A car with a faulty fuel injection pump loses power, increases fuel consumption, has problems starting the engine, increases smoke from the exhaust system, etc. There can be many reasons leading to pump malfunctions, from the appearance of moisture in the plunger pair to problems in the electronics. The best way to check the fuel injection pump is at a stand at a service station, but some faults can be determined independently in your garage. To learn how to do this, you should be able to identify the signs, and for this you need to know the reasons leading to this.
Operating principle of fuel injection pump
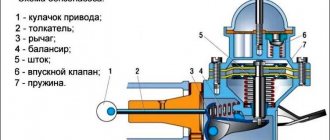
Despite the abundance of different types of pumps, all injection pumps operate on a similar principle and ensure the supply of portions of diesel fuel into the cylinders of a car engine under high pressure at strictly designated times. The size of the supplied fuel portions is determined by the load of the cylinders to the crankshaft. The basis of any type of injection pump is a plunger pair, consisting of a plunger (piston) and a sleeve (cylinder).
There are 2 main types of injection pumps based on their operating principle:
- Direct acting injection pump with mechanical plunger drive;
- Injection pump with battery injection.
The design also distinguishes several types of fuel injection pumps:
- in-line - pump sections are arranged in a row and supply fuel to a specific engine cylinder;
- distribution - one pump section can supply fuel to several different cylinders;
- multi-section (V-shaped) - for high-speed diesel engines.
In turn, distribution injection pumps can be single-plunger or double-plunger.
All direct injection injection pumps operate on the same principle:
- mechanical plunger drive;
- simultaneous pumping and injection processes;
- the pressure for fuel injection is created by the movement of the plunger.
Injection pumps with accumulator injection provide fuel supply in separate cycles: first, the fuel is pumped into the pump accumulator, then it enters the fuel injectors. Pumps with electronically controlled injectors are called the Common rail system.
Briefly, the operating principle of a high pressure fuel pump looks like this.
- Fuel from the tank enters the injection pump thanks to the booster pump. The fuel pressure at the inlet to the pump section of the injection pump is maintained by a pressure reducing valve.
- The movement of the plunger that supplies fuel to the engine cylinders is ensured by the cam shaft, which in turn is driven by the car’s crankshaft.
- The rotation of the cam shaft causes the plunger to move, which moves up the bushing. In this case, the outlet and inlet ports open sequentially.
- The pressure created by the movement of the plunger opens the discharge valve, after which the fuel flows to the fuel injector of the diesel engine cylinder.
- Excess fuel is drained from the plunger into the tank through a drain, screw, radial and axial channels through a drain fitting.
Signs of fuel injection pump malfunction
The injection pump is an expensive and rather capricious component of a diesel engine, extremely demanding on the quality of fuel and lubricants. The main reason for fuel injection pump failure is contamination of the pump plungers, which are installed in bushings with minimum tolerances, measured in microns. Contamination of the plunger pair with solid particles contained in low-quality diesel fuel can lead to failure of the injection pump. Water that may be contained in fuel is no less dangerous. Moisture erodes the protective oil film of the assembly parts, which can lead to jamming of the fuel injection pump parts. Also, a fuel injection pump malfunction may consist of physical wear of parts and damage to the pump housing.
A malfunction of the fuel injection pump usually leads to uneven fuel supply to the engine injectors and to a decrease in its incoming volume. To understand that the fuel injection pump is not working normally, it is not necessary to wait for it to break down. Signs of problems with the injection pump and the fuel system as a whole are:
- increased fuel consumption;
- unstable engine operation at low speeds;
- difficulty starting the engine;
- motor overheating;
- fuel leak;
- drop in power and efficiency of a diesel engine;
- increased exhaust smoke;
- the appearance of extraneous noise during engine operation.
Removing the injection pump from the engine
Removing the fuel injection pump may be necessary not only to find and repair faulty parts, but also to check the injectors and adjust the gas distribution mechanism. Removing the fuel injection pump is a rather labor-intensive task that not every car owner can handle. At a minimum, to carry out such an operation you must have considerable experience in independently repairing a car.
