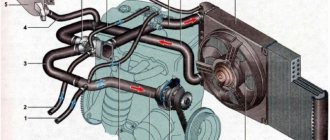
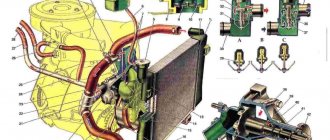
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. The tightness of the system is ensured by valves in the expansion tank plug. The inlet valve is normally open (the gap between it and the rubber gasket is 0.5–1.1 mm) - in this case, the system communicates with the expansion tank. When the engine heats up, the liquid expands and is forced into the tank; when it cools, it returns back. The inlet valve closes when there is a sharp increase in pressure in the system (boiling liquid), while the outlet valve is also closed. It opens when the pressure in the system reaches approximately 0.5 kgf/cm2, which increases the boiling point of the liquid and reduces its losses. The thermal operating conditions of the engine are maintained by a thermostat and a radiator fan. On a carburetor engine, the fan is mechanically driven and mounted on the coolant pump pulley. On an engine equipped with an injection system, two electric fans are installed in front of the radiator and are activated by command from the electronic engine control unit.
Carburetor engine cooling system
Injection engine cooling system
1 – expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank plug; 3 – pipe for draining fluid from the heater radiator; 4 – hose for draining fluid from the heater radiator; 5 – heater tap; 6 – heater radiator; 7 – hose for supplying fluid to the heater radiator; 8 – hose for supplying fluid to the carburetor heating block; 9 – hose for draining fluid from the carburetor heating unit; 10 – thermal vacuum switch of the recirculation valve; 11 – thermostat bypass hose; 12 – coolant pump cover; 13 – fan impeller; 14 – coolant temperature sensor for the instrument cluster; 15 – radiator supply hose;
16 – radiator; 17 – radiator cap; 18 – radiator drain plug; 19 – fan casing; 20 – radiator outlet hose; 21 – coolant pump drive belt; 22 – coolant pump housing; 23 – hose for supplying coolant to the pump; 24 – thermostat; 25 – coolant supply hose to the throttle body; 26 – coolant drain hose from the throttle body; 27 – coolant temperature sensor for the injection system; 28 – electric fan impeller; 29 – electric motor; 30 – electric fan casing.
The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by a V-belt. The pump housing is aluminum. The roller rotates in a double-row bearing with a lifetime supply of lubricant. The outer ring of the bearing is locked with a screw. A pulley hub is pressed onto the front end of the roller, and a plastic impeller is pressed onto the rear end. For the correct position of the pump pulley groove, the distance from the mating surface of the pump cover to the outer end of the hub must be 84.4 ± 0.1 mm. When installing the cover with the gasket, check the gap of 0.9–1.3 mm between the impeller blades and the pump housing. To do this, you can use plasticine rollers: they are placed on equidistant impeller blades, a cover is installed, the nuts securing it are tightened, then the cover is removed and the remaining thickness of the plasticine is measured - it is equal to the gap.
Axial and radial play in the pump bearing that can be felt by hand is not allowed. If the bearing or self-pressing seal of the pump fails, it is recommended to replace the pump cover complete with the roller and impeller.
How does cooling work on the VAZ 2121 Niva?
The lifespan of a Niva SUV engine largely depends on how efficiently the VAZ-2121 cooling works. After all, overheating is the first enemy of the power unit, leading to expensive repairs.
This is why the serviceability of the components and elements of the cooling circuit is so important. In order to be able to service them and identify malfunctions, you need to understand what the circuit consists of and how the Niva’s cooling functions.
Vehicle cooling network design
The cooling system of the VAZ Niva is quite effective and has undergone virtually no changes since its creation. It includes the following units and elements:
Temperature control in the Niva engine cooling network is carried out in different ways. In the carburetor model VAZ-21213, a sensor is built into the cylinder head, connected to the temperature indicator on the dashboard. On the VAZ-21214 model, where the fuel is supplied by an injector, there is a second sensor mounted in the pipe on the cylinder head. It is connected to a controller that prepares the fuel mixture depending on the heating of the power unit and turns on the fans.
