Ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115
Here we consider the ignition coil of VAZ 2114 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115 model 2111-3705010-02 (54.37005) with injection engine 11183 (l,6i). The ignition coil of the VAZ 2114 injection 8 valve engine is described. The diagram of the ignition coil for VAZ 2114, 2113, 2115 is shown. The electrical diagram for connecting the ignition coil for VAZ 2114 injector 8 . Malfunctions of the ignition coil of the VAZ 2114 8 valves are given. Shown is the pinout of the ignition coil for VAZ 2114 injector 8, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115
| Content: | |
| 1 | Description and purpose of the ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves; |
| 2 | The principle of operation of the ignition coil VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115 model 2111-3705010-02; |
| 3 | Explanation of the ignition coil designation (Catalogue number) - 2111-3705010; |
| 4 | Electrical diagram of the ignition coil VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves; |
| 5 | Where is the ignition coil of VAZ 2114 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115; |
| 6 | Analogues of the ignition coil VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115 type 2111-3705010-02; |
| 7 | Pinout of the ignition coil for VAZ 2114 model 2111-3705010-02 (54.37005); |
| 8 | Schematic diagram of engine control with an ignition coil VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves; |
| 9 | Electrical circuit diagram for controlling the propulsion system of model 11183 (l,6i).with ignition coil of brand 2111-3705010-02 (54.37005): |
| 10 | Signs of a malfunctioning ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves, 2113, 2115; |
| 11 | Checking the ignition reel of a VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves; |
| 12 | Replacing the ignition coil on VAZ 2114, 2113, 2115 cars; |
| 13 | Literature on passenger cars VAZ 2114, 2113, 2115 models and their modifications. |
Checking for errors
Checking the ignition device for malfunctions always concerns the location of the wires on the ignition module of the VAZ 2114. For simple diagnostics, we simply measure the resistance between the wires of the first and fourth cylinders and the second and third cylinders with a multimeter. If the indicator is 5.5 kOhm (switch the multimeter to ohmmeter mode!), then everything is in order. There are also other checks:
- The first thing to check is the wiring block; it is better to disconnect it and check it with a multimeter in voltmeter mode: we attach the multimeter probe to pin A, and throw the other one onto the ground of the sliders. We start and look at the voltmeter values: excellent. If the voltage fluctuates around 12 V. If there is no voltage, check the ignition coil fuse, it may blow, as well as the correct connection of all contacts. By the way, about that. Another way of checking can indicate that the circuit of contacts is closed incorrectly: by connecting a tester to both contacts - A and B - connect a multimeter to it; if it blinks, then the circuit is in perfect order.
- It’s worth checking all the high-voltage elements (with the same multimeter in ohmmeter mode); if they are installed incorrectly, the ignition coil will burn out.
- To understand whether the ignition module behaves correctly, move the wire block, you can knock on it. The contact should not disappear, if the engine responds to your movements, the contact is unclear. It can break at any moment.
Description and purpose
Ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115 are two two-output ignition reels mounted in a single casing. It is designed to convert low on-board voltage (12 volts) into high sparking voltage. Sparking occurs in two pots at once (1-4 and 2-3). The ignition solenoid is connected to the spark plugs by high-voltage wires with permanent tips.
Below, in the figure, the design of the ignition coil of the VAZ 2114 8 valves is presented
Functionality check
To accurately determine whether it is time to change the high-voltage wires of the VAZ, you need to check their performance with a multimeter.
This operation will take you no more than 15 minutes:
- Turn off the ignition;
- We remove the wires: disconnect the first end from the ignition module, the second from the cylinder;
- We switch the tester to ohmmeter mode and connect the multimeter probes to the wire contacts.
If the high-voltage wires on the VAZ 2114 are in normal technical condition, the multimeter will show a resistance within the value indicated on the wire insulation; if the readings are different, the armored wires on the VAZ 2114 need to be replaced. The process must be repeated on each wire in turn.
If the test shows disappointing results, there is a possibility that the problem of increased resistance lies in oxidized contacts. In this case, you can try to revive the VVP by wiping the contacts with VD-40 or carburetor cleaning fluid.
