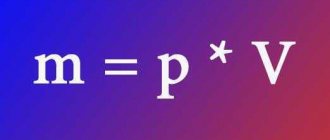“Diesel”, diesel fuel or “diesel” are common names for the fuel used in diesel internal combustion engines. This petroleum distillation product has been used for decades, mainly as fuel for agricultural and military equipment, railway transport, diesel electric generators and boiler houses, as well as in the processing of metals and leather.
The characteristics of diesel fuel, temperature parameters for use, chemical and physical properties are prescribed in GOSTs. Quality standards developed back in the Soviet Union 1666-42 and 1666-51 determine the quality of low-speed diesel oil, which is unsuitable for modern high-speed engines.
How is the density of gasoline measured?
The additives included in the composition determine the boiling and freezing points.
From the physics course we remember that density is nothing more than the ratio of mass to volume, and the value is calculated in kilograms per cubic meter. Usually, due to the difference between the declared and final indicators, the main disagreements arise between the manufacturer and the wholesale consumer. It is important to understand that fuel density does not reflect quality. All measurements must take place under the same conditions, that is, at the same ambient temperature
Average values:
When purchasing fuel, each driver has the right to inquire according to what standard this parameter was measured. The current GOST defines a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius, when the previous standard allowed 20 degrees. You can measure it even in a garage. It is enough to fill the container with gasoline, weigh it and divide the result by liters - the final figure is the density.
The procedure looks something like this:
- take any graduated container that can be weighed;
- weigh it and write down the result;
- fill the container with 100 ml of fuel;
- We weigh again, then subtract the first from the second result;
- We divide the resulting figure by the volume of fuel in the container.
A simple and quick method is to use a special device. One of these devices is considered to be a hydrometer - a device that, for the purpose of measurement, implements the Archimedes principle. In addition, a hydrometer allows you to determine the concentration and amount of impurities. It consists of a glass cylinder: on one side there is a tube with a rounded bottom, on the other there is a small diameter tube with markings. Based on the scale readings and the amount of liquid displaced, it is easy to determine the desired parameter.
What is the density of diesel fuel?
Density characterizes the mass of a substance that fits into one cubic meter. The higher the density, the greater this indicator. Enterprises that produce diesel fuel closely monitor this value. If it does not meet state standards, the fuel does not receive a passport and is not allowed for sale.
Density indicates the amount of energy released during fuel combustion. The denser it is, the more energy is obtained and the higher the efficiency of the unit.
Specific gravity of diesel fuel. Weight of diesel fuel in 1 liter
How much horsepower does a KamAZ 5320 have? How much does a KamAZ weigh?
cost and modifications “Diesel”, DT or “diesel” are common names for the fuel used in diesel internal combustion engines. This petroleum distillation product has been used for decades, mainly as fuel for agricultural and military equipment, railway transport, diesel electric generators and boiler houses, as well as in the processing of metals and leather.
The characteristics of diesel fuel, temperature parameters for use, chemical and physical properties are prescribed in GOSTs. Quality standards developed back in the Soviet Union 1666-42 and 1666-51 determine the quality of low-speed diesel oil, which is unsuitable for modern high-speed engines.
Classification of diesel fuel
Today, each country has its own quality standards for diesel fuel, but there are main classification categories that are common to any type of diesel fuel, prescribed in interstate GOSTs 32511-2013 (EN 590:2009), 305-2013 and 2517-2012.
There are low-viscosity fuels (distillate), used for high-speed engines, and residual, low-viscosity fuels. Unlike hydrotreated kerosene-gas oil fractions of discilate fuel, the residual consists of a mixture of fuel oil and kerosene-gas oil fractions.
The main principle of classification is seasonality.
It can only be used at positive temperatures. The specific gravity of summer diesel is 860 kg/m3 (the theoretical density of any type of diesel fuel is determined at +20ºС). With increasing temperature, the specific gravity decreases by approximately 0.0007 g/cm3, and with decreasing temperature, it increases accordingly.
At a temperature of –5ºС, the paraffins of summer diesel fuel thicken and clog the system. The use of additives helps delay thickening, but they do not change the increased density of summer fuel at subzero temperatures. Flash point 62ºС.
Recommended operating temperature is from –20ºС to –35ºС. The specific gravity of winter diesel fuel is 840 kg/m3. At -35 degrees Celsius it freezes. The outbreak occurs at +40 ºС.
It is recommended to use in the negative temperature range of 45–50ºС. The density of diesel is 830 kg/m3, and the flash point is +35 degrees Celsius. DF A is obtained by dewaxing summer DF or by adding cetane-increasing additives and motor oil to pure kerosene to improve lubricating properties.
