Functions and location of the VAZ 2107 charging relay
In early models, an external voltage regulator VAZ 2107 was used, which was installed on the left arch in the engine compartment. In newer models, the relay began to be installed together with the generator brush mechanism. Regardless of the location and design (relays are produced on printed circuit boards or in the form of a single semiconductor module), the functions of the devices are the same - adjusting the voltage at the output of the car generator.
To maintain the correct battery charging mode and the normal functioning of the vehicle’s on-board network devices, the voltage at the generator output should be in the range of 13.6-14.6 volts (preferably closer to 14). The regulator relay changes the voltage in the generator excitation circuit depending on the output voltage so that at any load and speed it produces the optimal voltage. If the VAZ 2107 charging relay malfunctions, the mains voltage may be lower or higher than normal. In the first case, the battery will discharge, in the second, it will boil and may fail.
Checking the VAZ 2107 voltage regulator relay
If you suspect a malfunction, you should check the voltage directly at the battery terminals. If the voltage is below 13 or greatly exceeds 14 volts, there may be several reasons:
- voltage regulator relay malfunction;
- generator breakdown;
- poor contact in the electrical connections between the battery, alternator and relay.
The serviceability of the VAZ 2107 charging relay can be checked by disconnecting it from the vehicle’s on-board network. This is easy to do with the external one - just remove a couple of terminals from it and unscrew the nuts securing it to the body using a size 8 wrench. It is more difficult to dismantle the internal relay, but the operation is quite feasible without dismantling the generator. To do this, you need to unscrew a couple of screws securing the relay to the generator housing.
There are three reasons for a relay malfunction:
- poor contact of the relay with the terminals of the brush holder (relevant for new types of relays);
- breakdown of semiconductors;
- open circuit in the device.
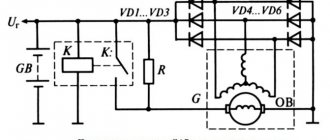
To check the VAZ 2107 relay-regulator, you need a voltmeter or test lamp and an adjustable current source with a voltage of 12-22 volts.
To check, you need to connect the minus of the power supply to the relay ground or terminal “W” (depending on the type of relay), and the plus to terminal “B”.
A voltmeter or test lamp must be connected to the brushes or relay output. If the relay is working properly, when a voltage of 12-14 volts is applied, voltage should appear at the output (brushes) (the control lamp lights up). When a voltage of 16-22 volts is applied, the lamp should go out. If the lamp is constantly on, then the relay is broken. If it does not light up regardless of the input voltage, it is broken. In both cases, the relay must be replaced, since it cannot be repaired.
Checking the combined relay-regulator of the car
First we will check the combined relay-regulator circuit together with the brush assembly. These are now installed on many foreign cars, and by the way, on many domestic cars (often labeled Y212A).
As you understand, it is necessary to remove the generator and disassemble it, since this combined unit is attached at the back next to the generator shaft, along which these brushes run. For this:
- We look for a special “window” on the back of the generator where the brushes are immersed.
- Unscrew the fastening bolt.
- Remove the brush assembly.
- We clean it - as a rule, it will be covered in graphite dust; the brushes are made of graphite, using special carbon.
Then we need to check it, but for this we assemble a certain circuit, it is advisable to use a power supply with an adjustable load or a charger. We also need to take a regular 12V light bulb from a car, for example from a “dimensions”, we will need wires to assemble the entire system.
We may need a battery, because many chargers do not work without it. But from the wire from the battery we connect the relay-regulator, to the brushes of which we connect a 12V light bulb, this can be done with small alligator clips, the main thing is not to break the graphite elements. A small diagram for understanding.
If you connect everything in a calm state, the light will simply light up and stay lit, this is normal, since the brush assembly is a conductor of electricity from the shaft. Let me remind you that in a calm state, the voltage on the brushes will be approximately 12.7V.
Now we need to raise the voltage on the charger to 14.5 V, the lamp will light, but when this threshold is reached it should go out! That is, 14.5 V is a kind of “cutoff” for a further increase in voltage! If you lower the value, the lamp should light up again. Then your relay-regulator is working, it passed the test.
