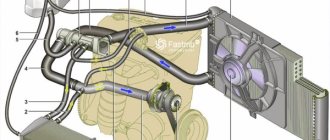
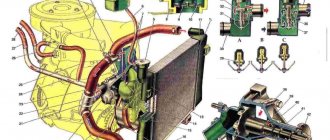
The engine cooling system is designed to ensure that the power unit operates within a strictly defined temperature range. In other words, both overheating and too intense cooling of the motor, which does not allow the internal combustion engine to reach operating temperature, are allowed.
Next, we will talk about how to diagnose the engine cooling system, as well as what you should pay attention to if the engine does not reach operating temperature (remains cold) or overheats, there are coolant leaks, etc.
Cooling system malfunctions
The need to repair the cooling system arises in the event of constant overheating or undercooling of the coolant (coolant), a decrease in the level of coolant in the system as a result of a leak, the occurrence of electrolysis in the coolant, etc.
Overheating of the coolant causes engine detonation, which sharply increases wear of the cylinders and piston rings, leading to burnout of pistons and reduced durability of plain bearings (liners). Disruption of the combustion process of the fuel-air mixture during overheating and an increase in friction forces lead to an increase in fuel consumption and a decrease in engine power. A decrease in coolant temperature in the engine cooling jacket increases wear of CPG parts due to oil being washed away from the cylinder walls by fuel. The oil is diluted by fuel entering the oil sump, resulting in more intense formation of resin and varnish deposits on the pistons and piston rings.
A decrease in coolant temperature for every 10 °C from the nominal value reduces engine power by 1.5% and increases fuel consumption by 2%.
Engine overheating can be caused by: lack of coolant in the cooling system due to its leakage or boiling over, clogging of the system, breakage or slipping of the fan drive belt, failure of the electric or fluid coupling of the fan, jamming of the thermostat in the closed position or the blinds in the closed position, incorrect setting the ignition timing.
Engine overcooling is possible when the thermostat is stuck open or the thermostat itself is missing, or the hydraulic or electric fan drive is faulty.
One of the malfunctions of modern cooling systems with a radiator made of aluminum and a energized fan temperature sensor (thermal switch) is the occurrence of electrolysis.
Electrolysis is the reaction of decomposition of a solution of chemical substances when an electric current passes through them. Characteristic signs of electrolysis: clogging of the radiator tubes, the presence of white deposits near its leaky places and greenish deposits near the thermal switch. If such symptoms occur, you must carefully check the connections of the electrical devices of the cooling system.
For radiators made of aluminum, it is not recommended to use water as a coolant, as this will cause corrosion of the tubes.
Coolant leakage can be caused by leaking connections between cooling system hoses and fittings and pipes, leaking connections of pipe flanges, leaking drain plugs and heater taps, damage to hoses, cracks in tanks and the radiator core, and wear of the self-clamping seal of the liquid pump.
How to get to us?
When moving from the street. Profsoyuznaya towards Leninsky Prospekt. You need to cross the intersection with the street. Academician Volgin straight ahead and drive to the pedestrian traffic light, after the traffic light after 50 meters there will be a right turn under the barrier (at the entrance you will need to tell the security that you are going to the Avangard Automotive Technical Center), then move straight 150 meters and you have arrived, Welcome!
When driving from Leninsky Prospekt. on the street Miklouho-Maklaya towards the street. Trade union. Before the pedestrian traffic light (this is the first traffic light from Leninsky towards Profsoyuznaya), before reaching it 50 meters there will be a left turn under the barrier (at the entrance you will need to tell the security that you are going to the Avangard Autotechnical Center), then move straight 150 meters and you have arrived, Welcome welcome! Tel.
Diagnosing the engine cooling system
General diagnostics of the technical condition of the cooling system consists of determining its tightness and heat balance.
A conclusion about the tightness of the system is made by visually verifying that there is no coolant leakage when the engine is running or not running, as well as by the rate at which liquid decreases from the expansion tank during vehicle operation.