Also, the cause of problems with ignition can be a breakdown of the GDP. You can determine it visually in the dark - take a flashlight and open the hood of the fourteenth, find and inspect the armored wires, if you notice a slight spark on the insulation - the air intakes are broken and need to be replaced.
The principle of operation of the ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves, model 2111-3705010-02
The current in the primary windings of the ignition coils is controlled by a controller that uses information about the engine operating mode received from the engine control system sensors. To switch the primary windings of the ignition coils, the controller uses two powerful transistor valves.
From the ignition coil of the VAZ 2114 8 valves, a high voltage pulse is supplied to two cylinders at once: 1 - 4, 2 - 3. In one cylinder the compression stroke ends (working spark), and in the second the exhaust stroke (idle spark) occurs.
Due to the constant direction of current in the primary and secondary windings, the sparking current of one spark plug always flows from the central electrode to the side electrode, and the second - from the side to the central one.
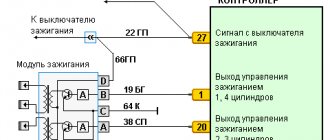
The ignition coil of the VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves works according to the following principle. The vehicle's electrical system voltage is supplied from the ignition switch to contact “15” of the ignition coil. Next, the controller switches the pulse to terminal “1b”, the circuit of the primary winding of the ignition coil, as a result of which the secondary winding outputs high voltage to the spark plugs of cylinders 1 and 4. And the controller switches the pulse to terminal “1a”, the circuit of the primary winding of the ignition coil, as a result which causes the secondary winding to output high voltage to the spark plugs of cylinders 2 and 3.
Possible reasons for failure of the ignition module
Before repairing the main part in, you need to understand the nature of the problem. To do this, the consumer must be aware of the signs of a malfunction, as well as the causes of the breakdown.
The main reasons for device failure
Causes of problems:
- The ignition system uses spark plugs that do not match the vehicle parameters. They may not have the gap specified by the manufacturer. Also, the spark plugs themselves may not be working or dirty; this can be determined by visual diagnostics. If there are traces of carbon deposits on the devices, they must be removed.
- Malfunctions in the operation of the MH can arise as a result of frequent spark checks. At the time of diagnosis, a high load is placed on the device. If it appears frequently, it will lead to equipment failure or incorrect operation.
- in the VAZ 2114 it functions with the high-voltage cables disconnected. This also leads to device failure. The products themselves may be damaged, which affects the functioning of the engine as a whole.
- The device operates under severe vibration conditions. Their impact may be due to poor quality fixation of the module in the seat. As a result of vibrations, the factory soldering inside the equipment structure is damaged. This leads to its incorrect operation.
- The contact inside the plug with the low-voltage cables is broken.
- Initial use of a defective device or module with poor build quality. This factory defect can only be eliminated by replacing the mechanism; repairing the equipment is pointless.
- Moisture getting inside the case. This problem is unlikely, but exposure of the device to liquid may cause it to short out and break.
Signs of coil malfunction
The main symptoms of a malfunction in the VAZ 2114 ignition module:
- Difficulties arise when trying to start the engine. Starting the car engine may be difficult due to the fact that there is no spark on a spark plug or several.
- When idling or parking with the internal combustion engine running, the speed of the power unit floats. Their change is not associated with pressing the gas pedal and other third-party factors. This happens randomly.
- There are dips in the power of the car's engine. This is especially felt when driving uphill or sharp acceleration. Problems can also occur when driving on a flat road.
- Several cylinders stopped working. Usually these devices operate in pairs, so elements 1-4 or 2-3 could fail. Non-working cylinders may be indicated by “triple movement” of the engine.
- A “Check Engine” warning light appeared on the dashboard.
If the ignition module malfunctions, problems will appear not only in engine operation, but also when starting it.
The “Simple Opinion” channel, using the Lada Priora car as an example, spoke in detail about the symptoms that appear in the operation of the ignition modules.
Explanation of the ignition coil designation (Catalogue number) - 2111-3705010;
The designation of a part or assembly is a unique number in a single form. Assigned to only one part. The numbering of designations for assembly units and parts is carried out according to a unified seven-digit system. Designation - 2111-3705010-02 is deciphered as follows. The first four digits before the dash indicate the model of the base car or engine, chassis, body. In our case: 2111 is the engine model. The first two digits after the dash indicate the group number, in this case 37 - electrical equipment. The next two digits are the subgroup number. In our case, 05 is the ignition coil. The last three digits of the seven-digit number indicate the serial number of the part. The last two digits after the second dash indicate the interchangeability of the part. ХХХХ-ХХХХХХ-00 (to-09) - interchangeable. ХХХХ-ХХХХХХХ-10 (up to 19) are interchangeable with each other but not interchangeable with ХХХХ-ХХХХХХХ-00 (up to-09) and so on.
Communities › VAZ: Repair and Modification › Forum › VAZ 2110, injector, 8 cells, won’t start, no spark
Good day to all. Yesterday my friend’s car stopped starting; as it turned out, there was no spark at the spark plugs. A new Ignition Module, new explosive wires, and a new DPKV were purchased at the store. ECU January 5,1,1 was replaced with exactly the same one that was known to work. But the engine still doesn't want to work. So far I have found out that on the chip going from the ECU to the Ignition Module, on the last contact (D) there is 12 volts when the ignition is turned on, and on the penultimate one there is ground. So, as I understand, the control signals for sparking go through the 1st and 2nd connectors (A and B). But how can you find out whether these signals are reaching the coil? I connected a low-power 5w light bulb to these connectors, that is, one end to the ground of the car, and put the other end into connectors A and B and turned the starter, the light did not light up. Maybe a very weak current is generated there? Or do you need to dig in the direction of the break in both wires (which is unlikely)?
Pinout, connection diagram and check of the VAZ ignition coil
Today we will look at the design and diagrams of ignition systems for VAZ cars of all major models. Since carburetor versions of VAZ are practically history, we will dwell in detail on the ignition systems of injection cars. Their ignition system is based on an electronic ignition module. We also recommend that you carefully consider the choice of spark plugs and the quality of high-voltage wires, because the quality of the spark and, accordingly, the operation of the ignition system as a whole will depend on them. The information is intended as a reference guide for self-repairing a car.
What's the difference between contactors and starters?
Both contactors and starters are designed to close/open contacts in electrical circuits, usually power ones. Both devices are assembled on the basis of an electromagnet and can operate in DC and AC circuits of different powers - from 10 V to 440 V DC and up to 600 V AC. Have:
- a certain number of working (power) contacts through which voltage is supplied to the connected load;
- a number of auxiliary contacts - for organizing signal circuits.
So what's the difference? What is the difference between contactors and starters? First of all, they differ in the degree of protection. Contactors have powerful arc extinguishing chambers. This leads to two other differences: due to the presence of arc arresters, contactors are large in size and weight, and are also used in circuits with high currents. For low currents - up to 10 A - only starters are produced. By the way, they are not produced for high currents.
There is one more design feature: the starters are produced in a plastic case, with only the contact pads exposed outside. Contactors, in most cases, do not have a housing, therefore they must be installed in protective housings or boxes that will protect against accidental contact with live parts, as well as from rain and dust.
In addition, there is some difference in purpose. The starters are designed to start asynchronous three-phase motors. Therefore, they have three pairs of power contacts - for connecting three phases, and one auxiliary one, through which power continues to flow to operate the engine after the “start” button is released. But since a similar operating algorithm is suitable for many devices, a wide variety of devices are connected through them - lighting circuits, various devices and devices.
Pinout and diagram of the VAZ ignition coil
Pinout of ignition coil modules for various car models of the VAZ family:
Ignition VAZ 2101
1 – generator; 2 – ignition switch; 3 – ignition distributor; 4 – breaker cam; 5 – spark plugs; 6 – ignition coil; 7 – battery.
Ignition VAZ 2106
1 – ignition switch; 2 – fuse and relay block; 3 – EPHH control unit; 4 – generator; 5 – solenoid valve; 6 – microswitch; 7 – spark plugs; 8 – ignition distributor; 9 – ignition coil; 10 – battery.
Ignition VAZ 2108, 2109
Ignition VAZ 2110
Ignition VAZ 2111
Ignition VAZ 2112
Ignition VAZ 2114
Diagram of a non-contact ignition system: 1 – non-contact sensor; 2 – ignition distributor sensor; 3 – spark plugs; 4 – switch; 5 – ignition coil; 6 – mounting block; 7 – ignition relay; 8 – ignition switch.
