Many car owners have encountered a situation where they were unable to start their car in the morning. And everything was fine in the evening. And the battery itself is new and in good condition. The reason here may be battery leakage current. This phenomenon exists on any car, but must fit within a certain norm. If the leakage current limit is exceeded, the battery will discharge while parked. As a result, you will have problems starting the engine. It's time to figure out what causes battery leakage current and how to bring it back to normal.
What is current leakage and why is it harmful?
Current leakage is an unplanned and uncompensated discharge of a vehicle battery.
Depending on the intensity and period of action, it may have virtually no effect on the performance of the car, or it may lead to complete consumption of the battery capacity, when it will be impossible to start the engine. However, not all leaks need to be repaired. Some devices consume a small amount of current when turned off, which is necessary to maintain their functionality. The only danger is high leakage currents, at which the battery discharges within a few days or even hours.
Diode bridge reverse current
At one time, this was the main reason for excessive battery discharge - the generator remained the only device directly connected to the battery after the ignition was turned off. A car generator is a three-phase (rarely four-phase) alternating current machine, which must be straightened for use in the on-board network. The diode bridge is responsible for this - a characteristic “horseshoe” of powerful semiconductor diodes, which is connected in the car circuit between the stator windings and the battery.
An ideal semiconductor diode conducts current in one direction, which is the basis for their use in AC rectifiers. But in practice, the diode also has a reverse current - when connected to the battery, the diode bridge slowly drains the battery onto the stator windings. Normally, the reverse current of the diode is several milliamps; taking into account the fact that there are several of them in the bridge, the normal reverse current of the assembly is considered to be 20-40 mA.
However, semiconductors degrade over time, which leads to a change in the parameters of the diode, including an increase in the reverse current. So leaks can increase significantly - and the constant load can be a hundred or two milliamps.
The principle of connecting current consumers to the on-board network
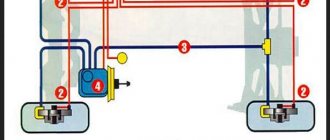
Electric current will flow through the conductor only if the electrical circuit is closed. Electricity consumption should be normal - battery terminal “plus” - consumer - terminal “minus”, and the circuit should not be broken. As an example, we gave the simplest scheme. In your car, consumers are connected to a circuit whose complexity is several times higher. Therefore, it will be difficult for a non-professional auto electrician to understand all the nuances.
How to check for current leakage in a car? Refer to the image above. On it you can see that there is a single “minus” between the lamp and terminal 85 of the relay; it is usually connected to ground (body).
In this case, a switch is installed on the positive wire, breaking the circuit. When the switch contacts close, electricity flows through the relay coil, which is connected to pins 85 and 86. Due to the electromagnetic field, the coil begins to close the 87th and 30th contacts, and the electric current flows through the lamps.
The described scheme is standard for most vehicles. However, usually the circuit is opened by an additional switch - the ignition switch, and the fuse is embedded in the positive wire. To make it more convenient, one or two mounting blocks combine relays with fuses. Knowing this, you won't be shocked when you see a lot of wiring harnesses. You can also, by dividing a huge number of connected circuits into mini-circuits, check for current leakage in a car using clamps.
Some car devices are combined into common networks. Imagine that this is one consumer, but simply expanded in space. Is a current leak detected in the car after checking? The reason is that different circuits are connected to each other or to the “ground” of the machine due to the fact that the wiring insulation has become unusable. Leakage can also occur due to electric current “bridges” that appear due to dirt.
Why the battery runs out - the main causes of leakage
The main reason for increased battery discharge is a malfunction of electrical equipment. Moreover, the malfunction may not be obvious. A starter with broken bearings can turn, but consume increased current. A severely discharged battery simply does not have time to replenish energy during a trip, and after several starts the battery is completely discharged.
A faulty security system or music center can do its job perfectly well, but consume several times more energy than, as they say, according to the state. Such a malfunction is especially unpleasant in a security system that has been operating in a parking lot for a long time.
Well, the most serious problem will be current leakage. If it is relatively small, say half an ampere, then it will be compensated by the generator during the trip. But when the ignition is turned off, the problem will really manifest itself - in the morning in a parking lot you may not be able to start the engine.
Important! There is current leakage in almost any car, but this value has its own standards (see section below), and if we meet these standards, then everything is in order.