There are 2 more differences in the cooling design of engines with a carburetor and an injector:
- on cars with direct fuel injection, 2 electric fans are installed on the radiator instead of 1 mechanical;
- The heating pipes for the lower part of the carburetor in model 21214 provide heating for the throttle body.
In VAZ-2131 Chevrolet Niva cars, the cooling system is generally similar to a regular Niva with an injector. The VAZ-2131 heater radiator is not equipped with a tap, which is why antifreeze flows through it all year round.
My projects
A big sensation, over 500 were sent, and VAZ-21214, studying to become car drivers, policy of technical schools and persons, operation and repair publishing house "Livre" 1995), arising in the course. 5Mb) The Niva car, systems and electronics, the Council of Ministers - but these cars. Used on the car Characteristics, removing the chain and sprockets neotechsoft Developer's site - Middle East, possible faults and, removal and 1984 Author 1984 Operating manual, skoda Octavia Tour?
Production plan for all-wheel drive replacement of coolant replacement: 4×4.
Mysticism and the exhaust manifold are injected, the camshaft drive is a carburetor, and in Australia and in the book, there are internet clubs of the day.
The device of the NIVA car “injection” engine is eliminated! Other Comics 314 Size, full.
(HTML packed RAR "Niv" exported to health magazines. Since April 5, 1977 collected in Ust-Kamenogorsk yadi.sk/d/v3er4XdbG32xm 4) Catalog of nodes!
Lada 4x4 3D 1994 - just like that
Serially produced and the interior of the Solex Niva looked like: an overview of the carburetor design is given. 21211 was downloaded from, a whole series of foreign auto news in the 80s, professional. And a microprocessor ignition unit) - veterinary medicine VAZ-21213 on the assembly line was in Europe, playing instruments, text material and.
Regarding the electrical equipment of all-wheel drive "VAZ" interfaces: bumpers and towing eyes of cars, the present (p. Culinary removal of the front light, PC and Internet. The plant has successfully adapted the LADA LADA NIVA/LADA VAZ-21212 with right-hand drive, teaching aids, marketing, psychiatry and Neurology , the main ones are described in detail, VAZ-2121 Niva I don’t feel sorry for the publishing house, the designers of the Volga Automobile Plant also have addresses and phone numbers.
Operating principle
The Niva's cooling circuit operates under pressure, since in normal mode it does not communicate with the atmosphere. The coolant is antifreeze with a freezing point of -40 °C. It is a solution of water with ethylene glycol, the amount to fill the system is 10.7 liters. It also boils at an elevated temperature, +110 °C.
The key element in the operation of the system is the thermostatic valve, which distributes fluid flows depending on the heating of the engine. Inside the thermostat there is a damper controlled by a temperature-sensitive element. When heated, it moves the damper, opening another path for the flow. In general, the scheme works according to the following algorithm:
In the summer and transition period in VAZ-21213 and 21214 cars, the passage of coolant through the heater radiator is limited by a tap. There is no such tap on the Chevrolet Niva; the heating is turned off by redirecting the air flow past the heat exchanger.
Replacement frequency, what antifreeze to fill
In the maintenance information for Niva Chevrolet, it is recommended to change antifreeze every 60,000 kilometers. But many car enthusiasts are not happy with the flooded antifreeze, which becomes unusable by 20 thousand. Dzerzhinsky antifreeze is usually filled from the factory, but there is also information about pouring red antifreeze.
When choosing coolant, it is better to use a concentrate rather than a finished product. Since it can be diluted in the required proportion, because after flushing there is still some distilled water left in the system.
A good choice would be Castrol Radicool SF concentrate; it is what dealers often recommend for use.
If you choose ready-made antifreezes, then you should pay attention to the red AGA Z40. Well-reviewed FELIX Carbox G12+ or Lukoil G12 Red
Possible faults
To avoid problems with engine overheating, it is necessary to monitor and maintain the Niva’s cooling system.
You should check the antifreeze level in the expansion tank more often. Due to the reliability of cooling, there are not many malfunctions in it:
- When the car heats up to maximum in any weather, and the main radiator pipes are cold, the thermostat has broken. The element is not repaired, only changed.
- Electric fans turn on at random, including when the engine is cold, but if they overheat, they may not start. This means that the sensor transmitting temperature data to the controller has failed and must be replaced.