The weight of diesel fuel in 1 liter is approximately 850 g or 0.85 kg
| Type of diesel engine | Temperature range (ºС) | Density (kg/m3) | Specific gravity (g/cm3) |
| Summer | +0 … | 860 | 0,86 |
| Winter | –35… –20 | 840 | 0,84 |
| Arctic | –50…–45 | 830 | 0,83 |
Main characteristics
Cetane is a hydrocarbon contained in diesel fuel, characterized by rapid ignition under the influence of hot compressed air formed in the combustion chamber of a diesel internal combustion engine. The cetane number determines the ignition quality of a diesel engine; it should not be lower than 45 - 50. We can conclude that the higher the cetane number, the faster the fuel will ignite. High-quality diesel fuel has a high paraffin content and a high cetane number.
Oil contains sulfur. The content of sulfur compounds in diesel fuel is strictly regulated. As part of the fight for environmental friendliness of fuel, as well as reducing the wear of internal combustion engine elements, the sulfur content should be reduced to a minimum. However, as the percentage decreases, the lubricating properties of the diesel engine deteriorate, so it is necessary to use special additives. The best performance indicators are considered to be EURO-4 and EURO-5 diesel fuel brands with a sulfur content of up to 0.05%.
Diesel fuel: density, consumption, operation
The density of diesel fuel, which makes it possible to determine the climatic purpose of the fuel, affects the starting characteristics and operation of the engine. If you select the wrong diesel fuel or use low-quality fuel, the starting of the engine deteriorates, which does not develop the rated power and torque. When driving in difficult road conditions, insufficient engine power leads to the inability to carry the required load or to increased consumption of diesel fuel and excessive wear of the power unit.
What does density say about the quality of diesel fuel?
The specific gravity of diesel fuel determines the ratio of the fractions that make up the fuel. With an increased parameter, the mixture contains an increased volume of heavy hydrocarbons, which reduce the possibility of diesel fuel being sprayed by injectors into the combustion chamber. Due to the presence of heavy fractions with a high boiling point, the mixing of fuel particles and air deteriorates. To ignite the vapors, an elevated temperature is required, which leads to interruptions in the operation of the power unit and increased consumption of diesel fuel.
State standard
The standards for diesel fuel in force in the Russian Federation were partially adopted back in the days of the USSR (GOST 305-82). According to regulations, the density of fuel used in summer is 0.86 kg/l. When operating vehicles with diesel engines in winter, it is necessary to use diesel fuel with a density reduced to 0.84 kg/l. The fuel is used to power naturally aspirated engines or those with turbochargers. For the Arctic regions in winter, fuel with a specific gravity of 0.83 kg/l is supplied.
Diesel fuel specific gravity standards
Specific gravity standards are prescribed in GOST R 52368-2005 and 305-82 standards. Regulations stipulate the amount of impurities in the fuel composition (for example, sulfur), which negatively affect the composition of exhaust gases and the durability of fuel injection equipment. The standards prevent the introduction of aqueous solutions into the fuel, which corrode spray tips and damage filters and high-pressure pumps. Water with foreign impurities is separated using special settling tanks (filtration occurs due to the difference in the densities of the liquids).
Why does diesel fuel consumption increase in winter?
An increase in fuel consumption at low temperatures occurs due to the heating of the power unit and increased friction in a cold engine. When driving, fuel consumption corresponds to summer values or differs to a lesser extent, since increased torque at low speeds reduces slipping of the drive wheels on snowy surfaces. Additional load is exerted by thickened oil in axle housings and planetary gearboxes; due to the increased resistance, fuel consumption increases slightly.
At low temperatures, air has an increased specific gravity, which leads to a violation of the composition of the working mixture. Motors with an electronic unit automatically adjust the fuel dose and injection phase, eliminating the negative effect of cold air. Engines with a mechanical high-pressure pump are not able to adjust to air temperature, which also affects fuel consumption. Cold air increases the drag coefficient, which slightly increases the cost of diesel fuel per 100 km of travel.
Why does diesel fuel freeze?
The composition of diesel fuel includes various fractions that thicken under the influence of low temperatures. The dependence of viscosity on the external temperature background is determined by density, which depends on the volumetric amount of fractions with an elevated boiling point. If water is present in the fuel, it sinks to the lower part of the tank, where it crystallizes when cooled below 0°C. Ice clogs the intake pipe, preventing diesel fuel from being supplied to the power unit. To restore engine performance, it is necessary to warm up the tank and fuel supply lines.
How to make sure you fill up your winter diesel fuel
When the winter season begins, special fuel for diesel engines appears at fuel pumps; information about the type of fuel is indicated on the pumps and in the gas station premises. The basic technique is based on pouring 50-100 ml of fuel into a transparent container, which is placed in the freezer compartment of the refrigerator. At a temperature of -20...-22°C, the liquid should not become cloudy (turbidity indicates the formation of a suspension of solid paraffin). For arctic varieties of diesel fuel, the turbidity threshold is at -34°C (not reached in the refrigerator).