The thermal balance of the system is judged by the time it takes for the engine to warm up and maintain its rated operating temperature under normal load. The check is carried out using a coolant temperature gauge.
The operation of the cooling system is considered satisfactory if the engine temperature is maintained within 85...95 °C when the loaded vehicle is moving at a speed of about 90 km/h.
You can check the general condition of the cooling system and find specific coolant leaks by supplying air under low pressure into the cooling system.
To check the tightness of the cooling system, you can use an air network (Fig. 1, a), and in case of its absence, an air pump (Fig. 1, b), which is connected to the plug of the expansion tank or radiator.
Using a reducer or pump, raise the pressure to the opening pressure of the expansion tank plug (0.09...0.13 MPa) for 2 minutes. Monitor the pressure gauge reading: the pressure must be stable, otherwise visually detect coolant leaks or check the coolers of individual engine components (recirculation systems, oil cooling radiator, etc.).
The reason for the rapid decrease in coolant in the system may be improper operation of the expansion tank plug valve and its insufficient tightness. If this malfunction occurs, it is necessary to check the condition of the plug valve and its opening pressure (the pressure value is indicated in the technical specifications of this engine).
Rice. 1. Checking the tightness of the cooling system using an air network (a) and an air pump (b) : 1 - pneumatic reducer; 2 - pressure gauge; 3 — sealing nozzle; 4 - radiator; 5 - pump; 6 - expansion tank plug
The performance of the radiator is determined by the difference in coolant temperatures in its upper and lower parts, which should be within 8...12 °C. A decrease in the temperature difference indicates the presence of scale in the radiator tubes or its contamination.
When checking the thermostat, it is removed from the engine and placed in a container with liquid at ambient temperature. You can use ordinary water, but given that the coolant temperature in modern engines can exceed 100 °C, it is advisable to use technical glycerin, whose boiling point is higher. In the case of using water, you can only set the beginning of the valve opening. The liquid is gradually heated; at a temperature of 70...80 °C (depending on the engine model), the thermostat valve should begin to open. The opening temperature is taken to be the one at which the stroke of the valve located on the side of the radiator inlet pipe is 0.1 mm. To more accurately determine the stroke value, you can use a dial indicator on the bracket. A further increase in temperature to 90...110 °C (depending on the engine model) should lead to full opening of the valve (6...8 mm). If, after carrying out the above check, it is determined that the thermostat does not meet the specified conditions, it is replaced with a new one, since it cannot be repaired.
If there is a coolant leak from the radiator, if it is not possible to find the location of the leak, the radiator is checked for leaks. There are two ways to check: directly on the car and with the radiator removed.
When checking on a car, the radiator is filled with water, all pipes are closed with plugs, leaving one open (through which air is supplied to the radiator at a pressure of approximately 0.1 MPa). The location of the leak is determined by where the water appears.
However, due to the difficulty of accessing the radiator, it is more convenient to check it by removing it from the car. After removal, close the filler neck and all radiator pipes, leaving one open, through which air is supplied to the radiator at a pressure of approximately 0.1 MPa. Place the radiator in a bath of water and observe the appearance of air bubbles, which will indicate the exact location of the leak.
The liquid pump is checked for leaks through the lower inspection hole. If the pump makes noise during operation, its axial play is also checked. If there is a coolant leak from the liquid pump, noise during operation and increased axial play of the pump, it is removed from the engine, disassembled, checked and, if necessary, the pump is repaired or replaced.
Electrical elements of the cooling system are checked using scanners and testers.
Reviews from our clients
Leonid
I went to the Avangard car service center for two years while I lived nearby, then I moved to Balashikha, went to a local tire shop, and then changed the oil filters to another one. And every time something is wrong, small shoals come out... I returned back to Avangard, even though it took longer to travel, but they do it conscientiously here, there have never been any problems.
