during operation.
- Impossibility of installation on high-speed transmission elements.
The freewheel is considered a structural component of the torque converter of a classic hydromechanical transmission, but is also used in the design of the generator and vehicle starter as a protective mechanism that limits torque and reverse oscillations.
Purpose
The function of the clutch is to remove inertia from the rotor, which is applied to the generator belt. This allows you to extend its service life from 30 thousand km. (as it was before, before the development of the device) up to 100 thousand km.
Jamming.
This is the most common malfunction. Occurs after 100-150 thousand kilometers. Unfortunately, the overrunning clutch is maintenance-free and has a finite life.
Jamming is unpleasant because it hardly manifests itself until the belt reaches critical wear (except that the tensioner jerks). Once the belt wears out, it will either squeak or come off.
Slipping.
If the overrunning clutch slips slightly, the generator will not develop full power. You'll see this in the voltage indicator, difficulty starting, and dimming of the headlights.
If measures are not taken in time, the overrunning clutch will completely lose contact with the generator armature and will rotate on its own.
You will see this by the lit no charge indicator:
With a high degree of probability, slippage of the generator overrunning clutch will be accompanied by whistling and noise.
Naturally, with such a malfunction you won’t be able to drive for long. You can simply stand in the middle of the road or not start the car after parking.
Device
The generator overrunning clutch consists of two cages:
- external, connected to the generator pulley;
- internal, connected to the generator armature shaft;
Between them there is a layer of special rollers laid in two layers:
- Level 1 - needle bearings;
- Level 2 - profiled figures. They are needed to act as a locking mechanism.
These clips are integrated into each other.
Principle of operation
When the engine starts running, the rotation of the outer clutch race begins to increase. The rollers acting as a locking device are locked. In this case, the outer part is connected to the inner one. At the same time, the generator shaft and pulley unwind.
When work stops, exhaust gases begin to escape. This slows down the rotation of the crankshaft. The inner part of the cage is faster than the outer one in rotation. At the same time, the locking mechanism opens and its connection with the outer part of the coupling becomes weaker. Because of this, the inner race stops braking.
This is a full cycle of operation of the device unit. One process follows another. In this case, the inertia from the belt is transferred to the pulley and the generator belt.
How to check the alternator overrunning clutch?
A clear symptom that the clutch and belt are failing is a rattling sound in the cabin (the driver will not confuse this sound with anything) and significant vibration when the vehicle is moving slowly (or when the car is on the brake or in gear).
You can check the serviceability of the overrunning mechanism as follows:
Elastic coupling VAZ 2107
- open the hood of the vehicle, start the car;
- spin the engine up to about four thousand revolutions;
- turn off the ignition.
After this, you need to listen to your “iron horse”. If you hear some residual sound, reminiscent of the sound of a turbine stopping, then the clutch is functioning quite adequately, and the problem is not with it. If the specified characteristic “sound” is not observed, most likely the overrunning clutch has exhausted its service life.
The overrunning clutch, like any car part, has its own service life, which is about 100,000 kilometers. In its structure, the coupling resembles a regular rolling bearing, and accordingly the faults are similar. Problems can be identified by some characteristic symptoms:
- when the engine starts, a whistle appears;
- Clicks are heard from the tensioner pulley;
- the belt begins to “jump”, it is difficult not to notice.
Malfunctions can occur for various reasons, for example, when dirt gets into the mechanism, due to improper installation of the generator and due to natural wear and tear. In principle, with a faulty overrunning clutch (if it is not jammed, of course), you can operate a car, but this is fraught with rapid wear of the belt drive and generator bearings. To avoid additional financial costs, it is better to fix the problem in a timely manner with your own hands or by contacting the nearest car service center. Repairing the coupling is not practiced; it is easier to buy a new part. You can change it yourself; to do this, you need to dismantle the generator and unscrew the coupling mounting bolt with a Torx bit, after which a new part is installed and secured with the same bolt.
Possible faults
Most often, the overrunning clutch suffers from the following malfunctions.
- Pulley failure. The internal part of this structural element ceases to engage with the locking rollers in whole or in part. As a result, the generator stops rotating or significantly weakens its rotation.
