What is the camshaft sensor responsible for and how to check it yourself
The camshaft position sensor (CPS) is used to determine the angular positions of the timing belt in relation to the position of the crankshaft. Signals from this sensor are sent to the engine ECU, which corrects fuel injection and ignition. The DPRV also works in conjunction with the crankshaft speed sensor.
Failures in the operation of the sensor on gasoline units, which manifest themselves in the absence of an impulse to the control unit, often do not allow the car engine to start. In diesel engines, starting can be difficult, but possible. The diesel engine will run and even restart after stopping, since the ECU receives pulses in parallel from the crankshaft speed sensor.
Read in this article
Purpose of the camshaft position sensor
The basis of the sensor for determining the position of the camshaft is the Hall effect. For this reason, the DPRV is also called a Hall sensor. The magnetic field in such a sensor changes at the moment when the magnetic gap closes.
The specified gap is closed using a special steel tooth. Such a tooth (reference point) can be located on the camshaft gear. Another location for this element is the drive disk, which is mounted on the shaft.
When a tooth passes near the camshaft position sensor, voltage appears in the sensor and a signal is generated. The specified signal is sent to the ECU.
This position means that the piston is at TDC (top dead center at the end of the compression stroke). This solution allows for timely fuel injection and subsequent formation of a spark by the spark plug to ignite the working mixture.
Engines with a variable valve timing system can be equipped with Hall sensors on both the intake and exhaust camshafts. In this case, the DPRV controls the specified system.
The main signs by which you can determine problems with the DPKV crankshaft position sensor. Causes of failures, breakdowns, self-check.
How the device works
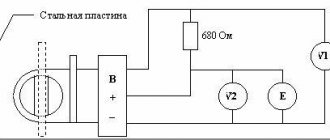
Electrical diagram of the sensor location
The operation of the crankshaft location sensor is based on an effect discovered by the American physicist Edwin Herbert Hall. The device monitors the slightest changes in the strength of the magnetic field induced by a piston magnet installed in the device body. Metal notches (teeth), which are located on the camshaft wheel or on the drive shaft disk, change the strength of the magnetic flux, which is fixed by a semiconductor element.
The camshaft sensor transmits electronic commands to the vehicle's control unit. Based on the data received, the control system accurately calculates the exact angular position of the cylinder piston. Thanks to the accuracy of this process, the gas distribution mechanism of the vehicle operates in optimal mode, effectively supplying the cylinders with an air-fuel mixture and carrying out the timely removal of exhaust gas.
Causes of breakdowns and frequency of regulator replacement:
The camshaft sensor is equipped with a semiconductor chip, the service life of which is reduced when overheated. Due to the fact that the sensor is located on the valve cover, the chip is exposed to increased temperature, which can cause sensor failure.
Over time, the mounting tabs can break, causing the sensor to become dislodged.
Short circuit of the semiconductor chip.
Broken toothed disc, etc.
There are reasons why a sensor can fail at the wrong time.
To ensure that the problem does not take you by surprise, you should practice periodic replacement of the sensor at least once every five years, or after the car has driven 100 thousand. km.
Replacement must be carried out even with smooth and stable engine operation. If the engine stalls for no apparent reason or problems appear with the ignition system, installing a new camshaft sensor is a top priority.
Camshaft sensor on a diesel engine
How to check the camshaft sensor! 2 ways
1st way to check with a multimeter. 2nd way to check with a metal object.
Camshaft sensor. Lifehack. How to check it yourself?!
Nissan camshaft sensor error
primera p12.
On a diesel engine, the camshaft position sensor works differently compared to its gasoline counterpart. Pulses from the sensor record the position of the piston at TDC not in the 1st cylinder, but in all. This solution makes it possible to achieve the most accurate determination of the position of the camshaft in relation to the crankshaft. In a diesel engine, the DPRV is responsible for the starting efficiency and stability of the power unit of this type in different operating modes.
