In the summer, probably every driver encountered such a problem as engine overheating. But if you frequently inspect the engine cooling system and eliminate any difficulties that arise in a timely manner, then overheating of the engine can really be avoided. As the temperature of the cooling water increases, there may not be enough natural cooling, which is when the fans installed on the radiator turn on and increase heat removal.
A sensor is responsible for turning on the fans, which is triggered when the temperature reaches a critical level. This sensor is located at the bottom of the radiator. In this regard, the sensor that turns on the fan in the summer must be in good condition.
Fan switch sensor
Refusal of constant rotation of the fan using a belt drive made it possible to reduce the engine warm-up time. The electric drive, which consists of a motor, relay, switching sensor and battery, allows the fan to turn on only when the engine temperature exceeds the optimal value.
Thanks to this approach, the cooling system of internal combustion engines has become more efficient. Periodically turning on the fan made it possible to reduce fuel consumption, because the engine warm-up time was reduced and power losses due to the constant rotation of the blades disappeared.
How does it work and where is the fan switch sensor located?
The sensor is based on a bimetallic plate, which changes its shape with increasing temperature. When the coolant temperature exceeds the value indicated on the sensor body, bending of the bimetallic plate causes the sensor contacts to close. The electric current that passes through the sensor contacts turns on the power relay that controls the fan motor.
The sensor is located on the side of the radiator. On some models it is located at the top, on others in the middle. It is not difficult to recognize him. It looks like a large brass nut, to which two (less often three) electrical wires fit. When planning to change the fan switch sensor, consider the following.
The lower the sensor response temperature, the lower it is set relative to the coolant level. The switching temperature of the sensors, which are installed at the bottom of the radiator, does not exceed 85 degrees. The temperature of the sensors is set in the middle of the radiator to 90 - 95 degrees.
How to check the fan switch sensor
The need to check the sensor arises after the engine overheats or there is a suspicion of poor performance of the cooling system. First of all, it is necessary to check not the sensor, but the wires and relays that turn on the fan. To do this, remove the wires suitable for the sensor and short-circuit them; if there are not two, but three wires, then you need to short-circuit the middle one and each of the outer ones one by one.
The fan should turn on at low and high speed, depending on which contacts are closed. If the fan turns on, it means that the wires and relays are working properly and you can start checking the sensor; if not, you need to find and eliminate the malfunction (broken wires, poor contact, blown fuse, burnt out relays or fan motor).
- After making sure that the relay, motor and wires are working properly, proceed to checking the sensor. To do this, you will need a basin for coolant, a 30 key, a thermometer up to 100 degrees, a pan of water, a stove and a multimeter.
- Remove the terminal from the battery and place a basin under the car so that the coolant from the radiator does not pour onto the ground, but into it.
- Wait until the radiator cools down to 45 - 50 degrees, then unscrew the drain plug (it is located at the bottom of the radiator on the left or right side).
- After the liquid has drained, screw the plug into place. Remove the wires from the sensor (if there are 3 of them, then mark each one so that when installing a new sensor you do not mix them up), then unscrew the sensor with a 30 mm wrench.
- Pour water into a saucepan so that it covers the working part of the sensor (up to the nut) and place it on the stove. Monitor the water temperature with a thermometer.
Instructions for replacing the regulator
Replacing the fan switch almost always follows the same pattern:
- We need to prepare the “ground”. In some cars, this happens as follows: you need to rid the system of cooling liquid if the fan is installed at the bottom of the radiator, or, if the system has enough, remove water from the expansion tank. If the antifreeze needs to be completely drained, then you need to open the heater tap so that there is no residue. Important: do not pour the remaining liquid onto the ground, because antifreeze is quite poisonous.
- After this, you can remove the sensor by disconnecting the connected wires. Then, using the key, you need to remove the housing and unscrew it by hand. The new fixture must be tightened by hand, then a wrench can be used to apply the finishing touches. To prevent leakage, you can use a special thread tape, which will make the connection tighter and more reliable. After this, you can restore the contacts by returning all the necessary wires to their place, and fill the system with coolant.
Price issue
In the photographs below you can see what the device looks like, as well as estimate the cost of various models.
The request returned an empty result.
How to choose a new sensor
To select the right sensor, you need to know the optimal coolant temperature at which it should turn on and off. For a VAZ 2110 car this is 92 and 87 degrees. The optimal sensor response temperature for another car is indicated in the repair and operating instructions for the car.