- Spring wear. A malfunction can occur on multi-disc clutches, the design of which involves the presence of a spring. If it wears out, the force with which the device's disks press against each other decreases. As a result, the energy from the transmission belt to the rotor is not transferred in full, and the voltage in the vehicle’s on-board network becomes less.
- Breakdown of the overrunning mechanism. The locking rollers can also fail. This can be expressed either in their inability to go into the grooves or turn, ensuring free rotation, or in constantly being in such a position. The result is either constant rotation of the generator, or its complete absence. Intermediate options are also possible.
- Wear. When a vehicle runs over 100,000 kilometers, the coupling simply wears out. Each of its elements therefore begins to function worse. The result is abnormal operation of the generator.
The following symptoms may indicate a faulty part:
- extraneous sounds coming from the generator;
- the generator does not work at all;
- when the engine operates at high speeds, you can hear a characteristic whistle;
- when starting or stopping the engine, a distinct crackling noise is heard;
- when moving at low speed, you can feel vibration (it also often occurs when the air conditioner is turned on);
- The voltage in the vehicle's on-board electrical network changes sharply.
The coupling is not repaired, as a result of which it is completely replaced.
Common signs of breakdown
Despite the multifunctional principle of operation of the automatic transmission overrunning clutch, this device can also fail under the influence of various unfavorable factors. By its design, the product is presented in the form of an improved rolling bearing. In the event of a breakdown, the unit will simply jam. This may indicate that the belt drive provided by the clutch instantly turns into a conventional one. As a result of this, the inertia simply ceases to be compensated, and accelerated wear of the belt occurs. In order to promptly detect a unit malfunction, you need to understand exactly what signs may indicate a breakdown. Experts note three main parameters:
- The characteristic clicking sound of the tensioner.
- Inconsistency of the belt drive.
- Strong whistling noise when the engine is on.
When at least one of these signs begins to appear, you need to contact a service station. Only a professional can correctly diagnose an overrunning clutch. If the unit is broken, it will have to be replaced, since repair is almost impossible. It is possible to perform all the necessary manipulations independently in rare cases, since this requires having the appropriate skills and equipment.
Typical malfunctions of the free movement mechanism and methods for diagnosing them
Like all moving mechanisms, the overrunning clutch is subject to natural wear, mechanical damage, blockages and contamination, or poorly performed maintenance work on the generator.
How to determine that the freewheel pulley has failed:
- when the engine starts, noise appears;
- during operation of the vehicle, clicks come from the alternator belt;
- The belt itself moves jerkily and vibrates.
Visual and auditory diagnostics without dismantling
- We turn on the engine in idle mode - when the belt tensioner is actively moving, the clutch is faulty.
- We accelerate the engine to 2 thousand revolutions and turn it off. A buzzing or whistling sound is a sign of faulty mechanism bearings. A cracking sound is evidence of clutch wear.
Methods for diagnosing a dismantled coupling
After visual diagnostic methods have shown the presence of a malfunction, we dismantle the coupling
. Upon closer inspection, you need to lock the inner race, and rotate the outer ring in the direction of its natural movement when working in the system or in the opposite direction.
If the inner race moves, the clutch is worn out. If the outer ring does not rotate in the direction opposite to the movement of the alternator belt, the pulley is faulty.
Overrunning and reversing mechanisms of free movement should spring when checked if the outer ring is set to the direction of direct rotation of the drive, and rotate freely in the opposite direction. If the coupling is not moving properly, it must be replaced.
Examples of using
Socket wrenches and screwdrivers
Socket wrenches equipped with a ratcheting mechanism are also called ratchets. In the simplest version of the design, two pawls are placed in the ratchet. By turning the lever, you can either unscrew the nut or tighten it without removing the key at each turn, as with a conventional tool.
Ratcheting socket wrenches
Cable ties
Cable ties are made of plastic in one piece. The pawl is pressed against the toothed plate by elastic force. After tightening, the tie does not loosen even with very great force.
Ratchet Cable Tie
Recoil devices
Ratchet recoil devices were originally used on railroads in the mountains of Pennsylvania, USA, to transport coal around 1846. To prevent a loaded train from rolling back down a steep slope in the event of a locomotive engine failure, “dogs” were installed on the cars.