In a diesel engine, certain design changes are present on the master disk. The teeth on this element are made for each cylinder of the internal combustion engine and are installed at a certain distance. As an example, consider a diesel engine that has 4 cylinders. In such a motor, the drive disk has 7 teeth (4 main teeth, located at an angle of 90 degrees relative to each other). There are also an additional 3 teeth to help identify the cylinders individually. These teeth are located at a certain distance from the main ones in order to accurately determine the position of the piston in each individual cylinder.
Why do you need a DPRV in a car?
To save the situation in the first types of engines, the stroke was determined by indirect signs.
When starting the internal combustion engine, the ignition pulse and the signal to open the injectors were sent regardless of the specific stroke. The spark during the exhaust did not interfere with anything, and the injection took place on a closed intake valve. And only then, using the signals from the crankshaft position sensor (CPS), the computer calculated the derivative of its rotation speed, thus assessing whether an attempt to ignite the mixture was made at the right moment.
If the ECU guessed correctly, and this was determined by the presence of positive angular acceleration of the shaft, then a synchronization sign was entered into the corresponding memory cell, and then injection and spark were carried out only at the right time.
Although many engines managed without these difficulties, two sparks and two injector openings in four strokes of one cylinder did not cause any significant deterioration in engine performance. It was only necessary to divide by two the amount of fuel supplied per cycle and monitor the ability of the ignition module to operate at double the frequency.
But as the requirements for engines became more stringent, every little detail had to be taken into account. It is uneconomical to store untimely injected fuel in the intake manifold until the valve opens, some of it will condense, and there is also no need to increase the power of the ignition system to form a useless spark at the exhaust.
The camshaft sensor (DPRV) solved the problem. This is a device that signals that the shaft is in a certain position, which accurately indicates the current phase of its operation. For example, the top dead center (TDC) of the compression stroke of the first cylinder, the position can be any, the ECU will find the necessary information using a calculation method.
The signal can also be of any type, the main thing is its phasing with the valves, and therefore with the camshaft:
- a logical level in the form of a certain voltage at the output of the sensor at the moment when the piston has entered the compression TDC, usually this coincides with a missing tooth on the reference setter of the crankshaft sensor, but only for the first cylinder, when there is a gap, but this is the exhaust TDC - the sensor does not produce a signal ;
- double impulse for TDC of the first cylinder, single - for all others;
- the number of pulses corresponding to the number of the active cylinder.
Formally, these are different signals, but since the ECU knows how to decode them, it will receive the same information.
A synchronizing software mark is generated, from which the processor with the required time sampling step can count any interval and accurately issue pulses that control the injectors and ignition drivers.
Such an injection is called phased, in contrast to the pairwise-parallel injection, which was considered earlier in the absence of the DPRV.
Where is the sensor located
Typically the sensor is located on the cylinder head next to the camshaft drive sprocket. Another option is also possible, then a separate reference disk is attached to the opposite end of the shaft.
There is a small gap between the disk with a magnetic mark on it and the sensitive element of the sensor, through which the magnetic field is easily captured.
Self check
A common malfunction of an internal combustion engine with electronic injection is a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor. The list of signs indicating problems with the sensor includes:
- difficult starting;
- unstable engine operation;
- the engine shakes and runs intermittently;
- “check” light may light up on the instrument panel;
- The first step is to locate the DPRV mounting socket, which is installed in the cylinder head area. You must find a special O-ring at the installation site. This ring must be inspected, since damage to its integrity and other deformations can lead to sensor malfunctions.
- Additionally, you will need to inspect the sensor housing itself, as well as the gear rotor. The presence of damage or the presence of metal shavings also indicates a sensor failure.
- Next you need to examine the connector itself. Such a connector must have contacts: positive contact, negative ground, contact for signal transmission.
- Then you need to turn on the ignition, after which a voltmeter is used to measure the voltage at the positive contact of the camshaft position sensor. The tester ground must be connected to the engine ground. This voltage measurement should be similar to the voltage at the battery terminals. If there are deviations in the voltage readings compared to the power supply, we can conclude that there is a malfunction in the electrical power supply circuit of the camshaft position sensor.
- The voltage at the sensor ground is measured in a similar way. The voltage at the specified contact should be zero.