How to check the density yourself
To check the correctness of fuel density, the following methods are used:
- Based on the fluidity of liquid applied at -10°C and below to a metal plate. High-quality fuel remains liquid, and the formation of cloudy streaks is not observed in the composition. If the fuel thickens or becomes cloudy, it is prohibited to operate the vehicle in winter. The engine will start, but when driving, the process of crystallization of diesel fuel will begin, which will lead to immobilization of the car.
- To accurately determine the density, an oil hydrometer is used (for example, model ANT-2, designed for densities from 830 to 910 kg/m³). A portion of fuel is poured into the container, then the tank is heated to a temperature of 20°C (controlled by a thermometer). The device is lowered into the liquid, the resulting value is checked against the standard specific gravity corresponding to the type of diesel fuel.
- At temperatures below -20°C, a quick way to determine the quality of diesel fuel is the drops that remain on the nozzle of the refueling nozzle. If the liquid has a thick consistency or the solution is cloudy, then pouring fuel into the tank of the car is not recommended. If refueling has already been done, then you should dilute the fuel with high-quality diesel fuel, this will reduce the temperature at which crystallization begins.
DT density change step
The concept of diesel fuel weight measurement step means a correction factor equal to 0.0007 units. For example, at a temperature of -30°C, the density of the Arctic type of fuel will increase by 50*0.0007 = 0.035 g/cm³. With a standard value of 0.83 g/cm³, the parameter will increase to 0.865 g/cm³.
Specific gravity of diesel fuel (diesel fuel)
How much does a car battery weigh?
To begin with, I would like to clarify what is meant by specific gravity (hereinafter referred to as SG) in physics and chemistry, and only then move on to the specific gravity of diesel fuel or, as it is also called, the specific gravity of diesel fuel.
Let's go over the theory.
Fuel Specific Gravity
Specific gravity is the ratio of the weight of any substance in question to its volume, namely weight, and not mass, as many people think. However, there is no particular difference for us here; these are only distinguishable concepts from a scientific point of view and cannot be confused in any way. It has become so common in everyday life that weight is mass.
The specific gravity of a substance can also be expressed through its density: y=p*g
where g is the acceleration of gravity at a specific point in space, it is usually considered equal to 9.81 m/s*s.
The unit of measurement for hydrocarbons is 1 N/m3 (Newton divided by cubic meter).
Fuel density
The density of a fuel is the amount of its mass in kilograms that fits in one cubic meter. This value is not constant and depends on the temperature of the diesel fuel, which has a bad effect on the operation of the car engine if the diesel fuel is of poor quality in terms of density. The higher the temperature of the liquid, the lower its density and vice versa. It is also a known fact that the higher the density of automobile fuel, the heavier its fractional composition. This leads to the fact that the processes of atomization and evaporation of gasoline or diesel fuel are significantly worsened, therefore, various types of deposits occur more intensively in the combustion chambers of the engine and in the fuel system, which over time increasingly complicates the movement of fuel through the system. This also contributes to the formation of carbon deposits on the engine valves.
Specific gravity of diesel fuel
The density of the fuel and, therefore, its specific gravity is measured with a special device called a hydrometer.
According to the current GOST, the following values are accepted for the specific gravity of diesel fuel (for diesel fuel temperature +20C):
the specific gravity of summer diesel fuel must be within 8440 N/m3; the specific gravity of winter diesel fuel is 8240 N/m3
density of summer diesel fuel – 860 kg/m3 density of winter diesel fuel – 840 kg/m3
Arctic diesel fuel density – 830 kg/m3
In practice, if we take into account only high-quality diesel fuel, it turns out that when the temperature of diesel fuel changes by one degree Celsius, its density changes by 0.00075. This coefficient can be used to recalculate the density of diesel fuel under different temperature conditions. But it is worth remembering that at most gas stations the quality of the product leaves much to be desired, and no one knows what impurities are present in it. While the density of pure fuel can be recalculated using this coefficient, the density of impurities in it is not always true.
Weight of 1 liter of diesel fuel (diesel fuel)
Based on the density values of diesel fuel given above, it is easy to calculate the weight of 1 liter of diesel fuel. It will vary from 830 grams to 860 grams, that is, the higher the temperature of the diesel fuel, the lighter 1 liter of it will weigh.
State standard (GOST)
There is a GOST, according to which the density of diesel fuel should be:
- 860 kg/m3 - density of summer diesel fuel;
- 840 kg/m3 - density of winter diesel fuel;
- 830 kg/m3 - density of active diesel fuel.
These density standards must be met at a temperature of +20C. Winter fuel for diesel engines has a lower density, which means greater fluidity and the ability to not freeze in cold weather. Therefore, many drivers of diesel cars have trouble starting when they do not have time to fill the appropriate fuel in time.
