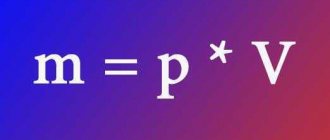042
01.11.2021 14:40
The operation of diesel engines in the climatic conditions of the CIS countries has its own specifics. In the warm season there are usually no problems, but in winter certain difficulties arise due to very low temperatures. The problems are related to the fact that diesel fuel contains paraffins, which crystallize in the cold, so the fuel becomes cloudy and thick. As a result, the fuel is not atomized by the injectors and, accordingly, the fuel mixture does not ignite. Owners of diesel cars need to carefully prepare for the cold season and choose the right fuel that will be pumped normally through the injection pump and fuel system and will not turn into gel in the cold.
It's all about the freezing temperature of diesel fuel. It is higher than that of gasoline, so using regular diesel fuel in winter is problematic. Certain types of diesel fuel can lose their normal fluidity and freeze already at –10 ᵒC. To solve this problem, special varieties of winter diesel fuel have been developed. It is these that drivers switch to when cold weather sets in. However, not everyone understands the differences between summer and winter diesel fuel and why you can’t use summer diesel fuel in winter and winter diesel fuel in summer.
Why you can’t use summer diesel fuel in winter
The production of diesel fuel is strictly regulated by a single GOST 305-82, which defines the characteristics of 3 brands of diesel fuel for operation in different temperature conditions:
- summer diesel fuel can be used at a temperature not lower than 0 ᵒС;
- winter diesel fuel is intended for operation in frosts down to –20 ᵒС;
- Arctic varieties can withstand temperatures down to –50 ᵒC.
There is also an intermediate type winter diesel, which can be filled at a temperature not lower than –30 ᵒС.
The main difference between winter and summer types of diesel fuel is their viscosity. Cold-resistant varieties have low viscosity, while summer varieties have high viscosity. This parameter is designated cSt and can range from 1.5 to 6 units. Winter diesel fuel contains a smaller amount of paraffins, and special decompression additives are also added. This prevents the fuel from freezing at subzero temperatures, while simultaneously guaranteeing highly efficient combustion in the engine. Additives and the absence of paraffins do not affect the power and service life of the internal combustion engine.
On the contrary, more sulfur and paraffin are added to summer diesel fuel, which makes diesel fuel more viscous. These components tend to crystallize when the ambient temperature drops below 0 ᵒC. Of course, we are not talking about any freezing, as is the case with ordinary water. But the structure of the fuel is still changing, and it is unlikely that the engine will start normally. As a result, the entire fuel system may become clogged, and to restore it, you will have to disassemble the engine and clean it from the inside. It will be necessary to carefully remove the crystallized paraffin molecules. That is why the use of summer diesel fuel in winter is detrimental both to the engine and to the entire fuel system as a whole.
Biodiesel
This type of diesel product deserves special attention. This is an innovative development of European engineers. The technology for the production of biological diesel fuel involves the use and processing of vegetable oils. The main difference between biodiesel and conventional diesel fuel brands is environmental friendliness. Complete disintegration of its combustion products without harmful consequences in the natural environment occurs within 30 days after entering the soil, water or atmosphere.
Biodiesel production
The governments of industrialized countries and international organizations specially created on this issue are now forced to act in the fight for the environment. By this time, new standards were introduced in the production and operation of biofuels.
Biodiesel is intended, first of all, for use in internal combustion engines of passenger vehicles, then for trucks and industry. Summer brands of high-quality diesel fuel are usually made on its basis. The cetane number of biodiesel is 58 units, and the combustion temperature is 100°C; it has excellent lubricating properties and a reduced percentage of CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Thanks to the combination of such characteristics, product developers have provided car enthusiasts and enterprises with the opportunity to not only significantly increase the service life of internal combustion engines and reduce maintenance and repair costs, but also significantly reduce the risks of explosions and fires.
A feature of biological diesel fuel is the presence of vegetable and animal fats in the mass. The structure of biofuel is natural, and the product itself is the result of processing agricultural crops such as rapeseed, soybeans and other oil-containing plant species, and cattle fat. The distinctive characteristics of this type of diesel fuel are that it can be used as an additive to traditional types of fuel.