Removal of the injection pump is carried out in several stages. Depending on the type of pump, there may be differences in the sequence and some details of the process. To remove the injection pump, in addition to standard keys, you will need special devices - gears for cranking the crankshaft, clamps, stocks, drive gear pullers, spline keys and special tools for dismantling. Therefore, when removing the pump, it is advisable to use a set of tools for repairing the injection pump.
- First, you should drain all the coolant in the car.
- Next, the negative terminal of the battery is disconnected.
- The fan and fan casing are removed, complicating access to the injection pump housing.
- Then the cylinder head cover is removed.
- Next, remove the timing belt cover.
- Then the intake manifold is dismantled.
- Next, the first cylinder of the engine must be set to the top dead center position (the maximum distance between the cylinder and the crankshaft). To lock the cylinder in this position, use special tool 11 2 300.
- Then it is necessary to remove the timing belt from the camshaft pulleys and the injection pump shaft.
- Next, you need to disconnect the fuel line and drain wire from the pump. The oil drain hose is also disconnected.
- Next, you need to disconnect the distribution lines from the cylinder injectors using tool 13 5 020.
- Next, the electrical wiring parts are disconnected.
- Then you need to remove the fuel injection pump fasteners. To remove the central nut of the injection pump, first remove the cap nut, and then unscrew the central nut with an 18-mm open-end wrench.
- Next, the bolts on the fuel injection pump housing are turned out.
- To disconnect the injection pump from the sprocket, use the ejector screw and fixture 13 5 120, which is first screwed into place of the central nut. When removing the injection pump, the device must remain on the central pulley until the pump is installed back to avoid the sprocket falling.
Once the injection pump is separated from the center pulley and sprocket, it can be carefully removed. Further disassembly to search for faulty parts can also be carried out using a specialized kit for repairing high-pressure fuel pumps.
Malfunctions of diesel injection pumps lead to loss of power, increased fuel consumption, difficult starting, increased exhaust smoke, and others. Typical breakdowns of a high-pressure fuel pump in a diesel car include water getting into the plunger pairs, a drop in pressure in the plunger pair, damage to the integrity of the sealing rings, sensor or wiring malfunctions (in electronically controlled diesel engines). Ideally, the injection pump should be checked at a special stand in a car service center, but simple checks of the fuel pump can be done in a garage.
Assembly and speed adjustment
When the unit is assembled, you need to fill it with diesel fuel by manually turning the drive roller, after which you can install it in place and connect the fuel lines, hoses and electrical wiring of the control system.
After the engine is started, you should make sure that the fuel injection advance machine is operating correctly, depending on the pressure in the cavity of the low-pressure vane pump. This unit has its own idle speed regulator. If necessary, adjust this parameter by screwing or unscrewing the adjusting screw.
Before performing this procedure, it is recommended to remember the position of the screw by counting the number of threads protruding from the locknut so that, in extreme cases, you can return to the original setting. The engine manual indicates the required number of engine idle speeds. Usually they drop from 1100 rpm after starting to 750 - after warming up a diesel engine with a manual transmission, and to 850 - on an engine with an automatic transmission.
Types of fuel pumps
First, let's look at the types of fuel pumps for diesel cars, since each of them has its own characteristics and typical fuel injection pump malfunctions. So, knowing what type of pump it is, you can better understand the principle of operation and the immediate cause of the breakdown. Regardless of the type of high-pressure pump, you need to understand that the main unit is the so-called plunger pair - a piston (plunger) and a cylinder (bushing).
There are two main types of injection pumps:
- with direct action and mechanical action of the plunger;
- with battery injection.
However, high-pressure fuel pumps are still divided into classes according to their design. In particular:
- Rows . As the name implies, their working sections are arranged in one row, and fuel is supplied to each cylinder in turn.
- Distribution . With such pumps, one section can supply fuel to several different cylinders. Such devices can be single- or double-plunger.
- Multi-sectional . Another name for them is V-shaped or hydraulic accumulators. They are used for highly powerful, but low-speed engines. They are quite rare.
With direct injection fuel pumps, pumping and injection occur simultaneously. The mechanical drive of the plunger is responsible for this. With battery pumps, fuel is supplied in separate cycles, first it enters the pump accumulator, and only then into the injectors. The most modern systems are controlled electronically and are called Common Rail. They work based on information from numerous sensors located in different parts of the car.
Another injection system is a pump injector. In this case, they are combined into one mechanism. This system simplifies pressure control and also increases reliability, because if one injector fails, the engine will continue to operate, albeit with less power.
High-pressure fuel pumps were also invented for gasoline engines. They are used in engines with direct fuel injection. The pump's job is to supply gasoline under high pressure into the cylinders, where the fuel is directly mixed with the air mass, forming a mixture that is ignited by the spark plug.
Signs of fuel injection pump malfunction
Despite the fact that high-pressure pumps belong to different types, the signs of their partial failure are typical and in many ways common to all. So, symptoms of a fuel injection pump malfunction include:
- increased fuel consumption in all engine operating modes;
- unstable operation of the engine, especially at low speeds;
- difficulty starting the engine, most often in the cold season;
- drop in engine power and dynamic characteristics of the machine as a whole;
- increase in engine exhaust smoke;
- fuel leak from the high pressure pump;
- the appearance of an oil emulsion in the engine coolant;
- increased engine noise.
Experienced car enthusiasts identify another sign of a faulty high-pressure pump plunger. It lies in the fact that when the engine is hot, it may stall when idling. And at the same time, it will be almost impossible to start it until the pump itself cools down. “When cold,” the engine starts without problems.
The main causes of fuel injection pump malfunction
The following are the causes of high pressure pump failure. Typically, the following structural elements fail:
- Plungers . Most often they are to blame, since the plunger pairs quickly become dirty. This is due to two reasons. The first is design features that provide a small gap that ensures high pressure in the system. The second is the low quality of diesel fuel, in particular, the presence of sulfur and paraffins in it, which, in fact, pollute the device. Dirt can also come from the engine (carbon deposits, dirt). Wear of the plungers leads to unstable engine operation at idle, increased fuel consumption, and decreased compression. Due to damage to the plunger pair, the bearings can significantly overheat.
- Water in diesel fuel . Also, domestic diesel fuel often has a high water content. Moisture washes away the fuel (at the same time protective) film from the surfaces of fuel injection pump parts, which causes the service life of precision parts to be significantly reduced. This may even cause the pump to jam.
- Dirty fuel filter . Due to a clogged fuel filter, the high-pressure pump, firstly, can become dirty (plunger pairs), and secondly, it wears out, which reduces its overall service life.
- Uneven supply and distribution of injected diesel fuel . This problem can also be caused by a malfunction of the plunger pairs, in particular, wear of the drivers, rack teeth, discharge valves, as well as dirty nozzles.
- Manufacturing defect . This situation is quite rare, but sometimes occurs on cheap pumps. Defects include cracks on the fuel injection pump housing, damage to its bearings, as well as jamming of the plunger bushing.
- Bearing wear . They usually wear out due to a critical decrease in service life (aging). Another option is a manufacturing defect. All this leads to the fact that the operating characteristics of the pump deteriorate, and the bearings and adjacent parts overheat, thereby reducing their service life.
- Piston and bushing jamming . This is a critical failure that can lead to breakage of the rack, cam shaft, gear, governor, keys. Often the cause of jamming is water getting into the cavity between the piston and the bushing.
- Wear of pump parts . This can occur both for natural reasons (with an increase in the mileage of the car) and when water gets inside it. It washes away the protective (working) lubricant from the elements, which significantly reduces both the service life of the pump as a whole and its individual parts.
- Corrosion of the plunger pair . Rusting spots may appear due to the increased water content in diesel fuel.
- Incorrect operation of the cooling system . That is, under prolonged and/or heavy loads, the high-pressure pump may simply overheat. The cooling system can be faulty for various reasons - low level of antifreeze or antifreeze, system clogging, breakdown of individual elements (pump, pipes, radiator, etc.).
If there is a suspicion that the fuel pump rack or associated parts are faulty, then you need to check for the presence/absence of the following defects:
- disconnecting the rack from the regulator parts;
- jamming or loosening of the clamps of the plunger leads;
- jamming of the coupling screws of the gear rims.
One of the most dangerous causes of a malfunction is a violation of the mobility of the fuel rail. In particular, if it jams at the moment of maximum fuel supply, and accordingly, the regulator does not have enough force to shift it to its original position, then an emergency increase in the number of crankshaft revolutions occurs in the engine, due to which the engine “goes into overdrive” all the ensuing consequences. If the rack is “bitten” while the gear is off, then in this case it will be impossible to start the engine at all. Partial jamming of the rack leads to unstable operation of the engine and an increase in its sound output (it begins to “growl”).
When using the machine in severe frost conditions, freezing of individual parts of the pump is sometimes observed, and its partial failure. To prevent this, it is necessary to use oils and diesel fuel with appropriate temperature ratings.
On common rail diesel systems, the control valve (or SCV flow valve) can fail. Usually it is replaced with a new one. Less often, they perform an audit and replace individual parts with new ones. In particular, the valve stem and core are often replaced.
Prevention methods
As you know, it is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. In the case of engines, a similar principle works. It is important to understand that the fuel pump is a very complex and expensive unit, so listen to the prevention recommendations prepared by our company’s specialists:
- Flush the fuel system at least once a year, and clean or change the clogged fuel filter.
- Drain any remaining fuel that has settled in the tank. They may contain large amounts of impurities and combustion products, which automatically leads to filter clogging and other problems.
- Leave your car in the parking lot only with a full tank. Condensation can form on the bare walls of the fuel tank, which then enters the fuel and through it into the injectors.
- Monitor the fuel level in the tank, do not drive at a critical level.
The key factor is the correct choice of fuel in autumn and winter. It is important to understand that summer diesel fuel, even with a slight drop in temperature, rapidly loses its fluidity. If cooling continues, chemical reactions begin, causing the fuel to become waxy. Reaction products clog both filters and fuel pump channels. If during a sudden cold snap you did not have time to replace summer diesel fuel with winter fuel, at least warm up the car with a heater before starting the engine.
Another myth is the effectiveness of mixing summer diesel fuel and gasoline. This does not lead to adaptation of the engine to cold weather, but on the contrary can lead to catastrophic consequences for the fuel system. Substances have different physical characteristics - density, ignition temperature, nature of combustion, explosion hazard. It is for this reason that you should not trust refueling your car at unverified gas stations. Check the quality of the fuel and its warranties. Don't try to save money by going to cheap gas stations. Very soon, the imaginary savings will turn into serious repairs.
How to determine fuel injection pump malfunctions
Please note that it is best to test the high pressure pump on professional stands specifically designed for this purpose. They allow you to find out the operating characteristics of the pump and other elements of the vehicle’s fuel system. However, such a check is only possible in a car service center, since such a stand is specialized and expensive equipment. In garage conditions, it is possible to carry out only a partial check of the fuel injection pump and determine only the main fault, while other possible faults will not be noticed!
Checking the presence of water in plunger pairs
To do this, you need to remove the timing belt and carefully twist the pulley. If it rotates with variable force, then everything is fine and there is no water in the pump. If rotation occurs under the influence of significant force and does not occur at all, then moisture is present. This is very harmful for both the pump and the engine as a whole, since the motor will work with increased effort when starting, until it completely jams (failure).
Checking the pressure in the plunger pair
There are special tools for this - testers, for example, KI-4802 or TAD-01A. If you don’t have such a tool at hand, you can use a pressure gauge with a high measurement range. So, it needs to be screwed into the seat of the fuel pipe, or into the central hole of the high pressure pump head. With a normal running engine, pressure readings should be approximately 300 kg/cm² and above (in fact, the corresponding value will vary for different brands of cars, as well as engine operating modes). If the fuel pressure is lower, it means that the plunger pair has worn out significantly and needs to be repaired or replaced (most often).
Pressure check
Finally, the pressure in the pressure line is checked, which is an indirect check of the condition of the plunger pair. For this purpose, you will need a pressure gauge rated for pressures up to 350 bar, a connecting hose for connecting to the pump and an adapter that includes a bleed valve.
The TAD-01A pressure gauge or the older KI-4802 pressure gauge is suitable as a measuring device. If the adapter is not available for sale, you will have to make it yourself.