Share your story
The tightness of the carbolite lid in the casing is ensured by a gasket. As a result, high voltage is formed in the secondary, which goes through high-voltage wires to the spark plug. According to the design of the magnetic circuit, ignition coils are divided into two types: - With an open magnetic circuit. Types of high-voltage elements Above is a description of a simple design of a voltage-increasing transformer that provides discharges to all engine cylinders.
When the engine crankshaft rotates, the sensor rotor rotates.
Replacing the ignition coil on a VAZ is quite simple.
Capacitors C1 and C2 and the inductor reduce voltage ripple in the switch's power circuit, and the VD6 diode KDB protects against reverse polarity. The dual system is used for cylinders that operate in the same phase. Direct current flows through the primary coil.
TB above emitter potential. When connecting the coil to the car’s ignition system, in principle, you should not have any difficulties if, during preliminary dismantling, you marked or remembered which wires are connected where. Ignition system contact and without 1 part
How to check the ignition coil of a VAZ
If the ignition coil is faulty, the engine will not start. A characteristic sign of a faulty coil is its increased temperature when the ignition is turned off. This is easy to determine by touch.
Signs of a faulty ignition module may include the following:
- hesitant engine starting or failure to start;
- failures during sudden changes in speed;
- high fuel consumption;
- two cylinders do not work, the engine is feverish;
- lack of dynamics;
- a sharp drop in power;
- drop in power and thrust after warming up.
These symptoms may not only be caused by the ignition module. To determine the malfunction, it is enough to spend a few minutes diagnosing spark plugs, high-voltage wires and caps. This will eliminate the remaining elements of the ignition system and make sure that it is the ignition module that is faulty.
Checking the ignition coil is performed in one of 2 ways. The simplest one is to remove the central wire from the breaker-distributor, bring it to the motor housing and turn it with the starter, and a running spark should appear. After this, we check the energy supply to a separate spark plug, for which we unscrew the working spark plug, bring its contact to ground and attempt to start the engine. In this case, the spark should come from the wire to ground. If it is absent, the reason will be a malfunction of a system element such as the ignition coil.
To check the module in the second way, we only need a multimeter, then follow the step-by-step instructions:
- We check the power supply and the presence of pulses supplied from the ECU. We check the power between the central terminal (15) of the wire block connected to the module and the engine ground. When the ignition is on, the voltage should not be less than 12 V. Otherwise, either the battery is dead or the ECU does not work.
- We check the pulses from the ECU on the wiring block. We install one tester probe on connector 15, the second on the far right, then on the far left. The assistant cranks the engine with the starter, and at this time we record short-term voltage surges with a tester. If there are no impulses from the ECU, it is he who is to blame.
- We check the resistance on the secondary windings of the coils. We put the tester in resistance measurement mode and measure it at the high-voltage terminals of the module cover. Between pins 1 and 4 and pins 2-3, the resistance should be 5.4 kOhm. Otherwise, the module must be replaced.
- We check the resistance of the primary windings between contacts 15 and the rightmost, then the leftmost terminals. Nominal - 0.5 Ohm. Deviation is not allowed.
- Check the module for a short circuit. In ohmmeter mode, install one multimeter probe on the central terminal, the second on the metal body. There shouldn't be any resistance. If the device detects at least some resistance (other than unity or infinity), the module must be replaced.
Ignition module repair
If the ignition module does not work, you can try to rehabilitate it:
- Take 10, 13 and 17 end keys, a 5 hex key, a regular screwdriver, a soldering iron, aluminum flux, nail polish, and stranded wires.
- Most often, the connection in the ignition system deteriorates - those same contacts.
- We turn the key in the ignition, start it, move the contacts, and get a comprehensive answer in the absence of their quality connection.
- Now we turn off the engine and remove the ignition module out.
- You need to open it, pry up its body with a screwdriver.
- Inside the board is covered with silicone film - remove it.
- We remove all aluminum from the explosive contacts.
- Now comes the hard part: we need to solder new wires to the plan from where we just removed the old ones.
