Maximum traction is achieved by a wheel that keeps its tread contact patch at rest relative to the road surface. Both braking and acceleration of the car can cause slippage in this friction pair. The physical phenomena here are the same, the only difference is in the sign of the acceleration, it will be negative in the first case and positive in the second. But this does not affect the essence of what is happening, since both cases do not bring anything good.
ASR - what is it in a car and how does it work?
Such equipment is classified as active security systems. The main task of the system is to completely, or as far as possible, prevent the possibility of wheel slipping when driving on a winter road, as well as when driving on muddy country roads. It is slippage that often becomes the reason that the driver cannot leave on his own; he has to turn to the help of a tractor or drivers of passing cars.
There are two main principles of operation of the ASR traction control system:
- The first scenario starts if the car is moving at a speed of up to 60 km/h. In this case, a pump with brake fluid connected to the ASR sensors quickly creates pressure and brakes the wheel that has slipped.
- The second operation option is activated at speeds above 60 km/h. In this situation, braking can be dangerous, so ASR sends signals through the ECU to the engine and reduces torque. This is not always 100% effective, but it is very safe for the driver.
There is an opinion that the division into two scenarios occurred in order to preserve the pads, which can overheat and even burn out at high speed. But manufacturers say that at high speeds you simply cannot initiate braking from one side. This can lead to skidding and will only complicate the situation for the driver on difficult roads.
The system is controlled by sensors installed on each drive wheel. On vehicles with all-wheel drive, ASR equipment is much more expensive and more complex, but here it brings its own advantages to cross-country ability and safety of off-road driving.
Pros and cons of a car's traction control system
By preventing the drive wheels from slipping, the system gives the car, especially with a very powerful engine, several useful features:
- confident start from a standstill in the most efficient mode, when the wheels are constantly supported on the verge of failure;
- rapid acceleration, limited only by the coefficient of road adhesion, and not by the driver’s abilities;
- reduced tire wear on the drive wheels;
- increased safety when cornering under traction on a slippery road, the system prevents the car from turning into an uncontrolled skid;
- fuel is saved, which is not spent on the useless burning of tire rubber when slipping on dry asphalt;
- increased cross-country ability when the rotating wheel is not allowed to dig a hole under itself, where it remains until the tractor arrives, while the second wheel will receive additional torque, which will allow it to successfully pull out of a mud ambush.
There are also disadvantages that developers struggle with, not always successfully:
- wear of brake pads and discs increases;
- the car’s differential is overloaded, which is not always designed to transmit significant power to only one wheel;
- difficulties of compromise when choosing the threshold for the system to operate, beyond which it actively intervenes in control;
- difficulties in selective shutdown if the machine has a large set of additional functions for autonomous control of brakes and traction.
Recently, ASR is almost not used independently, but works with other electronic assistants, for example with the ESP stabilization system.
Is ASR better or worse than traditional ESP?
The designation problem is one of the devils of the modern automotive industry. Drivers of Toyota cars could read the first part of the publication with a grin, since they know that the traction control system is called TRC (Traction Control), and other motorists even found other designations in the documentation for their car - TCS (Traction Control System), ETS, ASC and other abbreviations. In general, these are designations of the same system.
ESP is more than just traction control equipment. This is a whole complex of means for maintaining directional stability, which includes the following equipment:
- ASR or any other type of traction control from the above named options;
- ABS is an anti-lock braking system that reduces the risk of wheel locking when braking a car;
- MSR is also anti-lock braking equipment that prevents the wheels from locking during engine braking;
- EBV is a system for distributing braking forces between all wheels of your car.
In luxury cars you can find a dozen more abbreviations that call security and control systems. So it is impossible to find the differences between ASR and ESP - these are the names of completely different phenomena in your car. ACP is only part of the ESP complex, providing one of the factors reducing the risk of skidding or burying in a mud and snow hole.
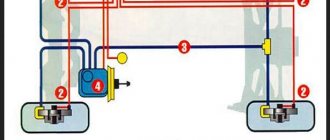
What does ABS consist of and what is its operating principle?
The design of the system implies the presence of a control unit, speed control sensors and a hydraulic modulator.
The functioning of the anti-lock braking system involves three stages: releasing pressure in the brake system cylinder, maintaining it and increasing it to the required level. In reality it looks like this:
- When braking, speed sensors transmit data to the control unit.
- The control unit smoothly reduces the speed of the car.
If one of the wheels begins to slip or has completely stopped, the sensor informs the control unit about this, which activates the exhaust valve. It blocks fluid from entering the wheel brake cylinder - the pump immediately begins returning it to the hydraulic accumulator. The result is that the blocking is removed. When the wheel speed has returned to normal, the control unit closes the exhaust valve and opens the intake valve. As a result, the pump starts working again, but now it performs the actions “in the reverse order”: it pumps pressure into the brake cylinder, which allows the wheel to be braked. All these operations are carried out very quickly. They are repeated until the vehicle comes to a complete stop.
Are there clear benefits from an ASR system?
The advantages are that when going fishing on a dirt country road, you don’t have to get out of the car and push it, getting all your clothes dirty. As soon as the wheel begins to spin, the system comes into action and practically locks it, allowing the other drive wheel with better grip to pull the car out.