Diesel fuel specific gravity standards:
- 8440 N/m3 (Newton per cubic meter) - this is for summer diesel fuel;
- 8240 N/m3 - this is for winter solarium.
What does this mean?
Specific gravity says that 1 liter of diesel fuel will weigh 830 to 860 grams, depending on the temperature and seasonal classification of the fuel.
Density of winter diesel fuel
How much does it weigh …?
This physical indicator has a noticeable, although ambiguous, effect on waxing and the degree of suitability of a certain brand of diesel fuel, while simultaneously setting the boundaries of its use at low temperatures.
Regarding winter diesel fuel, the nominal density should not exceed 840 kg/m³, with a cloud point of -35 °C. The indicated numerical values apply to diesel fuel, which is prepared using the technology of mixing purified primary and secondary hydrocarbons with a final boiling point of 180...340 °C.
Similar indicators for Arctic fuel are: density - no more than 830 kg/m³, cloud point -50 °C. Diesel fuel with a boiling point range of 180...320 °C is used as such hot fuel.
It is important that the boiling range of Arctic diesel fuel approximately corresponds to the same parameter for kerosene fractions, therefore such fuel in its properties can be considered especially heavy kerosene
The disadvantages of pure kerosene are a low cetane number (35...40) and insufficient lubricating properties, which determine intensive wear of the injection unit. To eliminate these limitations, components that increase the cetane number are added to Arctic diesel fuel, and in order to improve the lubricating properties, the addition of certain brands of motor oils is used.
Relationship between fuel density and diesel efficiency
There is no direct connection between the density of diesel fuel and the efficiency of a diesel engine. But in winter, the engine spends additional energy to warm up the cylinder block and the antifreeze poured into the cooling system. Part of the heat is taken away by the heater, which is responsible for heating the driver’s cabin and the lines through which fuel is supplied. The increased density of winter diesel fuel is determined by the temperature coefficient and different fractional composition (the components of the mixture differ in specific gravity and boiling point).
How many tons and liters in a cube of diesel fuel
How to calculate the density of diesel fuel Volume cubic meter. This volume (regardless of the temperature) will always contain 1000 (one thousand) liters or cubic decimeters. But the mass of diesel fuel varies greatly with temperature. They make money on this at gas stations, and especially the Donkermans on tankers. On a successful voyage on a tanker of 7,000 tons, you can float up to 25 tons of diesel fuel to the left)))))
As the temperature rises, the volume of petroleum products increases and is determined by the formula V 2 = V1 (1 + ∆tβ),
where V2 is the volume of petroleum product with a temperature increase of 1 °C; V1 – initial volume of oil product; ∆t – temperature difference; β is the coefficient of volumetric expansion of the petroleum product (Table 2). 2 Volumetric expansion coefficients of petroleum products depending on density at +20 °C per 1 °C
Density, Density, g/cm3 β g/cm3 β
0,700 …0,710 0,00127 0,800 …0,810 0,00095 0,710 …0,720 0,00123 0,800 …0,810 0,00092 0,720 …0,730 0,00120 0,800 …0,810 0,00089 0,730 …0,740 0,00116 0,800 …0,810 0,00087 0,740 …0,750 0,00113 0,800 …0,810 0,00084 0,750 …0,760 0,00110 0,800 …0,810 0,00082 0,760 …0,770 0,00107 0,800 …0,810 0,00079 0,770 …0,780 0,00104 0,800 …0,810 0,00077 0,790 …0,80 0,00098 0,800 …0,810 0,00072
One cube contains 1000 liters or approximately 850 kg (the latter is highly dependent on temperature)
1000 liters of liquid are placed in one cubic meter, the density of diesel fuel is no more than 860 kg/m³, from here we can conclude that the mass of the fuel will be 860 kg….
= * = 0.85*1000 = 850kg=0.85t (approximately) Cube of liquid = Thousand liters of liquid (volume = volume)
R.S. This is the same as about milk: 1 liter of milk is larger in volume than 1 kg of milk, and 1 liter of sunflower oil weighs less than 1 kg.
Specific gravity of summer diesel fuel
The specific gravity of summer diesel fuel directly depends on its temperature. The state standard is set within 8440 N/m3.
Specific gravity of winter diesel fuel
The specific gravity of winter fuel depends on its temperature. The state standard is set within 8240 N/m3.
Formula for determining the weight of diesel engines
The weight of the fuel is determined by multiplying the density of the petroleum product by its volume. 1850 liters of diesel fuel with a density of 0.840 kg/m3 will weigh 1554 kg. 1000 liters of diesel fuel with a density of 0.860 kg/m3 will weigh 860 kg.
Formula for determining the volume of diesel fuel
A pressing question for transportation, sales and accounting is: how to convert the weight of fuel into volume?
To find out the volume of diesel fuel, you need to divide its mass by its density. If there is 1 ton of diesel fuel, and its density is 0.840 kg/m3, the volume will be 1,190 liters 476 grams.
Formula for determining density of diesel fuel
The density of diesel fuel is the ratio of the mass of the petroleum product to its volume. If there are 860 kg of diesel fuel with a volume of 1000 liters, then the density will be 0.860 kg/m3.
The density of diesel fuel is regulated by GOST 305-82. The standard fixes the value at 20 degrees Celsius. The density of diesel fuel, depending on its seasonal type, is established by state standards as follows:
winter – 860 kg/m3;
summer - 840 kg/m3;
Arctic – 830kg/m3.
To determine the density of diesel fuel using another method you need:
In the passport data of the petroleum product, find the density of the petroleum product at 20 degrees Celsius.
Measure the actual temperature of diesel fuel in the container for transportation or storage.
We multiply the temperature difference by a factor of 0.0007.
Let's make an amendment. If the temperature is higher, we subtract the value from the passport density; if it is lower, we add it.
Everything has its time
What happens to summer diesel fuel at low temperatures? Just as water solidifies at freezing temperatures, summer-quality diesel fuel also crystallizes. Result: the fuel increases its viscosity and clogs the fuel filters. Thus, the engine can no longer receive high-quality diesel fuel in the required volume. The warning signal about impending troubles will come when stable frosts set in.
In the case of winter diesel fuel, the flow point is lowered, so that diesel fuel does not crystallize. Winter fuel for diesel cars exists in several classes, and additional differentiation is often made between traditionally “winter” and “polar”, arctic class fuel. In the latter case, the performance of diesel fuel is maintained even at very low temperatures.
Replacing diesel fuel grades is usually done by the gas station operators themselves. Before refueling, make sure that there is no summer fuel in the tank.
Formulas for calculating density, weight and volume of diesel fuel
To calculate the density, mass and volumetric amount of diesel fuel, an online calculator or calculation formulas are used. To calculate the parameters, it is necessary to take into account the ambient temperature and specify the type of fuel poured into the tank. When calculating, the correction factor and the difference in temperature (between measured and reference) are taken into account. The result obtained is approximate, since the measuring equipment has an error. Accurate data can only be determined through laboratory analysis.
Formula for determining the weight of diesel engines
To determine the weight, an equation of the form m=p*V is used, where:
- m—calculated mass (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the tank in which fuel is stored.
To determine capacity, you need to measure the dimensions of the container and then calculate the volume using formulas. At oil depots, tanks are used that have marks on them indicating that the tank is completely filled. On the outside of the tank there is a factory marking plate on which the volume and measurement error are indicated.
Formula for determining the volume of diesel fuel
To determine the volume, an equation of the form V=m/p is used, where:
- m - declared mass of cargo (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the tank in which fuel is stored.
The weight is indicated in the accompanying documents for the cargo. The attached documentation must contain a section indicating the type of fuel delivered. If the paragraph is missing, then the density is calculated using a hydrometer and correction factors (to determine the weight at a standard temperature of 20°C).
Formula for determining density of diesel fuel
To determine the density, an equation of the form p=m/V is used, where:
- m - declared mass of cargo (in kg or t);
- p—density reduced to temperature;
- V is the volume of the fuel tank.
The weight is determined from the accompanying documents or by weighing the tank truck or other container (you need to know the weight of the empty container or empty vehicle). To calculate the volume, a mark placed inside the container is used. The capacity can be checked by draining the liquid into a verified reservoir. Then the density is determined, which is reduced to reference values by summing or subtracting a correction factor multiplied by the temperature difference.
Amount of diesel fuel in liters - characteristics influencing the result
Density is a determining factor on which correct calculations depend. The quality certificate indicates this indicator at a temperature of +15 or +20 degrees. However, when the temperature changes, the density of the substance changes. It increases with increasing ambient temperature, and, conversely, decreases with cooling. That is, the higher the temperature, the greater the volume of fuel, and the less one liter of product will weigh. We will take these mass fluctuations into account, however, calculations are made for the values indicated in the passport.
How many kilograms are in a liter of diesel fuel?
Mass is a characteristic of a body, which is a measure of gravitational interaction with other bodies.
Volume is a quantitative characteristic of the space occupied by a body, structure or substance.
Density is a physical quantity defined as the ratio of body mass to body volume.
The relationship between liters and kilograms of diesel fuel is determined by a simple mathematical formula:
V – volume; m – mass; p – density.
In the calculation, the density of diesel fuel was taken = 840 kg/m3.
The density of diesel fuel can vary depending on temperature and pressure. You can find the exact density of diesel fuel in reference books.
If you need to convert m3 to tons, then see the program for converting tons to m3.
If you need to convert kg to m3, then see the program for converting kg to m3.
Question: How many kg are in a liter of diesel fuel?
Answer: 1 kg of diesel fuel is equal to 1.19 liters.
Question: How many liters are in a kilogram of diesel fuel?
Answer: 1 liter of diesel fuel is equal to 0.84 kilograms (kg).
You can quickly solve this simple mathematical operation using our online program. To do this, enter the initial value in the appropriate field and click the button.
This page presents the simplest program for converting kilograms of diesel fuel into liters. Using this online calculator, you can convert liters of diesel fuel to kg and back in one click.
To begin with, I would like to clarify what is meant by specific gravity (hereinafter referred to as SG) in physics and chemistry, and only then move on to the specific gravity of diesel fuel or, as it is also called, the specific gravity of diesel fuel.
Let's go over the theory.
What determines the correctness of calculations?
Diesel fuel is a petroleum product widely used in various industries. People often call it diesel fuel. It is used as a combustible material for diesel engines in many mechanical vehicles. These are, for example, heavy construction and agricultural equipment, trucks, and passenger cars. In practice, it is often necessary to make the necessary calculations, convert values from kilograms to liters and vice versa. To correctly calculate the number of liters in one ton of product, let’s read the following information.
How many tons and liters are there in a cube of diesel fuel?
Volume cubic meter. This volume (regardless of the temperature) will always contain 1000 (one thousand) liters or cubic decimeters. But the mass of diesel fuel varies greatly with temperature. They make money on this at gas stations, and especially the Donkermans on tankers. On a successful voyage on a tanker of 7,000 tons, you can float up to 25 tons of diesel fuel to the left))))) As the temperature rises, the volume of petroleum products increases and is determined by the formula V 2 = V1 (1 + ∆tβ), where V2 is the volume of petroleum product when the temperature rises by 1 °C; V1 – initial volume of oil product; ∆t – temperature difference; β is the coefficient of volumetric expansion of the petroleum product (Table 2). 2 Coefficients of volumetric expansion of petroleum products depending on density at +20 °C per 1 °C Density, Density, g/cm3 β g/cm3 β 0.700 …0.710 0.00127 0.800 …0.810 0.00095 0.710 …0.720 0.00123 0.800 … 0.810 0.00092 0.720 …0.730 0.00120 0.800 …0.810 0.00089 0.730 …0.740 0.00116 0.800 …0.810 0.00087 0.740 …0.750 0.00113 0.800 …0.8 10 0.00084 0.750 …0.760 0.00110 0.800 …0.810 0 .00082 0.760 …0.770 0.00107 0.800 …0.810 0.00079 0.770 …0.780 0.00104 0.800 …0.810 0.00077 0.790 …0.80 0.00098 0.800 …0.810 0.000 72.
You started selling fuel in cubes, and parts in piles? :))
A lot, cartoon, a lot...
One cube contains 1000 liters or approximately 850 kg (the latter is highly dependent on temperature)
1000 liters of liquid are placed in one cubic meter, the density of diesel fuel is no more than 860 kg/m³, from here we can conclude that the mass of the fuel will be 860 kg….
= * = 0.85*1000 = 850kg = 0.85t (approximately) Cube of liquid = One thousand liters of liquid (volume = volume) R.S. This is the same as about milk: 1 liter of milk is larger in volume than 1 kg of milk, and 1 liter of sunflower oil weighs less than 1 kg.
Don’t torture yourself with calculations; it’s better to use a ready-made density calculator:
touch.otvet.mail.ru
How much does a 20 liter canister of gasoline weigh?
The 20 liter steel canister SPEC 2770 is designed for storing and transporting gasoline and diesel fuel. Dimensions: 480x360x160 mm. Weight 2.2 kg.
Interesting materials:
What is the name of the sports hoop? What is health called in games? What is the name of the mirror in the dressing room? What are the doors under the bathroom called? What are the pills on clothes called? What are the people of the Kuril Islands called? What was the name of television in the USSR? How not to register a car? How do quail eggs lay? How is the watch worn?
Calculation of density of petroleum products
When buying and selling diesel fuel or any petroleum products, different units of measurement are used - liters and kilograms. These two parameters are interrelated, and they depend on the density of the fuel.
The density of a fuel is its specific gravity, namely the amount of mass per unit volume.
The density of the fuel largely depends on the density of the oil from which it is obtained. According to GOST R 52368-2005, the fuel density at a temperature of +15 °C should be in the range of 0.820-0.845 g/cm3, and according to GOST 305-82 it should not exceed 0.860 (at 20 °C)
The density of the fuel depends on the temperature, however, as for any other liquid: as the temperature increases, the density of the fuel decreases and vice versa - as the temperature decreases, the density of the fuel increases. There are special tables for converting fuel density depending on temperature. For diesel fuel, the temperature correction for density changes is, on average, 0.0007 g/cm3 per 1°C.