Buy a sensor only in large stores and be sure to take a receipt. Before installing the sensor on the vehicle, check it as described above. If the difference between the temperature indicated on the sensor body and the temperature at which it actually operates exceeds 5%, replace it. Operating the motor at a temperature different from the optimal one greatly reduces its service life.
https://vipwash.ru/sistema-ohlazhdeniya/datchik-vklyucheniya-ventilyatora
What principle does the fan switch sensor work on?
A car engine converts only part of the energy from fuel combustion into useful work. A significant percentage is spent on heating the body of the unit, which needs to be cooled. The reliable functioning of the cooling system directly depends on the health of the wiring and the fan switch sensor. The fan switch sensor is designed to perform the following functions:
- activation of the fan impeller when a certain temperature is reached;
- adjusting the fan speed during cooling (not on all cars);
- turning off the fan, which protects the power unit from overcooling.
Where is the sensor located and how does it work?
Fan switching sensors are located on the cooling system elements. The installation point is located in the path of the fluid flow supplied from the engine jacket to the radiator. This is due to the fact that the liquid in this line will have the highest temperature.
Possible installation locations:
- thermostat housing outside the valve;
- cylinder head;
- lower radiator hose;
- side of the radiator.
On some vehicles, the sensor is combined with a coolant thermometer. The fans are turned on by the control unit based on temperature data. In this case, there is an additional sensor on the radiator that is used to operate the climate control or air conditioning. Triggering of any of the devices turns on both fans (on the engine and air conditioner radiators).
A similar solution is found on Japanese cars. On cars, two fan switching sensors can be used, located at the inlet and outlet of the radiator pipes. This scheme allows you to maintain the temperature in a narrow range.
Varieties
On cars, the following types of sensors are used to turn on the fan:
- bimetallic;
- waxy;
- thermistor;
- a sensor that operates on a circuit break or short circuit.
The first two types of sensors have an electromechanical operating circuit and can be of two varieties:
- single-speed, equipped with a single contact group that controls the fan in one temperature range;
- two-speed, equipped with a pair of contact groups configured to operate at different temperature ranges.
Regardless of the type, the sensors are a metal housing equipped with a thread. The body material used is non-ferrous metals based on copper (bronze or brass), which provide increased thermal conductivity. There is a hex key on the body that is used for installing the part. The wiring connector is located on the top of the sensor.
Bimetallic sensor
A bimetallic sensor contains a metal plate. In normal condition the contacts are open. As the plate heats up, it deforms and closes the circuit, supplying a control signal to the impeller motor turn-on relay. There are sensors that activate the fan motor directly without a relay. When the liquid cools, the plate returns to its original shape and the current supply to the motor stops.
Wax sensor
Sensors were produced for which wax or ceresite (or another substance with a significant coefficient of thermal expansion) was used as a working substance. As it warmed up, it expanded and shifted the metal membrane associated with the contacts. As it cooled, the volume of the wax decreased, and under the action of the spring the contacts opened.
Thermistor sensor
The thermistor sensor works on the principle of changing the resistance of a resistor installed in the fluid flow. The temperature change is recorded by an electronic unit, which recalculates the temperature value in accordance with the schedule.
Sensors that operate on open circuit or short circuit
Devices that turn on the fan when the circuit breaks are often found on Japanese-made cars. You can check the sensor type by removing the plug. When the block is removed from the tensile sensor, the fan will turn on.
At what temperature does the fan switch trigger?
The temperature range of the sensor response depends on the type of engine power supply. On carburetor cars, devices with a switching range of 82-110 ºС are used. The activation temperature is stamped on the body of the part. On cars of the same model, there may be sensors calibrated for different temperatures. According to the standard, sensors are divided into four groups according to operating temperature:
- 82-87 ºС;
- 87-92 ºС;
- 92-99 ºС;
- 104-110 ºС.
Russian cars use sensors of the first three groups. The engines of foreign cars are designed for more severe temperature conditions, so devices of the fourth category are often found on them.
When you start using distributed injection systems, the temperature at which the fan turns on is determined by the settings of the engine control unit. The sensor simply transmits temperature information to the control unit, which decides to turn on the fan according to the programmed program.
On injection machines, you can program temperature thresholds at which the fan switch on sensor will work. This should be done carefully, since it is easy to disrupt the temperature regime and damage the engine.
It turns out that the sensors are different. Which ones?