- First, you need to clean the surface of the collector from plaque, then put the board on the stove and heat it to 200 degrees (approximately by eye, of course), it will start to smell a little when it reaches the desired temperature and soldering on it will become much easier.
- Now, actually, we solder: we connect the ends of the wires to the module.
- We cover all the contacts of the wires with the module and the board with nail polish.
- Now you need to put everything back together, put the ignition device in place and start the engine. Only after this, when you are convinced that everything is working properly, can you take the sealant and seal it tightly.
- Individual elements that have failed. They cannot be repaired, they are only for replacement. Fortunately, the price for them is adequate: a switch is within 200 rubles, a transistor is from 200 to 300 rubles.
A very important point: in common parlance, as here, the ignition coil and the ignition module are synonyms. But in terms of technical design, no. For fourteenths with different engine sizes, different spare parts are installed: for 1.5-liter Samaras of the old generation, it is the ignition module, and for 1.5 and 1.6 liters of the new generation Samaras, it is the ignition coil. The switch of the new type of machines is hidden in the electronic control unit, it turns out that the module was broken, and they began to call it by the name of its main part - the coil. Be careful when choosing a spare. parts from disassembly: do not confuse them, given this fact.
If we talk about service, the price is not worth the cost. It’s easier to figure everything out yourself, even more so. That there are a lot of resources where they can give you advice and help. The main thing is to remember the layout of the high-voltage wires and their good contact. It happens that incorrectly connected wires contribute to improper combustion, a spark hits the relay. And the ignition module completely burns out.
Connecting and replacing VAZ short circuit
The procedure for removing and installing the ignition coil on old VAZ models:
- First, disconnect the central high-voltage wire leading to the distributor (ignition distributor).
- Disconnect all power wires from the coil contacts. Since they are fastened with nuts, you will need an 8 wrench for this.
- If you don’t know which wires to connect to which connector later, it’s better to immediately remember or mark them somehow, so that later during installation you can connect them correctly.
- Unscrew the coil housing. It is attached to a clamp (clamp), which is pressed to the car body with two nuts.
- After the work has been done, you can remove the ignition coil and replace it if necessary.
For new type VAZ cars:
- We remove the “minus terminal” from the battery.
- Remove the top protective cover of the engine. If the engine volume is 1.5 liters, then this part is missing and this step is skipped.
- We remove the high-voltage wires from the coil.
- Now, using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the two fasteners.
- Using a 17mm wrench, loosen one bolt securing the coil.
- We take out the module.
- Use a hexagon to unscrew the coil from the holder.
- Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Particular attention should be paid to the connection, since high-voltage wires must be located in the strict order provided for by the design. If this is not done, the car will stall or the engine may not start at all.
Replacing the ignition coil on a VAZ is quite simple. Even a novice motorist can do this in his garage, and if everything seems too complicated, contact a car service center. Particular attention should be paid to the choice of product, since this will determine how well the engine and ignition system will work.
Signs
- If one of the module coils completely fails, then two cylinders do not work. This is clearly visible even to the naked eye - the engine is feverish at idle, starting is difficult, fuel consumption is sky-high, loss of dynamics.
- To eliminate all other components of the ignition system, make sure that the spark plugs are in working order. To do this, unscrew them and check the spark on each of the spark plugs by cranking the engine with the starter and placing the spark plug with the high-voltage wire on the head so that the body (threaded part) of the spark plug touches the engine mass. If there is no spark or it is weak, replace the spark plug with one that is known to work.
- If this does not lead to anything, check the high-voltage wires. Thus, we will exclude spark plugs, caps and high-voltage wires from the list of non-working elements. Next we will check the ignition module.
VAZ models 8 and 16 valves
Despite the similarity in engine design, the ignition system of the 1.5-liter injection 16-valve engine differs from the 1.6 16-valve engine. The 1.6 liter engine uses an electronic contactless ignition system with individual coils on each spark plug. Therefore, there was no need for an ignition module. Such a system is more reliable and cheaper to operate, since if one coil fails, there is no need to replace the entire module.
