The stabilizer link is one of the elements of the car suspension that belongs to the stabilizing system. The main operating mechanism of this system is the anti-roll bar (SST), which is necessary to prevent the car from tipping over and turning over during sudden maneuvers: braking, turning, etc.
Why change stabilizer bushings?
Stabilizer bushing
absorbs vibration from suspension components, thereby making the vehicle ride more smoothly and reducing noise.
The bushing
is an elastic part made of rubber by casting.
Interesting materials:
Who produces the Chevrolet Lacetti, country of origin? Who takes the original European protocol? Who is doing artificial intelligence? Who does the sewerage? Who handles off-street parking? Who fills out a receipt for receiving money? Who knew about Batman's identity? Who called 994? Where does antifreeze go if there is no leak? Where does fat disappear when we lose weight?
The purpose of the stabilizer bar in the car suspension
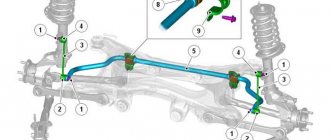
The front and rear stabilizer struts (they are also called rods, bones, less often - links) are hinged elements located at the ends of the stabilizing beam and ensuring their connection with the moving parts of the suspension (knuckles, hub, levers). With their help, the body and suspension of the car seem to be connected into one whole, while the dynamic characteristics of the car are improved.
In previous generations of cars, the anti-roll bar (anti-roll bar) was rigidly attached to the lower control arms. In such mechanisms, there was no need for stabilizer struts - its ends were pressed with brackets, and vibrations were damped by rubber bushings.
In a modern chassis, it is impossible to rigidly secure the SPU; in it, the fists and hubs turn simultaneously with the wheels.
In addition to providing a movable connection, the stabilizer struts have another important function - due to their mobility, the assembled SPU turns out to be slightly twisted, which increases its rigidity, and when cornering, the efficiency of the stabilizer increases.
Stabilizer malfunctions, their symptoms, condition check
Video: Knocking in the front suspension is the most common cause
But stabilizer struts are additional elements in the suspension, and not of a simple design. Therefore, they are an additional place where malfunctions can occur.
If you look at the VAZ-2108 element, rubber bushings are used in the design. During operation, rubber is exposed to various negative influences, which leads to its “aging” (decreased vibration properties, shrinkage, cracks).
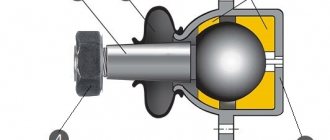
On the same racks where ball joints are used, they are the weak point. Over time, wear appears between the ball pin and the joint body, which causes a gap to form between them.
All these malfunctions have obvious signs:
- The appearance of knocking noises when overcoming bumps on the road;
- Increased car roll when cornering;
- The car “floats” on the road (the car spontaneously pulls to the side).
It is not difficult to check the condition of the stabilizer struts, and it does not matter what design it is. To do this, you only need a mount and an inspection hole. If you check on a VAZ-2108, then it is enough to swing the stabilizer near the rack with a mount. Its significant amplitude of vibrations and knocking indicate severe wear and the need for replacement.
As for checking Focus 2, you need to swing the stand itself. Ease of movement and knocking in the hinges will be a signal of their severe wear. But at the rear of this car you need to swing the stabilizer itself.
Malfunctions in the operation of stabilizer struts
Causes of breakdowns
The stabilizer link works on the principle of a damper, dampening high multidirectional forces. Under the constant impact of impacts, when passing through various irregularities, the hinge joints are gradually destroyed and the parts become unusable. There are a number of main reasons why racks have to be replaced:
- Poor quality of road surface, potholes, speed bumps.
- Careless or extreme driving, sudden turns and braking.
- Low quality of the racks themselves, use of cheap components instead of high-quality lubricant (many manufacturers use useless technical petroleum jelly to reduce the cost).
- Lack of care. The struts, like any other part of the car, need to be looked after. To do this, you should purchase a good lubricant at the store and periodically lubricate the hinge joints.
Signs of problems
It is quite simple to determine the defects of the bones. They are especially noticeable when driving on uneven road surfaces. The most obvious include the following:
- Strong roll of the car to one side (especially when cornering).
- The appearance of uncharacteristic knocking noises when passing even small obstacles.
- The car “steers” to the side, it loses directional direction and “walks” along the road.
- The body sways a lot when braking and when cornering.
To confirm the malfunction of the racks, you can independently carry out basic diagnostics.
- Turn the steering wheel as far as possible, all the way to one side, thereby freeing up space for access to the part.
- Find the middle part of the rack and try to swing it.
- If the play is noticeable, urgent replacement is required.
Driving with damaged rods is dangerous; the car loses control, becomes at great risk of overturning, and behaves unpredictably when braking.
This is interesting: How to install a navigator on a tablet
You can replace the struts at a car service center, or you can do it yourself; even a novice car enthusiast can do this process.
What are shock absorber struts used for?
The main task of the stand
– maintain the weight of the car, maintain the desired orientation of the wheels in relation to the body, transfer the adhesion forces of the tires to the road surface to the body.
Thanks to the durable body and reinforced rod, the rack
is capable of taking significant lateral loads.
Interesting materials:
How to pick up goods from Ozon Box? How to pick up a driver's license after revocation? How to book a taxi with Uber? How to cross out text in VK 2022? How to repair a side cut in a tire? How to enter a roundabout and which turn signal to turn on? How to enter the ring according to the rules? How to enter the ring? How to enter the parking lot in front? How to load a farm in Hay Day?