As can be seen from the question, now we will find out what varieties there are and how they differ from each other. So:
- The difference is in the manufacturer of the sensor. This does not play a special role. If a company is doing this, then it knows what it is doing. But still, don’t take one that’s too cheap, otherwise it may turn out to be a fake.
- Temperature conditions. Pay attention to the numbers that are engraved on the sensor. They will tell you a lot. For example, 92-87 are two temperature values.
- The first value, 92, is the temperature at which the sensor will operate and signal the fan to turn on and cool the liquid inside the radiator.
- The second value 87 is the temperature at which the sensor will stop cooling and fan operation. Thus, the temperature limit of this sensor is five degrees.
- This is the most common among coolant temperature sensors.
- But there are other sensors with other temperature conditions. They are created for the special conditions in which a particular vehicle operates.
- For example, in conditions of low temperatures or, conversely, increased temperatures, sensors are installed with different parameters.
We draw a conclusion. The most common sensor is the 92-87, but if necessary, you need to choose based on your climate and the weather conditions of your area. Here, for example, is a radiator sensor that is suitable for many cars with parameters 92-87 from LUZAR from St. Petersburg (see photo). Such a sensor costs no more than 150 rubles - that is, the price of the sensor is not high.
How to check the radiator sensor
This procedure is done in two different ways, which you will now learn about.
For the first procedure you will not need any equipment:
- If the temperature is already over 92 degrees, and the fan does not work, then a check is needed.
- Turn on the car ignition. We disconnect the two wires coming to it from the fan switch sensor.
- Connect these two wires together. If the fan turns on and works, then the failure is not in it, but in the radiator sensor.
- If the fan still does not work, then it should be repaired or even replaced.
The second method is carried out on a removed radiator sensor, or if you want to check the functionality of a new sensor before installing it on a car. So:
- For this you will need: a sensor, a container of water, a heater (stove, boiler), a multimeter, a thermometer with a scale of up to 100 degrees.
- Place the bottom of the sensor in a container of water and gradually heat it up.
- Using a tester, we check the short circuit and open circuit of the sensor contacts. To do this, we set the tester for continuity or resistance measurement, and connect the two ends to the two terminals of the sensor.
- If the sensor is triggered and then turns off, everything works and it can be installed on the car.
How to check the fan switch sensor?
The power sensor can be checked without removing it from the car, or in a dismantled form. Checking a device that has not been removed allows you to check the serviceability of the device, and the response temperature range can only be checked by removing the product from the car. Checking the removed sensor:
- Prepare a container, thermometer and multimeter. The multimeter is set to ohmmeter mode.
- Place the sensor in water and heat it to the required temperature. At low temperatures, the sensor resistance is shown as infinite.
- Wait until the resistance suddenly decreases. Check the sensor switch-on temperature.
- Gradually cooling the water, determine the contact opening temperature.
- Compare the obtained data with the passport values.
In the absence of a tester, the fan switching sensor can be checked with a test light, which lights up at the moment the contact group is activated.
In a car with a carburetor engine
The sequence of checking the sensor on a car with a carburetor:
- Turn off the ignition.
- Carefully remove the wires from the sensor. When dismantling, keep your hands and clothing at a distance from the fan impeller, since the electric motor can be started even when the ignition is turned off.
- Connect the wires in the plug.
- Turn on the ignition. The fan should start working. If the mechanism does not start to rotate, then the problem lies in the electric motor or wiring.
Radiator cooling fan sensor: how to check the response temperature yourself
The radiator cooling fan is one of the key elements that saves the engine from possible overheating. It should turn on when the coolant is too hot and not cool enough as it passes through the radiator. For example, this situation occurs when the engine is idling or the vehicle is moving at low speed, especially at high ambient temperatures.
The sensor is responsible for turning the cooling fan on/off. It should trigger at high temperatures, activating the fan. If this does not happen, the sensor will need to be replaced. In this article, we will look at how to determine that the radiator cooling fan sensor has failed.
1. How the radiator cooling fan sensor works 2. Where is the radiator cooling fan sensor located 3. How to check the radiator cooling fan sensor
How does the radiator cooling fan sensor work?
To understand how to test a sensor, you must first understand its operating principle. The design of the radiator cooling fan sensor is very simple, but it is somewhat different on carburetor and injection engines.
