If necessary, dismantling the ShPG engine can be done on the car without removing the engine.
For complete information on dismantling and disassembling and assembling the ShPG, see engine disassembly
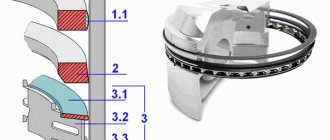
Main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group
Piston and connecting rod markings
1 – arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder; 2 – repair size; 3 – piston class; 4 – hole class for piston pin; 5 – connecting rod class based on the hole for the piston pin; 6 – cylinder number
Places where it is allowed to remove metal when adjusting the mass of the upper and lower connecting rod heads (to the specified dimensions)
Classes of connecting rods based on the weight of the upper and lower heads
| Mass of connecting rod heads, g | Class | Marking color | |
| top | bottom | ||
| 186+2 | 519+3 | A | white |
| 525+3 | IN | blue | |
| 531+3 | WITH | red | |
| 190+2 | 519+3 | D | black |
| 525+3 | E | violet | |
| 531+3 | F | green | |
| 194+2 | 519+3 | G | yellow |
| 525+3 | N | brown | |
| 531+3 | I | orange | |
We carry out the work on an inspection ditch or a lift.
Remove the engine oil pan (see here).
Using a 14mm socket, unscrew the two nuts securing the connecting rod cover (the piston must be at BDC).
Using a hammer with a plastic head (or a hammer with a soft metal head), apply light blows to the side surfaces of the cover to loosen its seat on the connecting rod bolts.
Remove the connecting rod cover.
Move the connecting rod up.
Using the wooden handle of a hammer against the connector of the lower head of the connecting rod, push the connecting rod upward until the piston exits the cylinder.
. and remove the piston and connecting rod assembly.
Similarly, we dismantle the pistons with connecting rods of other cylinders.
We install the ShPG in the reverse order (see also Engine Overhaul). (
Tuning options
When refining a Niva engine, a new crankshaft, cylinders and piston system are most often installed.
As a result, the car receives excellent speed characteristics and cross-country ability. There are two types of Niva engine tuning. The first includes chip tuning, and the second includes mechanical modification of the element. Chip tuning includes software upgrades, and is carried out only on new, fuel-injected SUVs. It includes flashing the control unit settings. It is performed by specialists quite quickly - within half an hour, but requires knowledge of software and additional electronic equipment.
Mechanical modifications are possible on any Niva, and this is the most popular type of tuning of a car’s power plant. With its help, you can significantly improve the technical characteristics of vehicles, and it is based on making some changes to the vehicle systems.
Peculiarities
Engines 21213 in their latest generation were equipped with an injector and ran on high-octane 93 gasoline. The cast iron cylinder block ensured maximum strength for this power unit.
The use of numerous automatic engine control systems made it possible not only to change the traction performance of this engine, but also significantly improved fuel efficiency. Niva in suburban mode consumes 8.3 liters of gasoline per 100 kilometers when driving at cruising speed.
Starting from 2014, Niva cars with a diesel engine are also offered to customers.
Main characteristics of internal combustion engine 21213
| Volume, cm 3 | 1690 |
| Main fuel: | gasoline AI-92 |
| Max. power, l. With. | 83 (at 5200 rpm) |
| Max. torque, Nm | 127 (at 3000 rpm) |
| Cylinder block configuration: | in one row |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Max. speed, km/h | 153 |
| Acceleration time to 100 km/h, sec. | 17 |
| Combined fuel consumption | 11,5 |
| Econorm | Russia-83 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82 with deviation up to 0.05 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 80 |
| Repair dimensions of pistons and cylinders, mm: | |
| first repair (marking on the piston - triangle, on the rings - 40) | 82.4 |
| second repair (marking on the piston - square, on the rings - 80) | 82.8 |
| Repair measurement of the diameter (for boring) of the crankshaft supports | 54.52 with deviation up to 0.013 |
| Compression ratio | 9,4 |
| Supply system | two-barrel carburetor |
| Cooling | liquid |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Presence of liners in cylinders | not provided for by design |
| Head material | aluminum alloy |
| Resource before major overhaul, km | 80,000 (actual ≈ 120,000 km) |
| Number of bars | four |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Max. speed, rpm | 8000 |
| Weight, kg: | 117 |
4.8.5.6 Checking the clearances between the piston grooves and piston rings
Checking the gap between piston rings and grooves
3 – set of feeler gauges
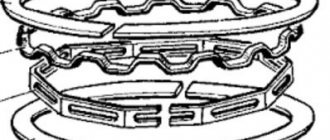
Location of piston rings in the piston grooves of the engine mod. 2106
2 – upper compression ring;
3 – lower compression ring;
4 – oil scraper ring
Tool for removing and installing piston rings
Check the height gap between the grooves and rings as shown in Fig. Checking the gap between the piston rings and grooves by inserting the ring into the corresponding groove.