Stabilizer link design
Main elements of the stabilizer link
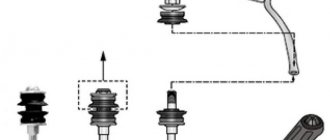
The anti-roll bar strut is a metal rod, 5 to 25 cm long (less commonly, a metal plate acts as the central part of the strut), with fasteners at the ends. The latter can be made either in the form of eyes with bushings, or in the form of hinges.
Types of racks
The rods differ depending on their location (on the front or rear stabilizer), as well as on the type of combination of fastening elements.
There are combinations of hinge - bushing, bushing - bushing, hinge - hinge, hinge - thread.
The rear stabilizer link is usually shorter than the front. Modern car manufacturers give the highest priority to racks with two hinges at the ends.
The articulated front strut has three versions:
- with two hinges at the ends, located symmetrically;
- with a ball pin installed on one end of the post, and with a thread on the other;
- with two hinges at the ends, rotated at a certain angle from each other.
This is interesting: Internal CV joint on Nissan cars: Almera, Primera, X-Trail
The hinge joints are protected with rubber boots coated with a special lubricant. It softens the operation of the components of the mechanism and extends its life.
Symmetrical struts fit equally on the left and right sides of the axle; other types of struts are strictly individual, each designed for a specific wheel, which must be taken into account during repairs.
Location of the part in the car
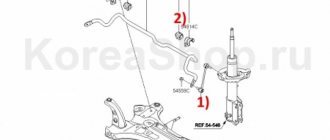
Stabilizer struts, as mentioned above, are located at the ends of the front or rear stabilizer and connect it to the moving elements of the car’s suspension, therefore, you need to look for them directly at the wheels of the car, from the inside.
Replacing stabilizer struts
To replace the bones with your own hands, you should purchase the necessary tools:
- Jack.
- Spray WD 40.
- A set of keys, a head, ratchets (for the lower bone), a spanner (the size of which can be found in the instructions for the car).
- Wheel chocks.
- Actually, the racks themselves.
Usually the rods are changed in pairs
The procedure for replacing the front stabilizer struts:
- Apply the hand brake and install wheel chocks under each wheel.
- The front part of the car is raised with a jack.
- The connecting elements are treated with WD-40 spray.
- A hexagon or ratchet head holds the axle shaft (from the end).
- The rod securing nut is unscrewed and the old part is removed.
- The installation site is cleaned and a new rack is installed.
- The nut securing the bone is tightened.
- The car is lowered.
- The nuts are tightened completely.
Replacement of the rear pillars (if they are provided for in the design) is carried out in a similar way.
After a run of two to three hundred kilometers, it is necessary to check and tighten the fastening nut.
How to “extend” the life of stabilizer struts: useful tips
According to many manufacturers, the service life of the struts is about 100 thousand km. For our roads, these figures, unfortunately, are not relevant, and sometimes decrease by one and a half to two times. But there are still a number of ways to make the bones last longer:
- On roads with poor surfaces, you must drive with extreme caution. Potholes and bumps are the main enemy of the suspension; when moving quickly over them, the entire car as a whole suffers, and it is the struts that take on most of the load.
- No matter how high the speed is, it is better to slow down when entering turns. This is safe and will significantly extend the service life of the stabilizing system.
- Buy a good lubricant for the hinges and a syringe, lubricate the joints periodically.
- Keep an eye on the anthers. Their tight fit to the hinges will protect them from moisture and prolong the life of the rack.
- Don't save extra money. It’s better to buy high-quality spare parts once than to change the bones every 10 thousand km.
What is a stabilizer bar used for?
To combat these rolls, an anti-roll bar is included in the suspension design. It looks like a bent U-shaped rod made of spring steel. Its ends are connected to the suspension elements, while in the central part it is screwed to the car body.
Its functioning boils down to the fact that when rolls occur, the stabilizer twists, which creates a force counteracting the roll, since the springy steel tends to take its original position when twisted. That is, this suspension element cannot eliminate the occurrence of rolls, it only reduces it.
The stabilizer is applicable only on independent type suspensions. Therefore, on most cars only one stabilizer is used - in the front suspension. This design, for example, is used on all cars of the VAZ family, starting from the VAZ-2101 model. Not so long ago, they began to install a stabilizer in the rear suspension of cars that use an independent type. The rear stabilizer is used on such foreign cars as Ford Focus 2 and higher, Mitsubishi Lancer 9, Nissan Primera, etc.
Rear pillars
On those cars that have an independent rear suspension, there are also struts, and of different shapes. For example, on a Ford Focus it is a regular bolt and nut with rubber bushings on them. This bolt is installed in the rear lower control arm. The stabilizer is fastened using an eyelet made at its end. To eliminate the appearance of knocks and the transmission of vibration between these elements, damper bushings are needed.
Some cars use L-shaped rear pillars (Mazda 3). In general, the design of the strut and its shape directly depend on the layout of the suspension itself and the position of the stabilizer in it. It doesn’t matter whether it’s front or rear suspension.
It is noteworthy that some cars use non-interchangeable struts, that is, for example, the right element cannot be installed on the left side. But there are also universal ones, and such a rack can be installed on any side.
That is, stabilizer struts have very different shapes, dimensions, mounting points, but they all perform the same tasks.
Something else useful for you: