When an engine is being repaired, car owners often ask what clearance should be on the piston rings. This question breaks down into two separate ones. For both compression and oil control piston rings, two parameters are standardized - the vertical (axial) gap and the gap size in the lock. Both parameters must be within certain limits, but we note right away that too much axial clearance, as well as excessive clearance in the lock, is nothing compared to what will happen if you install a ring with very small end clearance. In the latter case, of course, we were talking about the gap in the lock - it is otherwise called “end”, and we must talk about this value in more detail.
Why are there three rings on the piston?
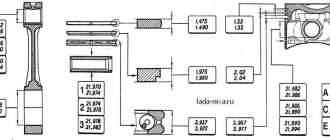
The two upper rings, installed in the piston grooves, are needed to maintain compression. In the figure, these elements are indicated by the numbers “1” and “2”. And the lower ring, designated as “3”, is an oil scraper ring:
Less than 3 rings on the piston are not used in 4-stroke internal combustion engines
When the engine is running, the parts heat up, the metal expands due to heating, and the size of all gaps decreases. If the gap between the ends of the ring is smaller than recommended by the manufacturer, then after warming up such a ring will scratch the cylinder walls. Measurements must be taken without heating the part, and the ring itself must be placed in the cylinder:
Gap measurement cannot be performed without access to the cylinder block
To find out the size of the gap, use special probes (bars). Typically recommended values are in the following range: 0.2-0.5 mm. Still, be sure to check the documentation!
Everyone knows what gap is recommended for VAZ engines: on piston rings that create compression, it should be 0.25-0.4 mm (not less than 0.25 mm). Other values are suitable for oil scraper rings - 0.25-0.5 mm. As you can see, the lower limit here is the same, but this is not true for all internal combustion engines.
Comprehensive repair of CPG
The so-called “capital” of the engine implies a complete troubleshooting of the cylinder-piston group, because it is this group that is subject to the greatest thermal loads during operation. Consequently, pistons, compression and oil rings are also subject to increased wear. In some cases, when the rings have not yet reached critical wear, they are left. On most modern internal combustion engines, a gap of 1 mm is considered critical, and in this case it is necessary to replace the rings. So, when overhauling an engine, it is recommended to change all the rings on the pistons, even if they still fit. This is necessary so that after 50,000 kilometers you do not have to disassemble the engine again.
It is also worth understanding that the gap for the first and second compression rings is not always the same. A striking example of this is domestic heavy equipment. For example, the thermal clearance of KamAZ piston rings should look like this:
- first compression ring - 0.20-0.40 mm (new);
- second - 0.30-0.50 (new);
- oil scraper 0.25-0.50 (new).
In this case, the permissible wear for all types of rings should not exceed 1 mm. Even 0.9 mm can already be considered critical. Although it is often clear even without disassembling the CPG that the rings are asking for replacement.
Measurement technique
It was not said above what vertical or axial clearance is. The essence of this parameter will become clear during the following steps:
- Bring the ring to the side of the cylinder;
- Place the ring with the outer side in the slot that is intended for it;
- Using a set of feeler gauges, determine the gap size (see figure).
The diagram shows how to measure the vertical gap.
This is how the axial clearance of the rings is always measured.
Now let’s determine what gap remains on the piston rings between the ends if they, that is, the rings, are inside the cylinder. The ring itself is immersed in engine oil, and then it needs to be moved along the walls of one of the cylinders - the same one where it will “work”:
The gap is measured when the ring is clamped by the cylinder walls
To perform this operation, a piston is usually used if the latter has already been removed. The point is to bring the ring to approximately the level at which it is when the motor is running. Let's say the block was bored recently. Then the ring is moved down 3-5 mm (this is enough). And then, using a set of probes, the operation is brought to completion.
The motor oil used to lubricate the rings can be any type. Everything in the engine burns successfully!
Why is a small gap bad?
It would seem that to achieve good compression, the gap needed to be as small as possible. In this case, the oil will not burn. All this is only partly true. The fact is that if, during expansion, the gap becomes smaller than permissible, then a violation of heat transfer will occur. This is partly due to increased friction between the rings and the cylinder. As a result, scuffing appears and wear of the cylinder and ring accelerates. In the end, the compression rings do not create the proper pressure, and the oil scraper rings leave oil on the cylinders. After some time, engine power is lost, lubricant consumption increases and the stability of the internal combustion engine deteriorates.
Ratings for different Lifan internal combustion engines
When installing new motor rings that do not have external defects, it is not necessary to measure the axial clearances. This is precisely why the values of these gaps are not given in the repair literature. But the gap in the ring lock needs to be measured and assessed using the manufacturer’s recommendations. The lock clearance limits are listed below.