Later, this scheme was used on roller coasters, so that in the event of a power outage, the train with thrill-seekers would not roll back.
Roller coaster trolley recoil device
Winches
Winches are a mechanism for moving objects using a rope. An electric winch is installed in SUVs to pull a stuck car out of a quagmire.
To prevent the tensioned cable from unwinding from the drum, a ratchet mechanism is used. Examples of its use on hand winches can be seen in these photographs.
Ratchet mechanism in hand winches
Bicycle freewheel
An overrunning clutch is also called a freewheel. It prevents the transfer of torque from the driven shaft (wheel) to the drive shaft (chain and pedals) if the driven shaft begins to rotate faster. For example, after stopping pedaling without a freewheel, the wheels would continue to spin the chain and pedals, as was the case in the first bicycles. The same would happen when going down a hill.
The first overrunning clutch with a simple ratcheting mechanism was patented in 1869 by William Van Anden from Poughkeepsie, New York, USA. The Van Anden overrunning clutch had a ratchet built into the front wheel hub of the bicycle.
Approximate diagram of a freewheel (overrunning clutch) with a Van Anden ratchet mechanism
Almost all modern bicycles are rear-wheel drive. The overrunning clutch is built into the rear hub or rear sprocket. Overrunning clutches with a ratcheting mechanism produce a characteristic sound and are also called bicycle ratchets.
Example of freewheel operation
Freewheel with ratchet mechanism in the rear sprocket of a bicycle
Car starter overrunning clutch
The ratchet freewheel mechanism is used in automobile starters as a safety device. A starter is a mechanism that, using an electric motor, starts an internal combustion engine by rotating its crankshaft through the flywheel.
The rotation speed of the starter driven gear is low - maybe about 3000 rpm. After starting, the engine idles at about 1000 rpm. But the starter-flywheel gear ratio can reach 20:1 due to the difference in gear diameters. Those. a running engine at idle speed can spin the starter motor up to 20,000 rpm.
To prevent the starter from failing after starting the engine, a freewheel is installed on it.
Car starter
Car gearbox
In this example, the ratchet pawl is used to place the automatic transmission into park.
Ratchet in a car's automatic transmission
Overrunning clutch diagnostics
When they began to use clutches with an overtaking effect, the service life of the belt drive and other parts increased approximately 6 times. In addition, belt drive noise and periodically occurring vibration have been reduced.
If at least one part of the coupling wears out and fails, then, as a rule, the coupling locks.
What is the service life of the alternator overrunning clutch? Answer: 100 thousand kilometers.
Diagnosis of clutch wear
Replacement of a faulty mechanism is carried out after diagnosis. The first and most obvious sign of wear on the overrunning clutch is the appearance of a characteristic noise inside the car when the engine is running. This sound resembles a rattling sound and is noticeably different from any other sounds. From time to time, quite noticeable vibrations appear when moving.
Diagnosis begins with an external examination. To do this, open the hood and check the integrity of the oil seal and the housing cover. If traces of leaking lubricant are noticeable, it means the unit needs urgent replacement. If nothing can be detected externally, you can conduct a control test. Leave the hood open and start the car engine. Accelerate the crankshaft to four thousand revolutions. After this, turn off the engine, and if the residual sound is accompanied by the same sound, it means that the clutch is worn out enough and must be replaced.
What happens if the clutch jams?
If locking occurs and the clutch bearings no longer rotate or move along the surfaces of the cages, then the belt drive turns into a regular one, that is, without a protective effect from the force of inertia. This means that at different speeds of rotation of the engine crankshaft and the generator shaft, the belt will quickly wear out, and if the belt is very strong, then engine parts may wear out.
Signs of overrunning clutch failure:
- The belt begins to jump strongly, that is, vibration appears.
- When starting cold (when the engine is cold), the belt makes a whistling or squeaking noise.
- Clicking sounds are heard in the belt tensioner.
Broken coupling parts look like this:
Checking the removed generator with clutch:
- Lock the anchor with a screwdriver through the hole in the cover. When the anchor is fixed, the outer ring should rotate in one direction only. It rotates easily in one direction, but not in the other. This is a good coupling. If it rotates both here and there, then the clutch is not working.
It is advisable to replace a non-working clutch with a new one, otherwise you will have to change the alternator belt very often and hear the whistling of the belt drive.
Where was it first installed?
The diesel versions had the shortest belt drive life (no more than 15,000 km), they have a higher rate of pressure rise (more torque ), as well as greater braking of the crankshaft during compression, something had to be done, it was these units that acquired overrunning components for the first time , which have proven themselves to be excellent.
Then there were executive class cars, namely large, large engines, with a lot of electronics in the cabin. The generators had to be more massive, the anchors were heavier, and the inertia was greater.
Today we see such couplings on almost all cars, as they say, from “small to large.” This is truly a very useful unit!
How long does the overrunning clutch last?
Unfortunately, like any mechanism, the overrunning clutch does not last forever and sooner or later it fails. Typically, experts recommend changing this unit every 100 thousand kilometers.
What breakdowns are most common? There are several options:
- the clutch jams and it stops saving the resource of the alternator belt;
- the clutch races do not engage at all, which is why rotation is not transmitted to the shaft at all.
In the first case, you risk quickly losing the belt, and with it, most likely, the tensioner, and in the second, the generator will stop performing its direct functions of powering the car’s electrical system.
Be that as it may, if you hear an unusual whistle or rattle coming from under the hood, and also if the generator has stopped recharging the battery and there is no power to the electrical systems, it is likely that the overrunning clutch has failed, and it’s time to stop by a car service center to replace it.
Fellow car enthusiasts, I think we have figured out what a generator overrunning clutch is, why it is needed, what it is and how it works.
Price issue
Actually, how much does the original overrunning mechanism cost? Here, as usual, there is a big difference from the car model class (I take original spare parts):
“B – C” class – issue price 2000 – 3000 rubles
“D” class – 3000 – 4000 rubles
Executive class - from 6000 to 12000. BUT you need to understand that there are very large generators there.
It is also advisable to budget for a new belt, tensioner and other drive rollers.
Of course, you can save on spare parts and, say, take non-original ones. BUT you should understand that it won’t cost much less, if for a middle class car you still have to pay about 2000, there are of course options for 700 - 1000, but this is “naked” China made from, don’t understand what and don’t understand how long it will work.
That's all, I think it was useful, read our AUTOBLOG, there will be a lot more useful information.
Similar news
- LED lamps in headlights – Allowed? Or suppose...
- How to install xenon. Is it possible to do this in the headlights of a regular car...
- How to check a fuse in a car. We use a multimeter (test...
Add a comment Cancel reply
How to determine that the clutch has failed
With the overtaking element, according to some experts, the service life has increased by about 5-6 times. The vibration (associated with the weakening of the belt), the inertial load on other elements in the system are gone, and the noise has become noticeably less. Only advantages!
But it is worth remembering that the clutch is not endless, it wears out like any other bearing and, as a rule, it immediately “jams”.
REMEMBER - the resource is approximately 100,000 kilometers, sometimes a little more, but after that it is advisable to replace it and DON’T DEAL WITH IT.
What are the consequences if it gets jammed? YES, the belt drive itself turns into a regular one, as it was 20 - 30 years ago, that is, there is no leveling of inertia, slippage, the belt wear increases significantly. And if it’s already worn out (after all, the mileage is often more than 100 thousand), then it will tear very quickly. By the way, its “tensioner” will also die quickly.
The first signs are:
- The belt drive begins to jump. That is, if before everything was smooth, now she is simply “sausage”, this cannot be confused with anything.
- Often in the morning a piercing whistle or squeak begins.
- “Tensioner” clicks appear
After you remove this check, lock the anchor (you can do it with a screwdriver through the top cover). It should not rotate in one direction (stop with a screwdriver), but in the other it should rotate easily. If this does not happen, it has failed. Let's watch a detailed video.
However, there is another, less common breakdown - when the clutch “does not lock”, but always turns in both directions, that is, it practically does not connect the armature and the outer cage. In this case, diagnostics are much more difficult, only when removing the generator. It is extremely difficult to understand that this particular unit is the problem, but an indirect reason would be an undercharged battery or a flickering battery icon on the instrument panel.