The 16-valve 1.5-liter VAZ 2112 injection engine used the same non-contact ignition system as the 8-valve engine, but a different ignition module was installed. Its catalog number is 2112-3705010. The design of the module remains the same - two ignition coils (for cylinders 1-4 and 2-3) plus switch keys in a single block. The spark is supplied to the cylinders in pairs using the idle spark method. This means that sparking occurs in two cylinders simultaneously - in one on the compression stroke (working spark), in the second on the exhaust stroke (idle spark).
We disassemble the design of the ignition module of a modern injector
As an example, consider a similar device used on injection VAZ cars. The module operates according to the good old principle: 12 volt power is supplied to the input, and a high voltage is generated at the output contacts for sparking.
The control is electronic, but the operating principles differ from a simple distributorless ignition system:
- All components are located in one housing. On the one hand, this is convenient - fewer wires and contacts - lower probability of breakdown. On the other hand, if the ignition module burns out, it must be repaired; simply replacing the failed element will not work.
- The device is compact and can be conveniently placed in the engine compartment.
- The ignition module is powered at low voltage, which increases the reliability of the device.
- The cost of the finished device is low.
- This ignition module has two coils. This contributes to the survivability of the device - each transformer is loaded twice as much.
The secret of the module’s operation is as follows: it uses not four, but two coils for 4 cylinders. Masters of the old school call this device a two-spark bobbin. Alternating connection of each coil produces two sparks: working and idle. Due to proper distribution among the spark plugs, the idle spark is ignited at the moment when there is no air-fuel mixture in the corresponding cylinder.
The signal for sparking is given by the switch (acting as an electronic distributor). Before checking the ignition module, you need to make sure that control pulses are coming to the contact blocks from the switch.
This block is responsible for the so-called ignition advance, that is, it generates a signal at the right moment. The control pulse about the position of the crankshaft is issued by the Hall sensor, which also synchronizes the operation of the entire system.
Video on repairing KZ VAZ
Source
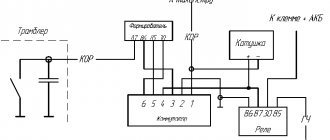
| 1 | accumulator battery; |
| 2 | main relay; |
| 3 | ignition switch; |
| 4 | spark plug; |
| 5 | ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves model 54.37005; |
| 6 | controller; |
| 7 | crankshaft position sensor; |
| 8 | master disk. |
| 1 | ignition switch; |
| 2 | main relay; |
| 3 | battery; |
| 4 | atmospheric filter; |
| 5 | diagnostic connector; |
| 6 | dashboard; |
| 7 | tachometer; |
| 8 | check lamp; |
| 9 | speedometer; |
| 10 | immobilizer sensor with indicator; |
| 11 | immobilizer manual device; |
| 12 | electric fan of the engine cooling structure; |
| 13 | electric fan relay; |
| 14 | controller; |
| 15 | DTOZH; |
| 16 | ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves, VAZ 2113, VAZ 2115; |
| 17 | spark plug; |
| 18 | DPRV; |
| 19 | sprayers; |
| 20 | throttle assembly; |
| 21 | TPDZ; |
| 22 | DMRV; |
| 23 | empty control; |
| 24 | Lambda probe; |
| 25 | car speed sensor; |
| 26 | DPKV; |
| 27 | DD; |
| 28 | crankshaft pulley; |
| 29 | gasoline filter; |
| 30 | petrol pump relay; |
| 31 | gasoline tank; |
| 31 | gasoline unit; |
| 32 | two-way valve; |
| 33 | gravity throttle; |
| 34 | reverse breather; |
| 35 | check valve; |
| 36 | adsorber purge throttle; |
| 37 | adsorber; |
| 38 | separator. |
| 1 | spark plug 4 pots; |
| 2 | spark plug 3 cylinders; |
| 3 | spark plug 2 pots; |
| 4 | spark plug cylinder 1; |
| 5 | ignition coil VAZ 2114 8 valves; |
| 6 | diagnostic connector; |
| 7 | 1 pot sprayer; |
| 8 | injector 2 cylinders; |
| 9 | 3 pot sprinkler; |
| 10 | 4 cylinder injector; |
| 11 | ECU; |
| 12 | fuel pump switch; |
| 13 | to the electric cooling radiator fan; |
| 14 | connector for connecting the engine radiator electric fan; |
| 15 | main relay for engine control mode; |
| 16 | DMRV; |
| 17 | remote sensing; |
| 18 | DTOZH; |
| 19 | empty traffic controller; |
| 20 | adsorber purge throttle; |
| 21 | DPKV; |
| 22 | DD; |
| 23 | oxygen concentration sensor; |
| 24 | to the ignition switch; |
| 25 | Immobilizer ECU; |
| 26 | immobilizer sensor with signaling device; |
| 27 | car speed sensor; |
| 28 | spare pad; |
| 29 | to the battery positive; |
| 30 | DPRV; |
| 31 | block for connecting to the car's electrical network; |
| 32 | fuel unit; |
| F1 | fuse for the ECU and engine control structure circuits; |
| F2 | ECU fuse; |
| F3 | fuel pump line fuse |
see also
Comments 20
Thanks everyone for the advice! I installed the VAZ coil, connected the wires, and started the car!