DENSITY OF PETROLEUM PRODUCTS
| PETROLEUM PRODUCTS | Density at 20* C, g/cm3 |
| Aviation gasoline | 0,73-0,75 |
| Automotive gasoline | 0,71-0,76 |
| Jet fuel | 0,76-0,84 |
| Diesel fuel | 0,80-0,85 |
| Engine oil | 0,88-0,94 |
| Fuel oil | 0,92-0,99 |
| Oil | 0,74-0,97 |
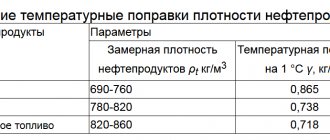
| Table of average temperature corrections for the density of petroleum products | |||
| Density at 20 °C | Temperature correction per 1 °C | Density at 20 °C | Temperature correction per 1 °C |
| 0,6500–0,6590 | 0,000962 | 0,8300–0,8399 | 0,000725 |
| 0,6600–0,6690 | 0,000949 | 0,8400–0,8499 | 0,000712 |
| 0,6700–0,6790 | 0,000936 | 0,8500–0,8599 | 0,000699 |
| 0,6800–0,6890 | 0,000925 | 0,8600–0,8699 | 0,000686 |
| 0,6900–0,6999 | 0,00091 | 0,8700–0,8799 | 0,000673 |
| 0,7000–0,7099 | 0,000897 | 0,8800–0,8899 | 0,00066 |
| 0,7100–0,7199 | 0,000884 | 0,8900–0,8999 | 0,000647 |
| 0,7200–0,7299 | 0,00087 | 0,9000–0,9099 | 0,000633 |
| 0,7300–0,7399 | 0,000857 | 0,9100–0,9199 | 0,00062 |
| 0,7400–0,7499 | 0,000844 | 0,9200–0,9299 | 0,000607 |
| 0,7500–0,7599 | 0,000831 | 0,9300–0,9399 | 0,000594 |
| 0,7600–0,7699 | 0,000818 | 0,9400–0,9499 | 0,000581 |
| 0,7700–0,7799 | 0,000805 | 0,9500–0,9599 | 0,000567 |
| 0,7800–0,7899 | 0,000792 | 0,9600–0,9699 | 0,000554 |
| 0,7900–0,7999 | 0,000778 | 0,9700–0,9799 | 0,000541 |
| 0,8000–0,8099 | 0,000765 | 0,9800–0,9899 | 0,000528 |
| 0,8100–0,8199 | 0,000752 | 0,9900–1,0000 | 0,000515 |
| 0,8200–0,8299 | 0,000738 |
In order to determine using this table the density of an oil product at a given temperature, it is necessary:
find the density of the petroleum product at +20 °C from the passport;
- measure the average temperature of the cargo in the tank;
- determine the difference between +20 °C and the average temperature of the cargo;
- using the temperature correction column, find the correction per 1 °C, the corresponding density of this product at +20 °C;
- multiply the temperature correction of the density by the temperature difference;
- subtract the product obtained in paragraph “d” from the density value at +20 °C if the average temperature of the oil product in the tank is above +20 °C, or add this product if the product temperature is below +20 °C.
Example No. 1
The density of the oil product at +20 °C, according to the passport, is 0.8240. The temperature of the oil product in the tank is +23 °C. Determine the density of the petroleum product at this temperature from the table.
We find:
- temperature difference 23 °C – 20 °C = 3 °C;
- temperature correction per 1 °C according to the table for a density of 0.8240, amounting to 0.000738;
- temperature correction per 3 °C: 0.000738 × 3 = 0.002214, or rounded 0.0022;
- the desired density of the oil product at a temperature of +23 °C (the correction must be subtracted, since the temperature of the cargo in the tank is above +20 °C), equal to 0.8240 - 0.0022 = 0.8218, or rounded 0.8220.
Example No. 2
The density of the petroleum product at +20 °C, according to the passport, is 0.7520. The temperature of the cargo in the tank is –12 °C. Determine the density of the petroleum product at this temperature.
We find:
- temperature difference +20 °С – (–12 °С) = 32 °С;
- temperature correction per 1 °C according to the table for a density of 0.7520, amounting to 0.000831;
- temperature correction for 32 °C, equal to 0.000831 × 32 = 0.026592, or rounded 0.0266;
- the desired density of the oil product at a temperature of –12 °C (the correction must be added, since the temperature of the cargo in the tank is below +20 °C), equal to 0.7520 + 0.0266 = 0.7786, or rounded 0.7785.