Solano 620
The engine of the Solano 620th model sedan is an analogue of the Toyota 4A-FE engine, the volume of which is 1.6 liters. So we will use the recommendations of this company (Toyota):
- Upper compression: 0.250 – 0.450 (1.050);
- Lower compression (AE-92, AT-180): 0.150 – 0.400 (1.000);
- Lower compression (AE-101, AT-190): 0.350 – 0.600 (1.200);
- Oil scraper: 0.100 – 0.500 (1.100).
The maximum limit value is indicated in parentheses. If it is exceeded, it is necessary to carry out major repairs - boring the block and so on.
Crossover X60
Here we have an engine, like in the Toyota RAV4 crossover (1.8). Therefore, we will again use Toyota’s recommendations:
- Upper compression: 0.250 – 0.450 (1.050);
- Lower compression: 0.350 – 0.600 (1.200);
- Oil scraper: 0.150 – 0.500 (1.050).
We hope no questions arise here. The values are suitable for the 1ZZ-FE engine (1.8 l).
Review of popular models of piston rings VAZ 2109 – 2115
There are many companies that produce piston rings, as well as many fakes, and there is simply not enough time to look through them all. Therefore, let's look at those manufacturers of piston rings that differ from others in normal quality and price. The first thing I want to recommend is SM piston rings.
Piston rings from SM
Piston rings from Mahle.
These companies produce piston rings for VAZ cars of various diameters and are perfect for us. They are most likely produced in China, because the original ones will cost much more. But this does not mean that everything is so bad, their quality is excellent. I still recommend rings from “SM”, because their price is much lower than that of “Mahle”, and the quality is the same, so why pay more and overpay for the brand.
The upper compression ring from these manufacturers is chrome-plated steel, but from the “SM” company it is copper-plated, this is clearly visible in the top photographs. The second compression ring is black and made of cast iron, but the ring from Mahle has a darker color. On the picture
The lower oil scraper rings are metal typesetting. The graphics on the left are “SM”, and on the right “Mahle”.
I recommend using metal oil scraper rings, because, unlike box-type rings, they fit perfectly in the cylinder, are resistant to overheating (they do not lose their spring properties) and their main advantage is that they work as two rings independent of each other. The rings are box-type, very afraid of overheating. When they overheat, they lose their spring properties and do their job poorly. And one more serious disadvantage: they require very careful running-in. At the slightest deviation from the running-in conditions, the working edges of the ring may break off in some places and allow oil to leak through.
Of course, there are other manufacturers of piston rings, but as usual they are complete fakes and sometimes it’s not possible to choose quality ones
Functions of piston rings
Piston rings are designed to perform the following functions:
- Sealing the piston space while maintaining pressure with the upper compression rings.
- Heat removal from the walls of the sleeve.
- Reduced oil consumption.
Checking the clearance in the locks inside the cylinders
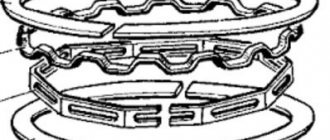
The piston ring lock is the joint between two ends that are capable of being compressed to hundredths of a millimeter. The ends have a straight or oblique cut, with a rectangular profile section.
When placing the rings in the grooves, the joints are placed at an angle of 120° (if 3), and with two rings - at 180°, which limits the leakage of gases and oil into the crankcase, under the piston.
Oil scraper rings are designed to remove excess motor lubricant from the cylinder walls. They are designed to leave a thin layer of film on the mirror, so small that it is measured in microns. The design provides radial, through slots through which the oil removed from the walls is drained into the crankcase.
Available in cast iron with slots or extensions. They represent two rings (upper, lower), a pair of radial or axial expanders.
About the thermal gap
Locks are considered a common element of the rings, since the goal is to compensate for thermal expansion during operation. Locks undergo gas pressure, temperature loads, and other inert influences. This tension is absorbed by the tiny distance between the ends of the rings.
Why is the thermal factor needed?
Let’s imagine the absence of a gap between the spans of bridges, railway rails or expansion joints on main pipelines. Solar heating and expansion, for example, of the metal of rails that do not have a gap during installation, lead to their inevitable bending with all the ensuing consequences.
In the case of piston rings, the lack of butt clearance leads to breakage of the piston.
So, the free rotation of the rings eliminates butt contact inside the piston groove. The design includes cuts to prevent jamming from overheating. This feature contributes to a tight contact with the cylinder mirror.
The permissible joint interval does not exceed 0.3-0.6 mm. With a small joint gap, for example 0.2 mm, heated parts can leave marks on the cylinder.
