Are you trying to get rid of the P0420 error code? Then this article is for you. The P0420 fault can be difficult to diagnose. You think you have fixed the error, but after 100 km the Check Engine light comes on again.
This code is triggered when the engine control module detects a faulty catalytic converter. It uses one oxygen sensor at the front of the exhaust manifold - before the catalyst, and another oxygen sensor - after the catalytic converter to measure the efficiency of the catalyst.
In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about the P0420 code to fix it once and for all.
What does code P0420 mean?
P0420 is triggered in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) when there is a problem with the performance of the catalytic converter. The controller uses two oxygen sensors - one before and one after the catalyst to measure its efficiency. The error occurs if the converter or oxygen sensor malfunctions, which begins to transmit incorrect data.
We receive many messages asking about the P0420 code. It keeps coming back after several repairs and you just end up spending more and more money on auto repair work. This trouble code may confuse you because there is a lot of misinformation about it.
Catalytic converter
- The front O2 sensor measures the air-fuel mixture. It tells the control unit if the engine is running rich or lean.
- The rear O2 sensor is the diagnostic oxygen sensor for this error code.
If the rear oxygen sensor receives incorrect values, a P0420 fault will be stored in the ECU. This could be due to a faulty catalytic converter or one of the O2 sensors failing. There may also be many other problems with the engine that are destroying the catalytic converter, and if you install a new one, it may be damaged again.
The oxygen sensor is also called a lambda probe.
Many people think that a lean or rich mixture can cause this error code. Yes, it is possible, but not in the way you think. A rich or lean mixture can damage the catalytic converter and when it is damaged/full of fuel it will be low in efficiency and the rear oxygen sensor will see this and trigger a P0420 code.
Symptoms of the error
You probably won't have any symptoms other than the P0420 check engine light coming on. You may experience other engine problems that damage your catalytic converter.
This could include a rough (“rough”) idle, acceleration problems, misfires, or harsh gear changes. Always fix these problems first.
- The Check Engine light is on.
- Misfires.
- Rich mixture.
- Poor mixture.
- Engine oil is burning/gray-blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe.
- Slow acceleration.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0420 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Acura (Acura MDX)
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi a6, Audi q5, Audi q7)
- BMW (BMW X5)
- Chery (Chery Tiggo)
- Cadillac (Cadillac SRX)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Captiva, Cruz, Lanos, Lacetti, Spark, Trailblazer, Epica)
- Chrysler (Chrysler Voyager, Pacifica, PT Cruiser, Sebring, 300c)
- Citroen (Citroen C4, C5, Berlingo, Xara Picasso)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Gentra, Matiz, Nexia)
- Daihatsu
- Dodge (Dodge Caliber, Caravan, Stratus)
- Fiat (Fiat Doblo)
- Ford (Ford Galaxy, Maverick, Mondeo, Fiesta, Focus, Fusion, Explorer, C-Max)
- Geely (Geely MK, Emgrand)
- Honda (Honda Accord, Pilot SRV, Fit, Civic)
- Hover
- Hummer
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Getz, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Elantra, i30, ix35, ix55)
- Infiniti (Infiniti fx35, qx56)
- Jaguar
- Jeep (Jeep Grand Cherokee, Compass, Liberty)
- Kia (Kia Karens, Magentis, Optima, Picanto, Rio, Sid, Sorento, Spectra, Sportage, Cerato)
- Lexus (Lexus gs300, gx470, ls430, lx470, rx300, rx330)
- Lifan (Lifan x60)
- Mazda (Mazda 3, Mazda 6)
- Mercedes (Mercedes w204)
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi Outlander, Lancer)
- Nissan (Nissan Almera, Qashqai, Micra, Murano, Note, Sentra, Patrol, Pathfinder, Primera, Teana, Tiida, X-Trail)
- Opel (Opel Antara, Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Insignia, Corsa, Meriva)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 107, 206, 207, 301, 307, 308, 406, 407, 408, 3008, Partner)
- Pontiac (Pontiac Vibe)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Kangu, Logan, Megan, Sandero, Scenic, Fluence)
- Saab
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Fabia)
- Subaru (Subaru Outback, Impreza, Legacy, Tribeca, Forester)
- Suzuki (Suzuki Grand Vitara, Ignis, Liana, Swift, sx4)
- Toyota (Toyota Avensis, Verso, Camry, Corolla, Land Cruiser, Matrix, Prado, Prius, Rav4, Celica, Highlander, Yaris)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Bora, Golf, Jetta, Caddy, Passat, Polo Sedan, Touareg, Tiguan)
- Volvo (Volvo s40, s60, s80, v40, xc70, xc90)
- Vortex (Vortex Tingo)
- Volga Cyber
- Gazelle Business
- Zaz Chance
- Lada Largus
- UAZ Bukhanka, Patriot, Hunter
You can sometimes encounter other errors with fault code P0420. The most common ones are: P0106, P0131, P0133, P0151, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0300, P0430, P0442, P0455, P0573, P069E.
Causes
The most common cause is the catalytic converter. It may simply be old and worn out. But there are many cases where the neutralizer is new, but at the same time it is a non-original part.
Some cheaper catalytic converters may not be efficient enough, and then you will have to buy an original catalytic converter.
Sometimes converters are installed too far back on the exhaust pipe. This will cause it to not get hot enough and cause a P0420 code.
- Damaged catalytic converter (most common cause).
- Non-original catalyst.
- Incorrect installation (placement) of the catalytic converter.
- Front oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault.
- Rear oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault.
- Exhaust gas leak.
- Leak on the intake manifold.
- Oil burns (damage to catalyst).
- Rich/lean mixture (damage to catalyst).
- Misfires (damage to catalyst).
- Faulty engine control unit (rare).
Causes
Error p0420 can also appear for many reasons. The operating conditions that most negatively affect the performance of the catalyst are:
- Use of low-quality fuel.
- Mechanical damage.
- Operating a car with a faulty ignition system (primarily with constant misfire in the cylinders).
They have a negative impact on the condition of the catalyst and the malfunction of other parts and elements. For example, malfunctions in the operation of this part can be observed if the oxygen sensor, manifold, or muffler are damaged. Burnout of gaskets in the exhaust system also has a negative impact on the performance of the catalytic converter and lowers the response threshold of the sensor that displays error p0420.
Once the causes of catalyst failure have been correctly identified, you can begin to eliminate them.
Trouble-shooting
These are just possible solutions and you should never change parts without proper diagnostics as you could be throwing money away if you are unlucky.