Check the gap in the piston ring lock with a set of feeler gauges, inserting the rings into a gauge having a hole diameter equal to the nominal diameter of the ring with a tolerance of ± 0.003 mm. If there is no gauge, it is possible to check the gap. by inserting the piston ring into the cylinder where it will work, and pushing it with the piston to a depth of 20–30 mm from the bottom edge of the cylinder.
The gap should be between 0.25 and 0.4 mm for all rings. If the gap is insufficient, the joint surfaces should be filed down, and if it is too large, the rings should be replaced.
Heights and end installation gaps of piston rings
Piston ring kits
As spare parts, rings are supplied as a set for one engine.
Rings of nominal size are used when replacing worn rings for cylinders of nominal size. To reduce the break-in period of rings in cylinders that have already been running, compression rings that are not coated with chrome are installed in the upper grooves of the pistons.
Rings with an increased diameter are installed in cylinders bored to repair size, or they are used to replace worn rings in such cylinders.
The rings are installed in the piston grooves so that the groove on the outer surface of the second (scraper) ring faces down, and the chamfers on the outer surface of the oil scraper ring face up (Fig. Location of piston rings in the piston grooves of the engine mod. 2106 ).
If this condition is not met, oil may penetrate through the rings into the cylinder, which will lead to carbon formation on the walls of the combustion chamber, smoky exhaust from the muffler and increased oil consumption. Putting rings on the piston, as well as removing them, should only be done in a special device or with special pliers (Fig. Device for removing and installing piston rings ), ensuring the same bending stress around the circumference of the ring.
After replacing the piston rings, the vehicle speed should not exceed 60 km/h within 1000 km.
Source
Oil pump work
Due to the low engine efficiency and low wear resistance, mechanical tuning of the Niva 4x4 engine is almost mandatory. Such work is called work to change the geometry of the power plant. You should start modifying the power plant by upgrading the carburetor. We do the following:
- We change jets with an indicator of 1 kam to a jet with an indicator of 2 kam;
- Renewing the accelerator pump nozzle.
If there is dirt or carbon deposits in the carburetor, we clean it manually. To do this we need a rag, gasoline and physical strength. If the dirt is very stubborn, a high-pressure cleaner or other device designed for washing the car will help. You can also use special “baths” to remove dried dirt from parts. In this way, the fuel supply to the gas distribution mechanism can be significantly improved.
If you are the owner of an injection Niva, then independently modifying the injector is unacceptable. Only a professional with knowledge of software can perform such tuning of the Niva engine.
Lubricant supplied through the oil pump extends engine life. To improve the performance of the oil pump when tuning the Niva engine, you need to take another pump and cut off part of the housing with the parting plane from it. The thickness of this “pancake” should be about 11 cm. Using milling, cut off the excess and leave a thickness of 10 mm.
Next, do the following to remove chamfers on the edges of the teeth:
- We compress, that is, remove, the drive gears.
- We trim one of the gears by 0.75 mm on each side.
- We cut the second gear to 11.5 mm (after trimming).
- We repeat the operation with the remaining gears (driven).
Let's start working on the body. To do this we do the following:
- We release the driven gear axis from the housing.
- We form a longer axis from the drive roller.
- We insert the resulting axle into the body.
- We press the narrow gear onto the second drive shaft.
- Press on the wide gear.