By the way, preference is given to parts with oblique cuts at the ends. Straight ends have a lot of pressure on the walls, which prematurely damages the liner, causing oil leakage.
Piston repair: what you should pay attention to
Modern materials and technologies for manufacturing parts make it possible to operate the engine under very intense conditions. The maximum crankshaft rotation speed reaches one hundred revolutions per second. In this case, the piston and connecting rod reach a translational speed of up to 30 m/sec twice for each revolution (two hundred times per second). and the same number of times they come to a complete stop, causing huge cyclic inertial loads (the weight with such acceleration increases by more than a thousand times). Therefore, technologists try to make the piston as light as possible, making it from an aluminum alloy with a cast steel plate that compensates for thermal deformations. The piston has stiffening ribs and hard anodizing, up to the fire zone, which protects the bottom and the groove of the upper compression ring from burning out. Friction is reduced by the most advanced brands of oils with additives. But it is impossible to avoid wear, so periodically, after a certain mileage, the piston VAZ 2106 is replaced. It is better to do this when the first symptoms appear:
Operating a car with wear and tear can lead to damage that will require major repairs, which will increase the price many times over.
How to dismantle the piston yourself
First of all, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the engine, since after disassembly it will be difficult to prevent grains of sand and dirt from getting inside. The engine must be placed on a sturdy rack at a height convenient for work. Prepare rags, a set of tools and accessories:
- socket, ring wrenches and heads 10 mm., 12 mm., 13 mm., 14 mm., 17 mm., 19 mm., 22 mm., and wrench 36 mm.;
- a set of thin flat probes;
- bore gauge;
- micrometer;
- calipers;
- torque wrench;
- device for compressing rings on the piston;
- bushing for installing piston pins;
- gas-burner;
- hammer;
- core;
- portable lamp;
- large flathead screwdriver.
Tip: Before disassembling with your own hands, all parts are marked with a core, and a photo of the initial location is taken with the numbers and marks of the removable parts so that they can be installed in their place if they are suitable.
Disassembly sequence
- The engine with the head, pan and side covers removed is laid on its side to allow access to the pistons and connecting rods. Wrench 36 mm. the crankshaft is rotated to the position of maximum extension of the nuts of a pair of connecting rods.
- Using a head and a long wrench, you need to unscrew two nuts each, securing the connecting rod cap of the first and fourth cylinders, you can use any one, but it is more correct to follow the chosen sequence. By lightly tapping with a hammer, the cover moves out of place, allowing you to easily remove it from the studs. It is advisable to first familiarize yourself with the stages of work via video.
Tip: The caps and connecting rods form a pair; during their manufacture, the final boring of the mounting hole is done in assembled form, so they are marked with the cylinder number and cannot be replaced. You need to make sure that the numbers match when assembling and are directed in the same direction.
- Using the wooden handle of a hammer, resting against the pin, the connecting rod with the piston is pushed out through the upper plane of the cylinder block. The crankshaft is rotated to the maximum extension position of the nuts of the other two connecting rods. All four pistons are disassembled in the same way. The main bearings are unscrewed and the crankshaft is removed for visual inspection.
Attention: The main bearing caps are marked with marks; it is very important to place them only in their place, since they are not interchangeable; this is required by the boring technology and assembly instructions.
- The liners are removed from the connecting rods and covers. When repairing a VAZ 2106, the piston rings are replaced, starting with the upper compression ring, all the rings are sequentially removed from the pistons, and the piston pins are knocked out with a bushing. If possible, it is better to use a press. The parts and the block are washed with kerosene, blown with compressed air, the cooling and lubrication channels are purged.
- Sanded surfaces are wiped and checked for damage. For inspection, a portable lamp is used, changing the angle of illumination to conveniently examine small scratches. Cracks are not allowed; if they are detected, defective parts will have to be replaced, including the block.
- Wear is measured using a bore gauge in four planes located from the top plane at a distance of 5mm, 15mm, 50mm. and 90 mm. In each plane, two measurements are taken in perpendicular directions.
Thermal clearance requirements
Functional requirements for thermal clearance include:
- Heat removal from the piston at the moment of ignition of the mixture . Otherwise, the piston will burn out under the temperature of the combustion chamber.
- Piston space sealing function . The resulting pressure should evenly press the rings against the cylinder walls. Achieving such touch requires setting the correct distance.
- Requirements for oil scraper discs responsible for supplying the required amount of lubricant. Compliance with this rule keeps oil and gasoline consumption at the level of factory standards.
Options
Set gaps on rings
The established gap should correspond to 0.6-0.3 mm, and the side gap between the wall should not exceed 0.08-0.04 mm.