Read the entire article if you want to learn how to properly diagnose this trouble code just like an experienced auto mechanic would. It will take time and may require some skill, but you won't spend $1000 to replace a good catalytic converter.
- Replace the catalytic converter.
- Replace with original catalyst.
- Replace the front oxygen sensor.
- Replace the rear oxygen sensor.
- Repair of faulty electrical wiring.
- Correct oil burning.
- Correct misfire.
- Correct lean/rich mixture.
- Check the data using an OBD2 scanner.
- Replace the engine control unit (rarely).
Error Resolution Table
| Code | Symptoms | Causes | Causes of catalyst damage |
| Error P0420 | Check Engine Misfire Rich mixture Lean mixture Oil burning/blue smoke from exhaust Slow acceleration | Faulty catalyst Front O2 sensor Rear O2 sensor Exhaust leak Oil consumption Misfire/lean mixture destroying catalyst | Misfire Oil consumption Exhaust leaks Intake leaks Rich mixture Lean mixture ECU malfunction |
How severe is the catalyst efficiency error?
With this error, the driver does not experience problems driving a Ford . This code can be ignored. However, if you do not pay attention to this problem, serious damage can be caused to other parts of the car.
If the cause of the error is not corrected promptly, the catalytic converter may be seriously damaged. Since the catalytic converter is an expensive part, it is very important that the cause of the problem be repaired as soon as possible. If the catalyst is destroyed, its remains may enter the engine cylinders, which will result in a major overhaul of the Ford or replacement of the unit.
Causes of damage to the catalytic converter
There are several causes of catalytic converter damage that can trigger the P0420 code. Here are the most common ones.
- Misfires.
- Oil consumption.
- Leaks at the outlet.
- Inlet leaks.
- Rich mixture.
- Poor mixture.
- Malfunction of the ECM/PCM control unit.
There are many reasons that lead to malfunctioning oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. You should make sure to correct these problems before you replace any part. Otherwise, they may be damaged again. Check the controller DTC memory for any other trouble codes.
Fix them first. Make sure your car is not burning oil by checking the exhaust smoke, blue smoke = oil, white = water, gray/black = rich mixture.
How to Diagnose Code P0420
Here is a guide on how a professional auto mechanic will diagnose a trouble code. This guide may require knowledge of vehicle electrical systems, and you may need some tools to complete the task.
But even if you have no idea about car electronics, you can still gain useful information.
You should always connect your car charger when troubleshooting your car. Low battery voltage can cause other unrelated error codes that will confuse you. Low voltage may damage the control unit or other electronics.
Connect the charger
Connect the charger to the battery and make sure it charges the battery correctly.
You should use a charger that provides at least 4 Amps while troubleshooting. A lower charging current may result in the battery being discharged when the ignition is turned on.
Connecting an OBD2 scanner
Connect an OBD2 scanner to read the P0420 code. You can use a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with the Torque program.
3. Check for other fault codes
Check for other errors that may cause damage to the converter or any oxygen sensor errors. If there is an error in the lambda sensor, then replace or check it first, this may also fix the P0420 code.
Correct all other trouble codes before correcting the P0420 code.
Always write down any error code numbers, do not simply erase them.
Check for blue smoke while the engine is running
Increase the engine speed and check for gray-blue smoke from the exhaust pipe. Blue smoke = burning oil. Replacing the catalyst will not help. It will most likely fail again very quickly. Burning oil can also damage the oxygen sensors and cause them to read the mixture incorrectly.
You should always check for white, gray and black smoke. White smoke comes from water in the exhaust pipe, gray/black smoke comes from a rich mixture.
Check for exhaust leaks
Raise the vehicle while it is running. Listen and look for any exhaust leaks in front of the rear lambda probe. An exhaust leak can cause the O2 sensors to receive incorrect data and may trigger a fault.
If you have an exhaust leak behind the rear oxygen sensor, this should not cause an error.
Tips on how to find exhaust leaks:
Test drive
Take the car for a test drive and make sure there are no leaks or other symptoms. Drive fairly vigorously for some time so that the catalytic converter warms up. If skipping or other strange behavior appears, start diagnosing it first.
Drive to the garage and lift the car
Raise the car and keep it idling. Make sure you have proper ventilation. Connect an OBD2 scanner and check the current data from both O2 sensors.
Open the signal graph from oxygen sensors. Start the car engine and make sure that the temperature of the catalytic converter is at least 400 °C. You can use a digital laser thermometer to check the temperature.
Both charts should be open so you can see them.
The front sensor should constantly jump between 0 - 1 Volt, and the rear sensor should show a stable 0.7 - 0.9 Volt. This means everything is working properly.
If the catalytic converter is damaged or not hot enough, the rear lambda probe signal will fluctuate in the same way as the front one.
You can also use a digital multimeter. To do this, you need to check the voltage from the rear O2 sensor. But the signals are high speed and it can be difficult to read such voltages with a multimeter.
Check catalyst temperature
You can also check the temperature on the neutralizer. Make sure it is still hot before checking. Use a digital laser thermometer to measure.
Check the temperature just before, in the middle and after the catalyst. If you get the same temperature at all points when the neutralizer is hot (over 400 C°), then it is most likely empty or damaged.
If the catalytic converter is working correctly, the temperature should be 100-150 C° higher directly behind it than in front of it.
If the temperature in front of the catalyst is much higher, the car may be running rich and the converter is working too hard. This may also be due to the catalytic converter being blocked or having poor exhaust flow.
Video on how to check your catalytic converter using the Torque Pro app:
Summarize your results
Summarize the diagnostic results. If you have no other error codes, the front oxygen sensor signal changes, the catalytic converter temperature is uniform, and you do not see blue smoke, replace the catalytic converter.
Code P0420 can be a problem to diagnose correctly. If you have read this repair guide and received incorrect results, you can replace your catalytic converter with reasonable confidence.
If your diagnostic results look good but you still get a P0420 code, there is a small chance that the catalytic converter is still causing the fault.
In rare cases, you may have a faulty ECM.
If you find any gaps, gray-blue smoke or other problems, correct them and remove the error. With luck, the P0420 code may not return.
OCTAVIA. SOLVING THE PROBLEM WITH THE CATALYST
Want to create a site? Find Free WordPress Themes and plugins. Promotion! When ordering the service of replacing the catalyst with a turnkey flame arrester, a 50% discount on the electronic decoy of the lambda probe is provided.