Biodiesel has special designations. For example, in the United States of America, biological fuel in the name includes the letter “B”, followed by a digital value indicating the percentage of bioadditive content in the total mass of the fuel. Cetane number not lower than 50 units.
Biodiesel is produced using a technology similar to the production of diesel fuel from oil. Today, there are brands of biodiesel not only for summer, but for off-season and winter conditions in temperate latitudes.
Summer diesel biofuel is used only at positive temperatures, intermediate grades - up to -10° below zero, winter biodiesel - up to minus 15-20°C. Frost resistance of winter grades is achieved through the use of special additives, originally developed to improve the properties of diesel fuel.
Is it possible to drive winter diesel fuel in the summer?
In winter, summer fuel thickens and can solidify, so its use is highly not recommended. But in the summer, winter fuel will definitely not harden, so many car enthusiasts are confident that it can be safely used without consequences for the engine. However, this is not so - it is strictly not recommended to fill it with winter diesel fuel in summer. And that's why:
- “Cold” grades contain sulfur, which at high temperatures becomes extremely harmful to a diesel engine. Mercaptan sulfur is not removed with combustion products, but accumulates inside the fuel system, which leads to the formation of deposits. Over time, fuel lines and the entire system become contaminated, which can ultimately fail.
- Winter grades of diesel are less viscous. Low viscosity does not allow the engine components to be provided with effective lubrication. As a result, the rubbing surfaces will wear out more actively.
Therefore, you can fill in winter diesel fuel in summer only if there is no other choice. The longer a car is operated on off-season fuel, the higher the likelihood of encountering unpleasant consequences.
Main performance characteristics of diesel fuel
Resistance to low temperatures is the main parameter of diesel fuel, which determines the conditions of its use and storage features.
Another main indicator of diesel fuel quality is the aforementioned cetane number. The higher its value, the more confidently one can judge the longer life of the internal combustion engine. The engine runs smoothly, detonation is eliminated, and the dynamics of the car are increased.
The ignition temperature indicator determines the degree of safety of using diesel fuel in internal combustion engines. The friction composition in diesel fuel determines whether the mixture will burn completely in the cylinders, the level of smoke and the degree of toxicity of the exhaust.
The density of diesel fuel determines how effective the supply of fuel through the channels of the fuel system, its filtration and spraying in the nozzles will be.
Sulfur content. Its absence in the composition makes the fuel too “fresh” - there is a lack of lubrication of the elements of the fuel equipment. However, increased sulfur content leads to premature corrosion on internal combustion engine parts, rapid accumulation of carbon deposits, and increased wear of the fuel injection pump.
The main characteristics of diesel fuel, especially in modern conditions, include the indicator of product purity. This is not only an extension of the life of components and elements of vehicles, but also maintaining environmental standards in places of industrial production.
Features of manufacturing winter diesel fuel
Main characteristics of winter diesel fuel:
- density not higher than 840 kg/m³;
- flash point +55 °C;
- pour point –35 °C;
- kinematic viscosity (cSt) 1.8–5 mm/s2;
- boiling point +180–340 °C.
In order to obtain the required density and achieve other important parameters that make it possible to avoid crystallization at subzero temperatures, it is necessary to fulfill a number of technological requirements when manufacturing the composition. The production process is very labor-intensive, which explains the higher price of winter diesel fuel compared to summer brands.
The production of this type of diesel fuel occurs as a result of oil distillation in several successive stages:
- The separation of oil into fractions after strong heating and reaching the boiling point. Usually it is +280–340 °C.
- Cracking (high-temperature refining of oil and its fractions), hydrotreating and subsequent mixing of the resulting fractions.
- Dewaxing is a technological process that involves the removal of hydrocarbons of the paraffin group at the production stage. It is performed to reduce the viscosity of winter diesel fuel.
High temperature treatment promotes the precipitation of long-chain paraffin molecules. After this they are deleted. As a result, it is possible to obtain a high-quality composition that does not freeze at subzero temperatures. To further reduce detonation, various additives are added to winter diesel fuel to protect engine components and systems. With the same volumes of raw materials, after distilling winter diesel fuel, the output is 30–40% less diesel fuel than when producing summer grades. This ultimately affects the cost of fuel.