What causes current leakage? There aren't many reasons. For example, poor car design. On some older VAZ models, in particular the VAZ 2110, the leakage current is initially high. It is not for nothing that the owners of this car, when parked for a long time, remove the tip from the battery terminal or install a ground switch and use it.
Next, wear and tear on electrical wiring and equipment. If the car is old, then the electrical equipment seems to work, but even when turned off it consumes energy. The pads become clogged with dust, the wires crack and become oily, and the insulation wears out.
Non-standard equipment can also cause excessive leakage if it is installed by a non-specialist and poorly thought out. For example, the navigator can continue to calculate its location, maintaining contact with satellites even when the ignition is turned off. Music systems, recorders and other similar service equipment may also not work correctly, continuing to consume energy even when the ignition is turned off and in the absence of the owner.
Expert opinionAlexey BartoshSpecialist in repair and maintenance of electrical equipment and industrial electronics. Ask a question From here we conclude: if our battery noticeably runs out even after not being parked for a very long time, then there is no need to run to the store for a new one or get into the generator. First you need to find out if increased current leakage is to blame for this problem.
Problems with alarms and security systems
Alarms and immobilizers must work while the car is parked with the engine turned off. This also contributes to leakage currents and, although when developing such systems they strive to reduce energy consumption to a minimum, they always need some current.
In modern security systems, controllers can “go to sleep,” but in the event of software failures or malfunctions, such alarms will continue to consume increased current. Cheap models also have more serious problems - for example, a car equipped with a simple Chinese two-way alarm system tightly blocked the operation of the automatic box doors and standard alarm systems of neighboring cars, clogging the radio range with the constantly working transmitter of the antenna unit. The battery of this car was regularly noticeably discharged in the morning.
Additional signs
If you don’t have a multimeter at hand, the presence of current leakage can be assessed visually at night. To do this, you need to turn off the ignition and all electrical equipment, open the hood, close the car, without arming the car alarm.
Next, you need to disconnect the positive terminal of the battery and wait about five minutes. After this, you need to connect the battery terminal. If a large spark is generated when the terminal is connected, there is most likely a leak.
Note: there will be a spark in any case, since during the connection of the terminal the emergency lighting and alarm may temporarily turn on.
Such a check can be done if there is a main sign of current leakage: battery discharge after a short stay. It is considered critical if a fairly fresh battery is discharged after one week of parking. It is not always possible to check this, since the car is in constant use.
Video - how to measure leakage current in a car with a multimeter:
Another sign is the presence of extraneous noise, crackling, buzzing, or sparking in the car when the electrical equipment is turned off.
The presence of foreign odors with a taste of smoke when getting into the car in the morning after parking is a serious sign of a malfunction. If there is a large current leak in a car, then, according to the laws of conservation of energy, it can manifest itself in the form of mechanical, thermal or light energy.
Unfortunately, using these methods is almost impossible to find the true cause. You need to use a multimeter. Auto electricians identify the causes and eliminate current leakage in a car as complex repair work.
see also
Battery charging lamp is on
Error P1602
How to charge a car battery correctly
Contact cleaner
Battery density
Excessive leakage current in the car will cause the battery to discharge while parked. The causes and verification of leakage should be dealt with separately. At the initial stage, the main thing is to understand what permissible leakage and how many milliamps are the norm for a particular car, since losses will depend on the number and name of energy consumption sources. An online calculator , using the formula - Battery capacity (A) * number k, will help you quickly calculate the permissible leakage current.
Current leakage should be checked as often as possible, especially in wet weather!
Diagnostics and standard battery leakage current
There are devices in the car that consume current regularly. These include:
- Watch:
- ECU memory;
- Immobilizer;
- Signaling.
Their functioning requires constant nutrition. After a reboot, the volatile memory starts working again, remembering the current installation functions. The vehicle is protected from the moment it is parked. All of these devices require current, which means it is possible to consume a small amount of energy on a regular basis.
Since current is used to operate many volatile devices, it should be indicated that there is a leakage rate. It is a constant value, which is calculated by summing the consumption volume of each device. If the constant consumers in a car are the clock, alarm system, and audio system, then the sum of their current consumption will be 1mA+20mA+3mA, respectively. When adding the current values for all devices operating constantly, a total sum is obtained in the range of 50–80 mA.
When compared to a headlight bulb, which consumes about 500 mA, a current leakage rate of 50 mA cannot affect battery discharge.