If the voltage reaches 15 - 16V and the light is on, this means the relay has failed and needs to be replaced! It does not cause a “cut-off” and will help recharge the battery. Here's a simple check. Now a short video on the topic.
Replacing the VAZ 2107 voltage regulator relay
If the external relay of the VAZ 2107 generator breaks down, you should replace it with a new one. If the cause of the breakdown lies in the brushes, only the brush assembly must be replaced.
The old internal relay-regulator can be replaced with a new “three-level” one, which provides more reliable voltage stabilization, taking into account the temperature conditions and the load on the generator.
They are called three-level because of three pre-configured adjustment modes that can be switched manually. The switch itself is installed separately from the relay, in a place convenient for the driver and protected from moisture and dirt.
When installing a new relay regulator, you need to pay special attention to the quality of the electrical contacts. If necessary, it is necessary to clean the terminals and nuts securing the external relay to the housing.
To avoid a short circuit, connect the ground wire to the battery only after installing the relay and power wires.
Not every driver knows what a VAZ 2107 charging relay is; in addition, this device is extremely rarely remembered. The charging relay is a voltage regulator or “chocolate bar” that is located in the generator. Owners of the Seven only pay attention to this detail after problems with the battery not charging begin. To prevent it from happening at one point, which negatively affects the engine, it is necessary to periodically monitor the operation of the charging relay.
Recommendations for increasing the service life of the regulator
In order to increase the service life of the voltage regulator, it is necessary to adhere to several simple rules aimed at implementing preventive measures. Among them:
- do not allow excessive contamination of the generator, periodically inspect its condition, and, if necessary, dismantle and clean the unit;
- check the tension of the alternator belt, tighten it if necessary (either yourself or in a car service);
- monitor the condition of the generator windings, in particular, do not allow them to darken;
- check the contact on the control wire of the relay-regulator, both its quality and the presence of oxidation on it;
- Perform periodic voltage checks on the vehicle battery with the engine running.
Purpose of the regulator relay VAZ 2107 injector and carburetor
The main purpose of the voltage regulator relay on the VAZ 2107, and any other car, is to maintain a stable and sufficient charging current for the on-board network and the car battery, as well as to level out voltage surges in the generator. Variations in the generated voltage would occur as the generator rotates at different frequencies. When the power drops below 12V, the battery stops charging, and the entire bot network no longer functions at 100%. If the voltage exceeds 16 Volts, this can lead to boiling of the battery, as well as failure of on-board devices.
On early production VAZ cars of the carburetor type, the voltage regulator is located on the left arch of the engine compartment. Such devices are also called external, since they were installed outside the generator structure. To be more precise, a brush mechanism was installed in the generator, and control was carried out via a printed circuit board, which was installed outside the product.
Most VAZ 2107 cars of the carburetor and injection type are equipped with generators with built-in charging relays. The charging relay on such VAZ 2107 vehicles is located directly on the side of the generator opposite the pulley.
To maintain an acceptable battery charge, the alternator requires 13.6 to 14.6 volts of power. The voltage regulation circuit is carried out using an electrical circuit, which is located on a printed circuit board (chocolate board) or in the form of a single semiconductor module (tablet) with brushes. The switch located inside the generator is usually not able to adequately respond to the ambient temperature due to its location close to the running engine. The built-in relay is sometimes replaced with a three-level voltage regulator, which is due to the greater efficiency of the product due to manual adjustment of the output voltage.
Checking an Individual Regulator
Checking the voltage regulator of the G-222 generator: 1 - battery; 2 - voltage regulator; 3 - control lamp.
As a rule, separate voltage regulators were installed on old cars, including domestic VAZs. But some manufacturers continue to do this to this day. The verification process is similar. To do this, you need to have a power supply with a voltage regulator, a 12 V light bulb, a multimeter and a directly tested regulator.
To check, you need to assemble the circuit shown in the figure. The process itself is similar to the one above. In normal condition (at a voltage of 12 V), the light bulb lights up. When the voltage value increases to 14.5 V, it goes out, and when it decreases, it lights up again. If during the process the lamp lights up or goes out at other values, it means that the regulator has failed.
