19.07.2019
| (No votes) |
Issues discussed in the material:
- How the rear suspension works
- What types of rear suspensions are there?
- What are the typical rear suspension problems?
- How to understand that your car's rear suspension needs repairs
- How to repair rear suspension
A car suspension is not only needed to ensure comfort while driving, but also affects the handling of the car. It is very important to perform timely maintenance and repair of your vehicle's rear suspension. The suspension of the front axle of the car is no less important. Every driver should know the structure of a car suspension, especially those components that most often fail.
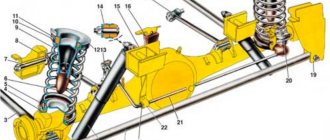
Car rear suspension device
The vast majority of cars today are equipped with multi-link independent rear suspension. The rear wheels in this configuration are independent of each other. This made it possible to reduce the risk of lateral skidding and generally increase the stability of the car.
The rear suspension consists of the following parts:
- trailing arms of each wheel;
- wishbones (2 for each hub);
- anti-roll bar;
- stabilizer supports;
- shock absorber
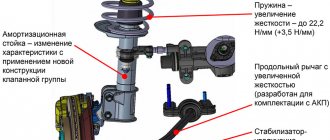
Most often, suspension repair means replacing shock absorbers. The operation must be performed in pairs, that is, on the left and right wheels at once. This requirement is due to the fact that during manipulations the center of gravity of the body cannot be allowed to shift. When replacing only one shock absorber, the body may skew to one side, which will entail a shift in the vehicle's center of gravity. The rear axle of a car usually experiences less load while driving than the front axle. Therefore, the rear suspension shock absorbers are changed less frequently than the front ones.
There are three main types of car rear suspension designs. The suspension can be based on springs, springs with shock absorbers, or an air shock absorber.
After replacing the rear shock absorbers, the air suspension must be adjusted. This cannot be done in a garage; special equipment is required.
The second most common type of suspension repair is replacing stabilizer bushings.
The stabilizer coordinates the operation of the rear wheel levers. In addition, thanks to the stabilizer, the car is more stable when driving on uneven roads. You can change the stabilizer struts of the rear arms yourself; no special tools or much experience are required. The work will take 1-2 hours, provided that the support nuts have not soured. If they are rusty, it will take some more time to unscrew them.
The levers are attached to the body and hub using silent blocks. These are metal bushings with a rubber or polyurethane gasket. Thanks to this layer, suspension shocks are compensated. However, road conditions - moisture, reagents, temperature fluctuations - have a destructive effect on silent blocks. After some time of operation, silent blocks can no longer cope with shock compensation.
The work of replacing a silent block is quite labor-intensive and difficult for an unqualified mechanic. Therefore, it is better to leave this operation to professionals.
What happens if you use faulty silent blocks? Worn bushings can cause a number of defects, including violation of wheel alignment angles, uneven tire wear and deterioration of vehicle handling. Ignoring the malfunction for a long time will lead to wear in the levers. If the situation escalates to such a phenomenon, then you will have to change the entire rear lever assembly.
We recommend
“Diagnostics of car suspension on a vibration stand: trust, but verify!” More details
What is it for?
An important part of the chassis - the rear suspension - levels out road irregularities, creates a smooth ride, increasing the comfort for the driver and passengers when traveling.
The design also implements a number of other functions:
- physically forms the connection between the wheel (unsprung mass) and the frame or body (sprung mass);
- resists skidding and rollover of the car when cornering;
- additionally participates in inhibition.
By performing the above tasks, the rear suspension contributes to better vehicle cross-country ability.
Types of car rear suspension
Depending on the suspension design, characteristic faults and methods for eliminating them are identified. Let us list the main types of rear suspensions of passenger cars.
1. Dependent
The wheels of one axle are connected to each other. That is, the movement of one wheel causes the movement of the other. An example is a suspension with coil springs serving as elastic elements. For example, the rear suspension of the Zhiguli has this design. The rear axle beam is attached to the springs. In addition to the springs, the beam is held in place by four trailing arms. Better handling is achieved by installing transverse torque rod, which also reduces body roll when cornering and increases the smoothness of the vehicle.
The main disadvantage of such a suspension is its heavy weight. If the rear axle is a drive axle, then the mass increases even more. After all, the transmission housing is also attached to the beam. As a result, the unsprung mass increases, affecting the appearance of vibrations and a deterioration in the smoothness of movement.
2. De Dion type suspension
Automotive designers in many countries have sought to reduce the weight of the rear axle. The result of these aspirations was the De Dion pendant, named after its French creator, Albert De Dion. Its fundamental difference is that the main gear housing is separated from the bridge beam. The crankcase is attached to the car body.
To transmit torque from the engine to the wheels, axle shafts are used that are attached to the angular velocity joints. This design is used in both dependent and independent suspensions. For example, the front suspensions of all-wheel drive vehicles are often of the De Dion type.
