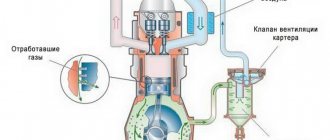
What is EVAP system
Before moving on to the description of error p0443, it makes sense to briefly describe the operation of the gasoline vapor recovery system (or in English - Evaporative Emission Control, EVAP). Its main task is to prevent the leakage of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. These same vapors are formed in the fuel tank at high ambient temperatures, or in more rare cases, when atmospheric pressure decreases. In this case, gasoline vapors accumulate in the system, and when the engine starts, they are discharged into the intake manifold and burned in the engine along with the air-fuel mixture. EVAP is used in almost all engines of modern cars.
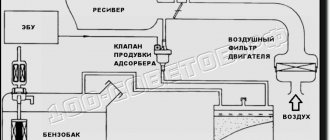
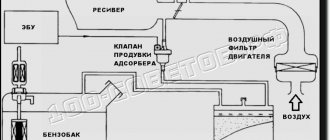
The gasoline vapor recovery system includes an adsorber (filled with coal granules, and, in fact, designed to accumulate gasoline vapors), an adsorber purge solenoid valve, and connecting tubes. Error code P0443 specifically indicates a malfunction of the mentioned solenoid valve, which is why it is sometimes called a fuel vapor valve error.
In engines with a turbocharger, the system is complemented by a two-way valve, which is designed to direct fuel vapors when purging the adsorber into the intake manifold (if there is no boost pressure) or to the compressor inlet (if there is boost pressure). A two-way valve is needed in the system, since in turbocharged engines a vacuum is not created in the intake manifold.
A special feature of the gasoline vapor recovery system is the fact that it has a built-in self-diagnosis module. This means that when the engine starts, this system is checked automatically for operability, in particular, for tightness and correct operation of its individual elements. This is done in order to minimize the likelihood of gasoline vapors entering the atmosphere, that is, for environmental reasons. In turn, this is dictated by the strict legislation in force in this regard in the countries of the European Union and some others, including the USA.
What is the EVAP system for?
The evaporative vapor recovery (EVAP) system collects fuel vapor from the fuel storage system (fuel tank, filler neck, and tank cap). Under operating conditions dependent on engine temperature, speed and load, the EVAP system stores and adds captured fuel vapors to the fuel-air mixture.
The EVAP system not only captures, stores and uses fuel vapor, but also has a self-test function that ensures the system is working properly. This is an important task, since about 20% of air pollution from vehicles is caused by faulty fuel storage systems.
There are many ways to "leak test" the EVAP system, but most of them perform the leak test while the vehicle is parked for a long time (for example, at night) or during the first start after being parked. System performance is monitored by the engine control module (ECM) by sensing changes in oxygen sensor voltage and briefly adjusting fuel flow as it releases or "purges" stored vapors into the engine cylinders. These values should indicate that fuel is being added to the system and that the overall mixture is becoming richer. Purge is performed when the vehicle is accelerating, when the vehicle requires additional fuel.
External symptoms of error P0443
In most cases, there are no external signs of the P0443 code, with the exception of an activated Check Engine light on the dashboard. In more rare cases, the smell of gasoline may appear in the cabin, caused by the fact that a significant amount of gasoline vapor has escaped from the vehicle's fuel system into the atmosphere or its ventilation system.
Also, occasionally, unstable engine operation at idle, “floating” speed, and even a complete stop of the engine are possible. While driving, a decrease in the dynamic characteristics of the car may be observed; it accelerates poorly and does not “pull”. However, such symptoms can indicate various other malfunctions, so additional diagnostics are necessary to identify the cause.
Occasionally, there are cases when error p0443 occurs when the air conditioner or climate control system is turned on. The fact is that when these systems are activated, the engine begins to consume more fuel, and accordingly, there is more gasoline evaporation in the system. And if their value exceeds the permissible norm, then this leads to conditions for the formation of an error, provided that the system purge solenoid valve is in an emergency condition.
Description and meaning of error P0444
On vehicles equipped with evaporative emissions control systems, also known as EVAP, the engine draws excess fuel vapor from the gas cylinder that would otherwise be vented into the atmosphere. Fuel vapor is directed through a vacuum line to the engine air intake and the purge valve/solenoid measures the desired amount of fuel vapor controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM) or engine control module (ECM). The PCM/ECM monitors the voltage to the purge control valve and did not detect any change in voltage when the purge valve was commanded on. Note: This code is similar to codes P0443 and P0445.