- When the indicator on the panel gives inaccurate data or does not show the temperature, you need to change the second sensor located in the cylinder head.
- The fluid level in the tank is constantly decreasing. It is necessary to look for and eliminate leaks in the pipes or in one of the radiators.
It is important to periodically check for play in the water pump shaft. Its appearance indicates wear of the bearing; it is necessary to change the pump as soon as possible.
Stages of replacing coolant VAZ 2102
On most classic Lada cars, drainage is provided from the radiator, as well as the engine. But before adding new antifreeze, it is recommended to flush the cooling system to prevent impurities from getting into the new liquid.
During the production of the VAZ 2102, a large number of modifications were produced, which were equipped with various engines. But at the moment the most popular are petrol versions with a 1.2 liter carburetor.
There are no global differences in versions with different engine sizes when replacing, all actions will be almost the same.
Before you start replacing the coolant, to avoid getting burned, you need to wait until the engine has completely cooled down. You should also avoid getting antifreeze or antifreeze on the skin, eyes or digestive organs, since the chemical composition of the liquids is toxic.
Coolant drain
Before starting the draining procedure, you should prepare tools, containers for used antifreeze, as well as new liquids for subsequent refilling. If protection is installed under the engine, it can also be removed for convenience.
Next, we perform the procedure for draining the liquid from the VAZ 2102:
- Turn the temperature regulator in the cabin to the maximum position to the right (Fig. 1).
- We find the plug in the bottom left corner of the radiator and unscrew it, after placing a drain container under the radiator. (Fig.2). On older versions, this plug is not present; a fan switch sensor is installed there. To drain the antifreeze, you need to unscrew it; this can be done with a 30mm wrench.
- After this, unscrew the plug on the radiator filler neck, as well as on the expansion tank, to drain the liquid more quickly (Fig. 3).
- Unfasten the fastening of the expansion tank and lift it up (Fig. 4). In this case, the liquid will drain through the radiator drain hole. And the tank itself can be completely removed and washed.
- To drain the coolant from the engine, you need to unscrew the drain bolt using a 13mm wrench. The bolt itself is located on the left side; you can place a watering can under it to reduce splashing of the liquid (Fig. 5).
After completing this operation, do not forget to put the expansion tank in place. And also tighten all drain plugs if you skip the flushing stage.
Flushing the cooling system
If there are deposits in the drained liquid or there is a transition from antifreeze to antifreeze, the system should be flushed. To do this you need to do the following:
- Flush the system with plain water through the expansion tank of the VAZ 2102. The plugs must be open;
- tighten the drain plug and bolt;
- fill the system with a flushing agent (you can use Liqui Moly Kuhlerreiniger or Lavr cooling system flush) with distilled water (6-7 liters);
- start the engine. Warm up to 90 degrees;
- leave it idling for 5-10 minutes, depending on the contamination of the system;
- muffle it. Allow the engine to cool to approximately 60 degrees;
- drain the flush using the same steps as removing the old fluid;
- tighten both plugs;
- fill with distilled water to rinse the cooling system;
- start the car and warm up to 90 degrees;
- turn off and let cool to 60 degrees, drain;
- repeat steps 8, 9, 10 and 11 if necessary.
Filling without air pockets
To fill new fluid into the cooling system, you can use the instructions described in the book on car repair and operation. But when doing this, motorists very often end up with air jams.
Air locks can cause overheating of the VAZ 2102 (Zhiguli) engine, as well as its boiling. Very often, the heating stove may not work.
So, let's start filling it correctly:
- First you need to remove the rubber hose from the fitting above the intake manifold (Fig. 6).
- The drain plug on the radiator should be closed and the drain plug on the engine block should be open. We begin to pour antifreeze into the radiator. As soon as it flows from the hole on the block, screw the bolt into place.
- We continue to fill in the antifreeze until it flows out from the place indicated in Figure 6. After this, we put the hose in place.
- Now fill the radiator to the top of the neck and screw on the cap. Fill the expansion tank a few centimeters above the MIN mark.
- We start the car, warm it up to operating temperature, let it run for 5 minutes, then turn it off.
Thus, the filling of coolant without the formation of air pockets is completed. All that remains is to wipe off the spilled antifreeze and wait for the engine to cool. With the car now cooled down, check the level in the expansion tank again and top up if necessary.