Anastasia
I would like to especially praise the Avangard dry cleaner! I had the opportunity to compare with several competitors, the prices are about the same, but the quality of the work is not to complain, not a hint of dirt, everything is clean, fresh, washed! The salon is like new!
Denis
We have two family cars serviced at Avangard, my Mercedes and my wife’s Lexus, we are very pleased. And we go through the MOT, and have already repaired everything (to the credit of the craftsmen - what they repaired did not cause any complaints for a long time), and my engine was somehow rebuilt. And we store the tires here, otherwise there would be nowhere to put two sets. We sincerely recommend, excellent service!
Paul
Thank you, guys! I stopped by last week for diagnostics and the muffler began to roar, although not even a year had passed since it had been completely changed. We carried out the diagnosis in 20 minutes, everything was clear. We found a small burnout and fixed everything. They explained why this happens, that I probably drive often and not far, that the car idles, that’s how it is. It’s good that I came right away, while the burnout was small, otherwise I would have had to change everything. Five stars for professionalism and speed!
Sergey
The automatic transmission jammed on the front-wheel drive, suddenly and without warning. I found the nearest service in Yandex, called, so and so, what to do? They say everything is ok, we’ll send a tow truck and pick it up, don’t worry, we’ll fix it. I thought it would be more expensive, but it turned out quite acceptable. Thanks to Avangard, then we did some general diagnostics, found several problems, and now we are slowly fixing them.
Dmitriy
At Avangard they reprogrammed the ECU on my Skoda after one craftsman. The machine is old, but it was possible to add functions by updating it with fresh firmware. But something didn’t work out, and in fact a bunch of bugs appeared, errors are showing up, the electronics are glitching. We rolled everything back to the original version and checked to make sure there were no problems. I am satisfied with the quality of the work. I will come again.
Elena
I had an emergency air conditioner repair done here, I was happy with everything, no flaws were found. Polite craftsmen with clean hands, everything was neat and fast. I will recommend it to my friends.
Nikita
The first time I came to Avangard was almost by accident, in the fall, I urgently needed to change my shoes, but there were queues everywhere, and I had to travel far. After 7 pm I called, I said, so and so, I’m looking for an urgent tire change, they tell me, we’re open until 21, if you have time, come, we’ll do it. I rushed, I made it. I’ll be undergoing seasonal maintenance soon, now I’ll go to Avangard right away, I liked the service.
Maksim
I contacted the Avangard technical center after a minor accident and compared offers. I really liked that you can send a photo, and the repair can be assessed based on the photo. There is no need to ride or describe over the phone “well, there’s a chip on the fender and there’s still a chip on the bumper.” Very professional approach! The price suited me, after 4 days I already picked up the car, there was no sign of impact at all!
Alexander
We service our corporate cars at Avangard; we like that we can address any problem and everything is resolved in one place, even though the cars are of different brands and models. We called, made an agreement, drove it, went through maintenance, and did some repairs. And we get a good price for it. We sincerely recommend it.
Cooling system maintenance
Currently, the cooling system is filled with special non-freezing liquids (antifreeze), which are a mixture of ethylene glycol and water (solution density 1067...1085 kg/m3) with the addition of anti-foam and anti-corrosion additives. It is also possible to use water, but in this case, deposits of calcium, magnesium and other metals contained in the water form on the internal surfaces of the cooling system elements.
Scale has low thermal conductivity and impedes heat exchange between water and cooling system elements, reduces the cross-section of radiator tubes, and impairs water circulation. For example, a layer of scale more than 1 mm thick increases fuel consumption by up to 20...25%, oil consumption by up to 25...30%, and reduces engine power by up to 10...20%. To reduce the scale layer, softened water with a low salt content, obtained by electromagnetic treatment of water, is poured into the cooling system (water is repeatedly pumped through a magnetic force field in the direction perpendicular to the power lines). As a result, the water acquires new properties: the salts it contains do not form scale and fall out in the form of sludge. In addition, it helps dissolve previously formed scale, turning it into an easily washable powder. You can also soften water: by boiling; adding soda, lime, ammonia; purification from salts by passing water through mineral, glauconite or sodium cation filters.