×Typical symptoms of a malfunction on a Skoda Octavia:
- reduction in engine power (deterioration in acceleration dynamics, decrease in maximum speed) coupled with increased fuel consumption
- Difficulty starting the internal combustion engine (it took longer to start)
- strong toxic odor from the exhaust system
- Extraneous noises are heard from the catalyst (ringing, rattling)
- diagnostics shows with corresponding errors indicating ineffective operation
If there is any suspicion of incorrect operation, come and we will carry out a free diagnosis. If necessary, we will make the necessary repairs.
We offer the most reliable option - replacing the catalyst with a high-quality factory-made flame arrester (see pictures) made of two-layer stainless steel with the installation of a controller for adjusting the readings of a lambda probe (blende) of our own production.
Rice. 1
Rice. 2
Rice. 3
There is a misconception that after removing the catalyst and replacing it with a flame arrester, the Octavia will run louder, no matter what flame arrester is installed.
The latest generation of flame arresters work as quietly as catalysts, and sometimes even quieter if two or three reflective, cooling and noise-absorbing chambers are made inside, and 2-3 types of packing are used to dampen noise, temperature and pressure.
The highest quality stuffing is made of stainless wire and Kevlar: it is not afraid of high temperatures and, due to its strength, is not blown out. It absorbs noise three times better than basalt (the most common). Products with such packing cool exhaust gases better than their counterparts, and last 10 times longer.
Comment. We do not replace universal catalysts for Skoda Octavia due to their unsuitability for our gasoline, coupled with low quality workmanship by manufacturers for the sake of low prices (mainly China).
All of the above operations are performed for all generations of the model and versions intended for any country:
II: 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2.0
I: 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2.0
and subsequent ones (unless an exception is specified).
1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 — y.o.
Did you find apk for android? You can find new Free Android Games and apps.
Source: https://www.exhaust-service.ru/skoda/octavia/katalizator/
What are the causes of oil leakage?
If you see blue smoke coming from the muffler and you have a P0420 code, you need to fix the oil leak first. But how to do this, you ask?
Internal oil leaks can often be costly. Sometimes complete disassembly of the engine is required, but in some cases this may be the cause of the error.
We will describe the most common causes of internal oil leakage. The best way to find the problem is to check the compression to see if there is any pressure loss in the cylinders due to the piston rings.
Clogged crankcase ventilation system (most common)
A clogged crankcase ventilation system is the most obvious cause of blue smoke. You can start by unscrewing the oil cap while the engine is running. The cap should be sucked back in because most engines have a vacuum if everything is working properly.
If you feel excess pressure in the crankcase, the first thing you should check is the crankcase ventilation. There are often 1-3 hoses running from the crankcase to the air filter housing. Check them and make sure the tubes are not clogged. A clogged crankcase vent can cause oil to be forced past the piston rings and valve guides.
Turbine wear
Another common problem if your car is turbocharged is oil leaking, which is sucked into the engine and burned there. How to find out? You need to check the presence of oil in the intercooler (intermediate air cooling radiator). In this case, your turbocharger may be worn out.
You can also remove the charge tubes and check the turbocharger impeller to make sure it feels good and isn't loose. The clearance should be ~1mm on the sides, depending on whether the turbine is ball bearing or not.
Worn valve guides
Worn valve guides and seats can cause oil to burn. However, this is not an easy fault to diagnose or repair. Always check the piston rings for leaks before replacing them. The easiest way to replace the valve guides is to lift the cylinder head and remove the valve springs.
There are tools that can be used to increase the pressure inside the cylinder and replace the liners without removing the head, but the procedure is not simple, we recommend having a qualified mechanic do this for you.
Worn/damaged piston rings
Worn or damaged piston rings are a fairly common problem when it comes to internal oil leaks. Most often this can be checked by measuring the compression. You can inspect the pistons with an endoscope in the form of a small camera through the spark plug holes.
If you find that the piston rings are damaged, the only way to fix this is to disassemble the entire engine and remove the pistons from the block.
If you are installing new piston rings, be sure to check the pistons and piston ring clearance.
Cracks in the cylinder head
Cracks in the cylinder head or engine block are also a possible cause of oil burning. However, this problem is not very common, but it is possible.
If you find cracks, you will have to contact a specialist who will weld them, if possible. In many cases, the entire cylinder head or cylinder block will have to be replaced. It is not always possible to weld cracks.
Error P0420 - what does it mean, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, solutionAre you trying to get rid of the P0420 error code? Then this article is for you. The P0420 fault can be difficult to diagnose. You think you have fixed the error, but after 100 km the Check Engine light comes on again. This code is triggered when the engine control module detects a faulty catalytic converter. It uses one oxygen sensor at the front of the exhaust manifold - before the catalyst, and another oxygen sensor - after the catalytic converter to measure the efficiency of the catalyst. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about the P0420 code to fix it once and for all. Contents What does code P0420 mean? P0420 is triggered in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) when there is a problem with the performance of the catalytic converter. The controller uses two oxygen sensors - one before and one after the catalyst to measure its efficiency. The error occurs if the converter or oxygen sensor malfunctions, which begins to transmit incorrect data. We receive many messages asking about the P0420 code. It keeps coming back after several repairs and you just end up spending more and more money on auto repair work. This trouble code may confuse you because there is a lot of misinformation about it. Catalytic Converter The front O2 sensor measures the air/fuel mixture. It tells the control unit if the engine is running rich or lean. The rear O2 sensor is the diagnostic oxygen sensor for this error code. If the rear oxygen sensor receives incorrect values, a P0420 fault will be stored in the ECU. This could be due to a faulty catalytic converter or one of the O2 sensors failing. There may also be many other problems with the engine that are destroying the catalytic converter, and if you install a new one, it may be damaged again. The oxygen sensor is also called a lambda probe. Many people think that a lean or rich mixture can cause this error code. Yes, it is possible, but not in the way you think. A rich or lean mixture can damage the catalytic converter and when it is damaged/full of fuel it will be low in efficiency and the rear oxygen sensor will see this and trigger a P0420 code. Symptoms of the Error You probably won't have any symptoms other than an illuminated Check Engine Light with code P0420. You may experience other engine problems that damage your catalytic converter. This could include a rough (“rough”) idle, acceleration problems, misfires, or harsh gear changes. Always fix these problems first. The Check Engine light is