In a carburetor, it has two contacts and a bimetallic plate. When the bimetallic plate is heated to a temperature determined during the production of the sensor, the contacts close and current begins to flow through them to the fan, turning it into operation. On the injector, the sensor activation system is almost the same, except that the command to turn on is sent by the engine control unit, analyzing the need to activate the fan based on information coming from several other sensors.
Sensors on carburetor engines operate when a certain temperature is reached, and the driver can look at the markings on the device body to determine in what temperature range the sensor will operate. Typically, such sensors are activated at temperatures between 92 and 97 degrees Celsius. If the driver is concerned about possible engine overheating, he can find a sensor on sale that operates at a lower temperature and install it. On injection engines, the sensor response temperature is stitched into the “brains” of the car control unit.
Where is the radiator cooling fan sensor located?
Manufacturers determine the location for installing the fan sensor, depending on the design features of the engine. Most often it is placed at the bottom of the radiator, but sometimes it is more expedient to place the sensor near the thermostat and cylinder block.
How to check the radiator cooling fan sensor
We recommend reading: Radiator cooling fan does not work or does not turn off: what to do
Methods for diagnosing the sensors in question will differ, depending on which engine they are installed on and how they are turned on:
- On the carburetor. To check the radiator cooling fan sensor on a carburetor engine, you must turn off the car. Next, find the sensor in the engine compartment and remove the wires from it that go to the connector. After this, we start the engine and bridge the connectors from which the wires were removed. If the fan turns on, you can diagnose a sensor failure. Please note: In a situation where the sensor fails on the road, in order to avoid engine overheating, you can bridge the sensor contacts in a similar way. It is important to insulate them so that they do not touch the housing and cause a short circuit.
- On the injector. In an injection engine, you can carry out computer diagnostics of the sensor. A number of modern cars have a separate diagnostic error indicating that the cooling fan sensor is faulty. If such an error has been identified, you can diagnose the sensor on the car as follows. You need to disconnect the connector from the sensor and wait a few seconds. The control unit will detect that the sensor is no longer connected and will start the fan.
The options with complete sensor failure are discussed above. In this case, situations are possible when it partially fails, for example, it operates at the wrong temperature. This can also be checked in the following way:
- Take a tester, a thermometer for measuring water temperature, a container for heating water, water and the sensor itself;
- Next, pour water into the container and set it to warm up;
- Place the sensor to be diagnosed in water so that its contacts are on top;
- Monitor the water temperature with a thermometer, while holding the probes of the tester (included in the resistance measurement mode - Ohm) on the sensor contacts;
- Until the water is heated, the sensor resistance will tend to infinity. At a certain heating temperature, the sensor should operate and the resistance will decrease significantly. It is necessary to determine at what water temperature this occurs.
Depending on the results obtained, you can make a decision about the serviceability or malfunction of the sensor. If it operates at a temperature lower than stated, then such a sensor has some problems, but it can prevent the engine from overheating by turning on the fan in advance. It is much more dangerous if the sensor operates at a temperature higher than stated, in which case it will need to be replaced.
( 440 votes, 4.52 out of 5) Loading...
Source: https://okeydrive.ru/kak-proverit-datchik-ventilyatora-oxlazhdeniya-radiatora/
How to properly replace the fan switch sensor?
Typical set of tools and accessories for replacement:
- set of heads;
- extension cord with ratchet;
- pliers;
- flat blade screwdriver;
- sealant;
- a socket for removing the sensor or a suitable wrench;
- container for draining liquid (5-6 l);
- coolant for topping up (0.4-0.5 l).
Sequence of steps for replacement:
- Cool the engine to a comfortable temperature.
- Place a container and drain the coolant from the radiator. To access the drain valve, you may need to remove the engine crankcase protection or plastic mud flaps. Some vehicles require removal of the heating system pipe.
- Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor. Inspect the terminals, clean them from dirt and traces of oxidation. Check the condition of the wires going to the plug. If the insulation becomes cracked or otherwise defective, the worn area must be replaced. Connecting new wires must be carried out in compliance with polarity.
- Unscrew the faulty sensor. It is not recommended to apply a lot of force, as there is a risk of breaking the radiator. To facilitate the process, the use of liquids such as WD40 is allowed. To access the sensor installation location, it may be necessary to remove the battery, its platform, or engine air ducts.
- Lubricate the threads of the new sensor with sealant designed for use in elevated temperatures.
- Install a new O-ring on the sensor. Reusing gaskets is not recommended since the joint is not sealed.
- Screw the sensor into place and tighten to the required torque.