The second production method is the use of special depressant additives. Additives act on paraffin crystals, as a result of which their sizes are reduced to 3–5 microns. This reduces the viscosity of winter fuel and increases filterability, as a result of which it is well pumped along the highway. Using this technology, the bulk of winter diesel fuel is produced with additives that reduce filtration temperatures from −5 to −15 °C. Today this manufacturing method is used less and less.
For particularly extreme operating conditions, arctic fuel is used. It is capable of maintaining its basic characteristics at temperatures down to –50 °C. The technology for its production does not differ from the production of ordinary winter diesel fuel, but the difference lies in the boiling point of the kerosene. Such fuel costs much more. However, there is no urgent need for the use of Arctic fuel in most of Russia. It is used mainly in Siberia and the Far North. In other regions of the country, temperatures rarely drop below –20–30 °C, and regular brands of winter diesel fuel will do.
Even 10–20 years ago, in order to avoid freezing of diesel fuel, motorists resorted to various tricks that forced the composition to work at subzero temperatures, because freezing of fuel led to very sad consequences. One of the most popular solutions was to add a small amount of gasoline or special antifreeze additives to diesel fuel. The fuel did not freeze, but the engine still suffered greatly. As a result, internal combustion engines quickly failed, and their restoration took a lot of time and money. With the advent of special winter grades of diesel fuel, the situation improved significantly, and drivers were able to operate their car without fear even in severe frosts.
Tips and tricks
Some experienced drivers use the following method to make starting a diesel engine easier in winter:
- First, the combustion chamber is heated by the glow plugs a couple of times;
- then about 10 ml is poured into the air filter housing from a syringe. gasoline;
- then the engine can be started;
Let us immediately note that this decision is an emergency measure, that is, this method cannot be used regularly. Starting with gasoline vapors leads to increased loads, which significantly reduces engine life.
Also, owners of diesel cars that operate in regions with fairly severe winters can be advised to install various pre-heaters (fuel filter and power system heater, engine oil heater in the sump, Webasto or Gidronik type engine pre-heater, etc.)
It is also recommended to insulate the engine compartment and engine separately. A car blanket is well suited for this, as it retains heat and prevents the internal combustion engine from cooling quickly. It would also be a good idea to insulate the radiator of the cooling system. For these purposes, you can use various solutions, the simplest of which is to install a thick cardboard “damper”.
Finally, we note that it is not recommended to warm up a diesel engine for a long time at idle, since this type of engine warms up only when driving under load. This means that after 3-5 minutes of starting work, you need to drive a diesel car, but drive for the first 5 km. should be smooth, without a significant increase in speed, sudden starts and braking, driving in high gears, etc.
Properties of summer diesel fuel
Summer diesel fuel (DSF) is the most commonly used type of diesel fuel. It ensures uninterrupted operation of the power plant at ambient temperatures up to 0 ᵒC. At lower temperatures, long-chain paraffin molecules, which are contained in high concentrations, begin to crystallize in summer diesel fuel. As a result, volatility deteriorates, and the fuel itself thickens and cannot pass through the filter system to the high-pressure pumps.
The composition of summer diesel fuel includes hydrotreated, secondary and carbon fractions, as well as straight distillation fractions. It is obtained by mixing diesel compounds and adjusting the cetane number to 45–55 units. using special additives. This type of diesel fuel is the cheapest, since its manufacturing technologies require minimal costs. It contains the least amount of additives, which makes the fuel stable from a chemical point of view.
Characteristics of summer diesel fuel:
- density no more than 860 kg/m³;
- flash point +62 °C;
- pour point –5 °C;
- kinematic viscosity (cSt) 8.94 mm/s2 at a temperature of 20 °C;
- boiling point +180–360 °C.
The maximum filterability temperature for these varieties is –5 °C, which is not enough for the harsh climatic conditions of central Russia. However, summer diesel fuel can be stored for a long time - this property is especially important, since fuel is often used to heat rooms or generate electricity. In this case, diesel fuel is purchased in large quantities and consumed slowly. Another important operational parameter of summer diesel fuel is its high lubricity, due to its significant viscosity.
