The oil pressure sensor is an engine condition monitoring device. Its purpose is to warn the driver about a critical decrease in pressure, so that he, in turn, can make a quick stop. To avoid troubles on the road, the motorist must know how this sensor works and where it is located.
Oil pressure sensor - operating principle
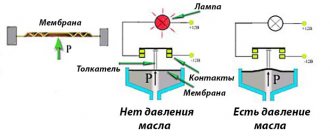
The operation of this device is based on a membrane mechanism. When the required pressure appears in the oil system, the sensor contacts close or open. In most cases, it is the opening that is used.
The oil pressure sensor is a whole system, the main one of which is the instrument panel. There is an emergency oil pressure lamp on the dashboard, which lights up when the ignition is turned on. A burning lamp indicates that the required pressure is not available in the system. After starting the internal combustion engine, the sensor contacts open and the lamp goes out, indicating that the pressure is normal. As a rule, the sensor itself is made of metal and is a mass, due to which only one wire fits to it.
In many modern cars, the lamp goes out after a certain period of time after turning on the ignition, indicating that the system is working and lights up if the pressure is lost. Also, many cars can be equipped with a special sound alarm, which also goes off when the sensor is activated.
A separate type of sensors is paired with a pointer. These first appeared on the VAZ-2106, but after a while they became unpopular. The bottom line is that the gauge shows the actual oil pressure in real time, including after increasing the crankshaft speed. Their principle is based on changing the resistance of the sensor, depending on the pressure. Despite the complex circuit, such sensors are the most informative, since they have ways to show a decrease in oil pressure beyond the threshold for the lamp to operate.
The tasks of any oil pressure sensor include the following functions:
- Warning the driver about emergency low oil pressure in the engine.
- Low oil level warning.
- Other problems with the lubrication system.
Attention! When an emergency oil pressure icon appears on the panel, it is recommended to immediately stop the engine and take the car to the nearest service station.
How to choose a new sensor?
In some situations, they try to select the model of the emergency oil pressure indicator based on the make and model of the car, but this approach does not provide a 100% guarantee of compatibility. Therefore, it is much more profitable to select by VIN code, this will help avoid problems with matching.
Rice. 8. Selection of emergency oil pressure sensor by code
Otherwise, in order to purchase a product of proper quality, you should follow several rules:
- Avoid temptingly low prices - if the cost is significantly lower than the market average, it is most likely a fake.
- The image on the label must be clear, the letters are clearly visible, and not blurred.
- In accordance with clause 3.2. GOST 22520-85 the body of the new part must have no visible mechanical damage - scratches, chips, cracks, etc.
- The kit includes both the sensor itself and the o-ring for it. In the case of a fake, quite often the product is not equipped with a gasket in order to save money.
Causes of low oil pressure
There are several reasons why the warning light may come on:
- decreased oil pump performance;
- oil filter check valve malfunction;
- dirt in the engine;
- wear of engine liners;
- increased wear of the camshaft and its bed;
These malfunctions can fatally affect the condition of the entire engine and should not be ignored. Driving with low oil pressure can lead to local overheating of parts, their deformation and jamming. This is especially true for moving parts between which friction occurs.
Oil pressure sensor response threshold
For most cars with an internal combustion engine, oil pressure of at least 1 bar at idle speed of the crankshaft is considered normal. If this value is lower, then there are problems in the oil system of the machine. In this case, appropriate repairs are necessary.
The sensor response threshold in most cases is 0.1 bar. For Mitsubishi this parameter is 0.7-0.8 bar. On Nissan cars there are sensors with a threshold of 0.6 bar. Subaru has the lowest response threshold - only 0.15 bar and this is bad. The higher the sensor response threshold, the better, since the decrease in oil pressure in the engine is a gradual process and occurs in the order of wear and it is better if the driver is aware of this in advance. This way there is a chance to save the engine before its “death”.
Replacement
Before buying a sensor to replace a faulty one, it is worth checking which model is installed on the car. Externally, all devices are similar, but their electrical and mechanical parameters differ.
Be careful. Minor discrepancies can significantly distort the readings. For example, similar car models are sometimes equipped with different instrument panels.
The sensor and the measuring device on the panel work in pairs, so installing a sensor whose resistance is higher than the standard one will underestimate the readings. At normal pressure the needle will barely move. Otherwise - if the sensor resistance is below the required value - the device will go off scale.
Replacement procedure
To replace the pressure sensor, no special pullers are needed. A standard set of car tools is quite sufficient.
- Since the sensor is an electrical device, before work it is a good idea to turn off the ignition and remove the negative terminal from the battery.
- After that, look around. Think about how best to get to the sensor. It may be necessary to remove some parts that make access difficult.
- Disconnect the sensor from the wiring. In some cases, it is enough to remove the contact connector from the external pin. Sometimes, if the sensor is difficult to reach, car manufacturers install an additional connector on the wire in a more accessible location.