- Install the wiring plug onto the sensor.
- Restore the coolant level in accordance with the vehicle service instructions.
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature and check the operation of the new device. During the first days of operation, carefully monitor the coolant temperature. This applies mainly to domestically produced cars, since the sensors are often defective or set to the wrong response temperature.
On some cars, after turning on the ignition, a new sensor is diagnosed, which consists of turning on the cooling fan for 15-20 seconds (on a cold engine).
How to choose a new sensor?
When purchasing a new sensor, it is recommended to purchase a device of the same type and range as the one you had previously. However, it is possible to replace the device with a similar one, similar in characteristics.
Recommendations for choosing a sensor:
- The operating voltage of the sensor must correspond to the voltage in the on-board network;
- the connection plug must match the wiring harness;
- the sensor must match the current in the circuit. It is unacceptable to use a device designed to operate with a relay in the direct fan connection circuit;
- the temperature range of operation should be close to the marking on the broken device;
- The sensor body must have threads and the length of the threaded part of the appropriate size.
On modern foreign-made cars, the fan switching sensor is selected according to the original spare parts catalogues.
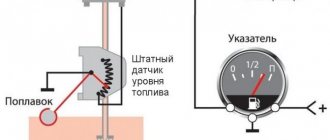
Description of the coolant temperature controller
The temperature sensor is a resistor element that performs the function of transmitting and receiving data about the temperature of the consumable in the cooling system. As the temperature increases, the sensor's resistance changes, causing it to supply voltage to the instrument panel. The latter has an indicator that shows to what temperature the car’s power unit has warmed up. Where is DTOZH located? The device is located on the cylinder head, behind the fourth cylinder.
In injection machines, the DTOZh gives the ECU temperature readings, and the ECU turns on the fan itself, the fan switch on sensor, as a rule, is a power sensor, closes the contacts at a certain temperature - turns on the fan relay and is located mainly on the radiator (in a carburetor car), since the DTOZH is located on the engine.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of DTOZH is the constant interaction of a magnetic field (constant) with the field of measuring devices. Voltage passes through all windings. The permanent magnet is connected to the indicator located in the dashboard. When the temperature changes, the resistance parameter of the device also changes, which leads to the oscillation of the needle.
Possible problems and methods for eliminating them
What malfunctions can occur in the operation of the device:
- The sensor has failed. This problem can be solved by replacing the controller with a functional one.
- The contact on the connector connecting the device to the on-board network is damaged. Also, the contacts may be oxidized. In case of such a malfunction, you can try to clean the contacts, but if their damage is very severe, then it is better to replace the connector.
- The device may stop working due to a damaged electrical circuit. It is necessary to diagnose the condition of the wiring with a tester; if the circuit is truly damaged, then the faulty section must be repaired or replaced.
Regulator diagnostics
To check functionality, you need to perform the following steps:
- First you need to warm up the power unit so that the temperature of the internal combustion engine increases to 90 degrees. After this, the engine can be turned off.
- Next, the ignition is activated and the car's capo opens.
- You need to disconnect the tip of the wire with the measuring device, and then short it to the motor housing.
- If, as a result of the actions performed, the sensor arrow on the control panel began to deviate to the right, entering the red zone, this indicates a breakdown of the controller. If the arrow does not move, then most likely there is an open circuit in the connection circuit.
The easiest way to check for an open circuit: on a working engine, remove the chip from the DTOZH, if everything is normal and there is no break in any circuit, then the fan will turn on at maximum speed (video shot by Dmitry Makarov).
How much does the sensor cost?
The cost of the sensor depends on its type and car brand.
| Name | Price, rub |
| Bimetallic for domestic cars | from 250 to 400 |
| Sensor for budget foreign cars | from 700 to 1500 |
| Prices are relevant for three regions: Moscow, Chelyabinsk, Krasnodar |
The cost of sensors for some types of vehicles can reach up to 3-6 thousand rubles.
https://avtozam.com/elektronika/sensor/datchik-vklyucheniya-ventilyatora-v-avtomobile/
Operating principle of the device
based on the difference in linear expansion of metals. When the coolant heats up, the bimetallic plate of the device changes its position. At a certain moment, the contact group closes. A signal is transmitted to turn on the fan. In some sensors, when the engine overheats, the circuit breaks.
Depending on the model, the sensors have different temperature response limits. So, to turn on the fan of the VAZ 2114-2115, a temperature of 102-105 ° C is required. The shutdown signal comes when the engine temperature drops to 85-87°C. When choosing a new sensor for his car, the car owner should focus on the old device.
