The engine cooling system is an important structural element of a car. Its malfunction leads to poor heating of the engine to the required temperature, which causes poor operation of the stove, loss of power and reduced service life of the power unit. On the other hand, the engine system may overheat, which causes breakdown of the cylinder-piston group.
The cooling system of VAZ 21093,2109,21099 removes heat from engine parts subject to heating through forced circulation. And the injector doses the flow of fuel. Structurally, the VAZ injector cooling system consists of:
- coolant pump,
- monoblock thermostat,
- electric radiator fan,
- radiator with expansion tank,
- pipelines, pipes, drain plugs.
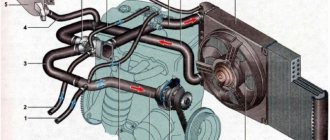
Engine cooling system VAZ-21083
1 – expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank plug; 3 – steam removal hose; 4 – hose from the expansion tank to the thermostat; 5 – radiator supply hose; 6 – radiator outlet hose; 7 – left radiator tank; 8 – aluminum radiator tubes; 9 – sensor for turning on the electric fan; 10 – right radiator tank; 11 – drain plug; 12 – radiator core; 13 – electric fan casing; 14 – electric fan impeller; 15 – electric motor; 16 – pump gear pulley; 17 – pump impeller; 18 – camshaft drive toothed belt; 19 – heater radiator outlet pipe; 20 – pump supply pipe; 21 – tap; 22 – heater radiator; 23 – hose for draining fluid from the heating of the inlet pipe to the carburetor heating block; 24 – carburetor heating block; 25 – exhaust pipe; 26 – heater supply pipe; 27 – hose for draining fluid from the heating of the inlet pipe and the carburetor heating unit; 28 – coolant temperature indicator sensor; 29 – thermostat.
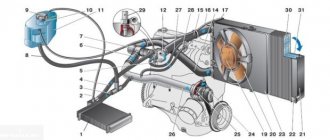
VAZ-2111 engine cooling system (with fuel injection system)
1 – expansion tank; 2 – plug; 3 – steam removal hose; 4 – hose from the expansion tank to the thermostat; 5 – coolant temperature sensor in the outlet pipe; 6 – throttle unit; 7 – radiator supply hose; 8 – radiator outlet hose; 9 – left radiator tank; 10 – right radiator tank; 11 – drain plug; 12 – radiator core; 13 – electric fan casing; 14 – electric fan impeller; 15 – electric motor; 16 – pump gear pulley; 17 – pump impeller; 18 – camshaft drive toothed belt; 19 – heater radiator outlet pipe; 20 – pump supply pipe; 21 – tap; 22 – heater radiator; 23 – coolant drain hose from the throttle pipe; 24 – coolant supply hose to the throttle pipe; 25 – coolant temperature indicator sensor; 26 – exhaust pipe; 27 – heater supply pipe; 28 – thermostat; 29 – coolant level sensor.
What should the temperature be?
The temperature arrow tends to the red zone - soon overheating
According to the international automobile convention of December 1, 1992, where 92 representatives of the auto industry gathered, it was decided to establish a single standard for engine operating temperature.
This indicator is 90 degrees Celsius with a maximum permissible deviation of no more than 3 degrees Celsius.
With the development of the automotive industry and a sharp leap in technology in the 2000s, in 2004 it was decided to revise this indicator. So, having considered all the facts and analyzed the design features of many cars, it was decided to establish a floating indicator with marginally acceptable standards, which, today, is 85-105 degrees Celsius.
Operating range on the VAZ-2114
If we consider cars produced at the AvtoVAZ plant, including the VAZ-2114, then the operating temperature range for engines is considered to be 87-103 degrees Celsius. If we consider this issue from the point of view of functionality, then this is the optimal indicator.
If the temperature drops below the limit level, then the Samara-2 engine loses dynamics and power, and if it is higher, it can simply boil and cause great damage. Therefore, if malfunctions associated with the cooling system occur, they must be eliminated as soon as possible.
Cooling system design
Before considering cooling system malfunctions, as well as methods for eliminating them, novice motorists should study the cooling system.