on. Misfires. Rich mixture. Poor mixture. Engine oil is burning/gray-blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe. Slow acceleration. Causes The most common cause is the catalytic converter. It may simply be old and worn out. But there are many cases where the neutralizer is new, but at the same time it is a non-original part. Some cheaper catalytic converters may not be efficient enough, and then you will have to buy an original catalytic converter. Sometimes converters are installed too far back on the exhaust pipe. This will cause it to not get hot enough and cause a P0420 code. Damaged catalytic converter (most common cause). Non-original catalyst. Incorrect installation (placement) of the catalytic converter. Front oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault. Rear oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault. Exhaust gas leak. Leak on the intake manifold. Oil burns (damage to catalyst). Rich/lean mixture (damage to catalyst). Misfires (damage to catalyst). Faulty engine control unit (rare). Troubleshooting These are just possible solutions and you should never replace parts without proper diagnostics as you could be throwing money away if you are unlucky. Read the entire article if you want to learn how to properly diagnose this trouble code just like an experienced auto mechanic would. It will take time and may require some skill, but you won't spend $1000 to replace a good catalytic converter. Replace the catalytic converter. Replace with original catalyst. Replace the front oxygen sensor. Replace the rear oxygen sensor. Repair of faulty electrical wiring. Correct oil burning. Correct misfire. Correct lean/rich mixture. Check the data using an OBD2 scanner. Replace the engine control unit (rarely). Troubleshooting Chart Code Symptoms Causes Causes of Catalyst Damage Error P0420 Check Engine Misfire Rich Lean Burning Oil/Blue Smoke from Exhaust Pipe Slow Acceleration Faulty Catalyst Front O2 Sensor Rear O2 Sensor Exhaust Leak Oil Consumption Misfires/Lean Mixture Damaging Catalyst Misfires Ignition Oil Consumption Exhaust Leaks Intake Leaks Rich Composition Lean Composition ECU Malfunction Causes of Catalytic Converter Damage There are several causes of catalytic converter damage that can trigger the P0420 code. Here are the most common ones. Misfire. Oil consumption. Leaks at the outlet. Inlet leaks. Rich mixture. Poor mixture. Malfunction of the ECM/PCM control unit. There are many reasons that lead to malfunctioning oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. You should make sure to correct these problems before you replace any part. Otherwise, they may be damaged again. Check the controller DTC memory for any other trouble codes. Fix them first. Make sure your car is not burning oil by checking the exhaust smoke, blue smoke = oil, white = water, gray/black = rich mixture. How to Diagnose a P0420 Code Here is a guide on how a professional auto mechanic will diagnose the trouble code. This guide may require knowledge of vehicle electrical systems, and you may need some tools to complete the task. But even if you have no idea about car electronics, you can still gain useful information. You should always connect your car charger when troubleshooting your car. Low battery voltage can cause other unrelated error codes that will confuse you. Low voltage may damage the control unit or other electronics. 1. Connect the charger Connect the charger to the battery and make sure it charges the battery correctly. You should use a charger that provides at least 4 Amps while troubleshooting. A lower charging current may result in the battery being discharged when the ignition is turned on. 2. Connecting an OBD2 scanner Connect an OBD2 scanner to read the P0420 code. You can use a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with the Torque program. 3. Check for other fault codes Check for other faults that could damage the converter or any oxygen sensor faults. If there is an error in the lambda probe, then replace or check it first, this may also fix the P0420 code. Correct all other trouble codes before correcting the P0420 code. Always write down any error code numbers, do not simply erase them. 4. Check for gray-blue smoke while the engine is running. Increase engine speed and check for gray-blue smoke from the exhaust pipe. Blue smoke = burning oil. Replacing the catalyst will not help. It will most likely fail again very quickly. Burning oil can also damage the oxygen sensors and cause them to read the mixture incorrectly. You should always check for white, gray and black smoke. White smoke comes from water in the exhaust pipe, gray/black smoke comes from a rich mixture. 5. Check for exhaust leaks Raise the vehicle while it is running. Listen and look for any exhaust leaks in front of the rear lambda probe. An exhaust leak can cause the O2 sensors to receive incorrect data and may trigger a fault. If you have an exhaust leak behind the rear oxygen sensor, this should not cause an error. Tips on how to find exhaust leaks: 6. Test Drive Take the car for a test drive and make sure there are no leaks or other symptoms. Drive fairly vigorously for some time so that the catalytic converter warms up. If skipping or other strange behavior appears, start diagnosing it first. 7. Drive to the garage and jack up the car. Raise the car and keep it idling. Make sure you have proper ventilation. Connect an OBD2 scanner and check the current data from both O2 sensors. Open the signal graph from oxygen sensors. Start the car engine and make sure that the temperature of the catalytic converter is at least 400 °C. You can use a digital laser thermometer to check the temperature. Both charts should be open so you can see them. The front sensor should constantly jump between 0 - 1 Volt, and the rear sensor should show a stable 0.7 - 0.9 Volt. This means everything is working properly. If the catalytic converter is damaged or not hot enough, the rear lambda probe signal will fluctuate in the same way as the front one. You can also use a digital multimeter. To do this, you need to check the voltage from the rear O2 sensor. But the signals are high speed and it can be difficult to read such voltages with a multimeter. 8. Check the temperature of the catalyst You can also check the temperature on the converter. Make sure it is still hot before checking. Use a digital laser thermometer to measure. Check the temperature just before, in the middle and after the catalyst. If you get the same temperature at all points when the neutralizer is hot (over 400 C°), then it is most likely empty or damaged. If the catalytic converter is working correctly, the temperature should be 100-150 C° higher directly behind it than in front of it. If the temperature in front of the catalyst is much higher, the car may be running rich and the converter is working too hard. This may also be due to the catalytic converter being blocked or having poor exhaust flow. Video on how to test your catalytic converter using the Torque Pro app: 9. Summarize your results Summarize your diagnostic results. If you have no other error codes, the front oxygen sensor signal changes, the catalytic converter temperature is uniform, and you do not see blue smoke, replace the catalytic converter. Code P0420 can be a problem to diagnose correctly. If you have read this repair guide and received incorrect results, you can replace your catalytic converter with reasonable confidence. If your diagnostic results look good but you still get a P0420 code, there is a small chance that the catalytic converter is still causing the fault. In rare cases, you may have a faulty ECM. If you find any gaps, gray-blue smoke or other problems, correct them and remove the error. With luck, the P0420 code may not return. What are the causes of oil leakage? If you see blue smoke coming from the muffler and you have a P0420 code, you need to fix the oil leak first. But how to do this, you ask? Internal oil leaks can often be costly. Sometimes