- We fix the wide driven gear in the housing.
- We install a narrow gear into the housing.
This sequence will prevent the gears from turning relative to each other. You can also improve the oil receiver of the Vase by cutting it a centimeter from the bottom. After this, we adjust the end gap and connect the entire structure with bolts.
Repair dimensions of cylinders and pistons of the VAZ 21213 engine during major repairs
| Repair cylinder size, mm | Piston and cylinder class | Piston diameter, mm | Cylinder diameter after boring, mm | Cylinder diameter after honing, mm |
| 1 repair | ||||
| 82,4 | A | 82,34-82,35 | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 |
| B | 82,35-82,36 | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | |
| C | 82,36-82,37 | 82,39-82,40 | 82,42-82,43 | |
| D | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 | 82,43-82,44 | |
| E | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | 82,44-82,45 | |
| 2 repairs | ||||
| 82,8 | A | 82,74-82,75 | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 |
| B | 82,75-82,76 | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | |
| C | 82,76-82,77 | 82,79-82,80 | 82,82-82,83 | |
| D | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 | 82,83-82,84 | |
| E | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | 82,84-82,85 | |
Refinement of the gas distribution mechanism
After replacing the jets and accelerator pump, you can proceed to the second stage of tuning the VAZ-2121 engine. It includes modification of the gas distribution mechanism (GRM), namely, an increase in the diameter of the valves with their subsequent sealing. Such tuning of the Niva 2121 engine will increase the power of the power plant by almost ten percent.
It makes sense to replace the pusher (with a new one with a diameter of at least 1 mm) during the modification of the Niva engine. Work is being done to increase the pusher wells of the intake and exhaust channels. The result of such modification will be especially good for the Niva 4x4.
Subsequent work concerns the replacement of injectors and the control unit itself. Tuning the VAZ-2121 engine will be incomplete unless the standard crankshaft is replaced with an advanced modification, which will significantly increase the power of the power plant. This is due to the increase in piston stroke. It is also recommended to replace the piston rings with new ones.
Such tuning repairs are capable of:
- increase smoothness;
- reduce wear of parts;
- increase power.
Marking of ZMZ pistons
Another category of car owners interested in piston markings have ZMZ brand motors at their disposal. They are installed on GAZ cars - Volga, Gazelle, Sobol and others. Let's look at the symbols on their bodies.
The designation “406” means that the piston is intended for installation in the ZMZ-406 engine. There are two markings stamped on the piston crown. According to the letter painted on the new block, the piston is matched to the cylinder. When repairing with cylinder boring, the required clearances are made during the process of boring and honing for pre-purchased pistons with the required size.
The Roman numeral on the piston indicates the correct piston pin group. The diameters of the holes in the piston bosses, the connecting rod head, as well as the outer diameters of the piston pin are divided into four groups, marked with paint: I - white, II - green, III - yellow, IV - red. On the fingers, the group number is also marked with paint on the inner surface or on the ends. It must match the group indicated on the piston.
Weaknesses of the VAZ 21213 power unit
- Water pump;
- Engine, manual transmission and transfer case oil seals;
- Generator;
- Starter;
- manual transmission;
- Valve cover gasket;
- Cooling system pipe connections;
- Radiator;
- Thermostat;
- Expansion tank;
- Vacuum brake booster.
The water pump (pump) is characterized by frequent failures on new cars after 2,000 km.
Due to poor quality, oil seals require more frequent replacement than required according to the operating manual.
Specifications
The Niva engine has high technical characteristics, and the car itself has increased cross-country ability, since there is a 4x4 option. Over the history of production, the VAZ 2121 has had different engine versions installed, from a carburetor version to an injector and even a diesel version.
