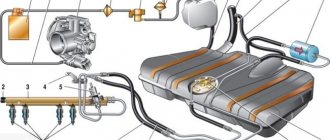
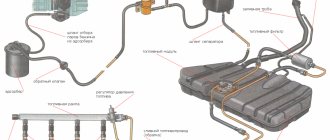
Cooling system pipes for VAZ 1118 Kalina and 2170 Priora...
Greetings to all readers of the autoblog RtiIvaz.ru. In the auto repair kit section, I published a story from a car enthusiast, where he asks a question to all car enthusiasts - why do the cooling system pipes of VAZs break?
Today I want to continue talking about the radiator pipes of the cooling system. The radiator pipes of VAZ, Kalina-1118, Priora-2170, Grant-2190 cars supplying “upper” and also discharging “lower” coolant through themselves are designed for an elastic connection between the engine and the radiator.
Replacing pipes for a Priora stove without air conditioning
Heater (stove) and air conditioner - design, service, malfunctions, removal and installation of the heater (stove) and radiator on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Priora (Priora)
What is a heater radiator for the cooling system of Priora, many people guess, but everyone knows for sure. Popularly, this heater has its own name: stove radiator. This means that it is first used in cool periods, when the air passing through the heater radiator is heated and supplied to the cabin. And if so, then they remember about this same heater radiator at the worst possible moment, when it’s already winter and cold outside, and then repair work and research begins on how to change it, and where to look and fix it. In fact, “how” and “what” are also an important factor, because without certain knowledge you cannot get into the Priora system, it will be of no use except for wasted time. So, in order to make it clearer to you what and why, and to make it easier to repair your stove on the Lada Priora, we have prepared this article. Kommersant
By the way, it’s not only about the stove, but also about the air conditioning system and air conditioning, so we’ll also talk about that.
Design features of the stove-heater Lada Priora VAZ 2170 2171 2172 (Lada Priora)
The Priora car is equipped with a stove - a heater (Fig. 1) of a liquid type, combined with the system
Main elements of the heater:
– heat exchanger of the heater (radiator), designed to heat the air entering the cabin with the heat of the water cooling the engine;
– an electronically driven fan (supercharger), providing a controlled supply of external air to the heater dampers;
– a damper for the air temperature regulator coming from the heater into the passenger compartment, the position of which determines the amount of air passing through the heat exchanger of the heater, and the amount of external air passing bypassing the heat exchanger;
– air heating distributor dampers 4, which distribute the air entering the cabin from the heater through air ducts 2, 6, 8 and 9 or for blowing the windshield.
Rice. 1. Priora interior ventilation and heating system: 1 – left side ventilation nozzle; 2 – left ventilation air duct; 3 – side window heating nozzle; 4 – air heating distributor; 5 – heater; 6 – right ventilation air duct; 7 – right side ventilation nozzle; 8 – air duct for heating legs; 9 – interior heating air duct; 10 – central ventilation nozzle.
In turn, the exposed components of the Pyrora stove can be divided into components. Let's start with the dispersal block
Now let’s take a look at what the stove heater consists of, which, like in the tenth family, is installed on the engine side, in other words, it is installed and removed from the engine side.
1, 3 — housing parts of the Priora heater, 2 — air filter, 4 — gear motor, 5 — heater radiator, 6 — sensor, 7 — heater (heater) fan.
Sketch 2 The main elements of ventilation of the central part in the Lada Priora car
Replacing the heater radiator of a VAZ 21072 Priora, in an hour
Replacing the stove radiator
VAZ
Priora without
removing the brake vacuum. This is the most important point where many became.
Replacing the radiator of the fan heater or damper of a VAZ Priora without removing the brake vacuum.
Quite a quick and less easy method to get to the stove
Lada Priora car
without air conditioning
. Saved.
(066) Pipes, blue silicone and more
Good day to all!
For those who read the previous post: Package from TimeTurbo, this post is a continuation! More than a month has passed since the installation of these attributes. Therefore, some conclusions have already been drawn and goals have been set. There won't be many words, more pictures! So, to install a set of pipes, you need to drain the antifreeze from the system. I won’t describe what and how, the sequence of actions, since there is a lot of information on this topic on the Internet. All that remains is to add a review. The pipes appear to be made of high-quality material, the installation is standard, everything fits without problems. The exception is the lower crankcase ventilation pipe; it had to be cut by 50mm, but this is due to the installed ProCar receiver. Well, if we change the pipes, then it is advisable to replace the coolant. In this case, the choice fell on SINTEC LUX-OEM G12 antifreeze. Anyone who reads the logbook again may remember that the coolant was replaced almost 2 years ago, but then it was not possible to find SINTEC and therefore last time the choice fell on
. I can't say anything bad about this antifreeze. A sea of information on the topic of O/F was shoveled, feedback from both site members, acquaintances and friends was listened to. SINTEC is beyond competition, X-FREEZE is inferior in some respects. Detailed information about antifreeze can be found here and here
I was pleased with the result. Let's see how this all manifests itself during operation. The price list for all products is in the previous post. The cost of Antifreeze SINTEC LUX-OEM G12 is 3500 * 2 = 7000 tenge or 1155 rubles
Now the pressing questions, conclusions and judgments:
1. Replacement of clamps (clamps) of the cooling system.
There are often cases when a regular clamp cuts a pipe and ends up with unpleasant consequences.
Does replacement make sense? What clamps? 2. The thermostat pipe was missing from the kit.
Where can I buy a silicone thermostat hose? Well, now the pictures! Peace, Good Luck, Goodness to Everyone!
Source
Replacing the heater radiator on a Lada Priora
If the stove on your Lada Priora starts blowing cold air instead of hot air, you should pay attention to the heater radiator. There are already discussions on our website about why the stove on a Priora does not work, but we still decided to publish additional material on replacing the heater radiator with our own hands.
Features of the design of the stove on the Lada Priora
Main elements of the heater:
– heater heat exchanger (radiator), designed to heat the air entering the passenger compartment with the heat of the engine cooling liquid; – an electrically driven fan (supercharger), providing a controlled supply of outside air to the heater dampers; – a damper for the air temperature regulator coming from the heater into the passenger compartment, the position of which determines the amount of air passing through the heat exchanger of the heater, and the amount of outside air passing bypassing the heat exchanger; – air heating distributor dampers 4, which distribute the air entering the cabin from the heater through air ducts 2, 6, 8 and 9 or for blowing the windshield.
Malfunctions
For normal operation, the heating system needs: tightness, integrity of parts and normal antifreeze. The first step is to check the relay and fuse - after all, this unit contains electrical appliances inside. If the unit's electrical network is not in contact with the ECU, there is no point in turning the controls on the heater control unit.
The heater fuse on Priora has the number F9. In order to get to it, you need to remove the plastic plug above the driver's left knee (under the headlight switch) by unscrewing three bolts around its perimeter.
Once the fuse has been inspected and no deficiencies have been identified, further diagnostics can begin.
Perhaps the most annoying thing in any car is the situation when, even at the hottest summer temperatures, the heater does not turn off. This happens because the damper does not block the air flow. The heater damper on the Priora is controlled by a gear motor, which stops after its operating life has expired - it will have to be replaced.
While driving a VAZ-2170, you should carefully look and listen to what you see and feel. If heat should come from the cracks, but it doesn’t, then something is wrong with the seal or the damper gear motor. For example, if the glass becomes greasy, as if it was smeared with your hands, it means that the heater radiator is leaking. However, these are not the only signs of a heater failure.
Priora: the stove blows cold air, does not heat - reasons
When cold air comes from the heating system and turns into the air conditioner, the following possible malfunctions are considered:
- The heater hoses do not supply coolant, or the radiator itself is not efficient enough and does not take heat from them.