complete disassembly of the engine is required, but in some cases this may be the cause of the error. We will describe the most common causes of internal oil leakage. The best way to find the problem is to check the compression to see if there is any pressure loss in the cylinders due to the piston rings. Clogged PCV System (Most Common) A clogged PCV system is the most obvious cause of blue smoke. You can start by unscrewing the oil cap while the engine is running. The cap should be sucked back in because most engines have a vacuum if everything is working properly. If you feel excess pressure in the crankcase, the first thing you should check is the crankcase ventilation. There are often 1-3 hoses running from the crankcase to the air filter housing. Check them and make sure the tubes are not clogged. A clogged crankcase vent can cause oil to be forced past the piston rings and valve guides. Turbine Wear Another common problem if your car is turbocharged is oil leaking, which is sucked into the engine and burned there. How to find out? You need to check the presence of oil in the intercooler (intermediate air cooling radiator). In this case, your turbocharger may be worn out. You can also remove the charge tubes and check the turbocharger impeller to make sure it feels good and isn't loose. The clearance should be ~1mm on the sides, depending on whether the turbine is ball bearing or not. Worn valve guides Worn valve guides and seats can cause oil to burn. However, this is not an easy fault to diagnose or repair. Always check the piston rings for leaks before replacing them. The easiest way to replace the valve guides is to lift the cylinder head and remove the valve springs. There are tools that can be used to increase the pressure inside the cylinder and replace the liners without removing the head, but the procedure is not simple, we recommend having a qualified mechanic do this for you. Worn/Damaged Piston Rings Worn or damaged piston rings are a fairly common problem when it comes to internal oil leaks. Most often this can be checked by measuring the compression. You can inspect the pistons with an endoscope in the form of a small camera through the spark plug holes. If you find that the piston rings are damaged, the only way to fix this is to disassemble the entire engine and remove the pistons from the block. If you are installing new piston rings, be sure to check the pistons and piston ring clearance. Cracks in the cylinder head Cracks in the cylinder head or engine block are also a possible cause of oil combustion. However, this problem is not very common, but it is possible. If you find cracks, you will have to contact a specialist who will weld them, if possible. In many cases, the entire cylinder head or cylinder block will have to be replaced. It is not always possible to weld cracks. How does a catalytic converter work? Here is a video of how a catalytic converter works: The picture shows the parts of a catalytic converter. The catalyst is used to purify exhaust gases. If you look at it, you will see that it looks like a honeycomb in a beehive. Engine exhaust produces hydrocarbons (unburnt fuel), carbon monoxide (from combustion in the engine), and nitrogen oxides (formed when heat in the engine causes nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen). The catalytic converter contains platinum and palladium (which is why you get paid for the used catalyst). The ceramic structure converts carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide CO) into carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide CO2). It also converts hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide. Nitric oxide is converted back to oxygen and nitrogen. If the conversion fails, the rear oxygen sensor will sense this and send a signal to the control unit, which will activate the P0420 code. How does an oxygen sensor work? Video of how the lambda probe works: What is the function of the front oxygen sensor? Oxygen Sensor The front O2 sensor is adjustable. It will measure the mixture of exhaust gases that pass through it. Using this data, the ECU determines whether the mixture is rich or lean. The front oxygen sensor can be installed either directly in front of the catalytic converter or on the exhaust manifold. Some vehicles use multiple front O2 sensors for different cylinders. There are two types of oxygen sensors: narrowband sensor (most common) wideband sensor (newer vehicles). A wideband sensor reads the signal much faster. Narrowband usually uses four wires. One is the power supply, one is the signal and two wires are for heating. You can simply determine whether you have a narrowband or wideband sensor. Look at the number of wires. A broadband sensor will have 5 or more wires, and a narrow-band-2-4 wires. If the front sensor O2 is faulty, then the ECU thinks that the engine works on a rich mixture, while it works on the poor in fact. This can cause an error P0420. What is the function of the rear oxygen sensor? The rear lambda-zond does not differ in the structure from the front. The difference is that the rear sensor does not provide any information for adjusting the mixture to the engine control unit. The purpose of the rear sensor O2 is only to check whether the catalytic neutralizer works correctly. If the rear sensor feels that the catalyst is working incorrectly, it will send this information to the control unit, which will launch and save the P0420 malfunction code. What does Bank 1, Bank 2 mean? The designation Bank 1 and Bank 2 is usually used if the car has more than four cylinders. But it is also used on four -cylinder engines. This means that you probably have two exhaust pipes or that the engine cylinders are divided into several O2 sensors. "Bank" means which side or on which exhaust pipe the sensor is located. Bank 1 is always installed on cylinders 1-3-5-7-9, etc. The Bank 2 sensor controls the cylinders 2-4-6-8-10. You can turn off one oxygen sensor and consider errors by the OBD2 scanner. This will find out where the sensor is installed-in Bank 1 or Bank 2. Is it possible to remove any detail to get rid of the P0420 code? You cannot just remove any details to fix the P0420. This will most likely provoke another error or other malfunctions. You can reprogram the control unit to remove the control of the catalytic neutralizer. But this is not recommended, because in most countries there is a law according to which the catalyst should work. If you reprogram the controller, you can also remove the catalytic neutralizer. Remember that if you remove the catalyst, then most likely you will not pass the inspection for the number of emissions into the atmosphere. There is another way to deceive the ECU-to replace the rear lambda zond. This method is for those who want to get rid of the P0420 error by any methods. We don't recommend doing this. Here you can see the prices and types of deceit of the oxygen sensor. How can the burned oil damage the catalyst? If there is an internal leak of oil in the engine that burns in the cylinders, it will go through the exhaust pipe. This creates blue smoke that we mentioned earlier. The oil stuck and burns in the neutralizer, damaging it. The catalyst temperature can reach more than 600 C °. And if it overheats, it is damaged. Then, if you replace the catalytic neutralizer without eliminating oil leakage, the oil will continue to get stuck and burn in it. Thus, you will also damage your new catalyst. How can a rich or poor mixture cause an error P0420? A rich or poor fuel mixture can damage your neutralizer in several ways. Due to the rich mixture, too much fuel will fall into the catalyst. It will ignite and destroy it. The poor mixture can cause a high temperature of exhaust gases. It can also damage the catalytic neutralizer. However, the catalyst is not damaged quickly due to this kind of problem. But in the long run, it wears out much faster than if the fuel mixture was correct. How can the passes cause an error P0420? Ignition misses are a