This is interesting: Recommendations for choosing fuel
The value comes from the fact that exhaust gases act on the rings from the inside of the groove, pressing them against the wall. The coordinated functioning of compression and oil scraper rings allows for complete combustion of the mixture. This depends on how they are placed in the piston groove.
Therefore, a small value between the ends after warming up will lead to scuffing of the cylinder mirror.
The gap is measured with a feeler gauge and is regulated at 0.2-0.5 mm. For VAZ model engines, a value of 0.25-0.04 mm is provided on the sealing rings. Oil scrapers have 0.25-0.5 mm.
The first ring on top (compression), as loaded from alloy cast iron, is sprayed with chromium. The porous coating of this metal is capable of holding the required mass of engine oil.
Plasma coating of a layer of molybdenum on the rings promotes wear resistance and low friction with the cylinder.
Memo
The lock on the separator is painted blue
When choosing a repair size, you need to be guided by the product designation, including the engine model, kit number, product size. Additionally, the markings, which are located in a certain place of the product (close to the end), are checked. Expansion springs with a ground surface are carefully considered.
Measurement technology
The first thing to do is bring the ring to the side of the cylinder. Then place its outer part in the designated groove. Next you will need a set of strips, with the help of which the gap is determined. If the ring is located directly inside the cylinder, then measurements must be taken separately, since the distance between the ends may vary.
The first thing to do is place the piston ring in the engine oil. The quality of the latter is not particularly important here, since absolutely everything will burn during operation. Then the ring moves along the cylinder wall. Moreover, this must be done only in the cylinder where this ring will be used in the future. It is especially convenient to perform such a calculation if the piston has already been removed. In the case of a recent block groove, it is enough to move the ring by 3-5 mm, approximately to the place where it will be during the operation of the internal combustion engine. After this, we use a set of probes (bars) and obtain the required values. Use the “manual” when selecting the piston ring clearance. The Ford Escort 1.6 diesel, for example, should have a gap of 0.3-0.5 mm for the upper compression rings and 0.2-0.45 mm for the oil scraper ring.
What gap should be on the piston rings?
The internal combustion engine is actually a heat engine. During the operation of such an engine, a number of loaded parts in the design of the CPG and timing belt are subject to thermal expansion as a result of significant heating. For this reason, for normal operation of the internal combustion engine, individual designs provide for independent adjustment of the thermal clearance of the valves (in the absence of hydraulic compensators).
Read in this article
Selection of piston rings: dimensions and materials of manufacture
A major overhaul or tuning of an engine usually involves the need to completely disassemble the internal combustion engine to replace the elements of the CPG and crankshaft. During the work, in some cases it is necessary to bore the cylinder block, then the cylinders are honed. Next, an accurate selection of pistons according to the size of the liners is required, at the same time the piston rings, piston pins and connecting rods are changed, the crankshaft is replaced or repaired, etc.
Replacing piston rings and the pistons themselves on a gasoline or diesel engine requires maximum sealing of the slot gaps. In this article we will talk about how to correctly select pistons, and then choose the right sized piston rings for them.
Read in this article
What gap should be on the piston rings?
There are two types of piston rings installed on the piston:
- compression rings;
- oil scraper rings;
Compression rings are also divided into upper compression ring and lower compression ring. The purpose of these rings is to seal the combustion chamber and prevent the breakthrough of a significant part of the exhaust gases into the engine crankcase. Oil scraper rings remove excess engine oil from the cylinder walls, so that excess oil does not enter the combustion chamber.
Such repairs usually involve boring the cylinder block and installing repair pistons and rings. The specified thermal gap is a tolerance that takes into account the expansion of the part with heating, that is, when certain parameters change. The permissible gap between the piston and the cylinder is the gap at which normal performance of all elements is observed. The parts fit very tightly to each other, but there is no damage or jamming.
In other words, the permissible piston ring clearance allows, after thermal expansion, to achieve such a thermal space (the gap between the piston and the cylinder) in which the piston rings tightly pressed to the cylinder walls create a reliable seal. At the same time, the rings, expanded under the influence of high temperature, must remain mobile in the grooves on the piston and create a reliable seal, without interfering with the normal movement of the piston. At the same time, the piston rings must effectively remove excess heat from the heated pistons.
The piston ring is not solid, as it has a cut (lock). Thanks to this cut, it is possible to avoid jamming when heated and achieve elasticity of the ring for tight pressing against the cylinder walls. After installing the ring on the piston and placing the piston in the cylinder, a gap is formed in the piston ring lock. This gap is 0.3-0.6 millimeters.