If scale still exists, it is removed using special substances, which are divided into alkaline and acidic.
The basis of alkaline compositions is caustic or soda ash (1 kg of soda and 0.15 kg of kerosene per 10 liters of water). Alkaline compounds are poured into the system for 5...10 hours, then the engine is started for 15...20 minutes and the solution is drained. After this, it is advisable to flush the cooling system with water, since alkaline solutions cause corrosion of non-ferrous metals (aluminum alloys of the cylinder head, brass radiator elements and their solder joints).
As acid compositions, a 5...10% aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid with the addition of 3...4 g/l of utropine is used to protect ferrous metals from corrosion. The sludge is washed off with water, passing it in the direction opposite to the circulation of the coolant.
After repairing or replacing elements of the cooling system, as well as every 60 thousand km, after three years, or according to the instructions of the vehicle manufacturer, the coolant should be replaced. The need for replacement is due to the fact that the anti-corrosion components contained in the system, during the process of filling it, are deposited on new or repaired and cleaned parts to form a persistent anti-corrosion layer.
Coolant replacement should be carried out on a cold engine or with heated liquid on a warm engine in order to avoid its damage due to sudden cooling of metal parts: set the heating regulator in the cabin to the maximum degree of heating so that the coolant fills the heater radiator, remove the cap from the expansion tank and open the tank taps radiator and cylinder block (if equipped).
Many modern cars have special plugs to remove air from the cooling system; There may be several plugs or one, usually located near the thermostat housing. Before filling the system, the plugs are unscrewed slowly in a continuous stream and the system is filled with liquid until it begins to flow out through the plugs. Then the plugs or taps are tightened, and the liquid is added to the expansion tank or, if there is none, to the bottom of the radiator neck. If the fluid level in the expansion tank has stopped decreasing, you should vigorously squeeze the lower radiator hose 2-3 times.
After filling the system, the engine is started, warmed up to operating temperature and allowed to run for 3...5 minutes, periodically changing the crankshaft speed from minimum to 3000 rpm. Stop the engine and add coolant if necessary.
Currently, special installations are used to replace coolant (Fig. 2). With this installation you can:
- replacing coolant without airing the system;
- checking the engine cooling system for leaks;
- checking the functionality of the overpressure valve on the radiator cap or expansion tank;
- checking the functionality of the car thermostat;
- checking the actual fluid temperature in the engine cooling system;
- checking temperature sensors;
- pressure control in the engine cooling system;
- checking the voltage of the car battery and generator.
Rice. 2. General view of the installation for replacing coolant
The unit is connected to the vehicle's cooling system in the upper radiator pipe. The coolant is replaced with the engine warmed up and turned off when new coolant is supplied under pressure (0.3 MPa).
The above installation can also be used to replace the coolant in the cooling system of an automatic transmission (AT).
3.1. The main work performed during maintenance of the cooling system
During maintenance of the cooling system, the work described below is performed. EO. Check: the operation of the heating system and glass heating (in the cold season), ventilation system; coolant level in the cooling system.
TO-1. Inspect the tightness of the engine cooling system (including the starting heater), as well as the fastening of equipment and instruments to the engine.
TO-2. In addition to the TO-1 work, check: by inspection the tightness of the heating system and the starting heater; condition and operation of the radiator blind (curtain) drive, thermostat, drain valves; fastening the radiator, its lining, shutters, hood, fan, liquid pump.
SO (seasonal service).
Check the condition and operation of the cooling system valves and drain devices. 034
Coolant circulation diagram
All drivers use coolant in their cars, but not everyone thinks: what is it actually doing there, inside? What exactly is an engine cooling system?
What is a cooling system and why is it needed?
Engine cooling system