No matter how hard engineers try to improve the design of the dependent rear suspension, their most important characteristic disadvantage remains - starting and braking the car causes negative phenomena in the suspension. During acceleration, the car “squats”, and when braking, the nose of the car “pecks”. To improve the smoothness of acceleration and braking, additional guides are added to the suspension design.
3. Semi-independent rear suspension
The suspension is based on two trailing arms connected in the middle. This design is installed only on the rear axle of the car. Semi-independent suspension is widely used in front-wheel drive cars. The design has a number of advantages: simple installation, lightness and compact size, which together reduce the unsprung weight. As a result, when using a semi-independent rear suspension, the wheel kinematics are most optimal. The only drawback of this type of suspension is that it can only be installed on the rear axle, if it is not a drive axle.
If the shock absorber and spring are mounted separately, then the spring can be replaced with a pneumatic element. In this case, the ground clearance can be adjusted using spacers of the required thickness.
If the spring and shock absorber are assembled into one block, as on the front strut of a car, then the pneumatic element is mounted directly on the shock absorber rod.
4. Double lever
The double wishbone suspension has two levers in its design, as the name implies. The upper lever is short, the lower one is long. The use of this design allows minimizing the lateral movements of the wheel, which lead to accelerated tire wear and reduce the lateral stability of the vehicle. When the wheel moves up and down, the double wishbone suspension allows only slight angular inclinations.
The wishbone is designed in such a way that each wheel reacts to road irregularities independently, while remaining in an upright position. The practical benefit of such an engineering solution is good grip on the road surface.
5. McPherson
The suspension was designed by engineer Earl McPherson in 1960. The main structural elements are a lever, a stabilizer bar and a shock absorber unit with a spring. The suspension uses telescopic shock absorbers of the “swinging candle” type. This name appeared because the shock absorber is attached to the body using a hinge, and swings while the wheel moves vertically.
The MacPherson suspension is inferior in kinematic terms to the two-lever design. This manifests itself in the deviation of the wheel angle from the vertical during suspension operation. However, thanks to cheaper and more technologically advanced production, MacPherson suspension is often installed in modern cars.
6. Multi-link
A multi-link suspension is, in fact, an improved version of a double-wishbone, with all the inherent advantages. The increase in the number of levers and other design elements led to an increase in cost. Design complexity has increased.
However, the advantages of the design are very significant - this is the smooth ride of the car and good handling. Silent blocks and ball joints used in the suspension perfectly compensate for impacts when driving over obstacles. The multi-link suspension is quite quiet, since the silent blocks, through which the arms are attached to the subframe, reduce noise from the wheels.
The outstanding driving characteristics of the multi-link suspension have earned it a place in business class cars. The use of this suspension gives the car a smooth ride and precise control when maneuvering and driving through any obstacles.
The main advantages of a multi-link suspension:
- wheels work independently of each other;
- low unsprung weight;
- adjustments in the longitudinal and transverse directions are carried out independently;
- good steering;
- Great for 4WD vehicles.
Two significant disadvantages of multi-link suspension are price and cost. Previously, it was used only in expensive cars. But recently, even some budget cars have rear multi-link suspension.
The pneumatic element on the suspensions described earlier is installed in approximately the same way, sliding onto the shock absorber rod. The use of seals ensures the tightness of the structure. The attachment of the pneumatic element to the rack is also protected from moisture.
We recommend
“How to remove the front suspension arm of a car” Read more
MacPherson struts
Many people know this type as a “swinging candle.” The main difference is the presence of a shock-absorbing strut, which performs several functions at once. In this case, all functions are performed simultaneously. The design involves:
- shock absorber;
- spring.
The element is attached to the wheel hub from below, and to the body from above. In the second case, additional supports are also used. Thanks to this type of fastening, it is possible to ensure reliable fixation of the wheel with the body when rocking. There is also a guiding system. Its role is played by levers having a transverse direction.
The stand is the most popular and in demand type. Its purpose is to ensure comfortable movement on the road. The suspension is valued for its reliability and durability.
Common car rear suspension problems
All automakers today strive to make the suspension of their cars as comfortable and reliable as possible. Moreover, cars produced for the Russian market are equipped with a reinforced suspension option. This strengthening is achieved by increasing the ground clearance and using stiffer springs. But operation on domestic roads sooner or later causes malfunctions even in the reinforced chassis, which puts the car owner in front of the need for repairs.
We list the main problems that arise in the suspension design:
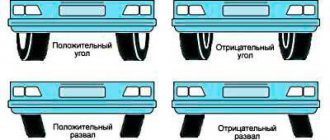
- violation of wheel alignment (wheel alignment angles);
- deformation of suspension arms;
- weakening or destruction of springs;
- various damage to the shock absorber;
- wear of the shock absorber support;
- bushing wear or damage to the anti-roll bar;
- Damage to rubber-metal or ball suspension mounting elements.