Formation conditions
Error code P0443 is generated when the ignition key is turned to the ON position, that is, the ignition is on, but the engine is not running, and the ECU diagnoses an open or short circuit in the electrical winding of the evaporative emission control valve. At the same time, the “check” signal light is also activated.
Also, some vehicles have additional requirements for generating the error code p0443. For example, for the popular Chevrolet Captiva, these conditions are the ignition on, as well as the voltage on the battery and in the vehicle’s electrical system in general ranging from 11 to 18 Volts DC. In addition, the ECU diagnoses an error after 6 seconds of meeting the mentioned conditions. Other machines may have different values, but the logic remains the same.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0444 code?
To properly diagnose the P0444 , a mechanic will need an OBD-II scanner. The mechanic will check all tubes and components related to the evaporative emission system for wear and damage. The mechanic will then perform a thorough check for vacuum leaks. He will start the car engine and check if there is a suction sound in the vacuum pipes. The mechanic will then perform a smoke leak test to determine if there is a leak in the evaporative emission system.
Possible causes of error code p0443
There are a number of typical reasons due to which the so-called absorber error occurs, as error p0443 is sometimes called. Among them:
Valve circuit open
- Complete or partial failure of the electro-pneumatic valve of the gasoline vapor recovery system.
- A break or short circuit (to “+” or “ground”) of the wire connecting the terminals of the electro-pneumatic valve and the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
- A break (or damage to the insulation) of the wire between the control unit and the ground, which is responsible for transmitting the signal to the solenoid valve.
- Broken (or damaged insulation) wire between the main relay and the terminal on the evaporative emission system solenoid valve.
- Mechanical damage to the purge valve. For example, it is stuck in the fully open or fully closed position.
- Damage to the connectors, the so-called “chips”. They will be different for each car model; it is necessary to check those contacts that are responsible for controlling both the gasoline vapor recovery system in general and for controlling its solenoid valve in particular.
- Incorrect operation of the ECU. This is a fairly rare reason, however, there have been cases where, after its flashing or mechanical damage (for example, damage to the electronic track), so-called “glitches” occurred. However, in this case, as a rule, not one, but several errors occur, often unrelated to each other.
However, most often errors associated with incorrect operation of the fuel evaporation recovery system (including 0443) occur due to clogging of the filter and tubes or other elements that make up the specified system. For example, a common reason is that the foam in the adsorber rots and crumbles over time, causing coal to enter the system, clogging it. The valve also becomes clogged, as a result of which it stops working correctly, causing corresponding errors. Rotting occurs for banal reasons - old age, constant wetting from condensation, temperature changes, and so on. Often, if the EVAP system valve is clogged and the front windows are open, you can smell a distinct smell of gasoline in the cabin. This is especially true for the warm season.
What repairs can fix the P0444 code?
- Thorough check of the fuel vapor recovery system.
- Repair or replace damaged wires.
- Replacement of faulty components of the fuel vapor recovery system.
- Clear the error code from the PCM memory and retest the system.
- Test drive the vehicle after the repair is completed to find out if the problem is resolved.
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0444
The fuel vapor recovery system is primarily designed to reduce emissions of harmful substances from vehicle exhaust gases. Failure of this system can lead to a significant increase in emissions.
Troubleshooting p0443
Methods for eliminating error p0443 depend on the reasons that caused it. First of all, you need to check whether the formation of error P0443 is not a so-called “glitch”. To do this, it is necessary to programmatically or mechanically delete error information from the ECU memory. There are ways to do this. The first, more “civilized” one, is to delete the mentioned information using a computer and appropriate software. However, to do this you need to have a computer or smartphone and software.
The other method is simpler. To implement it, you just need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery for 5...10 seconds, and then return it to its place. After this, the electronic control unit will restart and diagnose all vehicle systems again. If there was a false positive, then the error information will not be repeated. If the formation conditions exist, then further diagnostics need to be performed.
To do this, you need to do one or more of the following:
EVAP valve replacement
- Check the condition of the adsorber . To do this, you need to dismantle the EVAP system solenoid valve and see if there is carbon in its body. If this is the case, then the adsorber foam separator needs to be replaced. If its body is very rusty and/or damaged, then you need to consider completely replacing the adsorber.