The piston ring lock can be made in the form of a straight or oblique cut. A lock with a straight cut is less preferable, since in the area of the cut edges a strong pressure is created on the cylinder walls. This design feature of the lock causes accelerated wear of the cylinder mirrors, after which gas leaks occur and oil consumption increases due to waste. Increasing the piston ring gap beyond the permissible parameters worsens the seal. Reducing the ring clearance can lead to their destruction, jamming or the formation of scoring on the cylinder walls.
How to properly change and install piston rings? Detailed review
When repairing an engine, the question of how to properly change and install piston rings is very important. Before considering the procedure itself, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the signs that indicate the need for such repairs. Sometimes replacing the rings itself is not enough to return the engine to normal operation. Therefore, diagnostics and correct conclusions based on its results play a very important role here.
Before properly changing and installing piston rings
, you should monitor the general performance of the engine. The primary signs of ring wear are the following:
- The engine has lost power. When you press the accelerator pedal and try to accelerate the car, the engine refuses to respond, hesitates and does not pull;
- Engine oil consumption has increased. When the oil scraper rings wear out, oil enters the combustion chamber and is discharged into the exhaust system;
- Excessive fuel consumption. The symptom is a direct descendant of decreased compression. The engine loses efficiency and, as a result, fuel consumption increases.
If you have one of these problems (or all of them at the same time), you should pay attention to the condition of the piston system
To replace the rings, in any case, you will need to disassemble the engine. There are 2 options: either disassemble it on site, or remove it from the car. In any case, you should start by removing the timing cover and dismantling the cylinder head. Already at this stage it will become clear whether to replace the rings on the installed engine, or remove it completely.
If the sleeves are in good condition
, and there is no significant production on them, then you can limit yourself to replacing the rings.
After dismantling the pistons and connecting rods, you can begin to remove the old rings. To do this, you can use a special device, or simply carefully break them off, while avoiding damage to the piston. Fragments of rings can be used to clean the landing channels from soot and deposits. If this is not done, the new rings may simply not fit.
When purchasing new rings you should pay special attention. Normal quality ring kits should be from a recommended company, carefully packaged, and come with a quick labeling and installation guide.
If the purchased rings are simply wrapped in a piece of paper, then there is no need to talk about the quality of such spare parts.
Next, you can begin installing new rings.
When installing, it is very important to follow the sequence. The oil scraper ring is always put on first, then the compression rings.
It is also advisable to maintain the position of the ring in the “up-down” relationship. If there are special locks in the piston grooves, you should adhere to a uniform distribution of locks around the entire circumference.
For example
, in a piston with three compression rings, the locks should be located 120 from each other. All relevant sequences and order can be found on the ring markings and on the instructions from the manufacturer.
For better and more correct installation, you should use a special device. They can be found in automotive stores. Those who want to save money install the rings manually, using available materials and tools. At the same time, the savings are dubious, since very often with such an installation the rings break, which leads to the need to purchase a new set.
Also, often without the use of a device, the correct geometry of the rings can be disrupted. This means that if too much force is applied, the ring becomes oval. In this case, it completely loses its properties of a tight fit to the cylinder liner. The results of such repairs may be a waste of time.
When all the rings are in place, you can begin reassembling the piston system and other engine parts. A very important point in the question of how to correctly change and install piston rings during assembly is the procedure for shrinking the pistons into the cylinder liners.
Using a special device, the rings are pressed into the grooves and the piston is plunged into place. In this case, you need to be very careful not to damage the edge of the sleeve.
You should also pay attention to the correct position of the piston and connecting rod relative to the crankshaft. All subsequent assembly of the power unit and attachments is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly
How does the thermal clearance of piston rings affect oil consumption?
Recently, there has been a tendency among manufacturers to increase the thermal clearances of compression piston rings. The gaps on such rings range from 1 to 2 mm. Typically, such an increased gap is relevant for the second compression ring.
The fact is that the clamping of the piston rings (both the first upper and the second compression) depends almost entirely not on the degree of elasticity of the ring itself, but on the pressure that arises during the combustion of the fuel-air mixture charge in the working chamber. Exhaust gases enter the grooves on the piston and then end up on the back side of the rings. As a result, the pressing force of the rings against the cylinder wall increases. Gases most strongly affect the first (upper) compression ring, and also affect the pressure of the second compression piston ring.
Taking into account the above, it should be noted that when the engine is running at idle speed and at low loads, the gas pressure is noticeably weaker compared to the mode of medium and maximum loads. For this reason, the compression piston rings are not pressed so tightly against the cylinder wall at such internal combustion engine operating modes.