- Then you need to connect the positive and negative wires of the sensor. The middle contact of the sensor is connected through the tester. It turns out that one voltmeter probe is applied to the signal terminal of the sensor, and the other is powered to the input of the control system. To solve this problem, it is not uncommon for the signal wire to be cut and the multimeter probe to be applied to the exposed wires.
- The engine is then cranked by the starter. The working sensor will show voltage, which can range from 0.4 to 5 volts. Deviations from the specified values indicate the need to replace the DPRV.
How to determine a malfunction of the DPRV
An unexpected increase in fuel consumption, a drop in engine power, unstable engine operation are indications for checking the DPRV. These symptoms do not necessarily appear due to a malfunction of the sensor, but the check must begin with it. If the check engine light comes on on the instrument panel, determine the meaning of the error code using the vehicle's operating instructions. If the error code indicates a malfunction of the DPRV, it is necessary to check not only the sensor itself, but also the electrical wires that go to it. Indeed, often the cause of sensor malfunction is oxidized contacts of the terminal block. After cleaning them, the engine starts working normally. The operation of the sensor is also affected by the condition of the camshaft gear or reference point. Therefore, when replacing or servicing the sensor, it is advisable to check the condition of the reference point and signal disk. If the disk is bent, it must be replaced.
To check the serviceability of the DPRV you will need:
- digital multimeter (tester);
- thin flat screwdriver;
- wrench for the sensor mounting bolt;
- clean rag;
- needle.
First, remove the terminal block from the sensor and inspect the contacts. If they are dirty, you need to clean them or install a new pad. Insert the needle into the terminal block so that it touches the middle pin. Snap the block into place, attach the tester probe to it and bring a thin screwdriver to the working plane (it is located parallel to the camshaft disk or gear) of the sensor. The voltmeter reading should change from zero to 5 volts or more. If the readings have not changed, wipe the working surface of the sensor with a rag - there may be a lot of metal dust stuck to it, and repeat the test. If that still doesn't work, the sensor is faulty. If it is difficult to check the DPRV installed on the engine, unscrew the mounting bolt and remove the sensor. Then check.
Replacing the camshaft sensor
If checking the camshaft
showed its malfunction, then it’s time to replace it. The procedure is no more complicated than checking, if the gap calibration is not required. How to check visually with a tester and the desired ignition coil. How. In this case, the faulty element is removed and a new one is installed.
Things get more complicated if you need to adjust the gap. This is done using an oscilloscope. And you should immediately warn that for the first time such manipulation cannot be carried out independently; experience is needed or it is better to turn to specialists.
Faced with this problem, in the future the questions will no longer sound so scary - how to check the camshaft sensor
and who to contact? This can be done independently at home (garage). How to check and replace the camshaft sensor. Good luck on the roads and of course no breakdowns.
1200 rub. for the photo report
We pay for photo reports on car repairs. Earnings from 10,000 rubles/month.
Write:
Checking the camshaft sensor (DPRV) allows you not only to verify its functionality, but also to make sure that in engines with phased (sequential) injection, fuel is supplied in exactly the required sequence. Another name for the device is a phase sensor (it is often used by owners of domestic VAZs). The test can be performed using a multimeter in voltmeter mode and/or an oscilloscope. Checking the camshaft position sensor is simple in nature, and even a novice car enthusiast can handle it.
Troubleshooting
A sensor that is in doubt is definitely replaced with a new one. It is inexpensive, and even preventive replacement is recommended every five years to increase reliability. But at the same time, it is necessary to check the condition of the reference element. Distortions of geometry, chips, dirt and chips are unacceptable there.
All gaps and relative positions of parts must be standard. During repairs, this is not always observed, which can cause difficult-to-diagnose problems in the future.
It is worth paying attention to the condition of the wiring. Particularly affected by oxidation are the contacts of connectors, ground wires and places where wires are inserted into lugs. If there are traces of copper oxides there, the wiring must be sorted out and soldered, and oxidized and weakened connectors must be replaced.
What is a camshaft sensor
Before moving on to the question of checking the camshaft position sensor, you need to find out what kind of device it is, what it is needed for and on what principle it works. This will help clarify the details of the audit in the future.