To determine the rate of current leakage in your own car, you should carry out diagnostics. This is done by measuring current consumption. When a consumption value is detected that is greater than normal, it becomes necessary to troubleshoot electrical equipment or the on-board network.
Using a Multimeter
Modern cars have many stable devices for consuming electricity.
This could be a clock, on-board computer, alarm system and other equipment. They are connected and constantly use electricity, which is the standard situation. However, there is a norm for the loss of electric current in a car battery. To calculate this value, you need to understand how much energy each device on the network uses. For example, a car alarm consumes no more than 20 mA. The clock requires 1 mA to function. The stereo system uses up to 3 A. One indicator consumes from 50 mA, one headlight lamp consumes up to 6 A. A current leak of about 50 mA cannot serve as a basis for completely discharging the battery.
You can use a multimeter to determine which features are being used. If high current consumption is observed during the measurement process, network problems may occur. We need to find the source of such electricity costs that will help solve the problem. There are two main factors that greatly drain your battery .
This is additional equipment and a short circuit in the network. It is necessary to regularly measure the current leakage from the car battery using a multimeter.
How to find a leak
Leakage may be caused by an unauthorized consumer or a short circuit in the circuit. The search begins with non-standard devices and electronic components. Unlike factory wiring, newly installed equipment can be powered by wires laid in the first available location. If you want to quickly place everything, the master does not pay attention to the fact that the wiring may lie near the motor. During operation, the unit generates heat that acts on the insulating layer of the wires. As a result, melted areas appear.
When cables are located near metal places that are constantly in contact, chafing can occur. The integrity of the wiring is compromised, leading to a short circuit.
Therefore, after preliminary diagnostics using a multimeter, it is worth visually inspecting individual areas and elements of equipment placed after purchasing the machine. Often, alarm limit switches are placed where the doors touch. Look for burned, corroded or damaged areas. If these are not found, then it is worth moving on to the stage of in-depth diagnostics.
Finding the root problem
One of the key factors causing the problem is any electronic device or support for the operation of additional equipment.
These devices are being used more and more often in cars. During the search, devices installed independently of each other must be taken into account. The factory circuitry in the machine is well protected and a short circuit will only occur if there are significant defects. For example, if the protective cover is accidentally damaged. Sometimes the car owner misplaces the wires, placing them in the wrong position, which seemed most suitable to him. This usually causes a short circuit.
Failure results in loss of current in the battery . Wiring installed by the vehicle owner may be dangerously close to the engine. During operation, the motor becomes hot and the wire insulation may melt. The cord rubs against the edges of metal elements, especially in places where the door closes. As a result, the insulation is broken and a short circuit occurs in the electrical network.
After measuring the current consumption, it is necessary to begin a visual inspection of all equipment if the rate of loss of electricity in the machine does not correspond to the readings of the multimeter. It is necessary to take into account individual parts and assemblies that are subject to any mechanical stress. If it is difficult to identify breakdowns, you should move on to in-depth diagnostics.
What threatens a high leakage current on a car?
The most common (though not the worst) problem due to excessive current leakage in a car is a battery that discharges quickly and frequently. This is usually noticed when the battery has served for several years and is no longer capable of storing much energy. The excessive leakage current may have appeared on the machine much earlier. However, while the battery is “young and vigorous”, its reserves are enough for many days of consumption of several milliamps. The old battery has fewer ampere hours than the new one, so it runs out quickly.
For a new battery, large leakage currents are also far from useful. There will be a constant load, much or not - it doesn’t matter whether it drains the battery. And starter batteries retain their service life the longer, the more time they remain in a fully (or almost) charged state. If every single day the battery drains first a little, and then up to half, and so on, it will be possible to start the engine in the morning, but the battery life will quickly decrease. The plates will begin to sulfate, the capacity will gradually decrease, and goodbye to the new battery a couple of years after purchase.
More serious problems can arise when current leakage in the car is caused by short circuits, insulation damage and water ingress. In such cases, heating of conductors or parts of electrical equipment is possible. And this already threatens spontaneous combustion. And the worst thing is that because of this, the car often catches fire at night when no one is around. Accordingly, no one takes timely measures, as a result of which the car burns out to a bare body.
This, of course, does not happen all the time. But even less terrible problems, for example, when a new battery is discharged, are unpleasant and indicate a malfunction. This means that you need to know about the possible causes of current leakage.