- The air filter is dirty. If there is no new part nearby, try removing the filter and then starting the heating system without it.
- The damper gear motor is stuck.
- The control unit (switches) is broken.
- The temperature sensor in the cabin has broken (it is located under the roof).
The shutter does not move, and the modes: face, legs, glass do not work
Reasons for this problem include:
- Faulty air distribution gearmotor.
- Inoperative control controller (CU).
The stove blows hot air when turned off.
The most likely reason for this behavior of the heater is a failed damper gear motor.
It’s noisy – what to watch
When you hear an unknown noise, you need to check the heater motor bearing. The noise is caused not so much by the bearing, but by small debris that has gotten under the motor blade.
The stove does not blow and does not even turn on
There are only two reasons why air does not escape from the heating system of a Lada Priora car. When the interior heating does not work, you need to check fuse F9 and the switches on the center console - perhaps they are simply broken.
How to replace the radiator of a Priora stove without air conditioning
In winter, as you know, car enthusiasts turn on the stove to avoid freezing.
Its normal operation ensures a comfortable temperature inside the car, and this, in turn, is the key to safe driving. However, there are times when this unit stops supplying warm air. The reasons can be very different, for example, problems with the radiator. Many people, including owners of Lada Priora, both equipped with air conditioning and without it, encounter malfunctions of this kind. In some cases, it will only take a minute to fix the problem because you just need to replace the blown fuse. But there are situations when more serious repair work, such as replacing a radiator, cannot be avoided. However, there is nothing particularly complicated here. Everything can be done with your own hands - you just need the appropriate desire and a little time.
The advantages of this development
- The main and significant advantage of replacing the thermostat with a Grant thermostat is the warmth in the car interior. Warm air begins to blow from the nozzles already at a temperature of 50 degrees, and at 70 degrees it is hot.
- Quickly warms up the engine even in the most severe frosts, which will allow you to quickly warm up the interior and drive in comfort.
- The coolant temperature when driving will not drop below 85 degrees
- In summer, the engine will not overheat. The temperature will not exceed 100 degrees
How to replace a Lada Priora radiator heater without air conditioning
First of all, let's look at the main elements of the VAZ-2170 heating system. They are, in particular:
- heater radiator (heat exchanger) – this is where the coolant is heated;
- fan - with its help warm air is supplied to the car interior;
- regulators – heating intensity and heat distribution zones.
The scheme is, in principle, traditional, and there are no particularly complex technical delights here. If you notice that warm air is not flowing into the cabin while the heater is on, you should inspect the entire system. If a radiator leak is detected, the latter will have to be removed either in order to be soldered, or to be replaced with a new one. Let's look at how this procedure can be done with your own hands on a Priora without air conditioning.
The first thing that is recommended to do before starting the main work is to remove the negative terminal from the battery.
Do not neglect this advice, because it is, firstly, about your safety, and secondly, it is additional insurance against a number of different unpleasant surprises with wiring and electrical equipment.
First you will need to remove the hood seal. Please note that in the middle of the pad there is a screw with which the halves are pulled together. After this, use a screwdriver or knife to carefully pry up the plugs covering the screws and unscrew them. That's it - the cover can be removed.
If everything went well, then you can move on. At this stage, you should remove the sound insulation from the engine compartment. To do this, unscrew the screws with which it is actually attached, and then remove the lining, left and right (the order does not matter). After this, you can move on to the pipes leading directly to the radiator. In order to remove them, you will first need to loosen the retaining clamps. Place a container to drain the coolant first.
Now you can remove all the wires that lead to the heater from the connectors. Having disconnected them, take two keys - 10 and 8 - and unscrew the 4 nuts. The wiring harness should be moved to the side so that it does not interfere, after first removing the holder. After this, we move into the car interior and take a socket wrench size 13. With its help, remove the bracket from the brake pedal, and
move it to the side. That's all - you have free access to the heater radiator. In order to remove it, you need to unscrew 3 screws using a Phillips screwdriver, after which the unit can be easily removed. All work on installing the radiator is carried out in reverse order.