In the absence of the original, previous device, the necessary information can be obtained from special catalogs.
Most modern fan control systems do not have sensor limits. It does not operate in relay mode, but constantly transmits information about the engine temperature to the electronic control unit. The ECU itself sets the limits for turning the fan on and off. Changing the operating range will require brain reprogramming.
Diagnosis and common causes of cooling system problems
Closing contacts
One of the most common causes of this breakdown is a banal short circuit of the contacts of the coolant temperature sensor. In this case, when the ignition is turned on, the cooling fan turns on, since electric current is constantly supplied to the fan due to a short circuit. The consequence of such a malfunction may be, perhaps, accelerated discharge of the car battery.
We recommend reading an article on the topic: how to extend the life of a car battery. This article talks about the reasons for the short life of the battery, how to actually extend it, as well as the main signs of battery failure.
To diagnose this malfunction, you should disconnect the sensor and use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance at its contacts. If the sensor is working normally, then the resistance will be extremely high (the readings are only nines, which is analogous to “infinite” resistance). If the resistance is low, then the contacts are closed and the sensor must be replaced.
Also similar symptoms include a short circuit of the fan terminals to ground, in which case it will also work constantly as soon as the ignition is turned on. Since the voltage is supplied directly from the battery.
Small amount of antifreeze
Another common problem is too little coolant. It is to its temperature that the DTOZH reacts. With a small amount of antifreeze, the liquid warms up much faster than the engine itself warms up, as a result the fan turns on too early. Add fluid to the required level and, just in case, check for leaks in the cooling system.
Thermostat and its sensors
On some modern cars, the cooling system is equipped with thermostats with sensors that regulate the operation of the cooling system more efficiently. However, this design is more complex in structure than a conventional one, and due to its complexity it is susceptible to various problems. If the operation of a specific sensor that is connected to the thermostat is disrupted. Or the cooling control system does not receive data from the thermostat sensors, then, as a rule, it “goes into protection”, turning on the fan for constant operation. Checking these sensors is, in principle, similar to checking the contacts of a conventional DTOZH. We measure the resistance, and if it is low, then the sensor should be changed.
It is worth noting that the ECU can also “go into protection” in cases where the fan is controlled through the on-board computer itself. The reason for this may be problems with contacts. As a rule, contacts tend to oxidize over time, which greatly complicates the transmission of signals from sensors to the ECU. And if the required signal does not pass through at all, then in this case the control unit forcibly turns on the cooling fan, regardless of the engine temperature.
To eliminate it, you just need to clean the contacts and coat them with insulating grease to prevent the spread of corrosion. By the way, this procedure is recommended to be carried out 2 times a year to avoid unpleasant situations at the most inopportune moment.
Connection diagram for the fan switching sensor in injection engines
The carburetor has been used on gasoline engines for more than 100 years. Despite the new fuel injection systems, this technology has not lost its relevance due to the simplicity of the design and the ability to service the system with your own hands. An injector is an integral component of the fuel system of many modern cars.
- Despite the complexity of the repair, this unit characterizes itself exclusively on the positive side. This is largely due to its efficiency, ease of operation and high environmental friendliness.
- Unlike carburetor cars, where the sensor directly closes and opens the cooling fan circuit, in injection engines the device operates only with an information signal.
- After processing the received data, the ECU sends a control action to the fan relay installed on the radiator. The main advantage of this scheme is the possibility of emergency operation of the cooling system in the event of a loss of communication with the sensor or its failure.
- The ECU can also adjust the engine operating mode by influencing the injectors. To determine the location of the fan switch sensor, you need to pay attention to the thermostat. In injection engines they are located next to each other.
In some car models, wires go from the sensor to the dashboard to indicate the status of the device or to display the current coolant temperature.
Operation of the cooling fan in fuel-injected cars
The operation of the fan unit for cooling the temperature in injection engines is assigned to an electronic motor controller. Its software is configured to trigger the engine overheat protection system in the temperature range from 100 to 105 degrees Celsius. If a defect occurs in the operation of the fan switch on in a VAZ with an injector, the controller “remembers” the error code and the fan starts working when the motor is turned on.
However, there are separate precedents when electronics in the form of a controller “reads” a defect and the fan installation may not begin to function when extreme temperature values are reached, i.e. above 105 degrees Celsius. Then, to test the circuit and the device, you need to disconnect the contact of the cooling fan switch sensor with the engine turned on.
