What is the name of the chassis of the car?
To be more precise, freedom of movement of the body is ensured in relation to the wheels moving on the road surface. Suspension - chassis
car, which can be of two types: Independent - a type of suspension in which the wheels on one axle do not have a rigid connection and change position independently of each other.
Interesting materials:
How to leave a review on YouTube? How to leave a review in bla bla car? How to leave things in the storage room at the station? How to free up space on Mac? How to whiten the insoles of sneakers? How do we relax for the New Year 2022 2020 Ukraine? How do we relax for the New Year 2019 Ukraine? How do we relax for Christmas? How do you vacation in Kazakhstan in December 2022? How to format a flash drive for ps4?
Chassis features
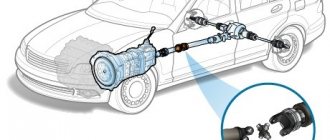
Chassis suspension elements reduce loads and compensate for vibrations when driving on bumpy roads and off-road. The subframe allows you to install the body, engine and other components on the chassis. The front and rear axles transmit rotational motion through the wheels and thus ensure the movement of the vehicle.
The first cars produced in the last century were somewhat different from those that drive on the roads today. All cars - both cars and trucks - used to have a frame on which all the units and components (body, transmission, engine, etc.) were installed. Over time, the frame chassis of the car remained only with trucks and buses. In passenger cars, the functions of the frame began to be performed by the body.
Body layout
The load-bearing part of the car can consist of a frame and body, only the body, or be combined. The body that acts as a load-bearing part is called a load-bearing body. This type is most common on modern cars.
Also, the body can be made in three volumes:
- single-volume;
- two-volume;
- three-volume.
The single-volume one is made as a one-piece body that combines the engine compartment, passenger compartment and luggage compartment. This arrangement corresponds to passenger (buses, minibuses) and utility vehicles.
Double-volume has two zones of space. The passenger compartment, combined with the trunk, and the engine compartment. This layout includes hatchback, station wagon and crossover.
The three-volume one consists of three compartments: the passenger compartment, the engine compartment and the luggage compartment. This is a classic layout that sedans follow.
Body layout
Truck chassis
The most common are spar frames. They consist of two longitudinal beams connected by cross members. The shape of such beams can be completely different: tubular, X- or K-shaped. In the most loaded part, the frame has an increased channel section. The parallel spars design (beams are located at equal distances along the entire length of the chassis) is used on trucks.
In off-road passenger cars, side members can be used that have some divergence of the axes in both the horizontal and vertical planes. The spinal frame consists of one load-bearing longitudinal beam onto which cross members are attached. Often this beam has a circular cross-section, so it can accommodate transmission elements. This frame provides greater torsional resistance than side members. Also, the use of a backbone type chassis involves the use of independent suspension on all wheels. The fork-spinal frame has a branching longitudinal beam in the rear or front part. That is, it combines spars and a center beam. Other types of chassis frame are not used for trucks.
CHASSIS SYSTEMATIZATION
Thus, we can distinguish two different chassis schemes.
- Frame chassis, which in general consists of several strong beams on which all components of the car are installed. This design allows cars to carry huge loads and easily handle different dynamic loads.
- Load-bearing body. In pursuit of reducing the weight of passenger cars, all functions of the frame were reassigned to the body. This frame does not allow moving huge loads, but at the same time provides greater comfort and speed.
Depending on the purpose of the car, the following types of structures can be used:
- spar;
- spinal;
- peripheral;
- fork-spine;
- lattice.
Main types
Before you understand what a car body is made of, you need to identify the main types of its design. Mass-produced passenger cars are produced in the following main types:
- sedan;
- hatchback;
- station wagon
There are other types, but these three are the main and most common.
The sedan body type is the most popular. The serial sedan has four doors for passengers, an engine compartment and a luggage compartment. This type of body is the most optimal for transporting passengers and small luggage.
A hatchback is a car with two doors for passengers, an engine compartment and a luggage compartment not shared with the passenger compartment. This type has limitations on the cargo it can carry, and is also not very convenient for transporting passengers. However, this implementation has its advantages. Cars in this type of body have a lower weight and size, which has a positive effect on its efficiency in relation to fuel consumption.
Station wagon passenger cars are designed for heavy loads. The luggage compartment of such cars is characterized by an increased volume, which does not prevent the interior from remaining at its full size. The station wagon design makes it possible to further expand the luggage compartment by folding the rear passenger seats.
Other meanings of the term
In addition to the definition above, the word “chassis” can be used to describe self-propelled vehicles designed to install various machines and mechanisms. This term is also used to refer to that part of the aircraft that is used to move around the airfield, take off and land. As with a car's landing gear, this part softens the shocks and stresses of aircraft moving on the ground. Aircraft chassis, unlike automobile ones, can be designed with wheels, skis or floats.
The meaning of the word chassis is often confused with the concept of a car's drive. The terms are misinterpreted due to the fact that they refer to almost the same part of the vehicle. Car owners freely say that their car has a 4x2 chassis. But it should be understood that 4x2 is just a layout diagram, from which you can find out the number of drive wheels, but no more. What a chassis is has already been discussed above. Although wheels and drive are part of the chassis system, it is inappropriate to use the term only for such a narrow description.
Classification
The chassis can be of a frame type or assembled on the basis of a monocoque body. Frames, in turn, are divided into:
- Ladder type in the form of two spars connected by power cross members;
- Volumetric, which is a spatial structure to which mounted body parts are attached;
- Spinal, when all the loads are taken on by a powerful pipe in the center of the car, onto which the transmission and suspension elements are hung, driveshafts often pass inside it;
- Integrated, that is, included in the power structure of the supporting body to take on the bulk of all loads, but not separated from the body parts;
- Distributed, with separate front and rear subframes connected by a load-bearing vehicle underbody with built-in side members and cross members.
The use of frames is limited to heavy cars, trucks, and all-wheel drive off-road vehicles, where strength and the ability to constantly withstand bending loads are important.
Sometimes, on the contrary, high rigidity is required from the body, then a space frame is used, for example in motorsport.
In all other cases, the use of a separate frame is undesirable, since this increases the weight and cost of the machine. Then a load-bearing body is used in cars.
The load-bearing structure, often made of high-strength steel, forms the body frame, fulfilling the requirements for strength and safety, but under conditions of constant shock and torsional loads it weakens due to metal fatigue. But for road cars this is not so important, but the design is light and rigid.
Advantages and disadvantages of ground vehicle chassis
Modern vehicles, be it a car, a tractor or a special self-propelled device, are equipped with a chassis that is equipped with the latest design ideas.
A positive quality of the chassis of modern cars is their high reliability and service life of the units, which allows them to operate for tens of thousands of kilometers without replacement. And using the ground as a support allows vehicles based on this chassis to move huge loads over long distances with low fuel consumption and optimal speed.
The main disadvantage of ground vehicle chassis is the lack of versatility when moving from one environment to another.
Electrical equipment
One of the most complex systems of passenger cars with many different elements and wires connecting them, entangling the entire car body, is electrical equipment, which serves to provide electricity to all electrical devices and electronic systems. Electrical equipment includes the following devices and systems:
- battery;
- generator;
- ignition system;
- light optics and interior lighting system;
- drives for electric motors of fans, windshield wipers, window lifts and other devices;
- heated windows and interior;
- all electronics of the automatic transmission, on-board computer and protective systems (ABS, SRS), engine management and others;
- power steering;
- anti-theft alarm;
- sound signal.
This is an incomplete list of devices included in the electrical equipment of a car and consuming electricity.
Every driver needs to know the structure of the car body and all its components in order to always maintain the car in good condition.
WHAT IS A CHASSIS NEEDED FOR?
Thanks to the chassis and suspension elements that are part of the chassis, loads are reduced and vibrations are compensated when the vehicle moves on uneven roads and off-road. Thanks to the subframe, which is part of the chassis, engineers were able to install a body, power unit, transmission and other units on the chassis. Due to the front and rear axles, the vehicle moves through the transmission of torque to the wheels.
Once upon a time, all cars (both cars and trucks) had a frame, which cannot be said about today's cars. The body, engine, transmission, as well as chassis attachments were installed on the frame. Over time, car manufacturers realized that there was no need for a frame for passenger cars, and a modified body began to perform all the functions of the frame. And the frame became the lot of heavy SUVs (frames) and trucks.
Control mechanisms
These devices consist of a steering system that is connected to the front wheels by steering and brakes. Most modern cars use on-board computers, which themselves control the controls in some cases, and even make the necessary changes.
Here we note such an important part as what the car wheel consists of. Without him, the car simply would not have happened. This is truly one of the greatest inventions and consists of two components: a rubber tire, which can be tubed or tubeless, and a metal rim.
Steering
Responsible for maneuverability and turning of the car. The steering wheel is turned by the steering rack.
Steering device:
- lateral thrust;
- lower arm;
- pivot pin;
- upper arm;
- longitudinal thrust;
- steering bipod;
- steering gear;
- steering shaft;
- steering wheel.
Brake system
Responsible for safety. Thanks to the brakes, the car stops. The braking system consists of : brake discs, pads, calipers, cylinders, circuits.
The higher the power of the internal combustion engine, the more powerful the braking system should be.