As you can see, there is really nothing particularly difficult here. In order to remove the heater radiator on a Priora without air conditioning yourself, you will need some time (it all depends on your skills) and a minimum set of tools. On the other hand, you save money because you do all the work yourself, rather than turning to specialists at a car service center. Even if you have never encountered this before, figuring out how to remove the Priora radiator will not be difficult. The eyes, as you know, are afraid, while the hands do. It’s probably worth listening to folk wisdom.
Do I need to replace a worn or damaged pipe?
Some motorists believe that you can drive with a cracked pipe, but this position is fundamentally wrong. Firstly, a damaged pipe will not be able to supply clean air to the engine. After all, through the gap, air from under the hood will enter it, which has not been filtered, and therefore carries abrasive particles (which, as mentioned, can quickly damage the engine).
Secondly, driving with a damaged corrugation also leads to faster wear of the air filter; it will have to be changed much more often. That is why a damaged or worn pipe should be immediately replaced with a new one.
Replacing the radiator of a heating device in a Lada Priora car
Almost every motorist who owns a domestic vehicle discovers a malfunction of the car’s heating unit in the winter. After all, only with the onset of severe cold does a person begin to think about how to avoid freezing while driving a car. Naturally, everyone uses a stove for this. However, what should those for whom this very device has ceased to function properly do? After all, only the heater can ensure that the cabin maintains a normal temperature, allowing for comfortable movement. In this article we will look at only one reason why the heating device stops working, we will learn about the principles of repairing and replacing the heater radiator installed in a Lada Priora car.
If the motorist is sure that it is necessary to replace the heater core, it may take a lot of time to eliminate the faulty object, since most likely, in the process it will be necessary to replace not just a blown fuse, but to carry out more serious repair work. True, you should not immediately despair because of your ignorance; the material contains detailed instructions to help everyone understand how to replace the stove radiator in a Priora with and without air conditioning.
The influence of the cooling system thermostat on the operation of the stove and its modernization
Lada Priora is equipped from the factory with a five-hole thermostat. The thermostat is directly responsible for the engine cooling and heating system of the vehicle. A malfunctioning product can completely paralyze the operation of the stove, and in winter it will be almost impossible to heat the interior.
First, you can replace the standard product with a six-hole thermostat. Warming up the vehicle heater radiator will be more efficient, since the updated part has modern technical indicators. There are no difficulties with installing the product; they are interchangeable.
Secondly, you can additionally adjust the flow of coolant to improve heating of the interior at idle engine speed. Aluminum plates are used for this. With their help, it is necessary to reduce the diameter of the thermostat bypass channel to six millimeters. Such changes will slightly increase the engine warm-up time, but the cabin will become much warmer.
And the last element of improvement. When installing the thermostat on a standard seat, swap the hoses of the heater radiator and the expansion tank. Such an upgrade will guarantee the operation of the heating system at any time of the year.
Replacing the radiator of a heating unit in a Priora that is not equipped with air conditioning
Replacing the heater radiator on a Priora without air conditioning may make sense if warm air has stopped flowing into the cabin, while the heater itself is working. If, in addition to the above problem, there is also a water leak from under the Priora stove, the motorist will have to remove the poorly functioning unit in order to solder the latter. Sometimes repairs are impractical and you have to replace the old device with a new one.
So, first of all, you need to start by removing the negative terminal from the battery. The fact is that the issue here is not only about the safety of the master himself, but also about additional insurance, which allows him to avoid several unpleasant surprises that, if handled carelessly, can arise not only with wiring, but also with electrical equipment.