There is no spark not with this not with the VAZ coil :(
Green, light green, yellow, brown + from distributor
The coil needs another one with two contacts B-battery K-cams, tachometer
Is the wire from the distributor also on “K”?
Yes, in the place with the tachometer, I have a green wire, and a yellow one is plus
The entire bunch is connected to terminal K green. and brown?
the coil is from Ufa, on the VAZ there is nowhere to connect the third terminal - there is no terminal for it on the starter... I would change the coil to the VAZ one... if you connect this one, you find the wire on which + appears when you turn on the ignition and hang it on B, you hang the rest if you look in the photo, then to the lower contact, these are wires from the distributor and from the tachometer...
I connected everything like this, but there is no spark! Even when you turn on the low beam, the side lights go out, and the turn signals on the rear headlights come on and the low beam doesn’t light up, the rear right side light doesn’t light up yet
Is the coil definitely alive? try to directly close the variator, they sometimes burn out, you can’t drive with it closed, the coil will burn out, but you can’t close it for long to check... well, and again check the contacts in the distributor, the capacitor... as for the light and music - look for where the ground on the headlights is lost...
The distributor is new! I plugged a light bulb into the high-voltage wire from the coil to the distributor, placing it on - (radiator) did not light up when starting the starter
Is the coil definitely alive? try to directly close the variator, they sometimes burn out, you can’t drive with it closed, the coil will burn out, but you can’t close it for long to check... well, and again check the contacts in the distributor, the capacitor... as for the light and music - look for where the ground on the headlights is lost...
I also accidentally connected the wire from the distributor to the terminal of the coil with the + terminal from the ignition; the distributor was short-circuited; the contacts in the distributor and the ends of the wires of the distributor and + from the ignition melted. Could this cause the coil to burn out?
Russian spare parts are so Russian that new does not mean working, everything needs to be checked. I don’t understand, why is there a light bulb there? you hold the high voltage wire with a gap from any ground and turn the starter, see if there is a spark... if the contacts in the distributor are already burnt, all the more you need to get into it, clean the contacts, set the gap... but I would still change the coil to a VAZ B117...
I replaced the shorted distributor with a new one, and I will change the coil tomorrow with the high-voltage wires! Does the coil take minus from the body?
the plus goes to the coil from the lock, and the minus comes from the distributor, the contact group is at ground...
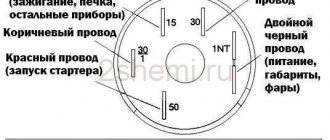
B - 'battery' - the wire on which 12V appears when the ignition is turned on. 'Unnamed' - to the distributor, there is also a wire from the tachometer. On 'Vk' there is a wire from the starter, to enhance the spark at the moment of starting
The colors of the wires do not match and in the diagram with the VAZ internal combustion engine there is a coil with 2 terminals
Source: www.drive2.ru
Repair or replacement?
As the practice and experience of car repair technicians shows, most often it is not possible to repair this device. The module can only be replaced. If you follow the principle, it is possible to carry out repairs, but it will take a lot of time, effort and even money.
Installing the module
The best option is to purchase a new device. It costs around 2-4 thousand rubles. It all depends on the manufacturer and condition. You can buy a brand new one, although many people prefer used devices. Here the choice is yours.