- Check the operation of the vacuum purge valve from the carbon adsorber. There are two ways to do this. The first is using a special diagnostic device, so it is more suitable for car service workers. To do this, you need to disconnect the vacuum hose of the purge valve from the canister, start the engine (after setting the speed to neutral and applying the parking brake) and connect the electronic diagnostic tool. Next, depending on the software used on it, look at the performance characteristics of the solenoid valve. It is much easier to check it manually. To do this, you just need to put your finger on the disconnected hose and check whether air is sucked into it or not. In working condition, it should be absorbed; if this does not happen, then most likely the solenoid valve has failed and additional diagnostics are required. When the valve is turned off, air is also not sucked in.
- If, as a result of the check, it was determined that the valve itself is in working condition, then it is necessary to inspect its wiring . To do this, you first need to disconnect the valve connector (VSV). Next, you need to use a multifunctional multimeter to measure the voltage supplied to the solenoid valve when the ignition is on. This value should be in the range of 11...14 Volts for standard passenger cars, which are designed for an electrical system voltage of 12 Volts.
- To check the integrity of the wire connecting the computer and the solenoid valve , it is necessary to disconnect them on both sides, that is, disconnect the connectors. Next, using the same multimeter (but switched to the “continuity” mode or to the resistance value measurement mode), check the integrity of the wire. The normal insulation resistance value should be between 1 ohm and 10 kohm. If the measured resistance value is outside these limits, it means there is a wire break or insulation damage. In any case, you need to understand in more detail and visually check the condition of the wire. If this fails, simply replace the wire or the entire harness with a new one.
- Check the condition of the wire between the solenoid valve and the integrated relay or fuse (this step may vary depending on the machine model, since this circuit may be implemented differently). The actions are similar to the previous paragraph. It is necessary to disconnect the wire at both ends and measure its insulation resistance value. The range here will be similar - from 1 Ohm to 10 kOhm. If the value is greater or less, it means the wire is damaged.
Automotive service technicians can check the evaporative emission system purge valve using the mentioned diagnostic tool and software. So, with the ignition on and the engine off, it is necessary to connect the device to the computer and, using software, send commands to the mentioned valve. In this case, clicks characteristic of its operation should be clearly audible. In particular, you need to give a command to open it by 50%. As this value increases, the cyclic speed of the valve should increase, and as the value decreases, it should decrease. When the value reaches 0%, the valve should stop clicking.
If the problem is mechanical damage to the valve, then you can try to “reanimate” it. The standard design of this valve implies the presence of an electromagnetic coil and a needle with a spring, which open/close this valve. Over time, the spring may “age” and not produce the required force. Or there will be an interturn short circuit in the coil. In both cases the valve will not work correctly. You can try replacing the spring and/or cleaning the mechanical valve actuator. However, in most cases, with this violation of operation, the technicians (car owners) simply replace the adsorber valve with a new one.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Use a scan tool to command the purge valve to activate. Listen for a clicking sound coming from the purge solenoid. It should click once, and on some models it may click again.
If a click does not occur when the scan tool is activated, disconnect the connector and check the solenoid and connector for damage. Then check the battery voltage at the lead wire with the key on.
If voltage is present, manually ground the contact using a jumper and see if the valve clicks. If so, then the solenoid is working correctly, but there is a problem with the control circuit. If it does not click when manually grounded, replace the purge solenoid.
To check for a control circuit problem, reconnect the solenoid and disconnect the ground wire from the connector. With the ground wire disconnected from the controller, turn on the key and manually ground the purge valve control wire.
The solenoid should click, meaning there is no problem with the control wire to the solenoid, and there is a problem with the purge valve actuator circuit from the ECM. If it does not click, there is an open in the wiring between the ECM and the solenoid.
When troubleshooting P0444, you must clearly understand what you are doing. Otherwise, seek help from a specialist.