Diesel fuel classification
To classify diesel fuel, two indicators are traditionally taken into account: the degree of sulfur content and the maximum cloud point. This is a standard adopted by the state, corresponding to the European system and specification EN 590. For the purposes of this article, temperature indicators are of greatest importance.
“Temperature” classification divides fuel into grades and classes, which are indicators of the lowest temperature at which the fuel can pass through the filter.
The maximum filterability temperature (t °C) is indicated in parentheses.
| For areas with temperate climates, fuel grades are determined | Fuel classes are determined for cold climate areas |
|
|
Depending on temperature indicators, diesel fuel is divided into three main types and one additional (last).
- Summer diesel fuel. Remains liquid down to -5 °C. Recommended for use at temperatures above 0 (filterability t °C is not determined).
- Winter diesel fuel. It should not thicken to temperatures below 35 degrees. Use in frosty conditions (-20 °C).
- Arctic diesel fuel. Recommended for severe frosts from -45 degrees (-38 °C).
- Interseasonal diesel fuel (-15 °C).
We recommend: What kind of fluid is poured into the power steering
Additionally, we advise you to read the material, which describes in detail the features of using antigel for diesel fuel.
For each of the three main types, its own standards for density and viscosity indicators are determined. It is these characteristics that determine the efficiency of the engine and when and what fuel to use. They are also often used to determine the quality of diesel fuel.
The viscosity standards are as follows:
- summer type - 3.8/6.0 cSt;
- winter type - 1.8/5.0 cSt;
- Arctic type - 1.5/4.0 cSt.
Density indicators will be discussed further.
Diesel fuel in tons and liters
Diesel fuel can be measured in tons or liters. Liters characterize the volume of the product, and tons characterize the weight, while converting diesel fuel from liters to tons and back is not particularly difficult.
The Sompex.ru trading platform is a place for buying and selling fuel and other petroleum products. Find out the price of diesel fuel today, quickly find a new supplier or attract new customers. Place your ads - buy and sell the best diesel fuel on the Sompex trading platform
How much does 1 liter of Euro diesel fuel weigh?
A liter is a measure of volume applied to liquids, equal to 1 decimeter (1 dm3). A thousand liters, respectively, is 1 cubic meter (1 m3).
1 m3 of liquid is almost never equal in weight to 1 ton, with the exception of rare exceptions, for example, distilled water, which is conventionally accepted as a standard value. Even ordinary water is a little heavier.
I sell diesel fuel, class diesel fuel or fuel at a wholesale price and you can order fuel delivery on the Sompex site.
The density of diesel fuel is less than water, and it weighs less. According to the average values of Rostekhnadzor, one cubic meter of diesel fuel will weigh 0.84 tons (accordingly, 1 liter of diesel fuel = 0.00084 tons, or 0.84 kg).
Please note that when calculating the density of diesel fuel, the default temperature value is set at 20 °C. The higher the temperature, the less diesel fuel weighs.
Specific gravity of diesel fuel
In addition to density, the term used is the specific gravity of the fuel. This is the ratio of the weight of a substance to its volume.
Specific gravity is measured in newtons per cubic meter (N/m3).
The Sompex.ru trading platform is a place for buying and selling fuel and other petroleum products. Find out the price of diesel fuel today, quickly find a new supplier or attract new customers. Place your ads - buy and sell the best diesel fuel on the Sompex trading platform
Tonne of diesel fuel in liters
Reverse conversion of Euro 5 diesel fuel is from tons to liters: provided that the density of diesel fuel is 0.84 t/m3, we obtain that one ton will contain 1.19 m3, that is, 1190 liters.
What does the density of diesel fuel depend on?
But such figures cannot be considered absolute and final. There is more than one type of diesel fuel, and the types have different densities, depending on the technical conditions - this indicator varies from 0.80 to 0.86 t/m3.
I sell diesel fuel, class diesel fuel or fuel at a wholesale price and you can order fuel delivery on the Sompex site.
The volume of diesel fuel is affected by the ambient temperature. It is believed that high-quality diesel fuel can change the density by no more than 0.00075 with an increase or decrease in temperature by 1 °C.
How to convert liters to tons of gasoline calculator?
Converting gasoline from liters to tons can be done using the formula:
- M = V * R, i.e.
- AI 76 - 0.715 g/cm3.
- AI 80 - 0.715 g/cm3.
- AI 92 - 0.735 g/cm3.
- AI 93 - 0.750 g/cm3.
- AI 95 - 0.750 g/cm3.
- AI-98 - 0.765 g/cm3.
Interesting materials:
How to move the kitchen into the hallway? How to eat coconut? How to qualify an industrial accident? How to heal in sniper elite 4 ps4? How to easily and quickly pluck a chicken? How to easily remove the label from a jar? How to easily remove film from plastic windows? How to easily remove protective film from furniture? How to fly on a plane with a one-year-old child? How to fly on a plane with a child?