common cause of damage to catalytic neutralizers. This is because during ignition passes, unbroken fuel appears, which enters the neutralizer through the exhaust manifold. Since it is hot, fuel is ignited and causes a reverse reaction. These ignitions are fatal for any catalytic neutralizer and can quickly damage it. Another option lies in the fact that unsecured fuel comes out, and immediately after that there is fire from another cylinder, which ignites the mixture, and it explodes inside the exhaust pipe. These explosions can quickly damage the catalyst. Tools for eliminating the P0420 error to correct this malfunction code, you may need several tools to make diagnostics much easier and better. OBD2 scanner is necessary to diagnose an error code for viewing data in real time, etc. We recommend lending or buying a diagnostic scanner that can show signals in the graphs to facilitate the diagnosis. You should always have a car charger when you diagnose a car. The low voltage of the battery can cause other errors that will lead to incorrect conclusions. Low voltage can also damage control units or other electronics, if you are not very lucky. The digital laser thermometer is necessary to check the temperature of the catalytic neutralizer. The temperature issued by the OBD2 scanner is calculated, not real. The thermometer is also useful for many other tasks when you repair the car. Ideal for eliminating the malfunctions of the cooling system. A digital multimeter is required for any electrical measurements and is absolutely necessary. You will need a multimeter to search for almost all electronics malfunctions. He is not so dear. Buy a multimeter depending on your needs - there are both very cheap and expensive. The deceit of the oxygen sensor can be used in order to deceive the control unit, and this can correct the error P0420. This is a non -recommended method. If you think that your catalytic neutralizer is contaminated or there is oil from earlier internal oil leaks, you can try to use the catalyst cleaner. It is also used for other tasks when cleaning the exhaust system. The known reasons for the error P0420 by car models in some cars P0420 error are better known than in others. Here is a list of the most common reasons for each brand. These cars, as you know, have problems with the P0420 error. Remember that these are only general recommendations, and you must make the correct diagnosis before changing any details. Toyota Corolla The most common cause of the P0420 error on Toyota Corolla is a catalyst malfunction. But, this can often be caused by oil passing through the piston rings, which stuck in a catalytic neutralizer. First, check the presence of leaks on the inlet and release. Then check if there is a gray -haired smoke from the exhaust pipe. If you see him, then this is an occasion to contact a car service to find the oil comes from. The standard reason may be the crankcase ventilation. If you do not see blue smoke at any engine speed, most likely your catalytic neutralizer is worn out. Ford Focus Ford focus usually has an air leak. It can also be any broken solenoid that causes an incorrect fuel-air mixture, activating the error. Check the controller’s memory using a diagnostic scanner to count errors associated with the air-fuel mixture. If everything looks normal, check the presence of exhaust gas leaks. Replace the catalytic neutralizer if you cannot find any malfunctions or other mixture problems. Subaru / Subaru Forester Subaru usually has the same problem as Toyota Corolla. Check the presence of air leaks or other malfunctions associated with the fuel mixture. Check the presence of exhaust gas leaks in front of a catalytic neutralizer. The most common problem on Subaru engines is the catalyst itself. Volkswagen (VW) / Skoda / Seat / Audi A4 1.8 T / V6 2.4 These VAG cars have some well -known malfunctions that cause the P0420 code. Check the work valves at the inlet. Make sure that the crankcase ventilation is not contaminated, as a result of which the engine burns the oil that clogs the catalytic neutralizer. Check the presence of exhaust gas leaks around any folds on the exhaust pipe (general reason). Check the presence of any codes of malfunctions O2. If no problems are found, replace the neutralizer. This is a very common problem both at 1.8 T and on V6 gasoline engines. The 1.8 T catalyst can be quite difficult to replace if you have no experience in this. V6 has two catalytic neutralizers, so make sure that you eliminate problems and replace the catalyst on the right side. The conclusion in most cases the catalytic neutralizer is faulty and this is evidenced by the error code P0420. But there may be other reasons why the catalyst was damaged. Always correct all other fault codes before eliminating P0420. You can use special tools or reprogram control unit to deceive it. This will help get rid of the P0420 error. Bank 1, Bank 2 (Bank 1, Bank 2) indicate which of the O2 sensors or which catalytic neutralizer is faulty. The catalytic neutralizer cleans the exhaust gases and its removal is illegal.
How does a catalytic converter work?
Here's a video of how a catalytic converter works:
The picture shows the parts of the catalytic converter. The catalyst is used to purify exhaust gases. If you look at it, you will see that it looks like a honeycomb in a beehive.
Engine exhaust produces hydrocarbons (unburnt fuel), carbon monoxide (from combustion in the engine), and nitrogen oxides (formed when heat in the engine causes nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen).
The catalytic converter contains platinum and palladium (which is why you get paid for the used catalyst). The ceramic structure converts carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide CO) into carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide CO2). It also converts hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide. Nitric oxide is converted back to oxygen and nitrogen.
If the conversion fails, the rear oxygen sensor will sense this and send a signal to the control unit, which will activate the P0420 code.
Tips to resolve the problem
Before running to a car service center, try to find out the reason yourself. To do this, you need to carry out a few simple checks. First, try to remember which gas station you last refueled at and whether you filled it with the correct fuel. If previously you always filled with A98 gasoline, and last time you decided to test A92, then it is quite logical that the system showed error P0420. In this case, just roll the remaining A92 and fill it with A98 this time. For many car owners, after changing gasoline, the error disappears.
Next, check the rear oxygen sensor connector. If he moved away a little, then this could very well cause an error. If everything is fine with this, then you will have to connect a computer to remove errors and data from the control unit.
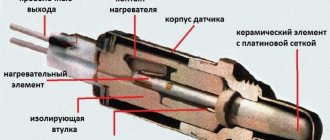
What is the function of the front oxygen sensor?
Oxygen Sensor
The front O2 sensor is adjustable. It will measure the mixture of exhaust gases that pass through it. Using this data, the ECU determines whether the mixture is rich or lean.
The front oxygen sensor can be installed either directly in front of the catalytic converter or on the exhaust manifold.
Some vehicles use multiple front O2 sensors for different cylinders.
There are two types of oxygen sensors:
- narrowband sensor (most common)
- wideband sensor (new vehicles).
A wideband sensor reads the signal much faster.
Narrowband usually uses four wires. One is the power supply, one is the signal and two wires are for heating. You can simply determine whether you have a narrowband or wideband sensor. Look at the number of wires.
A wideband sensor will have 5 or more wires, while a narrowband sensor will have 2-4 wires.
If the front O2 sensor is faulty, the ECU thinks the engine is running rich when it is actually running lean. This may cause the P0420 code.
What is the function of the rear oxygen sensor?