The main reason for suspension wear is the poor quality of roads. However, there are other factors that affect the durability of chassis parts. For example, driving style and skill, especially when driving over bumps. The qualifications of car service technicians servicing suspensions are important. And also a lot depends on the quality of the components used during repairs.
Suspension problems occur either gradually or all at once. This happens when driving over bumps and obstacles. Ignoring some faults may lead to the failure of other parts, since everything in the suspension is interconnected.
The car owner can understand from indirect signs that problems are starting in the suspension. Let's list these signs:
- the car does not keep the road (trying to go to the side);
- turning and braking are accompanied by rocking of the car body;
- the movement of the car is accompanied by vibration;
- suspension knocks while driving;
- “breakdowns” or increased rigidity when driving over uneven surfaces;
- tires wear quickly or unevenly.
However, you should know that similar symptoms are also typical for steering problems. Therefore, it is possible to specifically determine which component of the car needs repair only after a thorough inspection and check of all suspension elements.
The above symptoms may not be caused by malfunctions in the suspension, but by violations of the nominal operating parameters of the wheels. For example, with underinflated tires, the car may not hold the road and veer to the side. Vibration is also caused by insufficient air pressure in the tires. If the wheel is not balanced, then beating and knocking in the suspension is expected when driving. Therefore, when diagnosing the condition of the suspension, first of all, versions associated with a discrepancy in the operating parameters of the wheels are excluded.
Some motorists ignore faults and drive a car with a faulty suspension. But it is strictly not recommended to do this, since any malfunction in the chassis can cause an accident.
We systematize in the table suspension malfunctions and the signs that indicate them:
| Signs | Malfunctions |
| Pull to the side when driving | Front wheel alignment violation; violation of the geometry of the suspension arms; loss of spring stiffness; damage to the upper shock absorber support; failure of the anti-roll bar. |
| Rocking when turning and braking | Poor quality shock absorber; deterioration of bushings or breakdown of the anti-roll bar. |
| Vibration while moving | violation of the angle of installation of the front wheels; the shock absorber has lost its characteristics. |
| Knock when driving | Spring breakage; shock absorber malfunction; Rubber-metal or ball suspension elements require replacement |
| "Breakdown" of the suspension | Deformation of the suspension arm; reduction in spring stiffness; shock absorber malfunction; Rubber-metal or ball suspension elements require replacement. |
| Uneven or increased tire wear | Violation of the alignment angle of the front wheels; deformation of the suspension arm; Rubber-metal or ball suspension elements require replacement |
Principle of operation
The operation of a car's suspension is based on the conversion of the impact energy arising from a wheel hitting an uneven road surface into the movement of elastic elements (for example, springs). In turn, the rigidity of the movement of elastic elements is controlled, accompanied and softened by the action of damping devices (for example, shock absorbers). As a result, thanks to the suspension, the impact force that is transmitted to the car body is reduced. This ensures smooth running. The best way to see the system in action is to use a video that clearly demonstrates all the elements of a car's suspension and how they interact. Cars have suspensions of varying stiffness. The stiffer the suspension, the more informative and efficient the car control. However, this seriously compromises comfort. And, on the contrary, the soft suspension is designed in such a way that it provides ease of use and sacrifices controllability (which cannot be allowed). That is why car manufacturers are striving to find their best option - a combination of safety and comfort.
Checking the condition of the vehicle's rear suspension
To extend the life of your car's rear suspension, you need to follow certain rules. Every 20 thousand kilometers it is necessary to inspect the suspension. It is recommended to carry out an extraordinary check every time after hitting a large obstacle or falling into a hole.
Detailed instructions have been developed to help the car owner independently diagnose the condition of the suspension:
- Raise the rear of the car using a lift or jacks. Then, while rotating the rear wheel by hand, listen to see if it makes any extraneous sounds when rotating. See how easily the wheel rotates.
- Using pressure from below and above, swing the wheel vertically. Listen carefully to see if the movement of the wheel is accompanied by a knock, or if there are any backlashes. If these phenomena are present, it is necessary to repeat the operation with the brake pedal held down. You'll need an assistant here. If the knocking stops, it is highly likely that the problem is the wheel bearing. Otherwise, you need to continue diagnostics.
- Insert a screwdriver between the steering knuckle and the lever. The presence of play indicates the need to replace the ball joint. If only the cover is damaged, you can get by by replacing it.
- Using a screwdriver or small pry bar, move the eye by inserting the tool between the lever and the subframe. If it moves easily, the silent block of the lever has exhausted its service life and needs to be replaced.
