| The engine cooling system (ECS) is one of the main systems of a car. Is cold air blowing from the stove or is the engine on the LADA Kalina overheating? Then the inspection should begin with this system. In this article you will find all the information on the operation of the Lada Kalina cooling system. |
Design features of the LADA Kalina engine cooling system
The LADA Kalina engine cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation.
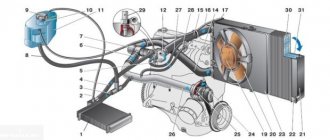
Consists of an engine cooling jacket, a radiator with an electric fan, a thermostat, a pump, an expansion tank and connecting hoses. Design of the LADA Kalina cooling system
Cooling system : 1 — expansion tank; 2 — radiator outlet hose; 3 - inlet hose; 4 - radiator; 5 — steam exhaust hose; b — radiator supply hose; 7 — electric fan; 8 — electric fan casing; 9 — coolant temperature sensor; 10 — coolant temperature indicator sensor; 11 — throttle assembly; 12 — bracket for the coolant pump pipe; 13 — coolant pump; 14 — coolant pump pipe; 15 — heater radiator supply hose; 16 — heater radiator outlet hose; 17 — exhaust pipe; 18 — coolant pump pipe hose; 19 — thermostat housing
| Expansion tank . Coolant is poured into the system through the expansion tank. It is made of translucent polyethylene, which allows you to visually monitor the liquid level. To do this, the marks “MAX” and “MIN” are marked on the wall of the tank. In the upper part of the tank there is a pipe for connecting to the radiator steam exhaust hose, in the lower part there is a pipe for connecting to the inlet hose. |
| Expansion tank cap with valves . The tightness of the system is ensured by the inlet and outlet valves in the expansion tank cap. The exhaust valve maintains increased (compared to atmospheric) pressure in the system on a hot engine (due to this, the boiling point of the liquid becomes higher, steam losses are reduced}. It begins to open at a pressure of at least 1.1 bar. The intake valve opens when the pressure drops to system relative to atmospheric pressure by 0.03-0.13 bar (on a cooling engine). |
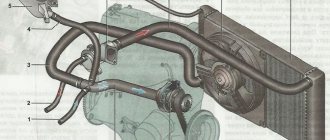
| The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by a timing belt. The pump housing is aluminum. The roller rotates in a double-row bearing. The bearing is lubricated for its entire service life. The outer ring of the bearing is locked with a screw. A toothed pulley is pressed onto the front end of the roller, and an impeller is pressed onto the rear end. A thrust ring made of a graphite-containing composition is pressed to the end of the impeller, behind which there is an oil seal. The pump housing has a control hole to detect fluid leakage when the pump fails. It is recommended to replace the pump as an assembly. The redistribution of liquid flows is controlled by a thermostat. |
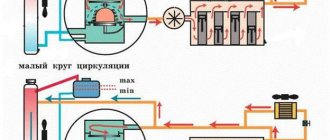
The cooling system consists of two so-called circulation circles:
- The movement of liquid through the cooling jacket and radiator forms a large circulation circle.
- The movement of liquid through the engine cooling jacket, bypassing the radiator, is a small circle of circulation.
The cooling system also includes a heater radiator and a throttle body heating unit. Liquid circulates through them constantly and does not depend on the position of the thermostat valves.
| Thermostat . It has a solid temperature-sensitive element and two valves that redistribute the flow of coolant. On a cold engine, the main thermostat valve blocks the flow of fluid from the radiator and the fluid circulates only in a small circle, bypassing the radiator. At a temperature of (85±2) °C, the thermostat valves begin to move, allowing liquid flow into the radiator and closing the bypass channel. At a temperature of about (100±2) °C, the main valve opens completely and the bypass valve closes. Almost all the fluid circulates in a large circle through the engine radiator. |
| Coolant temperature sensor . To monitor the coolant temperature, a sensor is screwed into the engine cylinder head, connected to the temperature indicator in the instrument cluster. In the outlet pipe, next to the thermostat housing, there is a coolant temperature sensor that provides information to the controller. |
The heater radiator is built into the engine cooling system and is designed to heat the passenger compartment by circulating hot coolant through it.
| The radiator consists of two vertical plastic tanks (the left one with a baffle) and two horizontal rows of round aluminum tubes passing through the cooling plates. The tubes are connected to the tanks through a rubber gasket. The liquid is supplied through the upper pipe and discharged through the lower. Next to the inlet pipe there is a thin pipe for the steam removal hose. The radiator has a casing with an electric fan. There is a drain plug at the bottom of the right tank. |
The fan maintains the thermal operating mode of the engine and is switched on via a relay based on a signal from the controller.