To reduce oil consumption, manufacturers increase the thermal clearances of the piston rings. Through the increased gaps, gases, even under relatively low pressure, penetrate much more actively into the annular groove, after which they end up on the back side of the ring.
The ring pressure is improved, the sealing of the combustion chamber remains at an acceptable level, and oil consumption can be reduced. The only drawback of the increased ring gap is the greater amount of gases that enter the crankcase through the increased gaps.
Design and principle of operation
The design of the compression ring is simple: it is a ring that has a gap so that its elasticity allows the ring to diverge and maintain the pressure of the working edge against the cylinder walls.
Material – high-strength cast iron, less often – high-alloy steel. The operating conditions of the upper compression ring are harsh: high temperature and pressure. At the moment the mixture ignites, the pressure reaches 90 bar, the temperature approaches 1500 degrees. As the cylinder wears, it loses its uniform diameter, and with each up-and-down stroke of the piston, the ring has to compress and expand, which contributes to the accumulation of fatigue stresses. To increase the service life, at least the upper ring is coated with a layer of chromium, which has high hardness.
The second compression ring operates in lighter conditions - in this place the piston is already colder, and direct heat transfer from hot gases no longer affects it. Therefore, it may not be chrome plated.
Oil scraper rings were initially made of solid cast iron; they had two working edges with a groove between them. The oil that passed through the lower edge was collected by the upper edge into this groove, and through the radial holes in it fell into the holes in the piston skirt and was discharged inside it. This design had a serious drawback: both edges worked simultaneously; in worn-out engines, where the ring was warped along with the piston, oil leaked past the ring. Therefore, composite structures were invented: in them, two thin rings are pressed against the edges of the groove with a spring expander, through which the collected oil flows into the piston. Due to the small width of the individual rings and their operation, this design remains effective when the piston is misaligned.
Let's sum it up
Both the service life of the rings themselves and the serviceability of the entire CPG depend on the correctly selected thermal clearance of the piston rings. Natural radial wear of the rings leads to an increase in thermal gaps, after which the sealing of the combustion chamber deteriorates.
It should be noted that a reduced clearance is much more dangerous for the engine. If the minimum gap in the locks (thermal space) is reduced to 0.2 millimeters, after the motor is heated and reaches operating temperatures, the gap in the lock may be completely absent. As a result, the ring puts a lot of pressure on the cylinder walls, ring wear increases significantly, heat transfer is disrupted, and the risk of scuffing increases.
How to choose the right piston rings. Correct selection of rings by size and materials, how to choose original rings. Useful tips.
When is it necessary to replace piston rings? How to install rings on the piston when replacing it yourself. Service life, rings, grinding in and running in.
Why do piston rings stick? The main signs for independently identifying a malfunction, diagnostics. Do-it-yourself decarbonization of piston rings.
Purpose, design features and principle of operation of piston rings of an internal combustion engine. Types of rings, gap size, main faults.
Purpose of the piston in the design of the internal combustion engine. Features and design of the piston, oil scraper and compression rings.
Purpose of the cylinder-piston group of an internal combustion engine. Design features, piston, rings, cylinder liner. CPG wear and repair.
Compliance standards
In its initial state, the cylinder fully corresponds to its name; it is a geometric figure with a constant diameter along the entire height and a circle in any section perpendicular to the axis. However, the piston has a much more complex shape, and it also has heat-setting inserts, as a result of which it expands unevenly during operation.
To assess the state of the gap, the difference between the diameters of the piston in the skirt area and the cylinder in its middle part is selected.
Formally, it is generally accepted that the thermal gap should be approximately 3 to 5 hundredths of a millimeter in diameter for new parts, and its maximum value as a result of wear should not exceed 15 hundredths, that is, 0.15 mm.
Of course, these are some average values; there are a great variety of engines and they differ both in different approaches to design and in the geometric dimensions of parts, depending on the working volume.
Thermal gap in the piston ring lock
The engine is the main part in any car. Thanks to him, the car moves forward and the electronics work. Therefore, it is so important that every element of the motor is in perfect condition. Otherwise, there is a risk that the car will stop in the middle of the road and refuse to start.
The main elements of the engine are the cylinders. The pistons move in them, and the operation of the entire system depends on how well these parts interact. That is why it is so important that the piston ring clearance clearly fits into the standard.
Essentially, a micro-explosion occurs inside the cylinders, which forces the pistons to move in the desired direction. As a result, the crankshaft rotates and mechanical energy is generated.
Therefore, the piston ring clearance is also affected by high temperature, which is the result of a reaction that occurs inside the cylinders. At least, this is how the process occurs in an internal combustion engine.