Additional errors
Often, an adsorber error is accompanied by other, parallel errors, which indicate problems with adjacent elements of the system. So, frequent “companions” of this problem are errors with codes:
P0444 . This error indicates that there is a short to power supply or an open circuit in the control circuit of the canister purge valve. Also, to generate an error with code p0444, the following prerequisites must be met (they may differ for different car models; the popular Hyundai Solaris is taken as an example):
- intact (not broken or damaged) electrical wiring, in particular from the ECU to the EVAP system solenoid valve;
- the value of the constant voltage on the battery and in general in the electrical system of the machine is in the range from 10.7 to 16 Volts;
- long diagnostic time;
- The Check Engine light on the instrument panel is activated after three driving cycles.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0444
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic code. Trouble code P0444 is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
This code indicates that part of the EVAP control system is no longer functioning properly. The EVAP system is made up of many parts, including (but not limited to) the tank cap, fuel lines, charcoal canister, purge valve, and others.
An emission control system (EVAP) prevents the release of fuel vapors from the vehicle's fuel system. Fuel vapor is directed through hoses into a coal canister for storage. Later, when the engine is running, the purge control valve opens, allowing fuel vapor to be drawn in under vacuum.
The purge of the EVAP canister is controlled by a valve that, thanks to the vacuum created by the engine, allows fuel vapor to be drawn in. They go from the fuel tank to the engine to be burned, rather than escaping into the atmosphere.
The purge valve measures the desired amount of fuel vapor. Controlled by the vehicle's powertrain control module (PCM) or engine control module (ECM). If the PCM/ECM does not see the expected voltages or detects an open circuit when commanding the purge valve, DTC P0444 will set.
Computer diagnostics
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the evaporative emission system (VAP) purge valve. The control unit regulates the operation of the EVAP purge valve by grounding the control circuit through an internal switch called the control unit. The main purpose of the control device is to ground the controlled component. The control unit monitors the state of the control device. When the control unit detects a voltage abnormality for the controlled state of the control device, a diagnostic trouble code is set. Conditions for the DTC to appear: Ignition switch in the on position. Conditions for setting the DTC.
The ECM detects an open wire condition in the purge solenoid valve circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets The MIL illuminates. The controller records the operating conditions at the time the malfunction is detected. This information is stored in the status record buffer and fault logs. An archive of diagnostic trouble codes is maintained. Conditions for clearing the fault code/malfunction indicator The fault indicator lamp turns off after 3 consecutive test cycles in which the diagnosis is performed without failure. The archived diagnostic trouble code is cleared after 40 warm-up cycles without failure. The diagnostic trouble code can be cleared by the scan tool. Test Description The number below refers to the step numbers from the diagnostic table. This step checks for the presence of a problem. The EVAP purge valve is pulse-width modulated (PWM). When a signal is applied to the purge valve at 50%, clicks should be heard. The clicking noise should stop when the 0% signal is sent to the EVAP purge valve. This is the rate at which the valve cycles must increase as the setpoint increases. The intensity should decrease as the set state decreases. Repeat these commands if necessary. This step verifies that the EVAP purge valve is always properly grounded.
This step verifies that the ECM provides a ground for the EVAP purge valve.
ERROR CODE databases are incomplete. Materials that were found in the public domain on various Internet resources are posted. If you have materials that can supplement this section, send them to:
Decoding Kalina fault codes
The on-board computer has an option that allows you to independently diagnose the systems and find certain faults. When performing an operation, faults encrypted in two-digit codes are displayed on the dashboard.
The following is a breakdown of popular faults encountered when performing repair work on a machine.
Error 3
The power supply to the fuel level meter in the tank is broken or the float itself is damaged. Check lines for damage.
Error 4 on Kalina
If this number is displayed on the instrument panel, it means that there is a problem in the coolant temperature sensor line. This happens for a trivial reason - oxidation of wiring contacts.
Error 5
The on-board thermometer is faulty. The cause may be a loose terminal.
Fault 6
The engine has overheated, the sound indicator is working. You should stop and let the engine cool.
Problem 7: solution to the problem
The pressure inside the engine oil lines has gone beyond the set threshold. Pay attention to the system status.
Fault 8: Kalina 8 valves
The pressure in the brake system has dropped. This indicates a breakdown in the line or a jammed brake.
Code 9
The battery is dead. Check the charging relay and battery wear.
Code 17: EUR Kalina
The module requires more thorough diagnostics. There is a problem with the wiring.
Code 34: problem solving
Critical malfunction of the mass air flow sensor.
Code 45
Incorrect data from the fuel level in the gas tank. You need to check the line.