So, let's look at what elements it consists of:
Cooling system design
1 – element in the form of a plug for the expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank; 3 – hose for draining liquid from the pipe; 4 – hose passing between the radiator and the expansion tank; 5 – hose leading from the radiator; 6 – tank to the left of the radiator; 7 – aluminum tube; 8 – plug systems; 9 – tank to the right of the radiator; 10 – drain plug; 11 – middle of the radiator; 12 – casing for electric fan; 13 – plastic wings of the electric fan; 14 – electric motor; 15 – toothed pump pulley; 16 – pump impeller; 17 – camshaft drive belt; 18 – engine block; 19 – pump pipe; 20 – radiator hose with supply function; 21 – heater radiator hose with drain function; 22 – hose supplying coolant to the throttle pipe; 23 – exhaust pipe; 24 – hose for refilling; 25 – heater radiator hose with supply function; 26 – thermostat; 27 – coolant temperature sensor; 28 – coolant level indicator sensor.
Main malfunctions and ways to solve them
The operating temperature of the engine is directly affected by the health of the cooling system.
Almost every node can affect changes in this indicator in both directions, so it is necessary to monitor its serviceability and prevent changes. It is temperature fluctuations that can lead to breakdowns of other engine systems. So, let's look at the components of the cooling system, their malfunctions and solutions.
Cooling radiator
Dirty engine radiator
The radiator is considered one of the most reliable parts. There are not many reasons that can lead to product failure, but they can be prevented. A clogged part can lead to an increase in engine operating temperature, but regular cleaning of the internal and external surfaces will bring it back to normal.
The formation of cracks can cause the radiator to leak, but this problem can be dealt with. There are two methods to solve the problem: soldering the surface or replacing the product completely. Thus, repair and restoration work normalizes the operation of the part, as well as the operating temperature in the system.
Pipes
Dirt and rupture of the SOD pipe can lead to a change in the operating temperature of the motor
The cooling system pipes can directly affect the temperature increase in the system. This is due to the fact that if cracks or delaminations form in them, it may happen that the coolant begins to leak out. In turn, the lack of “cooling” will lead to an increase in temperature, which can affect both the operation of the main power unit and increased wear.
Water pump
Leaks on the cylinder block from the timing side indicate that the pump has failed
The water pump or water pump should drive coolant through the system , but if this unit breaks down, low pressure can lead to slow cooling, which in turn will increase the operating temperature of the engine. Often, the water pump will simply leak and driving the car will no longer be possible.
The fault can be easily treated by replacing the part.
Thermostat
Thermostat operation diagram at different temperatures
Description of design
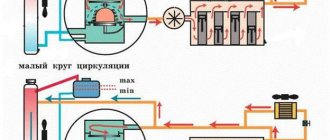
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. The tightness of the system is ensured by the inlet and outlet valves in the expansion tank plug. The exhaust valve maintains pressure in the system when the engine is hot (due to this, the boiling point of the liquid increases and steam losses are reduced), it opens at a pressure of about 1.1 kgf/cm2. The intake valve opens when the pressure in the system decreases relative to atmospheric pressure by 0.03–0.13 kgf/cm2 (on a cooling engine). The thermal operating conditions of the engine are maintained by a thermostat and an electric radiator fan.
The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by a camshaft drive timing belt. The pump housing is aluminum. The roller rotates in a double-row bearing with a “lifetime” supply of lubricant. The outer ring of the bearing is locked with a screw. A toothed pulley is pressed onto the front end of the roller, and an impeller is pressed onto the rear end. The distance from the mating surface of the pump cover to the outer end of the pulley should be 52±0.5 mm, and to the outer (facing the block) end of the impeller - 39.8±0.1 mm. A thrust ring made of a graphite-containing composition is pressed to the opposite end of the impeller, under which there is an oil seal. If the pump fails, it is recommended to replace it as an assembly.