The ASR traction control system is practically not installed in inexpensive cars. Most often, this is a privilege for a car of a higher class or more expensive configuration. If you have a choice whether to install ASR in your car, but you need to pay extra money for it, you should choose the option of installing this complex. This increases your confidence and safety in operation. Even the first winter with your car will show that you made the absolutely right decision.
Deciphering abbreviations
What does the brand owner want to say by indicating that his cars are equipped with an ASR system? If you decipher this abbreviation, you get Automatic Slip Regulation, and in translation - automatic traction control system. And this is one of the most common design solutions, without which modern cars cannot be built at all.
However, every manufacturer wants to show that their car is the coolest and most special, so they come up with their own abbreviation for their traction control system.
- BMW is ASC or DTS, and the Bavarian automakers have two different systems.
- Toyota – A-TRAC and TRC.
- Chevrolet & Opel – DSA.
- Mercedes - ETS.
- Volvo-STS.
- Range Rover - ETC.
It hardly makes sense to continue the list of designations for something that has the same operating algorithm, but differs only in details - that is, in the method of its implementation. Therefore, let's try to understand what the principle of operation of the system that prevents wheel slip is based on.
Are there any disadvantages to ASR equipment in your car?
Many experienced motorists will look at how the ASR system works, understand its primitiveness and say that it makes no sense. This is only partly true. If you are an experienced driver with 20 years of experience driving on difficult roads, then even without such help you are unlikely to get stuck in snow captivity. But for car owners with less vivid experience, such complexes will still be useful.
Among the disadvantages, it is worth highlighting only a few features:
- quite high cost if such a system can be installed on your car as an option when ordering a car in the showroom;
- not always effective response; very often the ASR initiates braking too late, when the car has already dug in;
- controversial work at high speeds, since here this equipment is powerless to do anything effective;
- the inability to disable on some cars that do not allow you to deactivate the entire ESP module;
- rapid wear of the pads if you constantly drive on rough or dirty roads with the risk of the wheels slipping.
ASR will not judge whether slipping is dangerous or safe on your car. It will work in any situation where the sensors indicate a slipping wheel. Of course, without turning off such a system, you will not be able to demonstrate the skills of sports driving, police turns and beautiful controlled skidding on the snow. The ASR will turn on at the most crucial moment and ruin your turn.
Is it possible to disable ASR?
If necessary, you can deactivate the system. Typically, this option is useful for beginners who want to practice their driving skills on an empty road.
The ASR OFF button, which allows you to disable the option, is located in most cars near the gearshift lever or on the dashboard. When you press a key, the corresponding light will light up.
Detailed instructions for deactivating the system in your car are presented in the car's operating manual.
Results: how can you evaluate the performance of ASR on a car?
It is difficult to give an unambiguous assessment of this set of security systems. As part of ESP, this unit copes well with certain nuances at low speeds. But when driving along the highway, ASR can even prevent the driver from correcting the situation on his own. The benefits of braking a wheel during slippage are also controversial.
Unfortunately, ASR is not a replacement for a good mechanical lock, as the electronics cannot distribute torque across all drive wheels as effectively. However, this is a solution for those cars in which there cannot be any blocking. If you have the choice of optionally installing such a system, then you should take advantage of this offer.
How does ESP work?
External sensors analyze various parameters - the functioning of the braking system, the characteristics of the vehicle's movement, the position of the accelerator, and changes in the steering angle. This data is transmitted to the control unit. He compares the information received with the actual movement of the car. If ESP decides that the driver has lost control of the car, it intervenes in the control, that is, it uses mechanisms that are associated with other active safety systems.
Correcting the trajectory of the machine is carried out in several ways:
- By braking specific wheels. The system itself decides which wheels will brake. So, when skidding, braking is carried out by the outer front wheel.
- Thanks to changes in engine speed.
The ESP control unit also interacts with the engine and automatic gearbox of the car. This allows the system to adjust their operation in force majeure circumstances.
Nuances worth knowing about
The effectiveness of the anti-lock braking system depends on the condition of the road. If you are driving on an uneven road surface with bumps and potholes, then the car’s braking distance will be much longer than usual. This is explained very simply. When a car slows down, its wheels “bounce” for a moment. This leads to loss of traction and, as a result, the cessation of rotation. ABS perceives this as a blockage and stops braking. When adhesion to the coating is restored, the system has to rebuild. This takes time - hence the increase in braking distance. To make the ABS work optimally in this situation, simply reducing the speed of the car will help.
It should be remembered that active safety systems help the driver in a difficult situation, and do not take control of the car, so the car enthusiast should not relax - he must be prepared for anything.
Maximum traction is achieved by a wheel that keeps its tread contact patch at rest relative to the road surface. Both braking and acceleration of the car can cause slippage in this friction pair. The physical phenomena here are the same, the only difference is in the sign of the acceleration, it will be negative in the first case and positive in the second. But this does not affect the essence of what is happening, since both cases do not bring anything good.
What does this give?
During emergency braking, cars equipped with ABS slow down smoothly rather than skidding. Consequently, even in difficult road conditions the car remains controllable. The driver only needs to monitor the direction of movement of the car until it comes to a complete stop. In other words, the anti-lock braking system provides controlled braking, which helps avoid an accident.
When emergency braking a vehicle not equipped with ABS, pressing the brake pedal hard means that no matter how much you twist the steering wheel, the car will not change its trajectory. This is because locked wheels will slip and prevent the driver from maneuvering. As a result, the car will drive in a straight line, which can lead to serious consequences.