If you are replacing the heater radiator on a Priora without air conditioning, after de-energizing the system, you can begin to dismantle the windshield trim. At the same time, the wiper levers, which can cause future discomfort during operation, should also be removed. After this, you should rid the unit of all plastic tubes through which the liquid located in the windshield washer reservoir goes directly to the nozzles. Only after all the above steps have been completed will it be possible to remove the decorative trim located along the edges of the windshield. In fact, it’s easy to carry out such a manipulation - just get rid of seven self-tapping screws.
Replacing the heater radiator on a Priora can only be done after removing the hood seal. Before dismantling, it should be noted that in the middle of the lining there is a screw that tightens both halves of the structure. Using a screwdriver or any knife, you can gently lift the plugs (this element serves as the “cover” of the screw) and unscrew them.
System parts and components
The design of the Lada Priora engine cooling device is quite simple and inherent in all injection versions. The coolant circulates in circles - large and small. Let's look at the details of the “cooler” assembly in more detail.
Radiator and electric fan
The radiator and electric fan ensure a constant engine temperature within the range of 87-103 degrees Celsius so that the engine does not overheat. On the first engine models, a three-row cooler of copper construction was installed. But, after unsuccessful tests, the designers decided to change the radiator to a three-row aluminum one.
The electric fan is turned on by a control unit, which regulates the engine temperature using a coolant temperature sensor. Temperature data is read from the cooling jacket and sent to the ECU, which turns the main fan on and off.
A malfunction of the fan and cooling radiator leads to poor circulation and insufficient cooling of the system. In this case, the motor may overheat.
If this is coupled with a faulty thermostat, this will lead to overheating of the motor, which will lead to more serious problems.
Thermostat
Provides transfer of coolant flows from a small to a large circle and vice versa. So, the thermostat opens at a temperature range of 60-70 degrees. This is one of the most important parts of the engine, since it is what regulates the efficient and rapid warming up of the engine, as well as the normal operation of the coolant system.
When the engine warms up, the thermostat is in the closed position and coolant circulation is ensured in a small circle without the participation of the radiator. After the thermostat opens, the liquid begins to circulate in a large circle, which ensures effective cooling thanks to the radiator.
A malfunction of the thermostat leads to the fact that the engine begins to heat up, since it is in a closed state and often this malfunction is accompanied by frequent activation of the electric fan. Changing the thermostat is easy; to do this, you just need to drain the coolant to a level below the part and unscrew the housing. The product is located under the body.
When replacing, it is worth changing the sealing rubber.
Water pump
The water pump or pump serves to circulate coolant throughout the system. Failure of this element leads to loss of fluid and overheating of the power unit. Typically, wear on the bearings inside the product will cause it to seize, causing the water pump to start leaking.
Heater
One of the integral elements of the cooling system is the heater system. It includes an inlet and outlet pipe, a radiator and an electric fan. In winter, it is actively used, which further cools the engine.
Expansion tank and plug
Gases and vapors that are formed as a result of the operation of the system are displaced into the expansion tank. There, this element also serves as the coolant level in the system. Air is forced out through the plug, as well as hot “coolant” when the power unit overheats.
Pipes
Pipes are intermediate elements through which coolant circulates and also connect different elements of the system. Failure of these parts can lead to loss of fluid, which can significantly reduce the level in the engine. Typically, depending on the mileage and terrain of operation, it is recommended to change these parts once every 100,000 km.
temperature sensor
The cooling temperature sensor reads temperature data and transmits it to the electronic control unit, which adjusts the temperature. It is installed on the thermostat. A faulty element may cause the motor to overheat because the electric fan will not turn on.
This is especially dangerous in the summer. Also, problems with the sensor can lead to a number of other problems associated with the motor.
Water jacket
The cooling water jacket is located inside the cylinder block and cylinder head. It ensures the removal of heat from these elements, which heat up during operation. So, with the help of a water pump and pipes, the liquid moves into the radiator, where cooling actually occurs, and then returns to absorb new heat.