The rear lambda probe does not differ in structure from the front one. The difference is that the rear sensor does not provide any information for adjusting the mixture to the engine control unit.
The purpose of the rear O2 sensor is only to check if the catalytic converter is working properly. If the rear sensor senses that the catalytic converter is not working properly, it will send this information to the control unit, which will trigger and store a P0420 trouble code.
How the car behaves (signs of error p0420)
Depending on which of the two variants of a catalyst malfunction occurs (clogged or destruction has begun), the car will exhibit their characteristic symptoms. In addition to the fact that the check engine light will light up on the instrument panel, and in some cars the catalyst overheating lamp will light up, the exhaust gases will no longer meet EURO 3-5 standards. In general, the signs that will trigger the P0420 (P0430) error may be:
Location of catalyst and oxygen sensors
- increased fuel consumption;
- decreased engine dynamics;
- changes in the smell of exhaust gases (became very unpleasant);
- rattling noise from the catalytic converter (if it crumbles);
- sometimes unstable idle;
- It may be difficult to start the engine. So, if you observe more than two of these signs at the same time, most likely the car has problems with the catalyst, and you cannot do without diagnostics to accurately find out the fault code!
What does Bank 1, Bank 2 mean?
The designation Bank 1 and Bank 2 is usually used if the vehicle has more than four cylinders. But it is also used on four-cylinder engines.
This means that you probably have two exhaust pipes or that the engine cylinders are split into multiple O2 sensors. “Bank” indicates which side or exhaust pipe the sensor is located on.
Bank 1 is always installed on cylinders 1-3-5-7-9, etc. Bank 2 sensor monitors cylinders 2-4-6-8-10.
You can disable one oxygen sensor and read errors with the OBD2 scanner. This will allow you to find out where the sensor is installed - in Bank 1 or Bank 2.
Is there any part that can be removed to clear the P0420 code?
You can't just remove some parts to fix P0420. This will most likely trigger another error or other malfunctions.
You can reprogram the control unit to remove the catalytic converter monitoring. But this is not recommended because in most countries there is a law that the catalyst must work.
If you reprogram the controller, you may also be able to remove the catalytic converter.
Remember that if you remove the catalytic converter, you will most likely fail the emissions test.
There is another way to fool the ECU - replacing the rear lambda probe. This method is for those who want to get rid of error P0420 by any means. We don't recommend doing this. Here you can see prices and types of oxygen sensor decoys.
How can burnt oil damage the catalytic converter?
If there is an internal leak in the engine oil that is burned in the cylinders, it will exit through the exhaust pipe. This creates the blue smoke that we mentioned earlier. The oil gets stuck and burns in the converter, damaging it.
The catalyst temperature can reach more than 600 C°. And if it overheats, it is damaged. Then, if you replace the catalytic converter without fixing the oil leak, the oil will continue to get stuck and burn in it. This way you will also damage your new catalytic converter.
How can a rich or lean mixture cause P0420?
A rich or lean fuel mixture can damage your converter in several ways. A rich mixture will cause too much fuel to enter the catalyst. It will ignite and destroy him. A lean mixture can cause high exhaust gas temperatures. It can also damage the catalytic converter.
However, the catalyst is not damaged quickly due to this kind of problem. But in the long run, it wears out much faster than if the air/fuel mixture were correct.
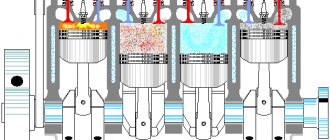
How can omissions cause P0420?
Misfires are a common cause of damage to catalytic converters. This happens because during a misfire, unburned fuel appears and enters the converter through the exhaust manifold. Because it is hot, the fuel ignites and causes a backlash.
These fires are fatal to any catalytic converter and can quickly damage it. Another possibility is that the unburned fuel comes out and is immediately followed by a fire from another cylinder which ignites the mixture and it explodes inside the exhaust pipe. These explosions can quickly damage the catalyst.
Diagnosis and elimination of errors
Although it is a faulty catalyst that most often leads to the appearance of error P0420, you should not rush to conclusions. The catalytic converter is not a cheap part, so sometimes a motorist in a hurry can waste a considerable amount of money.
First you need to do some diagnostics. In many ways, it allows us to confirm or refute the theory that the catalyst’s service life has come to an end.
The current task is to fix the problem that caused error P0420 to appear. To begin with, it is recommended to rule out simpler causes.
- Low quality fuel. If you have visited questionable gas stations or filled up with fuel that was not intended for your engine, it is better to drain the remainder and fill with normal gasoline. Then drive it, burn out the remaining fuel in the line and see how the car behaves with good fuel.
- Ignition. Or rather the lead angle. Check if the torque is set correctly. If not, the exhaust temperature may be higher than permissible, which will lead to a corresponding error.
- Oxygen sensor. In this case, the second or lower lambda probe is checked. To check, swap the two sensors, as they are identical and interchangeable. If this corrects the situation, replace the old sensor. However, if the second sensor breaks down, another error usually appears. This is P0134.
This is interesting: How Chery Tiggo is repaired and tuned
If the measures taken did not confirm your guesses and the reason is still in the catalyst, it will also need to be checked.
Diagnostics of the catalyst involves the use of a special stand and equipment. Therefore, such procedures are unlikely to be carried out in a garage environment.
The test generates a graph of the output voltage between a pair of oxygen sensors. Additionally, data on decreasing and increasing fuel supply is checked.
When checking the output voltage, make sure that the readings vary depending on the air-fuel mixture used.
If the mixture is lean, the voltage should be 100 mV or higher. If the mixture is enriched, then up to 900 mV.
If there are deviations from the norm, you can solve the problem with the catalyst in several ways:
- Replace the old catalyst with a new original one. Very expensive, but right. Prices for parts for foreign cars can be about 40-50 thousand rubles or more.
- Replace with an analogue one. These are Chinese and other catalysts. Here you will have to spend 5-15 thousand rubles. But keep in mind that metal, and not original ceramic, catalysts last literally 50 thousand km.
- Install the decoy. This is what they call the ECU firmware so that the unit does not react to the absence of a catalyst. An emulator is installed to ensure stable operation of the internal combustion engine and exhaust system.
If you remove the catalyst, the car will not meet the stated environmental standards.
Whether this is a serious reason to still spend money on a full replacement, decide for yourself.
If the catalyst is simply clogged, causing its performance to decrease, cleaning it can help. There are DIY methods for cleaning. Plus, many car services are ready to do this for money.