A camshaft sensor is a device that records the angular position of a specified shaft at a specific point in time. The information obtained with its help is transmitted to the electronic engine control unit (ECU), and on its basis this control element issues commands for fuel injection and ignition of the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder at a specific point in time.
Signs of DPRV failure
There are several typical signs that indicate that the camshaft position sensor has failed. It is immediately necessary to clarify that the symptoms listed below may indicate completely different malfunctions. Therefore, it makes sense to perform additional diagnostics. So, signs of a DPRV breakdown:
- Problems with starting the engine, under any conditions - “cold”, “hot” and in other modes. This usually results in having to crank the starter longer.
- Unstable engine operation, “floating” operating and idle engine speeds.
- “Dips” in the movement of the car; when you press the accelerator pedal, it does not respond immediately, the dynamic characteristics of the car are lost (it accelerates poorly, does not pull, especially when loaded and when moving uphill).
- When the accelerator pedal is released, the engine stalls.
- Increased fuel consumption (by 10...20%).
- The Check Engine warning light on the instrument panel activates. It is necessary to perform additional diagnostics using an electronic scanner (for example, an ELM 327 device or its equivalent). In this case, typical errors regarding the operation of the sensor are numbers P0340, P0342, P0343.
In fact, the camshaft position sensor is a fairly simple and reliable device, so it rarely fails. More often, its wiring is damaged - the wires fray, the insulation on them is damaged, the so-called “chip”, the place where the sensor is connected to the car circuit, fails.
However, for cars that run on gasoline, the problems described above are not so clearly expressed. But a failed camshaft position sensor will cause many problems for owners of cars equipped with gas equipment, in particular the fourth generation. The malfunctions and problems described above can appear on such machines “in all their glory.” Therefore, owners of cars equipped with HBO are strongly recommended to diagnose and replace the sensor as quickly as possible if it is suspected of being faulty.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, provided that there is a phase sensor, it is phased injection that allows you to get maximum power and efficiency from the engine. When the sensor is normal, the motor operates optimally in different modes, under load, etc. This is achieved thanks to the coordinated work of the DPRV and DPKV. In turn, the sensors allow precise control of injection and ignition.
We also recommend reading the article about what a mass air flow sensor is. From this article you will learn about the purpose, principles of operation, as well as signs of malfunctions, methods of diagnosing and repairing an air sensor using the example of a VAZ 2114.
Finally, we note that if the phase sensor fails, replacing the camshaft sensor is often the best solution. The fact is that such sensors are not particularly repairable and it is better to immediately replace the problematic element with a new sensor or a used one that is known to work. Taking into account the relatively affordable cost, it is replacement that allows you to quickly solve the problem and completely restore the performance of the internal combustion engine.
Sources
- https://AutoVogdenie.ru/kak-proverit-datchik-polozheniya-raspredvala.html
- https://DriverTip.ru/repair/proverit-zamenit-datchik-raspredvala-v-avtomobile.html
- https://astra-faq.ru/obslugivanie/kak-proverit-i-zamenit-datchik-raspredvala-v-avtomobile.html
- https://1gai.ru/baza-znaniy/poleznoye/517279-priznaki-neispravnosti-datchika-raspredvala.html
- https://krutigayki.ru/datchik-raspredvala-priznaki-neispravnosti-simptomy-oshibka/
- https://etlib.ru/blog/1003-proverka-datchika-raspredvala
[collapse]
Location of the DPRV on the engine
To check the camshaft position sensor, you need to know where it is located. As a rule, on eight-valve engines the DPRV is usually mounted at the end of the cylinder head. On sixteen-valve engines it is also mounted on the cylinder head, usually in close proximity to the first cylinder.
As for popular domestic VAZ cars, their owners call such units phase sensors. Their location in these motors is similar. So, on eight-valve engines, the sensor is located on the left side of the cylinder head (when viewed in the direction of travel of the car). On sixteen-valve engines - on the right front part of the engine. In the latter case, the sensor is not directly visible visually; its location can only be assessed by the signal and power wires suitable for it. The VAZ 2114 phase sensor is fixed in close proximity to the air filter, near the cylinder head.
Where is the sensor located
The location of the DPRV varies depending on the make of the car. In most cases, you can find it in the following places:
- near the cylinder head;
- near the wiring connectors on the front of the motor;
- near the toothed belt mount;
- on the rear side of the cylinder head;
- special compartment under the hood;
- inside the cylinder head.
First, consult your vehicle's manufacturer's repair manual. This contains all the necessary information.
Methods for checking the camshaft sensor
Before testing the sensor using a multimeter or other electronic tools, you must check its mechanical integrity. In particular, it is installed in a housing with an O-ring, ensuring its secure fastening. We need to check its condition. It would also be useful to check the integrity of the sensor body, whether there are cracks or other damage on it. It is advisable to check the drive disk to see if the teeth are damaged or if there are metal shavings on the sensor body or nearby.
On the Internet you can find information that supposedly the DPRV can be determined to work by simply checking its magnetic properties. In particular, bring a small metal part to its end (the working sensitive part), which should “stick” to the sensor. In fact, this is not the case , and a non-working DPRV may or may not have magnetic properties. Accordingly, verification must be performed using other methods.
Possible causes of malfunction
DPRV is a pulse generator that creates a very weak signal. There is a small chance that the current will gradually weaken the integrity of its winding. However, vibrations caused by magnetism travel through the gear teeth. When the camshaft is turned, the force changes just like the signal generated. These vibrations cause microscopic movements within the DRV, creating weak points in essential parts, especially the winding in the case of inductive type DRV.
With a Hall-type sensor it is a completely different story. This type of DPRV is a solid-state device, that is, its electronic component, such as a diode or transistor. Voltage can damage the sensitive parts of the DPVR. Short circuits and incorrect connections can also damage it. And remember that you need a polarity sensitive power supply.
Replacing the RV position sensor
If during the inspection it turns out that the camshaft position sensor itself has failed, then it must be replaced. As a rule, these units are non-repairable, since their body is sealed and cannot be disassembled. The sensor is inexpensive, and the replacement procedure is simple, and even a novice car enthusiast can handle it.
The sensor replacement algorithm is as follows:
- With the engine not running, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect the “chip” from the camshaft position sensor (as when checking).
- Depending on the vehicle model, it is necessary to remove parts that prevent access to the sensor. For example, on modern cars like the Lada Vesta, it is necessary to remove the bracket for auxiliary units.
- Using a wrench, unscrew one or two mounting bolts, depending on the type of fastening. The size of the wrench can be different, usually for VAZs it is a 10 mm wrench.
- After dismantling the mount, you must similarly remove the sensor from its seat.
- Installing a new sensor is performed in reverse order.
- Connect the negative terminal to the battery.
When purchasing a new camshaft position sensor, you need to pay attention to the condition of its O-ring. It is usually sold separately. When changing the sensor, it is advisable to also change the O-ring, since over time it wears out and loses its elasticity. You can use an old ring only in case of emergency, when it is not possible to buy a new one.
Conclusion
The camshaft position sensor is a simple but important device in the engine, and the normal functioning of the engine depends on its operation. Therefore, when identifying signs of its failure, it is advisable to carry out the appropriate diagnostic procedures as quickly as possible. They are simple, and even a novice car owner with no experience can handle them. The same goes for replacing it. The price of a phase sensor for VAZ cars as of winter 2019 is about 400 rubles.
What leads to malfunctions
Sensors are quite reliable, but, like everything else, they are subject to aging and gradual or instantaneous failure. This manifests itself in engine malfunctions, loss of sparks in individual cylinders, poor engine starting and an understandable increase in fuel consumption.
Typically, engine self-diagnosis notices this, turns on the Check Engine indicator light and switches the engine to parallel-pair injection.
This is interesting: Why valve stem seals wear out and how to replace them
Reading fault codes may indicate problems with the DPRV. But it's completely optional. The program does not always accurately understand the causes of the failure, so more careful diagnostics will be required.