Code 78
The error indicates the need for more thorough diagnostics of the vehicle. The code is often a glitch of the on-board computer.
Code 89
A standard cipher that combines two problems 8 and 9. When they appear, they need to be solved.
Code 234
Internal dashboard error. It is recommended to reset the encryption and continue operation.
Code 345
Standard ECU problem, requires more thorough diagnostics.
Code 456
This code represents an error directly from the dashboard. It is this module that needs to be checked.
Code 789
A set of three problems. The faults are listed in order.
Code 3456
Description of several problems at the same time, errors are listed in ascending order.
C1011 - malfunction
Insufficient quality of wiring contact in the power steering system. It is necessary to check the terminals for damage.
C1044 - Kalina breakdown, incorrect DPR sequence
Incorrect sequence of signals from the EUR rotor sensor. Error 1044 can be solved by replacing the sensor.
EUR failure - error C1642
Check the condition of the device's head module. There is a problem with transmitting and receiving information from sensors.
U0100 - error Kalina 2 automatic
Communication with the ECU is lost. Check the wiring for damage.
Code U3110
The diagnostic connector is faulty. The CAN bus requires diagnostics.
Code B1018
An emergency reset of the control unit has occurred. Perform a thorough system diagnostic.
B1030 - malfunction
This indicates that the oxygen sensor upstream of the converter is not working correctly. The problem is resolved by replacing the module or restoring the wiring.
Code 0030
DK1 – open circuit of the heater. It is necessary to restore the power lines.
P0036 - VAZ Kalina code
The signal indicates incorrect operation of DC1. Most likely the sensor is damaged.
Code 007
Represents the BC firmware version. There are no mistakes here.
Kalina 2: error code 009 219220
The pointer displays the instrument panel part number. The encoding does not indicate any problems.
Code P0101
The wrong signal is coming from the mass air flow sensor. The main reasons for this are the installation of HBO. The system does not understand what is happening with the power plant.
Code P0102
Error 0102 or 102 indicates that the signal from the mass air flow sensor is too low. You need to check the sensor and signal wires.
Error P0122
TPS A – incorrect signal level.
Error P0130
Here we recommend a complete replacement of the first oxygen sensor. Code 0130 indicates that there are problems with the Lambda probe.
Code P0131
The signal level from DC1 is too low. The formation of the fuel mixture does not occur correctly.
P0113 - code
The intake air temperature sensor has completely failed or is severely malfunctioning.
Code P0117
The voltage in the DTOZ is too low. You need to check the wiring for the presence of oxides.
Code P0118
The opposite meaning of the above error. The solution to the problem is similar.
Code P0122
TPS A – incorrect signal value. The throttle body needs to be cleaned of contaminants.
Error P0131
Incorrect fuel mixture ratio. The throttle and fuel mixing system need adjustment.
Code 0132
The voltage on DC1 is too high. This is usually the cause of a signal wire shorting to ground on another system.
AvtoVaz Diagnostics
Canister purge valve, control circuit open.
Procedure for checking and correcting problems:
1. Turn off the ignition, connect the diagnostic tool, turn on the ignition, warm up the engine to a temperature of 80 degrees. Let's check if the error is active.
2. If there is no error, check the correct connection and integrity of the wiring harness.
3. If there is an error, turn off the engine, unplug the wiring harness block, turn on the ignition, check for voltage between terminal “2” of the harness block and ground. If there is no voltage, there is an open circuit in the power supply circuit of the control unit.
4. If the voltage is less than 2 V, the control circuit of the control unit is broken or the ECU is faulty. If the voltage is more than 2 V, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between terminals “1” and “2” of the control unit.
5. If the resistance is less than 1MΩ, the ECU is faulty, if more, the control unit is faulty.
Computer diagnostics
Code P0445 is entered if: the engine is running; self-diagnosis of the canister purge valve driver detected a short to power supply or no load at the output. If a permanent malfunction occurs, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp lights up after 2 drive cycles. WHAT TO CHECK: 1. The presence of a short to ground in wire 52 ZZh is determined.