Installation of a new radiator in a Lada Priora with air conditioning
Replacing the heater radiator in a Priora car with air conditioning is a fairly simple process. The latter unit appeared only in newer cars, in particular, Priors began to be equipped with a HALLA or Panasonic climate control system. Thanks to the new component, you can replace any part of a non-working stove only by dismantling the frill, getting rid of the windshield wipers, the stove itself or the vacuum brake booster.
If a motorist wants to understand how to remove the heater radiator on a Priora with air conditioning, he must start by removing the sound insulation located in the engine panel. After this, you should dismantle the power unit air filter hose and remove the seal, which is located near the radiator hoses. Then you should drain the coolant and lift the radiator up towards the mechanic.
Cooling system pipe
What is a pipe? There are often several of them in a cooling system; they connect individual parts into one sleeve and are the basis for cooling.
Pipes can be divided into two types:
From the names it becomes clear that the outlet pipe is designed to drain coolant, and the inlet pipe is designed to supply it. To cool the engine, antifreeze or antifreeze is most often used, since at very low temperatures they tend not to freeze.
It is worth recalling that two pipes of different types should not be confused or swapped, since their operating temperature conditions are different.
Most often, the supply pipe fails, since the load on it is maximum, which leads to the rubber drying out, as a result it can leak or even burst.
SOD components
The cooling system includes many different parts that are responsible for the correct operation of the system. To understand the purpose of these parts, you need to take a closer look at them.
Cooling radiator
This part is designed to cool antifreeze while the car is moving. As coolant circulates through the radiator it cools and therefore cools the engine block. Inside, the radiator consists of many tubes connected to each other by a snake.
Possible breakdowns:
- Antifreeze leaking from radiator joints;
- Radiator clogged with oxidation products;
Water pump (Pump)
The pump is a pump that circulates liquid through the cooling system. Circulation is ensured by the pump impeller based on the principle of centrifugal force. The pump rotates using the crankshaft through the timing belt.
Possible breakdowns:
- Coolant leaks through the oil seal;
- Wear of ball bearings;
- Impeller failure;
Thermostat
The thermostat is one of the main elements of the Priora engine cooling system. Inside the thermostat housing there is a valve with a thermoelement, which is responsible for opening and closing a large circle. When the coolant is heated to a temperature of 85⁰C, the thermostat valve opens and the liquid begins to pass through the cooling radiator, thereby cooling down and preventing the engine from overheating.
Possible breakdowns:
- Valve jamming in one of the positions;
Expansion tank
The expansion tank is designed to compensate for the expansion of the liquid during heating, as well as the contraction during cooling. It is for these reasons that the amount of liquid in the tank is at an average level.
Possible breakdowns:
- Tank rupture due to a breakdown of the cylinder head gasket;
- Cracks in the tank due to old age;
Expansion tank cap
The main task of the tank cap is not only to close the opening of the coolant tank, but also to relieve excess pressure in the system. It is in the lid that a valve is installed that operates in two positions: pressure release and vacuum release (vacuum). If there were no valve, the pressure in the system would inflate the hoses and rupture the expansion tanks.
Signs of a broken cooling system pipe
The first and most common sign of a cooling system failure under the hood or under the car is wet and slightly greasy spots of coolant. These are the first signs that a pipe has burst somewhere. Also in the cabin on the instrument panel, there is a special indicator that will show the low fluid level in the expansion tank.
If the sensor fails, the engine temperature will rise rapidly, which may result in the engine boiling. It also happens that you can smell antifreeze in the cabin; this is an indicator that the pipe may burst not under the hood, but under the front panel or in the area of the interior partition and engine.
Many experienced car enthusiasts advise, from time to time, to simply check the level of antifreeze in the expansion tank. Inspect the pipes for greasy, oily stains and do not delay repairs if this is detected.
How to find a coolant leak in the system. First of all, it is worth inspecting the expansion tank for leaks. Next we move on to the radiator, since it is most often damaged. When inspecting, special attention should be paid to the joints of pipes (nozzles) and honeycombs, which are easily damaged.