Checking relay type 591.3702-01
Relay test diagram type 591.3702-01
You can also still find a voltage regulator of type 591.3702-01, which was installed on rear-wheel drive VAZs (from VAZ 2101 to VAZ 2107), GAZ and Moskvich. The device is mounted separately and installed on the body. In general, the test is similar to that described above, but the differences are in the contacts used.
In particular, it has two main contacts - “67” and “15”. The first of them is a minus, and the second is a plus. Accordingly, to check it is necessary to assemble the circuit shown in the figure. The verification principle remains the same. In normal condition, at a voltage of 12 V, the light bulb lights up, and when the corresponding value increases to 14.5 V, it goes out. When the value returns to its original value, the light comes on again.
A classic regulator of this type is a device of the PP-380 brand, installed on VAZ 2101 and VAZ 2102 cars. We provide reference data regarding this regulator.
Checking the removed voltage regulator
To clarify the condition of the regulator, it must be removed. It is better to test the device complete with brushes and brush holder. This will allow you to immediately detect:
- poor contact between the terminals of the brush holder and the voltage regulator;
- breaks in the output conductors of the brushes.
Electronic devices are produced already assembled with a brush holder and one-piece brushes. The relay regulator will need to be connected to the removed brushes.
A voltmeter or a 12 V lamp with a power of 1–3 W is connected to the brushes of the device removed from the generator 37.3701. For the regulator from the G-222 generator, the connection is made to terminals “B” and “W”. The “plus” of the power supply is connected to the terminals “B”, “C” (when they exist), and the “minus” to ground. First, a voltage of 12–14 V is applied, and after that – 16–22 V. A sign of the device’s serviceability will be the lamp lighting up (deviation of the voltmeter needle) in the first case and going out (zeroing the voltmeter) in the second.
When the lamp lights up in both cases, this means that there is a breakdown in the device. If in both cases the lamp does not light, then there is no contact between the regulator terminals and the brushes, or there is a break in the device. Another cause of improper voltage regulation can be worn or stuck brushes. They must protrude from the housing of the electronic device or the brush assembly of relay regulators by no less than 5 mm.
Symptoms of a problem
So, in case of low voltage, the battery simply will not charge. That is, in the morning you will not be able to start the car, the lights on the dashboard may not even light up, or troubles will arise while driving. For example, dim headlights at night, unstable operation of the electrical system (problems with electrical appliances - wipers, heaters, radio, etc.).
In case of increased voltage, there is a high probability of a decrease in the electrolyte level in the battery banks, or its boiling. A white coating may also appear on the battery case. When overcharging, the battery may behave inappropriately.
Signs, malfunctions, repair of generator and voltage regulator
In addition, you can also identify the following signs of a faulty voltage regulator (in some cases, some of them may or may not be present, it all depends on the specific situation):
- the control light on the dashboard (although this may be a sign of other malfunctions, for example, that it has burned out, the contact has fallen out, and so on);
- after starting, the battery indicator on the dashboard does not go out, that is, there are obvious malfunctions in charging the battery;
- the brightness of the headlights becomes dependent on the engine speed (you can check this somewhere in a deserted place by placing the car against a wall and accelerating - if the glow changes, then most likely the voltage regulator is faulty);
- the car stopped starting normally the first time;
- The battery is constantly ;
- when the engine speed exceeds 2000 rpm, the indicators on the dashboard turn off ;
- the dynamic characteristics of the car decrease , this is especially noticeable at high engine speeds;
- In some cases, the battery may boil .
Replacing the voltage regulator VAZ 2107
If the regulator is faulty, the brushes are worn out or stick, then the device must be replaced. It cannot be repaired. For a relay-regulator in case of brush failure, it is sufficient to replace only one brush assembly. Usually they change it to a new electronic one, but you can install a three-level one, like 67.3702-02. They provide better voltage stabilization than standard regulators, taking into account the ambient temperature and vehicle operating conditions.
They are called three-level because they contain 3 voltage regulation modes. Their selection is carried out manually with a switch on the regulator, which is installed separately from the generator itself in a convenient protected place. The device is connected to the generator by wires through a brush assembly, which is supplied complete with the regulator.