HOW TO CHECK:
Connect the adapter cable to the diagnostic connector. Start the engine. Using the Errors menu, check whether the fault code is currently active. The fault code may not be active at this time. Code P0445 is intermittent. The MP7.0N controller uses an adsorber purge valve driver that has a self-diagnosis function. It can detect faults such as an open, short to ground or power supply to the purge valve control circuit. If there are no other codes, analyze the conditions under which the code occurred. Also use “Fault Cards”.1. Turn off the engine. Disconnect the harness block from the controller. Check the resistance between pin “5” of the harness block and ground with a multimeter. Resistance less than 1 Ohm means a short circuit of wire 52 ZZh to ground. If the resistance is greater than 1 ohm, the controller is faulty. After repair, start the engine, reset the codes and make sure there is no signal from the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp.
ERROR CODE databases are incomplete. Materials that were found in the public domain on various Internet resources are posted. If you have materials that can supplement this section, send them to:
Modern technologies are developing, equipment is becoming more complex and sophisticated, and progress does not bypass vehicles. Carburetor cars were very simple, and any driver could figure them out, but on cars with injection engines, new components were added, in particular, a fuel vapor recovery system appeared, the main element of which is the adsorber. The main task of this circuit is to remove fuel vapor from the tank into the intake manifold at the time the internal combustion engine is started, and the adsorber purge valve plays an important role here. This article will discuss the operating principle of this system, the procedure for replacing the valve, and possible malfunctions that may arise during the operation of a Lada Kalina passenger car.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0444 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- BMW (BMW X5, E39, E46, E53, E60, 330i, 530i)
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Handicap)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Lacetti)
- Chrysler
- Citroen (Citroen C4)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Ford (Ford Focus)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Genesis, Creta, Santa Fe, Solaris, Elantra)
- Infiniti
- Kia (Kia Optima, Rio, Sorento)
- Mercedes
- Nissan (Nissan Altima, Qashqai, Tiida, X-Trail, 350Z)
- Opel (Opel Corsa)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 207, 307, 308, Partner)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Rapid, Fabia)
- Subaru
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Passat, Polo Sedan, Tiguan)
- VAZ 2107, 2114, 2115
- Gazelle
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- TagAZ Accent
With fault code P0444, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0010, P0031, P0033, P0036, P0037, P0056, P0102, P0243, P0245, P0300, P0440, P0441, P0442, P0443, P0445, P0446, P0447, P0448, P0449, P045 2, P0453, P0455, P0456 , P0500, P0505, P0700, P0722, P1403, P2008.
How does the Lada Kalina gasoline vapor recovery system work?
The EVAP system in question was created to prevent the release of harmful gasoline vapors into the surrounding atmosphere resulting from fuel evaporation; it includes:
- fuel shut-off valve;
- adsorber;
- solenoid valve for purging the absorbent element;
- connecting pipelines.
The most important component in the system is the adsorber (also called a carbon filter), the basis of which is activated non-edible carbon, enclosed in a plastic housing. The resulting gasoline vapors are absorbed by the carbon of the absorbent element, gradually accumulating in it. When the engine starts, the canister purge valve (KPA) is turned on, and due to the vacuum, all accumulated vapors enter the intake manifold and then burn out.
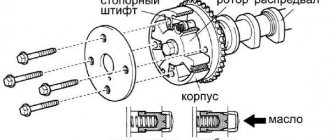
Design of the VAZ Kalina adsorber purge valve
KPA is present on all modern injection internal combustion engines, and Lada Kalina is also no exception. The purge valve (another name is Evap-Solenoid) is connected on one side to the carbon filter, on the other to the intake manifold, when there is no electrical signal to the control unit, the pipeline channel is closed, and vacuum is not created in the system. When an electrical signal is supplied while the engine is running, the valve is activated, the channel opens, and gasoline vapors freely pass from the adsorber into the intake manifold.
Diagnosis of error P0444
The definition of P0444 can be misleading because it actually indicates that the EVAP purge function is not producing the specified vacuum during its self-diagnosis. This vacuum is measured and monitored by the fuel tank pressure sensor. The vacuum may be too high and too long (stuck open purge valve) or too low or absent (stuck closed purge valve, system leak, or faulty fuel tank pressure sensor).
Source
Malfunctions in the fuel vapor recovery system Lada Kalina
Since the solenoid valve itself is not a complex device, it has few malfunctions as such - it may not open or close when necessary, or may freeze in a certain position. But the culprit of the breakdown may not only be Evap-Solenoid; the gasoline vapor recovery system does not work correctly for other reasons:
- connecting pipes are pinched or clogged;
- normal vacuum is not created in the system;
- due to an open circuit, there is no voltage on the valve;
- the carbon filter is completely clogged (which is rare);
- The control unit malfunctions.