A few important nuances
The service life of the cylinder-piston group and, in fact, the rings itself depends on how correctly the thermal clearance of the piston rings of a diesel or gasoline engine is selected. The appearance of scoring due to friction of the rings on the cylinder leads to a loss of not only compression, but also geometry. This is not very pleasant, since to restore the working condition you will need grinding, and in the most advanced cases, boring the cylinder block.
If radial wear of the rings occurs, the seal in the combustion chamber is significantly deteriorated. This leads to deterioration in engine dynamics and increased engine oil consumption.
Operation of diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines
To better understand the importance of piston ring clearance in engine operation, let's consider how the two most common systems work. In reality, the difference between them is not that great, at least in terms of design.
The main difference is the ignition process. In diesel engines it occurs due to increased pressure. As a result, the temperature rises, after which the nozzle injects fuel inside, and ignition occurs on its own.
The gasoline engine is designed a little differently. Instead of an injector, spark plugs are installed at the top of the pistons, which supply sparks. Naturally, with such a design, normal piston ring clearance is very important.
This is interesting: Comparative characteristics of 16 and 8 valve engines
How to check the clearance between the piston and cylinder
To check the gap, measuring equipment is used in the form of a micrometer and a bore gauge; this pair has an accuracy class that allows it to respond to every hundredth of a millimeter.
A micrometer measures the diameter of the piston in the area of its skirt, perpendicular to the pin. The micrometer rod is fixed with a clamp, after which the inside gauge is set to zero by resting its measuring tip on the micrometer rod.
After such zeroing, the bore gauge indicator will show deviations from the piston diameter in hundredths of a millimeter.
The cylinder is measured in three planes, the top, middle and bottom, along the piston stroke area. Measurements are repeated along the axis of the finger and across.
As a result, the condition of the cylinder after wear can be assessed. The main thing that is required is the presence of irregularities such as “ellipse” and “cone”. The first is the deviation of the section from the circle towards the oval, and the second is the change in diameter along the vertical axis.
The presence of deviations of several hundredths indicates the impossibility of normal operation of the rings and the need to repair the cylinders or replace the block.
What is piston ring clearance?
Every part of the internal combustion engine is exposed to high temperatures. As a result, expansion occurs. Due to this process, the initial parameters of the part change. This has the greatest effect on elements that are adjacent to each other.
The disappearance of thermal space negatively affects the piston ring clearance. This, in turn, has a bad effect on the operation of the piston, and therefore the entire engine. In order for the entire system to work without interruptions, this parameter must be monitored.
The thermal clearance of the piston rings is an important structural element that ensures the normal operation of the piston rings. For it to function properly, there must be enough space in the groove for free rotation. If the part gets stuck, then you will have to forget about normal heat dissipation.
conclusions
Properly selected and correctly placed rings guarantee a long service life.
We also recommend reading the article about what a hydraulic compensator is. From this article you will learn about the purpose, design and operating features of hydraulic pushers.
It is necessary to adjust the thermal clearances of the valves every 30-40 thousand km. mileage, as well as in the event of valve knocking on a cold or hot engine. The thermal gap between the piston and the cylinder, or more precisely the thermal gap of the piston rings, also requires special attention.
What should the gap be?
Rings in the piston can be compression or oil scraper. The main task of the former is to retain the burnt gases inside the cylinder. In turn, oil scrapers must remove excess oil from the walls.
The piston rings are not solid. They have a small cut, which is called a gap. Thanks to it, the rim does not jam when heating occurs. Moreover, this structural element ensures that the piston is pressed as tightly as possible against the cylinder walls.
If the described range is not observed, there is a high risk of damage to the cylinder and failure of the entire engine. An oblique cut is considered optimal for normal operation. Thanks to it, the pressure exerted on the walls is more uniform. A similar effect can be achieved due to thinner edges.
In most cases, amateur mechanics try to minimize the piston ring clearance. Therefore, by all means, bring the distance to 0.2 mm. The result of excessive zeal is scoring on the rings and cylinders. Such deformations appear due to the fact that when heated, the space in the lock decreases. Because of this, cutting into the cylinder wall occurs.
Signs and causes of wear (breakage) of piston rings
On VAZ cars, the engine wears out during operation, and the PCs also fail. Rings can:
- break into two or more parts;
- wear out in thickness;
- have general wear and tear.
Parts often break down due to overheating of the internal combustion engine; in this case, compression in the cylinders decreases and the engine loses power. Signs of a faulty PC are:
- bluish smoke from the muffler pipe, especially often it appears after a long period of idling when the gas pedal is sharply pressed;
- increased engine oil consumption;
- drop in power, the motor stops pulling;
- coking of spark plugs.