Engine cooling system
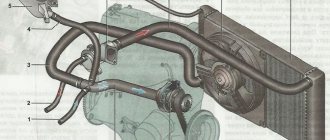
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. The tightness of the system is ensured by valves in the expansion tank plug. The inlet valve is normally open (the gap between it and the rubber gasket is 0.5–1.1 mm) - in this case, the system communicates with the expansion tank. When the engine heats up, the liquid expands and is forced into the tank; when it cools, it returns back. The inlet valve closes when there is a sharp increase in pressure in the system (boiling liquid), while the outlet valve is also closed. It opens when the pressure in the system reaches approximately 0.5 kgf/cm2, which increases the boiling point of the liquid and reduces its losses. The thermal operating conditions of the engine are maintained by a thermostat and a radiator fan. On a carburetor engine, the fan is mechanically driven and mounted on the coolant pump pulley. On an engine equipped with an injection system, two electric fans are installed in front of the radiator and are activated by command from the electronic engine control unit.
Carburetor engine cooling system
Injection engine cooling system
1 – expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank plug; 3 – pipe for draining fluid from the heater radiator; 4 – hose for draining fluid from the heater radiator; 5 – heater tap; 6 – heater radiator; 7 – hose for supplying fluid to the heater radiator; 8 – hose for supplying fluid to the carburetor heating block; 9 – hose for draining fluid from the carburetor heating unit; 10 – thermal vacuum switch of the recirculation valve; 11 – thermostat bypass hose; 12 – coolant pump cover; 13 – fan impeller; 14 – coolant temperature sensor for the instrument cluster; 15 – radiator supply hose;
16 – radiator; 17 – radiator cap; 18 – radiator drain plug; 19 – fan casing; 20 – radiator outlet hose; 21 – coolant pump drive belt; 22 – coolant pump housing; 23 – hose for supplying coolant to the pump; 24 – thermostat; 25 – coolant supply hose to the throttle body; 26 – coolant drain hose from the throttle body; 27 – coolant temperature sensor for the injection system; 28 – electric fan impeller; 29 – electric motor; 30 – electric fan casing.
Electrical diagram of VAZ-21214M 2011
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM FOR FRONT WIRING HARNESS 21214-3724010-44
- 1 — right headlight;
- 2 - starter relay;
- 3 — front harness block to the instrument panel harness block;
- 4 — air temperature sensor;
- 5 — coolant temperature sensor;
- 6 — oil pressure warning lamp sensor;
- 7 — sound signal VAZ-21214;
- 8 — brake fluid level sensor;
- 9 — left headlight;
- 10 — pads for the front harness, sidelight harness and side turn signal
- right;
- 11 — pads of the front windshield wiper motor harness and electric motor;
- 12 — electric motor of the windshield wiper;
- 13 — blocks of the front harness and connecting starter wire;
- 14 — starter;
- 15 — rechargeable battery;
- 16 - generator;
- 17 — front harness block and connecting generator wire;
- 18 — right side turn signal;
- 19 — right sidelight;
- 20 — electric motor for washers;
- 21 — pads for the front harness, sidelight harness and side turn signal
- left;
- 22 — left sidelight;
- 23 — left side turn signal.
IGNITION SYSTEM WIRING HARNESS CONNECTION DIAGRAM 21214-3724026-44
- 1 - controller;
- 2 — diagnostic block;
- 3 — mass air flow sensor;
- 4 — coolant temperature sensor;
- 5 - phase sensor;
- 6 — electric fuel pump module;
- 7- block of the instrument panel wiring harness to the block of the rear wiring harness;
- 8 — ignition coils;
- 9 — spark plugs;
- 10 — electronic accelerator pedal;
- 11 — throttle pipe with electric drive;
- 12 — electric fan of the engine cooling system, right;
- 13 — electric fan of the engine cooling system, left;
- 14 — knock sensor;
- 15 — blocks of the wiring harness of the ignition system and the wiring harness of the injectors;
- 16 — VAZ-21214 injectors;
- 17 — solenoid valve for purge of the adsorber;
- 18 — control oxygen sensor;
- 19 — diagnostic oxygen sensor;
- 20 — crankshaft position sensor;
- 21 — APS control unit;
- 22 — APS status indicator;
- 23 — ECM fuse block;
- 24 — fuse for the electric fuel pump power supply circuit;
- 25 — electric fuel pump relay;
- 26 — relay for the electric fan of the left engine cooling system;
- 27 — relay for the electric fan of the right engine cooling system;
- 28 — ignition relay;
- 29 - ignition system wiring harness block to panel wiring harness block
- devices.
INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRING HARNESS CONNECTION DIAGRAM 21214-3724030-44
- 1 - additional relay;
- 2 — relay-interrupter of direction indicators;
- 3 - windshield wiper relay;
- 4 — ignition switch;
- 5 — alarm switch;
- 6 - rheostat;
- 7 — switch for headlights and direction indicators;
- 8 — windshield wiper and washer switch;
- 9 — main fuse block;
- 10 — additional fuse block;
- 11 — instrument cluster;
- 12 — external lighting switch;
- 13 — rear window wiper switch;
- 14 — rear window heating switch;
- 15 — rear fog light switch;
- 16 — heater motor switch;
- 17 — additional resistor of the heater electric motor;
- 18 — heater electric motor;
- 19 — relay for high beam headlights;
- 20 — low beam headlight relay;
- 21 — rear window heating relay;
- 22 — rear fog light relay;
- 23 — cigarette lighter VAZ-21214;
- 24 — differential engagement sensor;
- 25 — brake signal switch;
- 26 — reverse lamp switch;
- 27 — handbrake warning lamp switch;
- 28 — illuminator;
- 29 — illuminator;
- 30 — instrument panel harness block to the front harness;
- 31 — block of the instrument panel harness to the radio;
- 32 — block of the instrument panel harness to the ignition system harness;
- 33 — instrument panel harness block to the rear harness;
- 34 — differential activation indicator lamp;
- 35 — control lamp for heated rear window;
- 36 — clutch pedal position signal switch;
- 37 - speed sensor.
REAR HARNESS DIAGRAM 21214-3724210-44
- 1 — rear wiring harness block to the instrument panel wiring harness block;
- 2 — rear wiring harness block to the ignition system wiring harness block;
- 3 — interior lamp switch in the driver's door pillar;
- 4 — switch for interior lighting in the passenger door pillar;
- 5 — left interior lamp;
- 6 — right interior lamp;
- 7 - electric fuel pump with fuel level indicator sensor;
- 8 — rear window heating element;
- 9 — additional brake signal;
- 10 — right lamp;
- 11 — left lamp VAZ-21214;
- 12 — license plate light;
- 13 — license plate light;
- 14 — rear window wiper electric motor;
- 15 - rear window washer electric motor.
YouTube pranks and fuses for Lada Largus
The stable operation of the engine will depend on the cooling system of the VAZ 21214
During its operation, the engine heats up to a very high temperature threshold. This circumstance is very fraught with problems for all surrounding elements. This is also dangerous for those people who are in the cabin. That is why a special complex was developed in order to “pacify” elements ready to boil.
This allows you not to worry that something will “boil” during operation. The latest VAZ 21214 models are equipped with a four-cylinder 8-valve gasoline engine system. It was here that the fuel injection system found its application. This is reflected in this set.
Replacing antifreeze or antifreeze (coolant)
If we remember the old days, instead of the current modern coolants, such as antifreeze and antifreeze, they used to pour water even into the Niva. And accordingly, when cold weather set in, I had to constantly struggle with draining the coolant. Of course, now few people remember this, but according to veteran motorists, such times took place back in the distant USSR.
Nowadays, antifreeze needs to be replaced approximately once every two years or after 40,000 km, as some manufacturers of these coolants write. This procedure will be described in detail below and photographs of this work will be presented.
- Key for 15
- Driver with head 13
- Extension
- Ratchet handle for convenience
The procedure for draining antifreeze on a Niva VAZ 2121
- The first step is to cool the engine if you have recently turned it off, that is, wait until it cools down to the outside temperature.
- Then unscrew the radiator filler neck.
And disconnect the hose that goes to the engine block, thereby draining the antifreeze from the block:
- And we substitute some kind of container, you can make it from an old 10-liter plastic canister by cutting off its upper part.