If the circuit is functioning, then the fan unit should turn on and turn off with reverse action. If the circuit does not function, a test should be carried out to determine the suitability of the safety device and the technical readiness of the wiring and relay.
A quick check of the system is carried out as follows: we bridge the two contacts of the fan relay. If the product works in this position, then, without disconnecting the relay from the wire block, bridge the body of the relay and its contact using a “control”. In this position, the relay should function like the fan unit, which means that the controller or the relay connecting wire to the contact of this device is faulty.
If there is no sound of relay initiation, there is only one conclusion - the part requires replacement. If the fan unit does not start working when the relay terminals are closed, it is necessary to test the fuse for integrity and the power supply to the terminals of the fan unit. If power is supplied to one contact and not to the other, this may indicate defects in the EDC of the fan installation.
Checking the functionality of the sensor
Checking the functionality of the device should begin with monitoring the response temperature. To do this you will need a thermometer and a multimeter. All actions can be performed independently, without resorting to a visit to the service center. If the multimeter is equipped with a thermocouple, then there is no need for a thermometer. To check the sensor, follow the instructions below:
- Switch to resistance measurement mode. For convenience, you can select the dialing mode;
- Immerse the threaded part of the sensor in water;
- Start gradually heating the water. You can control the temperature using a thermometer, or temporarily switching the multimeter to the thermocouple mode;
- Wait for the device to respond;
- Compare the temperature to which the sensor responded with the nominal value.
If there is a critical deviation of the response limit, the sensor must be replaced. After purchasing a new device, you must check its suitability. Defective products are very common on sale, so checking whether the sensor turns on correctly is the responsibility of every car owner.
Replacement with draining antifreeze
If you discover that the device is not functioning correctly or is completely inoperable, you need to replace it with a new one. To perform dismantling, you must follow the instructions:
- If the engine is hot, it must be allowed to cool;
- De-energize the vehicle ground by disconnecting the negative terminal;
- Remove the expansion tank cap;
- Remove ;
- To prevent contamination, it is necessary to place a container under the drain hole;
- Drain the antifreeze from the . There is no need to drain antifreeze from the cylinder block. To unscrew the drain plug, just a hand is enough, so no tools are needed;
- When the liquid stops flowing out, you should return the plug to its place to avoid its loss;
- Remove the terminal with wires;
- Use a wrench to carefully unscrew the sensor.
Installing a new sensor without draining the coolant
In the injection engine of most car models, the sensor is located high in the cooling system, which allows it to be removed without a significant spill of antifreeze. To do this, you must follow the instructions below:
- Do not unscrew the sensor completely. In this case, a slight leakage of antifreeze will begin;
- Check the copper washer on the new sensor;
- Unscrew the old device with one hand and quickly bring the new one in with the other;
- After tightening the regulator, thoroughly wipe the area from any coolant drips;
- Check the quality of installation for leaks.
With this method, the car owner can significantly save time. The disadvantage of this method is the need to make a replacement quickly, which can cause difficulties for inexperienced car enthusiasts. If the circumstances are unfortunate, a large amount of antifreeze may spill from the cooling system.
Keeping all elements of the cooling system in working order will protect the engine from overheating and unpleasant consequences. It is necessary to carry out timely monitoring of the operation of the regulator, especially when the first symptoms of overheating appear. Since the work requires the presence of heated fluid, all manipulations should be performed on a cooled engine. This will protect the car owner from thermal injuries.
https://swapmotor.ru/ustrojstvo-dvigatelya/datchik-vklyucheniya-ventilyatora-v-inzhektore.html
Causes and symptoms of sensor failure
Typically, such a sensor is a bimetallic thermal switch that operates at certain temperatures. Since its working area is in constant contact with an aggressive liquid (antifreeze), oxidation of the contacts occurs and, as a result, the sensor fails. If you experience the following symptoms, then you urgently need to contact a car service:
- The fan does not turn on
- The fan turns on but runs unevenly
- The fan turns on when the temperature is too low or high
- The fan runs constantly
The design of many foreign cars involves a constant supply of voltage to the fan. In this case, the sensor simply interrupts the circuit, that is, turns off the fan when necessary. In other cars, it’s the other way around – the sensor closes the circuit, thereby turning on the fan. As a result, a malfunction of the sensor can lead to the cooling fan running constantly, thereby preventing the engine from reaching operating temperature, or, conversely, not turning on at all, which can lead to engine overheating.