Summer diesel fuel is used to operate high-speed power plants of ship and land equipment, as well as special vehicles, industrial generators, boilers and heat guns. It is most widespread in the central and southern regions of Russia, where climatic conditions are not so harsh. In other areas, summer diesel fuel can only be used during the appropriate season or special additives can be used.
Nissan X-Trail 2010, 161 l. With. gas station
Comments 21
Winter solarium, when used in summer, causes greater engine vibration, which is not good.
There is no vibration, 50 liters of two-stroke oil and everything is fine, I began to do the same in winter
Well, I don’t add oil, I tell it as it is without any additives.
Winter solarium, when used in summer, causes greater engine vibration, which is not good.
Do you have different engine operating temperatures in winter and summer?))
the same, but what does this have to do with it? Winter diesel fuel has different parameters; the cetane number differs from summer diesel.
I quote, “Winter solarium, when used in summer, causes a lot of engine vibration, which is not good.”, but in winter the vibration disappears and the engine is only good, right?
I didn’t drive with winter fuel in the summer, but I assume that the vibration will not go away. Again, in winter, driving on winter fuel is a necessary measure, but in summer I don’t see the point.
the same, but what does this have to do with it? Winter diesel fuel has different parameters; the cetane number differs from summer diesel.
“Winter diesel fuel has different parameters; the cetane number differs from summer diesel.” Wow, live and learn, can you be more specific from now on? To what extent does the cetane number of winter differ from summer?
Transition nuances
Considering that the pour point or freezing point of different brands of diesel fuel is different, it is important to follow certain recommendations when switching from winter to summer fuel, and vice versa.
The procedure involves performing several simple steps:
- The old fuel is drained. This can be done using a regular pump, but mixing summer and winter brands is strongly not recommended.
- A new type of diesel fuel is poured, but not more than 10% of the tank. You need to drive it for several kilometers to burn off the remnants of the previous diesel engine and pump new diesel fuel throughout the system.
- After this, the remaining diesel is drained again. The fuel system is now perfectly clean. Then you can add new seasonal fuel in the quantity you need.
This transition scheme is considered the most optimal, since it allows you to prepare the fuel system and the engine itself for the use of fuel with slightly different physical and mechanical properties and chemical composition.
In any case, both winter and summer diesel fuel must be purchased only from trusted suppliers. Questionable savings can lead to very serious expenses, including a complete flushing of the fuel system with removal of the internal combustion engine or a major engine overhaul.
Conclusion
Diesel fuel has relatively recently emerged as the second main fuel for passenger cars, although it has been used for heavy vehicles and in industry for many decades. Due to the widespread use of diesel fuel in passenger vehicles, demand for it has increased, and therefore the market has responded by increasing its cost.
And if in the recent past it was profitable to purchase diesel cars only because of savings on the price of diesel fuel, now the feasibility of using diesel cars is based on environmental friendliness, the service life of the internal combustion engine and the same savings. DT is still, although not much, cheaper than gasoline.
And if you have made the choice to purchase a car with a diesel engine, then it is very important to know as much as possible about its fuel. This is the only way you will be able to avoid difficulties in operating equipment associated with the characteristics of this type of fuel.
Basic chemical composition of diesel fuel
Speaking about the technical indicators of diesel fuel, one cannot remain silent about its chemical composition. We will not go deep into it, but we will talk about the main elements that make the fuel diesel.
The main chemical composition of diesel fuel is hydrocarbons:
- paraffin (alkanes) - from 10 to 40%;
- naphthenic (cycloalkanes) - from 20 to 60%;
- aromatic (arena) - from 15 to 30%.
Diesel fuel also contains other components: resins, sulfur, mechanical impurities and even water. And each of these components is allowed by GOSTs in a certain quantity.
The composition of diesel fuel, of course, depends on the refinery. However, not completely. It is also influenced by other factors, such as the oil field and the additives used by the diesel fuel manufacturer.
Fuel may differ in chemical composition, but the indicators will be within the limits permitted by GOST.
As a result, gas stations receive good quality diesel. The main thing for the driver is to fill the car’s tank with the brand of diesel that suits the weather conditions.