The redistribution of liquid flows is controlled by a thermostat with a solid heat-sensitive element. On a cold engine, the thermostat valve closes the pipe leading to the radiator, and the liquid circulates only in a small circle (through the thermostat bypass pipe), bypassing the radiator. On VAZ-2108, -21081, -21083 engines, the small circle includes the heater radiator, intake manifold, carburetor throttle assembly heating unit (on engines with semi-automatic starting - and the liquid chamber of the semi-automatic starting device). On the -2111 engine, fluid is supplied to the heater and the throttle assembly heating unit.
The principle of operation of cooling VAZ 21093,2109,21099
The cooling pump drive is driven by the timing belt. The total volume of the system, including the stove, is 7.8 liters. Temperature control is carried out using a sensor installed on the cylinder block jacket. The temperature indicator is displayed on the instrument panel.
During operation of the VAZ engine, liquid from the block jacket passes into the radiator (where heat is removed) or into the thermostat (short circuit - to warm up the engine). Next, the liquid is pumped into the cooling jacket of the VAZ injector power unit. The pipelines circulate and heat the fuel mixture in the intake manifold and throttle valve area.
The cooling system communicates through pipes with the radiator of the interior heater of VAZ 21093,2109,21099. The coolant pump is centrifugal. The system is equipped with a collapsible tubular plate radiator with plastic tanks.
The internal surface of the radiator is increased by using aluminum tubes and cooling plates; it does not have a filler hole; topping is done in the expansion tank. Which also has a sensor for turning on the electric fan. The tank has a filler plug with valves (inlet and outlet). To drain the cooling liquid from the system, unscrew the drain plugs of the tank, cylinder block, and radiator.
System operation
The VAZ engine cooling system injector is required to maintain normal operating conditions inside the unit. When the motor and parts located next to it overheat, there is a risk of their partial destruction; cooling prevents this. Of course, the system does not guarantee a strong decrease in the temperature inside the unit, but its resource is quite enough to maintain the operation of the “nine”. The VAZ 2109 cooling system circuit works by distilling a special liquid through tubes placed between the car parts. As the liquid passes through hot areas, it partially reduces the temperature of the parts and heats up itself. The heated liquid is then cooled, after which the operating cycle is repeated. Now in more detail about the structure of the cooling system. It looks like this:
- pipes of the VAZ 2109 cooling system, connecting the cooling fluid (coolant) storage tank, engine and radiator;
- radiator - a device in which the coolant is cooled;
- liquid storage tank;
- pump - ensures the movement of coolant inside the system;
- a thermostat that divides the system into 2 separate circuits.
In addition, there are several small tubes that connect some parts to each other, operation sensors and various valves. Here's how it all works:
- Engine cooling begins when the temperature of the unit reaches 93ºС. A sensor inside the cylinder block measures the ambient temperature and gives a signal when the indicator reaches the limit values.
- The pump starts working, forcing the liquid to move along the lines. First, the liquid leaves the cylinder block jacket and, already heated, is directed to the radiator.
- Reaching the radiator, the coolant is distributed into several flows, filling the thin radiator tubes (thanks to this design, cooling occurs faster).
- The fan turns on, and air flows cool the coolant, after which it leaves the system through another channel and again goes to the cylinder block jacket.
- The cycle repeats.
- When warming up the engine, a small circuit is used, in which a thermostat is built-in, the principle is the same, but everything happens much faster.
The volume of the system tank is 7.8 liters; if repair of any cooling element is required, the tank is emptied. Regular maintenance and fluid replacement should be carried out regularly - every 3 months. It is recommended to use antifreeze or other brands of antifreeze as a coolant.
Features of the fan and thermostat VAZ 21093,2109,21099
The electric fan includes an electric motor and a four-blade impeller, the blades of which have a variable angle of inclination and pitch to reduce noise levels. To increase efficiency, the VAZ fan system is equipped with a casing attached to brackets.
The electric fan is mounted on rubber bushings. The fan is triggered by a signal from a sensor installed in the radiator tank. In this case, the contact closure temperature is approximately 99'C, and the fan shutdown temperature is 94'C.