What if you don't change the overrunning element? Your belt will break in a very short period of time, because the armatures of modern generators are quite massive. In the morning there will be a whistling sound and strange vibrations will appear.
DIY replacement
To ensure the service life declared by the manufacturer, the overrunning clutch is equipped with a protective cover. If the owner/service employee forgot to install it or it falls off during use, dirt/dust penetrating into the clips may jam the rollers.
Tool
A special head will help you unscrew a jammed overrunning clutch. The asking price is 170 – 500 rubles, there are several options for equipment:
Service keys allow you to dismantle the coupling without removing the generator from its seats.
Rice. 9 Set of sockets for dismantling overrunning clutches of any manufacturer
Diagnostics
Incorrect operation of the generator overrunning clutch is determined “by ear” and mechanically:
If the clutch races jam, you should immediately replace the consumable with a new product.
Dismantling
Even with an external inspection of the coupling after removing the protective cover, it becomes clear why it is necessary to use a special service key. Instead of a conventional mounting bolt, a serrated surface is used here, which requires a tool with counter splines.
Rice. 10 Dismantling the coupling
The equipment is inserted inside the coupling, the teeth are engaged, the part is unscrewed with an open-end wrench or a socket with a ratchet.
Installation of the coupling
The new coupling is installed in place of the removed one in the same sequence
It is important not to use impact instruments - this may cause damage.
Checking the operation of the new clutch consists of twisting it in different directions. It should only rotate in one direction. When turned in the opposite direction, the clutch moves along with the generator pulley.
Errors when removing the overrunning clutch
What else do you need to know to replace this part? Firstly, do not forget to disconnect the battery - after all, you are working with electrical equipment. Secondly, remove the alternator belt - this is logical, of course, but don’t forget. Third, never try to remove the coupling using any other method than the one described above.
- Hammer blows can bend the generator shaft.
- Heat can melt the grease in the generator bearings or even their seals.
- Jamming the generator armature with a screwdriver instead of buying a special wrench can also damage the generator.
And fourthly, never forget to wear the protective boot , which always comes with parts from good manufacturers. Without it, the clutch will fail prematurely.
Choosing a new mechanism
Finding a new generator freewheel is actually not very difficult. The car enthusiast has several search options. We recommend that you first search for information in online stores and save the codes of suitable spare parts - they can be extremely useful in the future. The required part can be found in offline or online spare parts stores at:
- VIN code;
- Vehicle parameters (make, model, year, engine);
- Catalog number of the spare part.
Practice has shown that purchasing original spare parts
not necessary. Overrunning clutches for the original equipment of cars are produced by a limited number of companies. They are also presented on the secondary market. In the secondary market, their products are sold under the names of their own brands. Although the quality of non-original spare parts may be slightly inferior to the quality of the originals, their cost is much more affordable. It is worth paying attention to overrunning clutches under the names of the following brands:
- Valeo (France);
- INA (Germany);
- Gates (USA);
- Magneti Marelli (Italy);
- LUK (Germany).
Cheaper, but not as high-quality analogues are offered by WAI (USA), Nipparts (Netherlands), ERA (Italy), ZEN (Brazil), Lynxauto (Japan). Clutches from Lynxauto are especially common, but many buyers agree that this is not a Japanese product - the quality of spare parts for this brand can vary greatly. We recommend purchasing couplings from manufacturers who are also conveyor suppliers
. When purchasing an auto part, it makes sense to check each product for mechanical defects, as well as look at the country of manufacture (in the case of packagers, the country may reflect the quality of the product).
Removing and replacing the generator overrunning clutch
Despite the fact that outwardly there is little difference between a conventional generator unit and an improved one, the method of dismantling them is somewhat different. In some models, the freewheel mechanism is extremely difficult to remove due to the fact that the distance between the car body and the generator itself is so small that it is simply impossible to get to it with a key. There are frequent cases of problems with fasteners; often even WD-40 does not help. To solve this kind of problem, professional auto mechanics recommend using a special key consisting of two removable parts.
Replacing the mechanism on SsangYong Kyron 2.0
To dismantle the overrunning clutch on a SsangYong Kyron SUV with a 2.0 engine, you need to equip yourself with a special key Force 674 T50x110mm. The wrench consists of a Torx-type slot, which is useful when removing rollers, and a socket with an external polyhedron. On the other side there is a hexagon for an additional key to release fasteners.