- Moving the ball joints, assess the presence of play. If play is detected, the ball joint struts must be replaced. Inspect the covers of the ball joints and steering gear. There should be no cracks or other damage. Inspect the shock absorber for oil leaks. Leaks indicate the need to replace the shock absorber. Inspect the bushings, springs and motion buffer.
We recommend
“Checking current leakage in a car: step-by-step instructions” Read more
Screw
Helical suspension is a general name for several types of suspensions, the design of which provides the ability to regulate the degree of spring pretension. The advantages of this design are:
- ease of maintenance;
- strength;
- durability;
- good job for Russia.
She is tough and almost indestructible. If it breaks, you can fix it yourself. At the same time, manufacturers recommend inspecting the structure as often as possible. To avoid frequent breakdowns, you can lubricate the surface of screw-shaped shock absorbers with a special lubricant.
DIY car rear and front suspension repair
It is quite possible to repair the rear suspension yourself. The process is quite labor-intensive, but does not require special skills and knowledge.
You just need to acquire the following tools:
- jacks;
- lift or pit;
- set of hexagons;
- open-end wrenches and sockets;
- hammer;
- puller;
- spring ties;
- penetrating lubricant type VD-40;
- Litol lubricant;
- grinder - in some cases you can’t do without it.
With this set of tools, you can safely begin repairing the rear suspension yourself.
The front wheels of passenger cars are usually equipped with independent suspension. Comfort of movement in this case is excellent, because each wheel is securely connected to the road.
But the rear suspension is dependent, the wheels are connected by a beam. That is, the vibrations of one wheel are transmitted to the other, reducing its grip on the road surface.
You can determine the serviceability of shock absorbers and springs by pressing and releasing a corner of the car body. A working shock absorber should return the body to its original position without vibration. If vibrations occur, the shock absorber, spring, upper and lower strut mounts must be carefully inspected. Visually assess the geometry of the rear wheels. If their angles are not the same or the wheels are located at different heights from the body, this indicates a defect in the beam that needs to be replaced.
Driving on a bad road with potholes is accompanied by a knocking sound in the suspension.
Knocks appear due to wear and aging of silent blocks. The result of destructive processes is the appearance of gaps in silent blocks, play of the beam and lever relative to each other. If the movement of the car is accompanied by an unusual hum in the wheel, you need to check the wheel bearing play.
We will describe the procedure for replacing the rear shock absorber. Beforehand, a few hours before work, it’s a good idea to treat all bolted joints with VD-40 lubricant. If the shock absorber is located inside a spring, to replace it you need to compress the spring. This is done using a spring tie. Unscrew the shock absorber fastening to the suspension. If the nuts are stuck, use key amplifiers or heating the bolted joints. After unscrewing the nuts, remove the bolts from the eyes and remove the faulty shock absorber.
Installing a new shock absorber is done in the reverse order. To align the lower shock absorber mount with the eye in the suspension, you need to lift the car with a jack. All nuts must be tightened with a torque wrench, observing the tightening torque given in the vehicle's operating manual.
We recommend
“A dent on the threshold of a car is not a death sentence, but only an annoying nuisance” Read more
Independent
The difference between this suspension and others, as you might guess, is the lack of connection between the wheels, which are on the same axis and located parallel to each other. This way, if for some reason the position of one wheel changes, it will not be reflected in the other.
They are divided into several types, and each of them deserves special attention.
Car beam replacement
It is necessary to raise the rear of the car, securely blocking the front wheels. Then remove the rear wheels. Disconnect the shock absorbers and springs from the beam. Release the beam from the hand brake cable. The brake system lines are also partially disassembled, disconnecting them from the hose tip. At this point, brake fluid may begin to leak from the system. To prevent this undesirable phenomenon, you need to plug the brake hoses using any available means. For example, brake bleeder caps work well.
Next, unscrew the bolted connections securing the beam to the body and dismantle the beam. Installation of the new part is carried out in the reverse order. The only caveat is that after lowering the car onto the wheels, you must once again tighten the bolted joints securing the beam to the car body.
Purpose and design
A vehicle's suspension performs several functions. Basic:
- ensuring elastic fastening of the wheel to the body
- vibration damping
- ensuring contact between the wheel and the road surface
It was invented at the same time as cars. She is as old as the first car released from production. At the same time, it has still not been possible to create an optimal suspension that would suit any car.
Despite the varieties, the products are similar to each other in their components. The design contains:
- Elastic elements - leaf springs, springs, etc. Their main task is to absorb the loads received when the wheel hits the chassis.
- Damping elements or shock absorbers. They dampen vibrations received from elastic elements through absorption and dissipation of vibration waves. That’s why they are usually installed next to elastic elements.
- Guiding systems. Designed to connect the wheel with the supporting part, which ensures the ability of the machine to move along the desired trajectory. This group includes levers, rods, beams.
All components perform a number of specific functions, and even without one element it does not constitute a single structure.