Principle of operation
The operating algorithm of this system consists in the close interaction of various sensors, parts and elements, including devices that measure oil temperature, outside temperature and many other factors. Taking into account all these points, on the VAZ Kalina the cooling system automatically sets the optimal switching conditions and operating time of all structural elements, thereby ensuring effective engine cooling.
It should also be noted that depending on the temperature, the liquid can pass through a small or large circle. In the first case, the antifreeze passes through all the channels of the system, bypassing the radiator. The thermostat is in the closed position during such circulation. When the engine temperature increases, this part gradually opens, and the antifreeze begins to “run” in a large circle, getting into the radiator. The latter is cooled by a counter flow of air, and if the SOD is not enough, it will send a signal to the fan, which will force cold air onto the cells.
After cooling, the coolant flows back to the small circle. Then, depending on the engine temperature, the system automatically circulates antifreeze either in a large or small circle, maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the internal combustion engine (95-105 degrees Celsius).
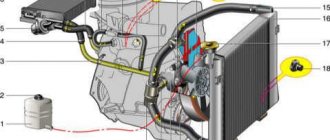
LADA Kalina engine cooling system diagram
Cooling system : 1 — coolant drain hose from the heater radiator; 2 — hose for supplying coolant to the heater radiator; 3 — coolant pump supply pipe hose; 4 — expansion tank hose; 5 - expansion tank; 6 — steam exhaust hose of the engine radiator; 7 — thermostat; 8 — hose for supplying fluid to the throttle assembly; 9 — hose for supplying fluid to the engine radiator; 10 hose for draining fluid from the engine radiator; 11 — engine radiator; 12 radiator drain plug; 13 electric radiator fan; 14 coolant pump; 15 supply pipe of the coolant pump; 16 coolant drain hose from the throttle body
“Lada Kalina” and an airlock: how to remove airlock?
The first step is to open the expansion tank cap. Next, start the engine and, periodically pressing the gas pedal, warm up the engine until the temperature gauge rises to the red scale. After turning on the fan, give it a little more gas and turn off the ignition. If the airlock cannot be eliminated in this way, you will have to move on to more radical measures.
How is this done? First, the plastic engine screen is removed (it can be removed with a simple upward movement). Next, use a screwdriver to loosen the clamp, and remove one of the two tubes from the throttle assembly heating fitting. Then the cap of the expansion tank is unscrewed. Cover the neck of the container with a clean rag. Next, you need to blow into the expansion tank until coolant flows out of the removed tube. If you are unable to break through the container, close the lid and put back the throttle assembly tube. Next, you need to warm up the engine again and turn off the ignition. After this, without removing the cap from the tank, remove the heating tube again and wait until antifreeze flows out of it under pressure.
Basic radiator malfunctions
Malfunctions of this Kalina unit do not occur so often and are the result of wear and tear due to natural causes of the car owner’s negligence. There are two most common types of problems:
- coolant leak;
- coking of cavities inside the radiator.
Leaks are dangerous because a decrease in coolant level leads to an increase in engine temperature. This leads to overheating and jamming of the motor. A leak of hot antifreeze can be dangerous. The fluid in the system is under pressure, a leak can form a fountain, and contact of hot antifreeze on exposed skin will cause burns.
Coking disrupts the antifreeze circulation process. As a result, the lower part of the radiator begins to cool, and then the entire heat exchanger. The liquid will not cool, causing the engine to overheat. In most cases, the cause of coking is ordinary scale. This happens when tap water is poured into the SOD. Less commonly, blockages occur due to mixing oil and antifreeze. In this case, the reason is the loss of tightness of the cylinder head gasket.
At an early stage, coking is difficult to detect. In advanced cases, mixing oil and antifreeze forms a consistency similar to jelly, which makes the heat exchanger tubes difficult to pass or completely impassable.
Conclusion
The Lada Kalina 8 valve cooling system has a fairly simple design and a standard set of components. Thus, a malfunction of one or more elements can lead to negative consequences that will significantly hit the car owner’s pocket.