To disconnect the wiring, unscrew the mounting bolt and remove the terminal
To unscrew a sensor that is disconnected from the wiring, you will need an open-end wrench.
First of all, without lubrication, the crankshaft and connecting rod bearings will suffer. The plain bearings in these units can operate without oil pressure only without load, and even then after a few minutes the wear will become too severe. Under load, the liner instantly “smears” over the surface of the crankshaft journal, the oil supply is completely shut off, and further developments depend only on the design or chance.
Boris Ignashin
https://www.kolesa.ru/article/ne-vosstavshie-iz-ada-kak-i-pochemu-umirayut-motory-ot-peregreva-i-poteri-masla
For more detailed replacement recommendations, please refer to your vehicle's owner's manual. For example, some manufacturers recommend installing the sensor on sealant. Listen to their advice.
Where is the DDM sensor located?
There are only two installation locations for such devices:
- Cylinder head;
- Cylinder block;
The first place is one of the best. The fact is that in order to push the oil to the camshafts, good pressure is necessary. At the top of the engine this pressure is already reduced and without taking into account losses this value should be at least 1 bar. Sensors located at the top of the engine record losses and can warn the car owner about the beginning of engine wear. In this case, the CPG is considered not yet damaged.
The oil pressure sensor, which is screwed into the cylinder block itself, cannot boast of such an advantage. While the pressure in the block is still within normal limits, it begins to drop in the head. Ultimately, the motor will wear out, but there will be no warning about this on the panel.
Checking the serviceability of the sensor with a light bulb
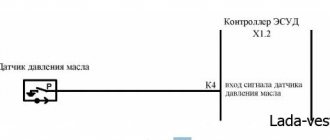
You can also check the electronic oil pressure sensor using a 12 V light bulb instead of a tester. To carry out such tests, you will need a charger (or battery) and a compressor (preferably with a pressure gauge). Diagnostics are carried out in the following sequence:
- Wires of sufficient length are soldered to each contact of the light bulb (0.5 - 1 will be enough).
- One end of the wire is connected to the output contact of the DDM.
- The “negative” terminal of the charger (or battery) is connected to the sensor body.
- The second wire from the lamp is connected to the “positive” terminal of the charger or battery. If the sensor is fully operational, after applying voltage from the charger (or connecting all elements of the circuit in the case of a battery), the light should light up. If it does not light up, the sensor is faulty. If it lights up, check further.
- The circuit includes a pump or compressor to pump approximately 0.5 atmospheres of pressure onto the sensitive part of the oil pressure sensor. The value may vary, it depends on the type of device and what operating pressure it is designed for. But more often it is precisely the floor of the atmosphere.
When the specified pressure is reached, the light should turn off, since in a working sensor the electrical circuit is broken. If this does not happen, the sensor must be replaced.
Oil pressure sensor malfunctions
As with any device, this sensor is characterized by certain malfunctions. They are as follows:
- the lamp on the panel does not light up;
- the lamp is constantly on;
- the sensor is leaking;
The reasons for a particular breakdown can be very different. Therefore, the diagnostic method will be different.
If the lamp on the instrument panel does not light up, first of all, you need to check the operation of the sensor. To do this, remove the chip from it and connect the contact to body ground. If the lamp lights up, then the sensor needs to be replaced; if not, then the lamp in the instrument panel may require replacement. It is also possible that the sensor circuit is broken.
If the lamp is constantly on, you must first check the wiring - disconnect the chip from the oil pressure sensor and turn on the ignition. If the lamp continues to burn, then the problem is the short circuit of the “plus” from the shield to ground. The second option is a malfunction of the sensor itself. But this can only be checked by measuring the oil pressure. To do this, instead of the sensor, you need to screw in a measuring device. If the readings are within normal limits, then the sensor requires replacement, but deviations from the norm no longer indicate a malfunction of the indicator, but problems in the engine.
The oil pressure sensor may leak due to mechanical damage or natural wear. Recently, devices with plastic casings have become popular, which tend to crack during operation. Through these cracks, oil can leak out, “marking” the area with an oil stain.
The second option is a failure of the oil pressure sensor seal. Most devices use a copper washer that is clamped when the sensor is tightened and seals the joint. This washer cannot be reused. If the oil pressure sensor is leaking through the threaded connection, this indicates an outdated copper washer that needs to be replaced.
Features of work
Then, membrane sensors began to be used on machines to determine the operating parameters of the lubrication system. They come in two types:
- Mechanical.
- Electrical.
Mechanical ones are outdated and not used. The measuring device consisted of two sensors - membrane and measuring. They were connected by a tube filled with oil. The essence of the work is very simple - increasing pressure in the system leads to bending of the membrane installed inside the sensor. The membrane moves, pushes the rod, which squeezes out the oil in the tube. The resulting pressure caused the needle on the measuring sensor to move, and the driver determined the pressure in the system using a set scale. This is how diagnostic analog pressure gauges work now.