Read also: Installation of fuel injection pump on the engine, design of the high pressure fuel pump
It is recommended to adhere to the following operating procedure:
- The first step is to dismantle the engine protection and remove the fan casing.
- The Torx 8 driver should be rested against the body and using a curved spanner set to “17”, unscrew the coupling.
- After freeing the part, lubricate the threads and seat.
- Lubricate the bearings, tensioner bushings and pulley.
- Reassemble the unit in reverse order.
After finishing work, it is important to replace the protective cap.
Removing and installing the overrunning clutch on a Volvo XC70
The appearance of extraneous sound and vibration on a Volvo XC70 at low speeds is the first symptom indicating the need to diagnose the inertial pulley and, possibly, replace it. To carry out a quick and effective procedure for removing and replacing a structural element on this machine, you must do the following:
- Arm yourself with a special head ATA-0415.
- Remove the drive belt and remove the generator.
- A hard-to-reach bolt can be easily released with a socket and a pneumatic impact wrench.
- A new part is installed (INA-LUK 535012110).
- Lubricate the parts and assemble in reverse order.
At this point, the work of dismantling and subsequent installation of a new mechanism can be considered complete. If necessary, bearings are also replaced at the same time.
Replacing the mechanism on Kia Sorento 2.5
A pulley from one of the most famous companies producing auto parts, INA, is suitable as a new copy of the overrunning clutch for the Kia Sorento 2.5. The price of the part ranges from 2000 to 2500 thousand rubles. It is also important to arm yourself with a special key - Auto Link 1427 worth 300 rubles.
Once all the necessary tools and auxiliary materials are at hand, you can start working:
- Release the bracket for the decorative engine cover.
- Dismantle the “chip” and remove the positive terminal.
- Disconnect all kinds of tubes: vacuum, oil supply and drain.
- Using a 14 key, loosen the two generator mounting bolts.
- Unscrew all tightening bolts.
- Clamp the rotor in a vice, having previously prepared the gaskets.
- Using a socket and a long wrench, remove the pulley from the shaft.
After which the failed mechanism is replaced. Next, you need to assemble the whole thing and install it back in its place. But spring-loaded brushes can interfere with this. To cope with the task, you need to unscrew the vacuum pump and find the hole opposite the brush assembly. The brushes are pressed and fixed in the hole with a characteristic sound.
Removing the inertia pulley of the Toyota Avensis generator
On a Toyota Avensis with a 1AD-FTV diesel engine, to remove the clutch you also have to remove the entire generator, which is located in the right corner of the engine compartment, below, closer to the front passenger. In addition, here, in order to get to the desired unit, you have to jack up the car and unscrew the right wheel.
Unscrewing the generator mount is generally not difficult; the whole problem is how to remove this device. The overrunning pulley itself is removed as standard with a special key, and in this case it is also better to halve the body, and to unscrew the OMG, use a hexagon, holding the armature in a vice.
You need to carefully and carefully separate the parts of the generator housing; in a hurry, you can break the stator winding and break the wires.
Removing and installing an inertial pulley on a Skoda Octavia-2 car
On the Octavia, the overrunning clutch can be replaced on site without removing the generator unit; the free space in front allows you to get to the desired mechanism. We perform the operation in the following order:
- turn off the ignition, for safety reasons, disconnect the battery ground terminal;
- remove the absorber tank together with the hose; first of all, disconnect the pipe fitting;
- lift the tank upwards, then remove the generator belt; to do this, loosen the 17 mm nut on the tension roller;
- the special device for removing the pulley has a fairly long rod and is installed in the splines with a bias, so it is better to modernize the key - replace it with a hex bit;
- Having secured the device to the pulley, we try to unscrew the coupling.
When the OMG is screwed very tightly, you have to remove and disassemble the generator, clamp it in a vice, there is no other way out. Installation of the coupling is carried out in the reverse order; it is not necessary to tighten it very tightly. You also need to remember to put on a protective cap; if this is not done, moisture and dirt will get inside the mechanism, the parts will quickly rust and fail.