The system thermostat provides priority warming up of the engine and regulates the thermal regime. The optimal coolant temperature is within 90-98'C. The thermostat includes a body and a cover, rolled together with the valve.
Features of the VAZ injector cooling system
Cooling in cars 21093,2109,21099 is liquid, but you need to understand that the radiator is cooled by the flow of incoming air and a fan, which increases the cooling intensity. Also, part of the heat is removed by the car's interior heater radiator at low temperatures.
The expansion tank is designed to compensate for the volume of liquid when heating, to top up and control the level of antifreeze.
The thermostat system provides temperature control, preheating of the VAZ engine, initial heating of the interior in winter, and only then ensures the inclusion of a large cooling circuit.
The temperature sensor provides control of the cooling system, allows you to monitor the engine temperature and regulate the operation of the fan.
The entire operating cycle of the cooling system is controlled using a power unit control system that takes into account all temperature parameters. It determines the optimal switching conditions and operating time of the structural elements of the system.
Diagnostics of the VAZ 21093,2109,21099 engine cooling system and fault detection
If problems arise with the engine cooling system, the causes should be determined, starting with the most probable and simple ones:
- If there is a coolant leak, first check the fluid level in the system. In cars 21093,2109,21099 this is done using the level indicator or when inspecting the expansion tank.
- If the level has changed, inspect the engine compartment for leaks. As a rule, the main reasons are: worn pipes and clamps, damaged engine cooling radiator or heater.
- In case of jet changes in the tank at 3000 rpm. It is necessary to check the fluid circulation. To do this, open the cap of the expansion tank and determine the uniformity of antifreeze flow. The causes of poor circulation may be a clogged system or a malfunction of the circulation pump.
Antifreeze boils in the expansion tank: causes of the problem and ways to fix it
For proper and efficient operation of the internal combustion engine of a car, antifreeze is used, which is designed to cool the engine . Antifreeze or antifreeze, as a solution, has a higher boiling point and a lower freezing point compared to ordinary water, however, in some cases, this liquid, unable to withstand loads, is capable of boiling directly in the engine cooling system.
Every motorist sooner or later encounters this problem and immediately wants to know why the antifreeze is boiling in the expansion tank. There can be quite a lot of reasons.
Causes of VAZ engine overheating
- A faulty thermostat can cause the engine to overheat. If on a warm engine the upper pipe is hot and the lower pipe is cold, the thermostat is jammed and the antifreeze flows only in a small circle. Or the thermostat will only turn on a large circle, which will not allow the VAZ engine to warm up to the required operating temperature. In this case, the thermostat should be replaced.
- Another reason for excessive engine heating may be airing of the cooling system; in this case, the system must be pressed and air removed from all cavities.
- At high temperatures, the fan does not turn on - there is a problem with the temperature sensor, fan relay or the wiring harness to it.
- Sometimes the radiator honeycombs become clogged, which sharply reduces the intensity of heat transfer. It is necessary to thoroughly clean the radiator; it must be done carefully to avoid damage to the cells.
These are the main reasons that affect the quality operation of the VAZ 21093,2109,21099 engine cooling system; with their help, you can identify and eliminate malfunctions, ensuring reliable and durable operation of the engine.
Useful tips
For the purposes of this article, we note that antifreeze can not only boil, but also foam. At the same time, the temperature of the antifreeze does not increase. This happens when:
- air entering the expansion tank;
- low-quality antifreeze;
- mixing antifreeze from different manufacturers;
- using coolants not recommended by the car manufacturer due to different chemical compositions;
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket. Then it allows air to pass through, and when it enters the cooling system, it forms foam.
It must be taken into account that minor foaming is acceptable, but if there is a large amount, it is necessary to flush the cooling system and replace the antifreeze with a higher quality one.
We also recommend reading an article about what consequences can occur for the engine if antifreeze gets into the engine cylinders. From this article you will learn about the reasons why antifreeze or antifreeze gets into the cylinders, as well as what this leads to.
Antifreeze has its own service life and with its long-term use the chemical composition changes and the cooling properties decrease. This fluid must be replaced with a new one; replacement is carried out with flushing.