If the CPA is stuck in the open position and does not block the channel, the following defects may occur:
- the fuel mixture becomes richer, causing “blackness” to appear on the electrodes of the spark plugs;
- the engine begins to operate unstably, this is especially noticeable at idle;
- gasoline consumption increases;
- The throttle response of the internal combustion engine decreases.
When the EVAP channel is constantly blocked by the purge valve, excess vapor pressure is created in the gas tank, due to this:
- there is a risk of fuel pump failure;
- The fuel level sensor may fail.
It should be noted that purge occurs in a certain mode after starting the engine, the program is executed depending on the crankshaft speed, and the system does not work at idle. An impulse arrives at the CPA if:
- the coolant has heated to a temperature of at least 75 degrees Celsius;
- the throttle valve is open at least 4%;
- the car is moving at a speed of more than 10 km/h (but this is not a necessary condition).
Problems in the electrical part of the EVAP are detected by the control unit, and the Check Engine warning lamp lights up on the instrument panel. The fault code can be determined using a special diagnostic scanner or a computer with a program installed; the most common errors in the vapor recovery system detected by the diagnostic device are P0441 and P0455.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0444 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine may run lean or run rough if the purge valve is stuck open.
- Excess pressure in the gas tank in the form of a "whistling" sound when the cap is removed, this indicates that the purge valve is not working at all or is stuck in the closed position.
- Slight increase in fuel consumption.
The severity of the P0444 code is moderate. The car will be able to continue driving, but harmful emissions into the atmosphere will increase. Which in practice will not allow you to pass the toxicity test.
Replacing the adsorber purge valve on Kalina
If the check shows that the Evap-Solenoid is faulty, the part must be replaced (catalog number - 11181164200). There is no point in repairing the device:
- the price of the valve is in the range of 400-800 rubles;
- You can buy the device in almost any store that sells VAZ spare parts;
- changing the KPA is very easy and simple.
But before making a replacement, it would be a good idea to check the control circuit; quite often the valve does not work due to a break in the wires going to it. To complete the work, you will not need a pit or a lift, and the procedure itself will take no more than one to two hours, even if the operation is performed by an inexperienced worker without metalworking skills.
We change the valve as follows:
- turn off the ignition, raise the hood;
- find Evap-Soleno />
- We dismantle the valve together with the tube, and the disassembly is almost complete.
Replacing the purge valve could be considered a very simple task, if not for one “but” - it is very difficult to remove the plastic tube from the CPA without damaging it, and it does not come with the new valve. There are two options here:
- try to carefully heat the connection with a hairdryer and pull off the pipe;
- cut the tube at the connections, and instead buy an ordinary fuel hose with a diameter of 8 mm and two clamps.
Having measured the required length of the hose, cut it, connect it to the valve and connector, we get approximately the same design as in the figure below.
We install everything in place, start the engine, and test the car on the move.
How to resolve the P0444 code?
Engine Wire Harness - Check ALL connectors to ensure they are connected properly, look for loose or damaged wires.
Typically the control valve is powered by the battery and is triggered on and off via the PCM/ECM. Using the manufacturers' electrical diagrams, determine which type of circuit is being used and check for the presence of battery voltage with the on/off switch on the power side of the control solenoid connector using a digital ohm volt meter (DVOM) set to the volt scale. If there is no battery voltage, trace the wiring and determine the cause of the voltage loss. Test the continuity of the control side of the wire harness after disconnecting the plug from the control valve solenoid and the PCM wiring harness. Locate the correct wire on the PCM and control valve wiring and check for continuity using the ohm scale on the DVOM, if excessive resistance is found then repair the circuit. If there is no continuity on the circuit, check all connections for damaged wiring, loose terminals, or disconnected harnesses and repair the circuit. Purge control solenoid - Check continuity at the purge control solenoid connector pins after removing the harness plug using a DVOM set to the ohm scale. Check that the resistance is within manufacturers specifications. If there is no continuity, suspect the solenoid is internally open and replace the part with a known good unit. PCM/ECM fault - Since EVAP is only enabled under certain driving conditions, it will be necessary to monitor the operation of the evap control using an advanced scan tool capable of and perform road tests under the driving conditions required to activate the EVAP system. Some advanced scan tools have an internal test to manually activate the EVAP system. Check that the PCM/ECM controls the EVAP system. If the system is operating correctly, it will be necessary to back up the probe at the PCM/ECM wiring harness connector using a graphing multimeter or oscilloscope with a duty cycle characteristic with the positive lead on the purge control valve pin and the negative lead connected to a known good ground. The duty cycle must match that controlled by the PCM/ECM during EVAP operation. If there is no duty cycle, the PCM/ECM may be faulty. Other Evap DTCs: P0440-P0441-P0442-P0443-P0445-P0446-P0447-P0448-P0449-P0452-P0453-P0455-P0456 Machine translation is used in this article.