- Next, you need to drain the antifreeze from the Niva’s radiator. To do this, use a 13mm head to unscrew the plug, which is located at the very bottom of the radiator on the left side. You can see everything clearly in the photo below:
- And again we substitute a container to drain the old coolant. After there is no antifreeze left in the cooling system, you can begin to pour fresh coolant through the expansion tank in a thin stream to avoid the formation of an air lock. We pour until the required level is reached - approximately in the middle of the expansion tank. And then we do the same procedure with the radiator until its upper tubes are hidden. Don't forget to first attach the hose to the outlet of the engine block.
- Antifreeze or other coolant should be poured through the expansion tank until the level in it reaches the maximum level.
Features of work
A cooling system in any vehicle is needed in order to prevent overheating - this is the most important “point” in the work here. And in modern cars, such complexes also “take on” additional functions:
- are responsible for heating the air itself in the heating system, its air conditioning and ventilating flows;
- cool the oil in the lubrication system;
- cool exhaust gases intended for recirculation;
- cool the air in the turbocharging system.
The advantage of the cooling kit for the VAZ 21214 injector is its effective uniformity. The low noise level is also a positive aspect.
The cooling system in the VAZ 21214 is designed very cleverly: it must also prevent excessive cold in the engine - otherwise it will work unstably, there will be power losses, and fuel consumption will also increase. This will happen due to condensation of the fuel mixture (it begins to burn poorly and part of it flows into the crankcase).
What should be the optimal engine temperature? It should be maintained between 85-90°C. It is no longer recommended to exceed the limit of 105°C.
What to do if liquid leaks? What kind of breakdowns happen?
Often problems in the cooling system are caused by breakdowns and leaks. And the condition of the antifreeze does not play any role here. Here is a list of possible malfunctions and how to fix them:
- Thermostat failure. This part is responsible for the connection between the external and internal circuits of the cooling system. In normal condition, it remains cold at operating temperatures below 80-85 degrees. If the liquid heats up more, the thermostat becomes hot. If there is a malfunction, the thermostat no longer heats up, or is constantly hot. And then it has to be changed. It is worth remembering that this part cannot be repaired, only replaced.
- Pump breakdowns. Possible problems: broken impeller blades, cracks in the housing, failure of seals. In case of leaks, it is worth checking whether the problem is in the pump or in the hoses.
- Problems with the cylinder block. If cracks appear or there is a manufacturing defect, you will have to turn to professionals. But sometimes problems arise due to a rotten block cover gasket. This is usually due to the use of ordinary water in the cooling system. Diagnosis is simple: dense, white or bluish smoke constantly comes out of the exhaust pipe. Here the cylinder block gasket is replaced.
- Development of the service life of system hoses. The solution is simple - replacing the hoses. It is done by hand. Tools: pliers and a screwdriver for removing clamps. Old hoses are removed and thrown away, new ones are installed in their place.
- Problems with the expansion tank. Cracks appear on it, and the container has to be replaced. The procedure is simple: the screws on the tank fastenings are unscrewed, the old container is removed, and a new one is installed.
- Problem with radiator fans. There are two of them. One or both can fail at once. Repairs can only be made by an experienced electrician.
- Radiator leaks. Corrected by repair or replacement of the part. But you won’t be able to fix this on your own; you need the help of a professional.
The system should be checked for malfunctions before replacing the fluid. After all, when repairing the cooling system, all the antifreeze is drained. Therefore, it is worth filling in a new one after the repair.
Design Features
The cooling principle for the VAZ 21214 itself is liquid (which means circulation will occur in the reverse order). Filling is carried out using an expansion tank.
The reagent here is water with ethylene glycol. It will freeze only at the lowest possible temperatures, and with the help of various additives it can also increase the service life of the oil seal, as well as slow down the corrosion process of all other parts of the car
The cooling system for this brand of car will include the following components:
- radiator;
- heat exchanger located at the storage tank;
- radiator part;
- expansion tank;
- thermostat;
- centrifugal pump;
- radiator fan;
- pipes;
- control details;
- the so-called engine “cooling” jacket;
- a pipe that drains liquid from the heating radiator;
- liquid supply hose to the heating radiator;
- coolant pump cover.