Connection schemes
In VAZ 2110 injection and carburetor engines, the TM-108 bimetallic temperature sensor is used in different ways to control turning the fan motor on and off.
For carburetor engines it is located on the radiator on the left in the direction of travel. When the threaded part located directly in the coolant is heated, the bimetallic plate bends and closes the contacts. The voltage from the battery is supplied through a fuse to one contact of the electric motor, the second, when the sensor is triggered, is connected to the housing, setting the impeller in motion.
For VAZ 2110 and TM-108 injectors, it is located near the thermostat, the signal is sent to the electronic control unit (ECU). The control signal from the ECU is sent to the cooling system fan relay, which, similar to the sensor of a carburetor engine, controls the electric motor.
All engines have another device in the cylinder block, the signal of which is used to indicate the coolant temperature on the panel in the cabin.
The fan does not turn on
There may be several reasons for this:
- Fuse. In the mounting block, fuse F7, rated 20 amperes, may be faulty - it is responsible for powering the electric fan and sound signal circuits;
- Thermostat. The liquid circulates only in a small circle, the radiator and sensor do not heat up, and accordingly, the fan does not turn on. You can check by simply probing the pipes; those connecting to the radiator should begin to warm up after opening the thermostat;
- Sensor. For a VAZ 2110 with a carburetor, the contacts are closed for testing; if the device malfunctions, the electric fan will turn on. The connector of the injection motor must be disconnected; with the remaining elements working, the ECU will detect a break in the circuit and issue a constant alarm signal to the relay, which will forcibly turn on the electric motor for cooling;
- Cooling system fan relay for VAZ 2110 injection engines. The sensor is turned off and the power contacts on the relay located in the additional fuse box are closed. If everything works, then we check the control winding: on one contact there is always a positive from the main relay, connecting the second to the body, we try to hear the operation click. But it’s better to simply replace the relay for testing, temporarily, with a known good one;
- Electric motor. During testing, the connector is disconnected; to force the impeller to turn on, voltage is supplied directly from the battery.
If all the elements are working properly, then you need to look for a break in the wires, “ringing” them one by one. Poor contact of the relay and sensor connection wire terminals with the car body is also possible. The worst case scenario would be an ECU failure, in which case the signal from “leg” 46 usually “floats” and does not reach the values of +12 volts (off) and 0 (on).
Procedure for checking
The operation of the fan on the VAZ-2114 is connected through 2 fuses. One of them is also responsible for the sound signal.
You can check it by pressing the horn. If there is no sound, replace it with a whole one. It is located in the mounting block, it is 20 ampere, marked F5.
Check and, if necessary, change fuses
The second one is located under the dashboard, on the passenger side.
Under the casing there are 3 relays with a fuse for each. The middle pair is responsible for the operation of the cooling fan. Replace the blown element with a new one (the fuse can be “ringed” with a multimeter or limited to a visual inspection. To check the functionality of the relay, you will need an ohmmeter). When checking their condition, at the same time make sure that the contacts are in normal condition, and if oxide is detected, clean them.
Important! If you find a blown fuse, you should not limit yourself to replacing it with a new one. It is imperative to find the cause of the break, since in the near future the new one will burn out again.
Checking the fan switch sensor
If the cause is not found, the next step should be to check the functionality of the fan switch sensor
. It's not difficult to do this. Disconnect it and turn on the ignition, while paying attention to the fan. The rotation of the blades indicates that the cause of the problem is in the sensor.
Checking the cooling system fan switch sensor
Due to the fact that very often the sensor begins to malfunction, sending erroneous signals, it is recommended to check it in another way
. To do this you will need a container, a thermometer and a multi-mert. Wires from the measuring device are connected to the sensor terminals, the threaded part of the sensor is immersed in the liquid. Heat the contents of the container to the temperature at which the fan operates (on a VAZ 2114 - 92 degrees). When the contacts close, the multimert will sound a sound signal. This means the sensor is working, if this does not happen, you can safely throw it away and buy a new one.
Healthy! Before installation, it is advisable to check the functionality of the purchased sensor in the same way.
Video about checking the cooling fan switch sensor
Final check
Having eliminated the problem, start the car engine. The fan motor should start after about 5 minutes of idling.
. If this does not happen, and the temperature has reached the desired level, diagnose the faults again.