Measuring current leakage in a car with a multimeter
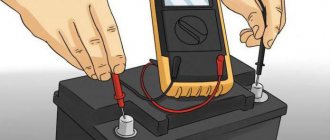
Now let's look at the most important thing - how to measure current leakage in a car. All you need for this is absolutely any multimeter. When taking measurements, it is extremely important to adhere to safety rules. Otherwise, you can burn the multimeter, get injured, and damage the car’s electronics.
The verification algorithm is as follows:
- Open the hood and lock the button, which sends a signal to the security system to open it.
- Put the car in park mode - turn off everything except what would normally remain in standby mode. For example, an alarm system, a video recorder, and so on.
- Remove the negative terminal from the battery. Contrary to popular belief, you can also shoot plus. However, disconnecting the “mass” is more correct and 100% safe.
- Set the multimeter to current measurement mode in the range of up to 10 A. Reposition the positive probe on the device accordingly. Never attempt to measure leakage current on a vehicle using the low range on the multimeter (up to 200 mA). When the terminal is connected, there will be a current surge that the fuse in the measuring device may not withstand.
- Attach one multimeter probe to the removed negative clamp, and the second to the battery terminal from which this clamp was removed. This type of connection is called an open circuit. When you removed the terminal, you broke the circuit, and now you connected a multimeter into the gap.
- If the security alarm is reset as a result of disconnecting the battery from the on-board network, turn it on again.
- Wait a while. In some cases, there is no need to wait - the leakage current can be detected immediately. In cars packed with electronics, it is necessary to give time for all systems to go into standby mode. In rare cases you have to wait up to 5 minutes. If you don't pay attention to this, you can panic for no reason.
- When the multimeter readings are level, record them. This is the current leak in your car.
- Under no circumstances turn on anything while taking measurements! Even a light load is switched on with a current surge, which can lead to a blown fuse in the multimeter.
- Moreover, do not try to start the engine when there is a multimeter in the open circuit!!! It is designed for only 10 amperes, and while the starter is operating, a current of 100 - 200 A will flow through the circuit.
Then all that remains is to compare the obtained indicators with the standards described above. In general, if the multimeter reads less than 0.12 A (120 mA), then there is no cause for concern. If the current leakage is greater than this figure, then you should start looking for the cause.
Connecting the device
Every car owner needs to know what leakage current should be in the car. Before determining current losses, the device must be connected to the network. Devices that consume battery power must be turned off. The multimeter is connected to the system:
- The cable from the positive output of the battery is removed.
- One contact of the multimeter is connected to the battery positive.
- The second contact is connected to the wire that is disconnected from the network.
Do not connect the device to the plus and minus of the battery at the same time - this may cause a short circuit. The car will be fine, but the fuse will burn out quickly. If everything is connected correctly, the display shows an indication of the electrical current that is constantly flowing through the electrical device.
If the permissible loss of electricity in the machine is lower than the measurement result, you should continue to search for the cause of the leak.
Determining the source
To determine the source of the leak, it is necessary to turn off standard and non-standard devices and instruments one by one, analyzing the readings of a multimeter operating in ammeter mode. Checking current leakage in a car with a multimeter will be completed as soon as the device detects acceptable current readings of one of the disconnected devices. Do not forget to carefully examine the condition of the wiring and insulation. It is also worth determining the performance of the generator in order to exclude current leaks due to its defects.
If the voltmeter readings do not exceed 12.8 V, the generator should be repaired or replaced, since the battery is not receiving charging from it.
Malfunctions of switching equipment
Loads connected to live wiring through switches or relays may cause increased leakage current. In any case, the source of problems is the contacts, no matter the switch or relay - burnt and deformed from overload, they may not open completely, maintaining, albeit large, resistance through which current will flow.
However, such cases are rare. But in modern cars with complex control systems for on-board consumers, the circuits are switched by semiconductors, and not by classic relays. And any semiconductor also has a reverse current - in switching transistors it is negligible, but in the event of a malfunction it increases to noticeable values, not to mention cases of breakdown of the transistor when the load is no longer disconnected from the power supply.
Video: Finding a current leak in a car
FAQ
What is the normal leakage current in a car?