Common diagnostic mistakes
The most common error when diagnosing P0422 is due to failure to follow the diagnostic protocol. Failure to follow the protocol may result in unnecessary catalyst replacement that will not correct the problem.
Oxygen sensors are also often mistakenly replaced. Oxygen sensors should be checked before replacement and should not be considered the only problem causing P0422.
Tools to troubleshoot P0420
To fix this trouble code, you may need a few tools to make the diagnosis much easier and better.
- OBD2 scanner - essential for diagnosing error codes, viewing real-time data, etc. We recommend borrowing or purchasing a diagnostic scanner that can show signals in graphs to make diagnosis easier.
- You should always have a car charger when diagnosing your car. Low battery voltage can cause other errors that will lead to incorrect outputs. Low voltage can also damage control units or other electronics if you're really unlucky.
- A digital laser thermometer is required to check the temperature of the catalytic converter. The temperature value produced by the OBD2 scanner is calculated and not real. The thermometer is also useful for many other tasks when you are working on your car. Ideal for troubleshooting cooling system problems.
- A digital multimeter is required for any electrical measurements and is absolutely essential. You will need a multimeter to troubleshoot almost all electronics problems. It's not that expensive. Buy a multimeter depending on your needs - there are some very cheap ones and some expensive ones.
- Oxygen sensor spoofing can be used to fool the control unit and this may correct the P0420 code. This is not a recommended method.
- If you think your catalytic converter is dirty or has oil in it from earlier internal oil leaks, you can try using a catalyst cleaner. It is also used for other tasks when cleaning the exhaust system.
Symptoms
If an error code with the value P0420 is registered in the ECU, this can be guessed not only by scanning the control unit and connecting it with a scanner.
Most often, suspicions about a faulty catalyst arise from indirect signs. Yes, they can indicate other possible problems.
Since error P0420 appears not only in a situation where the catalyst fails, the symptoms can be quite varied. Namely:
- the engine does not work as well as before;
- dynamics decreases;
- at idle the engine behaves unstable;
- engine starting becomes more difficult;
- fuel consumption increases noticeably without increasing the load;
- during movement, a cracking sound occurs on the side of the catalyst;
- the exhaust gas changes its composition and color may change;
- the smell from the exhaust becomes more pronounced and unpleasant, sometimes sharp;
- The warning light on the dashboard, known to everyone as the Check Engine, comes on.
The majority of signs, apart from the crackling sound from the catalyst itself, potentially indicate various problems. But the manifestation of any of the symptoms discussed is a good reason to engage in diagnostics, find out the causes and try to troubleshoot.
Known Causes of P0420 by Vehicle Model
Some vehicles are more familiar with the P0420 code than others. Here is a list of the most common reasons for each brand. These vehicles are known to have problems with the P0420 code. Please remember that these are general guidelines only and you must make a proper diagnosis before changing any parts.
Toyota Corolla
The most common cause of the P0420 code on the Toyota Corolla is a faulty catalytic converter. But, this can often be caused by oil passing through the piston rings getting stuck in the catalytic converter.
First check for leaks at the inlet and outlet. Then check to see if there is gray blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe. If you see it, then this is a reason to contact a car service to find where the oil comes from. The usual cause may be crankcase ventilation.
If you don't see blue smoke at any engine speed, your catalytic converter is likely worn out.
Ford Focus
Ford Focus usually has an air leak. It could also be any broken solenoid that is causing the fuel/air mixture to be incorrect, activating the fault.
Check the controller memory using a diagnostic scanner to read errors related to the air-fuel mixture. If everything looks normal, check for exhaust leaks.
Replace the catalytic converter if you cannot find any trouble codes or other problems with the mixture.
Subaru / Subaru Forester
Subaru usually has the same problem as Toyota Corolla. Check for air leaks or other fuel mixture related trouble codes.
Check for exhaust leaks in front of the catalytic converter. The most common problem with Subaru engines is the catalyst itself.
Volkswagen (VW) / Skoda / Seat / Audi A4 1.8 T / V6 2.4
These VAG vehicles have some known faults that cause code P0420. Check the operation of the inlet check valves. Make sure the crankcase vent is not clogged, causing the engine to burn oil that clogs the catalytic converter.
Check for exhaust leaks around any bends in the exhaust pipe (common cause). Check for any O2 sensor trouble codes.
If no problems are found, replace the converter. This is a very common problem on both 1.8 T and V6 petrol engines. The 1.8 T catalytic converter can be quite difficult to replace if you are not experienced with it.
The V6 has two catalytic converters, so make sure you troubleshoot and replace the correct side of the catalytic converter.
For which cars is this relevant?
It is impossible to say that error P0420 is typical for a specific make or model of car. This is a common mistake.
Basically, error P0420 appears on cars whose mileage is more than 100 thousand kilometers.
In this case, the first error P0420 may appear closer to 100 thousand km. or it may appear when the engine has worked for over 300 thousand km.
Diagnostics of the control unit and error code P0420
If you look at the statistics of calls from motorists to service stations with such a problem as error P0420, you can identify several brands and models of cars that are susceptible to this problem. This may include:
- Ford Focus 2.
- Toyota Corolla.
- Kia Rio.
- Nissan Qashqai.
- Renault Logan
- Hyundai Solaris.
- UAZ Patriot.
- Opel Antara.
- Mazda 3.
- Suzuki Grand Vitara.
- Kia Ceed.
- Skoda Fabia
- Honda Accord, etc.
The ECU compares the values of oxygen sensors on vehicles that meet the Euro-3 environmental standard and higher. Therefore, this error cannot appear on older cars.
It is important to take into account that error P0420 can equally affect both an expensive foreign car and an inexpensive domestic car.
Troubleshooting the catalyst and oxygen sensor
This is mainly a problem with budget models or cars that have traveled a significant number of kilometers. For them, error P0420 appears a little more often.
The lower the quality of the fuel used, the faster the ECU will encounter an error indicating low efficiency of the catalyst.
This is another reason to give preference to good quality fuel, use the services of trusted gas stations, and perform timely maintenance.
Conclusion
- In most cases, the catalytic converter is faulty and is indicated by the P0420 code. But there may be other reasons why the catalyst was damaged. Always correct all other trouble codes before troubleshooting P0420.
- You can use special tools or reprogram the control unit to trick it. This will help get rid of the P0420 code.
- Bank 1, Bank 2 indicate which O2 sensor or catalytic converter is faulty.
- The catalytic converter cleans the exhaust gases and its removal is illegal.
Previous post Error P0123 - what it means, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, solution
Next entry Error P0190 - what it means, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, solution