So, let's look at the main characteristics of modifications to the Niva power unit:
VAZ 2121
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.6 liter (1580 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Power | 80 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 12.2 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 79 mm |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 21213
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.7 liter (1690 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Carburetor |
| Power | 82 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 11.0 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 21214
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.6 liter (1580 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Injector |
| Power | 83 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 8.4 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Econorm | EURO-4 |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
VAZ 2131
| Name | Index |
| Engine capacity | 1.8 liter (1779 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 16 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Injector |
| Power | 94 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 9.2 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm |
| Econorm | EURO-4 |
| Valve mechanism | SOHC |
Engine XUD9SD manufactured by Peugeot
| Name | Index |
| Motor type | Diesel |
| Engine capacity | 1.9 liter (1905 cc) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| Fuel | Diesel fuel |
| Power | 75 horsepower |
| Fuel consumption | 7.1 l/100 km |
The power units of the VAZ 2121 were equipped with 4-speed manual and 5-speed manual transmissions.
We increased the compression ratio on the Niva’s native internal combustion engine: how does it drive now and what is the consumption?
The compression ratio of the Niva engine is 9.3 units. This compression ratio is excellent for its operation on AI-92 gasoline. To calculate the compression ratio, take the working volume of the cylinder (piston in the lowest position) + the volume of the combustion chamber (which is the sum of the volume created by the gasket, the volume at the bottom of the piston and the volume of the chamber in the cylinder head). Dividing the sum of volumes by the volume of the combustion chamber we obtain the compression ratio. However, this is a geometric compression ratio, it may differ from the real one and this is due to the filling.
Using the example of an 8-valve Niva engine: the intake valve opens, the piston goes down, the working volume of the cylinder begins to fill with a fuel-air mixture, it is not a fact that during the opening of the valve (with the original camshaft it is definitely not a fact) the mixture will have time to fill the entire working volume.
It is generally accepted that the efficiency of modern gasoline internal combustion engines is about 30%. However, back in 1997, during tests of the production electric car from GM EV1, it was calculated that per 100 km of travel it consumed the amount of electricity contained in 1 liter of gasoline. This is quite possible if we assume that the efficiency of a gasoline internal combustion engine is about 7%.
In general, let's return to the Niva and its 1.7-liter engine. At a certain point, it was time to do a major overhaul on a friend’s car, which it was decided to combine with minor modifications. Actually, the modification consists of increasing the compression ratio, and as a result, increasing engine efficiency.
According to unofficial data, increasing the compression ratio in the range from 8 to 10 allows you to get an increase in efficiency of up to 10%, but from 10 to 14 it’s already 7%, from 14 to 17 it’s already +1%.
To increase the compression ratio, it was decided to follow the road trodden by many - mill the surface of the cylinder head (1.7 mm was removed), replace the original gasket with a thinner one (another -0.7 mm), 0.5 mm was removed from the block. To align the camshaft with the marks, a split gear was purchased, and the chain tensioner was also modified (a small extension was welded on).
According to preliminary calculations, taking into account the boring of the cylinders to the repair size, the geometric compression ratio should be about 11.5 units.
The engine is an injection engine with a January 5.1 ECU; the owner had previously configured it online, but this did not give much effect. After reworking the engine, we again went to real-time firmware. The master reconfigured the ignition timing, slightly changed the mixture settings, since increasing the compression ratio allows you to drive on a leaner mixture without loss of traction and with later ignition angles.
What about gasoline?
After assembly, there was noticeable detonation at 92, so as not to ruin the engine during the trip, the electrician decided to fill it with 98, there were no problems on it. After updating the firmware to the new characteristics, it turned out that you can drive the 92, but the 95 is noticeably more economical and the traction is very pleasant.
Source
Basics of overhaul
Engine overhauls, except for diesel engines, are carried out typically for all models of Lada power units. So, if you do not take into account the 2131 model with a 16-valve engine, then all versions have a timing chain instead of a belt.
Taking into account the design and manufacturer's manuals, the Niva has a low engine life compared to passenger versions of VAZ cars. So, on average, the mileage before major repairs will be 100-120 thousand km.
Therefore, in order not to spend extra money, many vehicle owners try to repair the engine on their own. Considering the weight of the engine, you will naturally need helpers, at least to remove the engine from the car.
So, what manipulations need to be performed to carry out a major overhaul of the power unit.
- Removing the engine from the car. To carry out this operation, you will need to disconnect all auxiliary systems and components.