If there are signs of a malfunction in the piston group, the piston rings are replaced first. But replacing a PC does not always give the desired effect; often after repair the engine continues to smoke and consume oil. The reason for this is simple - there is wear in the cylinders themselves. In the block, the liners usually wear out unevenly - they take on an oval shape; due to wear, the piston rings do not fit tightly to the cylinder walls and do not provide a tight seal.
The role of piston rings in engine operation
There are a number of conditions, the observance of which guarantees long-term operation of piston rings. They largely depend on the characteristics of the gap. In order for the engine to last a long time, the correct clearance is necessary, which helps in controlling parameters such as:
- Temperature. The ability of the system to operate depends on this parameter. If the temperature is too high, the piston will melt in a few seconds.
- Pressure. In this case, the piston rings play the role of seals. It goes without saying that without the correct clearance this function will be difficult to implement. When pressure occurs, the circles are pressed against the plane of the cylinder. The correct gap allows the pressure force to be distributed as consistently as possible.
- Oil supply. Oil scraper piston rings are responsible for this parameter. They have two jumpers. They are the ones who regulate the supply of the substance in the right quantity. Typically this parameter is set at 1-2 microns. With optimal supply, gasoline consumption is reduced.
When these parameters are set correctly, the service life of each engine part increases several times. Piston rings and their clearances play a big role in their adjustment.
What should it be like?
The piston has two types of rings: compression (prevent burnt gases from passing through) and oil scraper (remove excess oil from the cylinder walls). By design, they are not solid, but have a cut that allows the rim not to jam when heated. The cut also promotes elastic pressing against the cylinder walls. The presence of thermal space in the locks plays a very important role in the operation of the rings and cylinder. Its permissible range is from 0.3 to 0.6 millimeters. Failure to comply with the range may result in missing or severe damage to the cylinder.
An oblique cut is much better valued. Since the pressure on the walls occurs more evenly due to the fact that its edges are slightly thinner.
It is useful to know about the gaps in the locks. Sometimes mechanics try to make the thermal space in locks as small as 0.2 millimeters. This often leads to scoring of rings and cylinders. And this is natural, since when the part is heated, the space in the lock becomes smaller (or completely absent) and it crashes into the walls of the cylinder.
The simplest lock with a straight cut has one drawback - its ends have high pressure on the cylinder, or rather on its walls. This leads, first of all, to oil leakage and premature wear of the walls.
In order to summarize the above, we list what characteristics the piston rings should have and what the thermal clearance of the piston rings should be:
- Temperature regulation. This is one of the most important functions, since a large mass of heat that is absorbed by the piston during the combustion period will be removed. If there is no such heat removal, the piston will melt in a matter of seconds.
- Pressure. The main function is to compact. And full implementation of this characteristic is possible only with appropriate pressure. When pressure appears, it affects the piston circles, and they, in turn, are pressed against the cylinder walls. In order for the pressure to be uniform, uniform distribution and correct clearance in the piston rings are necessary.
- Reliability and oil supply - oil scraper. They have two oil scraper bridges, which are responsible for the required amount of oil supply in the amount of 1-2 microns. If the oil is supplied correctly, then its consumption is not high, as is the fuel consumption. In this case, the wear rule will be observed as much as possible and the service life will increase.
As a result, I would like to wish every motorist and driver, regardless of whether he has diesel or gasoline, to check on his own or contact specialists in this matter. Especially when it comes to cars with high mileage and more than 5 years of constant driving.
How to measure piston ring clearance
At the first stage, you just need to visually inspect the part. It should not have cracks or any other defects. If you notice even minor mechanical damage, the element must be replaced with a new one.
Some preventive procedures will also not hurt. The piston head must be cleaned of carbon deposits, and special attention must be paid to the grooves that are located under the rings. Only after these procedures can you begin to inspect the gap.
Since there are only three rings in the device. Each has its own parameters:
- Upper compression 1-0.04-0.075 mm.
- Lower compression 2-0.03-0.065 mm.
- Oil scraper 3-0.02-0.055 mm.
Be extremely careful when taking measurements. Each ring has its own optimal gap size. For greater accuracy, use a micrometer. This is a device that allows you to measure all the parameters you need with extreme accuracy. For this purpose, there are special probes that allow you to easily and quickly take readings from the grooves.
This might interest you too
Use of cookies and data protection
The Motorservice Group uses cookies on your device in order to optimally design and continuously improve its web pages, as well as for statistical purposes.
Here you will find further information about the use of cookies, our Imprint and Privacy Notice. By clicking "OK" you confirm that you have accepted the information about cookies, the data protection declaration and the imprint. You can change your cookie preferences for this website at any time [link]