Source
Basic data for monitoring, adjustment and maintenance
Temperature at which the main thermostat valve begins to open, °C
Full opening temperature of the main thermostat valve, 'C
Opening pressure of the outlet valve of the expansion tank plug, kPa (bar)
Opening pressure of the inlet valve of the expansion tank plug, kPa (bar)
Coolant temperature in a warm engine at an ambient temperature of 20-30 °C and a fully loaded vehicle moving at a constant speed of 80 km/h, no more, °C
Resistance of the additional resistor. Ohm
Volume of liquid in the engine cooling system, l
OZhK-KHT; OZh-40-ХТ; OZh-65-ХТ; OJ-CTosol; Coolant-40Tosol; Coolant-65Tosol; OZh-40; OZh-65; OJK-KSK; OZh-40SK; OZh-65SK;
Lada-A40; OZh-Ktosol-TS; OZH-40TOSOL-TS; OZh-65 Tosol-TS; Antifreeze G-48; AGIP Antifreeze Extra; GlysantmG03; GlysantinG913
Tightening torques for threaded connections
Name of units and parts
Tightening torque, nm (KGS-M)
Coolant temperature gauge sensor Coolant pump mounting bolts Thermostat pipe mounting nuts
Bolts securing the cooling system pipe flange to the cylinder block
24-27 (2,5-2,8) 7,6-8,0 (0,8-0,8) 16,0-22,6 (1,6-2,3) 4,2-5,2 (0,4-0,5)
Cooling system: 1 — coolant drain hose from the heater radiator; 2 — hose for supplying coolant to the heater radiator; 3 — coolant pump supply pipe hose; 4 — expansion tank hose; 5 - expansion tank; 6 — steam exhaust hose of the engine radiator; 7 — thermostat; 8 — hose for supplying fluid to the throttle assembly; 9 — hose for supplying fluid to the engine radiator; 10 — hose for draining fluid from the engine radiator; 11 — engine radiator; 12 — radiator drain plug; 13 — electric radiator fan; 14 — coolant pump; 15 — supply pipe of the coolant pump; 16 — coolant drain hose from the throttle body
The engine cooling system is liquid, closed type with forced circulation of coolant and an expansion tank.
The engine cooling system uses special fluids based on a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. They have a low freezing point and a high boiling point. In addition, thanks to the complex of added additives, the coolant prevents corrosion of the channel walls, does not foam, and extends the service life of the coolant pump seal.
Is the fluid circulation in the system ensured by a centrifugal pump? installed in the cylinder block. The pump is driven by a timing belt.
The cooling system consists of two so-called circulation circles. The small circle does not include the engine radiator, and the fluid washes only the cylinder block and cylinder head, and also flows through the throttle body channel and the heater core. The heater radiator is built into the engine cooling system and is designed to heat the passenger compartment by circulating hot coolant through it. When moving in a large circle, the coolant passes through the engine radiator, where it is cooled by the incoming air flow. The thermostat controls the direction of fluid flow in the engine cooling system. It contains two valves - the main one and the bypass (additional). The main valve controls the circulation of liquid in a large circle, and the bypass valve controls the circulation in a small circle. The valves are interconnected: when one opens, the second closes, and vice versa.
When the engine is cold, the thermostat bypass (additional) valve is open, and the fluid circulates only in a small circle. At a temperature of about 87 °C, the main thermostat valve begins to open and the bypass valve begins to close, and for some time the liquid circulates in the small and large circles simultaneously. At a temperature of 102 °C, the main thermostat valve is fully open and the bypass valve is closed, and all fluid flow passes through the engine radiator. If the air flow is not intense enough, the radiator is cooled by an electric fan. It is installed behind the engine radiator and is activated by a signal from the electronic engine control unit. An additional resistor is built into the power supply circuit of the fan motor.
Features of the design, maintenance and repair of the 1.6i engine are described in the chapter “Features of design and repair of modifications of the LADA KALINA* car.
The connecting rod and its cover are first manufactured as a single (one-piece) part. After making holes in the upper and lower heads of the connecting rod, the lower head is “split” using a special method. This technology allows for a perfect connection between the cap and the connecting rod.
To compensate for the thermal expansion of the liquid, an expansion tank is installed in the cooling system. The tank plug contains inlet and outlet safety valves, which allows you to maintain optimal pressure in the system when the liquid is heated, and also compensate for the vacuum when it cools.
Source
How to improve SOD?
At the moment, there are several ways to improve ODS:
- Reworking the cooling system. “Kalina” in this case is equipped with a new 6-hole thermostat. This action will make maintaining the temperature of the antifreeze in the system more stable, and will also normalize the operation of the heating elements of the cabin.
- To reduce cooling system malfunctions, the Lada Kalina is equipped with a coolant filter.
- Installation of the stove faucet.
- Additional pump in the engine cooling system. It will not only prevent you from freezing in your car during winter cold, but will also force antifreeze to circulate faster through the channels, which will significantly reduce the risk of engine overheating.
So, we found out how the cooling system in the VAZ Kalina is designed, what problems can arise with it, and how to fix these problems.
| The engine cooling system (ECS) is one of the main systems of a car. Is cold air blowing from the stove or is the engine on the LADA Kalina overheating? Then the inspection should begin with this system. In this article you will find all the information on the operation of the Lada Kalina cooling system. |