Next, we inspect the pipes and hoses themselves along their entire length, since it is through them that the coolant circulates. Do not forget about the clamps at the connection points; due to engine vibration, the clamps may become loose, which means the pipe may come off the mounting point and leak.
The last and most unpleasant failure of the cooling system is liquid getting into the oil jacket. As a result, checking the oil level with a dipstick or opening the filler cap to fill the oil, you can see how it foams. This is the first sign that coolant has gotten into the oil.
Description of design
Cooling system
: 1 — radiator of the cooling system; 2 — steam removal hose; 3 — electric fan; 4 — fan casing; 5 — radiator supply hose; 6 — engine control system coolant temperature sensor; 7 — thermostat housing; 8 — hose for supplying fluid to the throttle assembly heating unit; 9 — hose for draining fluid from the throttle assembly heating unit; 10 - inlet hose; 11 — steam removal hose of the heater radiator; 12 — heater radiator supply hose; 13 — expansion tank; 14 — heater radiator outlet hose; 15 — coolant pump pipe; 16 — thermostat cover; 17 — coolant temperature indicator sensor; 18 - radiator outlet hose
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. It consists of an expansion tank, a coolant pump, an engine cooling jacket, a throttle body heating unit, a thermostat, connecting hoses and a radiator with an electric fan. The cooling system also includes a heater core (see “Removing the heater core”).
Coolant is poured into the system through the expansion tank. It is made of translucent plastic, which allows you to visually monitor the liquid level. To do this, the marks “MAX” and “MIN” are marked on the wall of the tank. In the upper part of the tank there are two pipes for connecting the steam removal hoses of the radiator of the cooling system and the heater, in the lower part there is a pipe for connecting the inlet hose of the cooling system.
Expansion tank cap with valves
The tightness of the system is ensured by the inlet and outlet valves in the expansion tank cap
Coolant pump
: 1 - impeller; 2 - pump housing; 3 - toothed pulley; 4 - control hole in the pump housing
The circulation of coolant in the system is ensured by a pump. The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by a timing belt. It consists of a housing, a bearing assembly with a seal, an impeller and a toothed pulley. There is a control hole in the pump housing to detect fluid leakage when the pump seal fails. The pump should be replaced as an assembly.
Jamming of the pump pulley due to failure of its bearing assembly or due to freezing of highly diluted coolant will lead to breakage of the timing belt and, as a result, to expensive engine repairs. The liquid enters the pump through a supply pipe located on the rear wall of the cylinder block under the catenary collector.
Direction of coolant flow in the thermostat housing and cover
: 1 — supply from the cylinder head cooling jacket; 2 - to the heater radiator; 3 - to the throttle assembly heating block; 4 - from the expansion tank; 5 - to the supply pipe of the coolant pump; 6 — from the radiator of the cooling system; 7 - to the radiator of the cooling system
From the pump, liquid under pressure is supplied to the engine cooling jacket, and from there to the thermostat housing. Two thermostat valves - main and bypass - redistribute fluid flows in the cooling system. On a cold engine, the main valve closes the channel in the thermostat cover connecting the lower (outlet) radiator hose with the pump supply pipe. The bypass valve of the thermostat is open, and the flow of liquid from the engine cooling jacket enters through the thermostat housing into the supply pipe of the coolant pump, bypassing the radiator of the cooling system - a small circulation circle. As the engine warms up, at a fluid temperature of 85±2 °C, the thermostat valves begin to move, closing the bypass channel and opening the main channel, passing the fluid flow through the radiator of the cooling system. At a liquid temperature of about 102 °C, the bypass valve closes completely, and the main valve opens to its full stroke - 8 mm, and the liquid enters the radiator of the cooling system, where it gives off heat to the surrounding air. The movement of fluid through the engine cooling jacket, thermostat housing and radiator of the cooling system forms a large circulation circle.