The adsorber valve is knocking on Kalina
Many owners of Lada Kalina cars are faced with a problem - while the engine is running, an incomprehensible clattering sound is heard from under the hood; when identifying the cause of the noise, it turns out that the sound comes from the purge valve. Although the knocking does not affect the operation of the car in any way, some car owners are annoyed by it, and car owners want to get rid of it. You can “overcome” the unpleasant clattering sound; you just need to do the following:
- remove the valve and inspect it carefully;
- Find the adjusting screw on the side; it will be filled with epoxy resin on top;
- pick out the epoxy, tighten the screw half or three-quarters of a turn;
- install the valve in place, check for changes in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
You cannot tighten the screw any more, in this case the control panel will stop opening, and the engine diagnostic lamp on the instrument panel will record an error. It is also worth noting that some drivers confuse the clatter of the solenoid valve with detonation, but in principle, the sounds can be distinguished. You just need to take into account that detonation occurs under load, for example, when a loaded car is moving uphill, in this case they say “fingers are ringing.”
How to remove the error?
After fixing the problem, it is necessary to delete the corrected error from the on-board computer’s memory. Otherwise, the code will be displayed again in subsequent diagnostics. The difficulty of resetting is that everything is done with a stopwatch.
The procedure for removing an error code in a Nissan Qashqai:
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Next, within 5 seconds you need to press the gas pedal 5 times. Then release the gas pedal.
- Wait 7 seconds, and on the eighth, press the gas pedal and keep your foot pressed for 10 seconds. At the tenth second, the Check Engine light will start flashing on the instrument panel.
- When the light starts flashing, release the gas pedal. Now you will see if the errors have been reset. If the lamp blinks 4 times, that is, the combination “0000,” this means that all errors have been erased from the memory of the control unit.
- When the light stops flashing, press the gas pedal and hold it for 10 seconds.
- Then you can turn off the ignition.
This way, combinations of faults in your car will be erased.
Do you have any questions? Our consultants will help you.
Error P0441
Owners of Lada Kalina often note that during the operation of the car, error P0441 appears, indicating that the gasoline vapor purge system is not operating correctly (the air flow differs from the norm). The cause of this malfunction may be:
- inoperative adsorber valve;
- clogging of the air line from the control unit to the air filter;
- air leakage through connecting pipes.
What should not be immediately considered is the line from the gas tank to the adsorber; here, a breakdown does not in any way affect the readings of the computer or diagnostic scanner. Still, most often Evap-Solenoid fails; this is a characteristic “disease” on Kalina.
If the EVAP valve stops functioning normally, it is not at all necessary that the engine will lose power, the fuel pump will fail, and so on. Mainly due to problems with the control gear, exhaust toxicity increases, and the Check Engine on the dashboard periodically lights up. There are car owners who do not pay attention to the diagnostic warning light, continuing to operate the car, but do not experience any great inconvenience. And most often in such a case, gasoline consumption does not exceed the norm, the engine starts normally, and no serious problems occur in the fuel system.
Error codes Lada Kalina
Standard fault codes for the Lada Kalina are a set of alphanumeric codes that describe problems associated with the car's electrical systems. Due to the high cost of specialized service, experienced drivers decide to troubleshoot problems on their own. The car is equipped with a self-diagnosis system. On-board equipment does not stand out for its increased accuracy. The codes found usually only indicate the circuit where the fault is located. The system is unable to mark the damaged element.
The following is a description of errors for simple versions, Cross and other modifications.