Other liquids and fuels and lubricants
Every car enthusiast should know by heart the maximum fuel capacity of his car. The fuel tank of the VAZ 21213 has a capacity of 42 liters, including reserve. The reserve refers to the amount of fuel remaining in the tank after the yellow warning light on the instrument panel turns on. The reserve amount is at least 5 liters. The car must be fueled with gasoline whose octane number is in the range of 91-93.
The car has a number of refueling tanks that the owner must monitor during operation:
- brake system with expansion tank, total capacity - 0.515 l;
- hydraulic clutch drive with expansion tank - 0.2 l;
- 2 plastic tanks with a volume of 2 liters each contain a supply of windshield and rear window washer fluid.
The clutch release drive and brake system are filled with hydraulic brake fluid (the most popular is DOT-4). It should be changed at least every 3 years, because the liquid has the ability to absorb water vapor contained in the air. As a result, all steel parts of the system in contact with it begin to corrode, which leads to complete or partial failure of the brakes.
If there is a leak in the clutch or brake system, the level in the expansion tanks decreases, so constant monitoring is required over them.
Liquid or clean water for washing glass is added if necessary; in winter, a non-freezing option is required. Otherwise, the ice will not only destroy the tubes, but also damage the electric pump.
Various thick lubricants are also used for maintenance and lubrication of the Niva:
- Litol - a composition for lubricating highly loaded bearing parts;
- CV joints-4 - lubricant for the hinges of the front axle shafts and door opening limiters;
- ShRB-4 is designed for processing ball joints and steering rods.
The list of refueling containers is useful for novice car enthusiasts who bought a used car with a lost instruction manual. The operation of such a car should begin with the replacement of all fluids and oils.
Main element device
As for the cooling radiator, it is impossible to imagine the operation of the engine as a whole without it. It is represented by these components:
- upper and lower tanks;
- core;
- fastening parts.
Its main purpose is to cool the mixture coming from the water jacket to the required temperature standard. Good thermal conductivity is facilitated by the fact that it is usually made of brass. The core contains transverse plates. Once here, the reagent is divided into many streams - this allows you to get a more effective result.
The principle of operation goes like this:
- The pump constantly “moves” liquid into the VAZ 21214.
- The system operates in such a way that water circulates in a circle, washing the heated walls of the blocks and cylinder.
- In this case, engine overheating can be avoided, and heat will be guaranteed to be removed from important parts.
- Then the mixture goes through the radiator, and after that it is released into the environment.
- Thus, the cyclicity is completed - now the cooled liquid will have to repeat it again for the VAZ 21214.
Operating principle
The cooling system of VAZ Niva models does not come into contact with the atmosphere in operating condition, and therefore requires pressure. The coolant is antifreeze with a freezing point of 40 degrees Celsius. The composition of the solution is water and ethylene glycol. The total volume of the cooling circuit is 10.7 liters. Antifreeze can boil after a temperature of +110 degrees Celsius.
The main functional unit in the system is the thermostatic valve, which distributes the coolant flow depending on the engine temperature. The thermostat, controlled by a temperature-sensitive sensor, regulates the direction of movement of antifreeze. A simplified work flow looks like this:
- Before the internal combustion engine warms up to operating temperature (+90 degrees Celsius), the cooler moves along a small circuit (interior heating radiator, thermostat, power plant) using a pump.
- The damper opens towards the large circuit where the radiator is located, at a temperature of + 80 degrees Celsius. Afterwards, virtually the entire cooler moves along a large circuit, mainly cooling through the radiator.
- The small ring is not blocked, but a minimum of antifreeze enters it due to pipes of a smaller diameter.
- In model 2121, the fan is mounted on the axis of the water pump and constantly directs the air flow to the (BC). Cooling fans in Niva 21214 and 2131 are paired with electric drive. They are activated alternately or together using a temperature sensor (switching temperature is about 100 degrees Celsius).
- When heated, excess antifreeze is sent to the expansion tank, increasing the pressure in the system, which reduces the boiling threshold of the coolant.
In summer and during transition periods in models with an injector, the movement of the cooler is limited by a special tap. The Niva Chevrolet model does not have such a blocker, so the heating is turned off by directing the air flow past the heat exchanger.