- Disassembly and diagnostics of the motor. At this stage, the head, pan and valve cover are separated from the cylinder block. Also, you will have to remove the piston mechanism and crankshaft. Don't forget about disassembling the cylinder head.
- Next comes the process of boring the cylinder block, which is carried out on a special boring and honing wall. Also, the surface of the block is often polished.
The size of the piston group for VAZ 2121 engines with a standard piston size of 82 mm:
| Repair | Size |
| Standard | 82.0 mm |
| 1 | 82.5 mm |
| 2 | 83.0 mm |
| 3 | 83.5 mm |
| 4 or more | Block sleeve (installation of sleeves of standard size 82.0 mm) |
- Next, you need to grind the crankshaft to the appropriate size. Also, at this stage, the liners, both main and connecting rod, are tried on.
Chevrolet Niva is a wonderful SUV with universal functions
If you want to buy a car for traveling, not only off-road, but also on asphalt, it is best to choose a Chevrolet Niva. This car is equipped with a fairly modern design, as well as technology that makes driving on a normal road quite comfortable. Undoubtedly, in relation to all of the above, you can find a huge number of disadvantages, however, it is worth taking into account the cost of the car, as well as making a discount on domestic production. In this simple way, these same disadvantages can simply be written off.
Most Chevrolet Niva owners chose this car because they were pleasantly surprised by its appearance. Indeed, the interior of this car inspires confidence and amazes with its spaciousness literally at first sight. In this regard, only at the acquaintance stage the car leaves a good impression and invites further inspection, as well as purchase.
- The Chevrolet Niva engine was taken from the good old Niva and produces 1.7 liters, with 80 horsepower. However, some manipulations were made to it, as a result of which the engine became more modified;
- The engine loves to be revved up. This state of affairs was achieved due to good torque;
- Fuel consumption, in comparison with other SUVs, is quite high and reaches 14 liters during city driving. Nevertheless, the car feels quite confident in an urban environment;
- The Chevrolet Niva has such necessary SUV functions as permanent all-wheel drive, forced locking of the transfer case, and a locking differential;
- there is an independent suspension in front and a dependent suspension in the rear;
- When driving off-road, the car handles confidently.
All of the above features of the car make it comfortable for any ride. Therefore, if you need a car for driving not only off-road, but also for long trips on the highway, you can safely purchase a Chevrolet Niva. This car model has quite a wide range of capabilities for a comfortable, and most importantly, safe ride. True, the concept of “comfort” here is very relative, used only for comparison with other domestic SUVs.
Engine tuning
Tuning a VAZ 2121 engine is an art. Since the car has the characteristics of an SUV, the engine is tuned accordingly. The air filter duct is installed as high as possible, and the motor from below is protected by a special tray, the purpose of which is not to allow water to pass through.
So, the modification of the Niva’s power unit is designed to increase cross-country ability and traction capabilities, since the vehicle is mainly designed for operation on rough terrain. So, many car enthusiasts bore the power unit in such a way as to add not only horsepower, but also traction.
As practice shows, tuning of VAZ 2121 engines and its modifications is carried out by tuning studios that are well versed in which unit needs to be modified.
Also, in the process of refinement, the ignition system and fuel injection are being modernized. For carburetor engines, an additional carburetor can be installed to increase the amount of fuel entering the combustion chamber.
For injection versions of engines, chip tuning is carried out, which can be aimed at increasing power or the balance between consumption and traction capabilities. Many car enthusiasts install additional sensors that help control the operation of the power unit.
Maintenance
For normal operation, engine 21213 should be serviced within the specified periods:
- 10,000 km - change the oil along with the filter;
- 20,000 km – checking the functionality of the thermostat, updating the cabin filter;
- 30,000 km – replacement of the fuel and air filters;
- 60,000 km – spark plugs and batteries are renewed and the crankcase ventilation is cleaned;
- 100,000 km – reinstallation of the oxygen sensor;
- 200,000 km - the timing chain may need to be replaced.
Despite the fact that the internal combustion engine device is copied from longitudinal engines with a much higher service life, it is used on an SUV with non-disconnectable all-wheel drive, so the components wear out more intensively.
Also interesting: Dynamic vibration damper @ Niva 4×4