Of course, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the connecting thread and where you plan to screw the connecting hose. To measure, the device is connected to the central hole of the distribution block or to one of the pressure fittings.
After connecting the pressure gauge to the injection pump, rotate the pump shaft using the starter and record the reading of the dial indicator. If the device shows more than 250 atmospheres, this is normal (the pressure will be higher when the engine is running).
Injection pump repair
Troubleshooting methods for a high-pressure fuel pump depend on the type of device, as well as the cause of the breakdown. We list the most common repair measures.
Replacing the plunger pair with your own hands
Before performing an independent check (without using a special stand), you must have handyman tools and a new plunger pair on hand, as well as have experience in performing repair work. We will describe the description of checking the condition of the high-pressure fuel pump using the example of a common Bosch injection pump.
Bosch injection pump repair
It is necessary to understand that dismantling the pump depends on the specific model and even the car engine, so the procedure will be described in general terms. So, to replace a plunger pair (the most common type of repair) you need to:
- remove the terminals from the car battery;
- disconnect all wires and hoses suitable for it from the high-pressure pump;
- dismantle parts that prevent its removal from the car;
- unscrew the fasteners and dismantle the pump;
- carefully disassemble the pump, it is important not to lose small parts, and also remember the disassembly sequence (you can photograph this process step by step on your phone);
- unscrew and remove the plunger from the pump;
- clean all pump parts from dirt (you can use special carb cleaners or similar cleaners for this);
- check the rollers, bearings and racks on the pump; they should not show significant wear;
- remove the valves and the so-called “silencer” from the old plunger pair, and then install them on the new pair;
- Carry out installation work in reverse order.
Rack jamming
If you find that the rack is sticking, then the first thing to do is to find the place where it is “sticking”. This can be done by pumping up the ring gear relative to the rack in the corresponding section. If the rack does not jam, then there will be a small gap.
In this case, independent repair is hardly possible. However, in any case, it is necessary to dismantle the pump and show it to a specialist!
Preventive measures
As you know, prevention is the best repair, therefore, to save money and ensure normal engine operation, it is advisable to carry out simple preventive measures that will help extend the life of the high-pressure fuel pump. In particular:
- flushing the fuel system should be performed approximately once or twice a year;
- be sure to change the fuel filter on time (it is not advisable to clean it, because small particles of dirt will most likely remain on the filter);
- use high-quality fuel (at any gas station there is documentation indicating how long ago the fuel was delivered, as well as information about its composition, tolerances and seasonality );
- in winter, it is important to use winter diesel fuel, or to lower the freezing point (increase fluidity) of diesel fuel, you can use special compounds - antigels;
- it is advisable to leave the car for long periods of time (especially in cold weather) with a full tank, since moisture condensation forms on the inner walls of the tank overnight, which flows down and mixes with the fuel; instead, you can use the moisture removers mentioned above;
- do not allow the fuel level in the tank to drop critically;
- in winter, it is imperative to warm up the engine for several minutes before driving, taking into account the coolant temperature and oil pressure gauge readings;
- use special lubricating additives for diesel fuel if there is a suspicion of low quality diesel fuel.
The measures listed above will contribute to the normal operation of not only the high-pressure pump, but also the entire fuel system of the car as a whole.
Why should you contact us?
Experience in the diesel engine maintenance and repair market shows that the fuel pump is one of the most vulnerable and sensitive elements of the engine design. It is important not only to monitor suspicious symptoms from the power unit, but also to pay due attention to the maintenance of the injection pump. Such serious work can only be entrusted to experienced and trusted specialists. Our technicians have been specializing in the repair and maintenance of diesel engines for many years. We are well aware of the design and maintenance features of units of different years of production. We have high-precision diagnostic equipment that will help you quickly identify the problem. Here are a few more arguments in favor of service at Diesel-Master:
- Repair within 1 day.
- Convenient location.
- Guarantees for all types of work.
- Use of certified equipment and original spare parts.
To become our client, fill out an application on our website or call us at +7 (921) 932-25-54,, 8 and choose a convenient time for your visit. If you have any questions regarding our work, you can ask them directly on the website - our specialists will contact you in a short time and provide all the necessary information.