Thermostat
: 1 - plate; 2 — bypass valve spring; 3 - spring; 4—cylinder with heat-sensitive filler; 5 - main valve; 6 — rod; 7 - bypass valve
Fluid circulates constantly through the heater radiator and the throttle body heating unit and does not depend on the position of the thermostat valves.
Location of the coolant temperature indicator sensor
(for clarity, the radiator hoses and ECM wiring harness blocks are disconnected): 1 - cylinder head; 2 — coolant temperature indicator sensor; 3 — engine control system coolant temperature sensor; 4 — thermostat housing; 5 - thermostat cover
What does damage cause?
The most common cause is engine overheating. failure will occur in a very short period of time. As a result of overheating, the cylinder block becomes deformed, cracks may appear and the piston may become deformed.
But it is much worse when the piston is completely deformed and makes a hole in the cylinder block. Such a breakdown usually leads to a complete replacement of the damaged engine with a new unit.
How does oil get into the air filter?
Having figured out the reason for oil getting into the filter, we can indicate who is the “culprit” of this phenomenon. These could be the following internal combustion engine mechanisms:
- Main oil deflector. If its drain becomes clogged, excess oil leaves the car's engine with crankcase gases, rather than returning to the crankcase as it should.
- Filter element. The engine “chokes” due to the fact that this element is operated in a clogged state. The engine simply does not have enough air, and it tries to compensate for its lack by starting to suck it in from all available sources, including the crankcase.
- Piston rings. When they are critically worn, poor-quality oil collection is observed (it can safely be called excess), penetrating into the crankcase from the cylinder. The increased pressure that arises in this case leads to squeezing out the lubricant through the ventilation valve and oil deflector.
- A channel (or hose) designed to divert crankcase gases beyond the boundaries of the throttle assembly. If it is clogged, not only gases but also grease enter the filter.
The process of replacing the pipe
The first thing to do before replacing the pipe is to completely drain the coolant from the system. If the liquid is clean and drained into a clean container, it can be reused. Now it’s time to remove the clamps on the missing pipe. It happens that they rust, so you should prepare all the necessary tools and WD40 in advance to facilitate the removal process.
It is worth remembering that all procedures must be carried out on a cooled engine, especially draining the coolant, otherwise you may be injured.
A similar, new pipe must already be prepared in advance. The old pipe should be removed slowly and without much effort, since the radiator necks are not strong enough and break easily. If it cannot be removed, it is recommended to twist it from side to side, but not bend it in any way.
As a last resort, you can cut it to length, this way you can remove the old pipe. Taking it off is often not a problem, but putting on a new one is much more interesting. If the new pipe does not lend itself to the procedure, then its inside should be lubricated with a solution of soapy water. But in order to soften it, you need to lower the desired part into hot water.
Under no circumstances should you use oil or related materials, as the pipe may corrode over time, and oil may also get into the cooling system.
The last step is to put the clamps on the pipe, and only then put it on the radiator neck and water jacket. Make sure that the pipe is correctly positioned and not twisted. Now we tighten the clamps on the necks and begin to fill in the coolant.
After filling, make sure once again that there are no leaks in the places of replacement and repair. It is worth remembering that when draining, there may be some coolant in the heater radiator. Now we start the engine and check the serviceability of the system. After filling in the new one, you need to turn on the stove, then add liquid to the expansion tank.
If you manage to break one of the necks, you should immediately solder it using argon welding.
About the system
The cooling system in Grant is significantly different from the Priora one; it quickly warms up the engine to operating temperature even in the most severe frosts with the heater on and maintains a higher operating temperature, which helps quickly warm up the interior. The main difference in the cooling systems of these two cars is the thermostat. It is the Granta thermostat that ensures faster warming up of the car.
A clear difference between the two systems can be seen in the pictures below.
As you can see, the heater on the Grant is connected in series, and on the Priora in parallel. On the Priora, part of the heat goes into the expansion tank, but in the Grant, the antifreeze in the expander almost does not heat up and all the heat is transferred to the heater radiator.