There is a current leak in almost every car, and the rate will depend on the amount of additionally installed electronics, which can consume energy even in standby mode, as well as the power supply characteristics of the on-board network. Therefore 0.05 Ampere
– this is the norm for a modern car. And in some cases, even 70 mA is also acceptable.
What is the leakage current through the alarm?
In operating mode, the security device consumes up to 200 mA of current, depending on its complexity, the number of sensors and the connection method. current through the alarm – 20-30 mA
this is normal, the main thing is that consumption decreases to this level 5-10 minutes after turning it on. The problem areas are considered to be the limit switches of the hood and trunk doors, as well as the communication module (oxides appear on the board).
What is the leakage current through the radio?
On a car with a properly connected 1 din radio, the leakage does not exceed 0.01A
or
0.02A
if it is 2 din. The main problem is connecting the power wire (red) and the wire responsible for saving the settings (yellow in one twist) and directly to the battery. Only the yellow “memory” wire should receive constant power. Also, the leakage current through the radio, as in the case of the alarm system, when the ignition is completely turned off, should decrease after 10 minutes of rest.How to measure leakage current?
You can measure the leakage current with a multimeter or a current clamp (allows you to measure the leakage current without contact) by first setting the car alarm and waiting 10-15 minutes since there are ECUs that do not go into sleep mode immediately. To measure leakage current with a multimeter
It is necessary to connect in series to the power supply circuit of the on-board network, before the negative terminal on the battery.
First, you need to set the DC current measurement mode to 10A when the tester is turned on. Then, having removed the negative terminal from the negative terminal on the battery, connect one of its probes to the negative terminal of the car, and the second (red) to the negative terminal of the battery. Current leakage will be displayed on the dial. When measuring leakage current with clamps
, you need to set the DC current measurement on the device, and the conductor being measured, maybe the entire twist going to the negative terminal of the battery, or from individual consumers, is placed in the clamp ring after turning off the ignition completely. On the display you can immediately see the current consumption of the car’s electronics at rest.
Battery and quiescent current, current consumed by a stationary car
Lorderon
Master Advisor
I invite all car owners (any) to unsubscribe from who knows how much the car consumes in standby mode.
It is advisable to write down what equipment is standard and not standard (alarms, heaters, etc.). I think it will be useful for everyone when finding the culprit “Who drained the battery?” I'll start with myself. Idle current – 0.17A. I think it's still too much. Frankly speaking, not the best result. In the morning there were problems with engine cranking. Battery VARTA Silver 77Ah.
Correction: The equipment is standard. ABS, ESP, Air conditioning. The car radio has a standard cassette player and a separate CD player. switched off by button. Climatronic is switched off. True, there is also a comfort block that smoothly turns off the lights, etc. but I think it’s not him since the light in the cabin is not turned on.
VW Golf 4 2000 engine ATD 1.9 TDI. Added StarLine B9 signaling.
DASHOUMANTAMTAKOE?!
Cenmax Vigilant alarm + Alpine CDE-9874 radio, the radio was connected constantly, bypassing the ignition switch + active antenna, parallel to the radio. All this consumed 0.2A in standby mode. at -25 -30 it drained the battery in just over a day.
I hung the control signal of the radio and the antenna on the ignition wire (I don’t have ACC), the current dropped to 0.02A, I consider this current acceptable
Cruser
Regular
Vaxa20
Samodelkin
A current of up to 50mA = 0.05A is considered normal on any machine; if this value is exceeded, one must already think that it is not working as it should!
You have 170 mA, so something consumes a lot. A current of 50 mA will bring a fully charged battery down to zero in a month -2 downtime depends on the capacity of the battery. in your case, it’s good if there’s enough downtime for a week! This is a fully charged battery! Look for those that consume, otherwise you will ruin the battery.
And I also advise you to measure the quiescent current not just after closing the car, but for at least 20 minutes, I’ll explain, the fact is that modern cars have comfort units that can consume voltage for some time after closing all the doors, also if something in its circuit is switched on for some time After about 15 minutes, it will automatically turn off this load and go into sleep mode! Example: BMW 535 2003, after closing all the doors, it consumes 2.5A, within 10-15 seconds then the current drops to 0.5-0.7A (although all the lights are extinguished) after 10 minutes the quiescent current becomes only 20mA, with its full power and a bunch of control units!
On the former Passat, the quiescent current was 35mA; when the additional equipment, radio signal and amplifier were turned off, the current was only 5mA.