Strengths and weaknesses of the device
The main advantage of the carburetor is its affordable maintainability. To this day, there are special repair kits on the market that allow you to return the carburetor to operation quickly enough. Repairing a carburetor does not require an arsenal of any special equipment, and almost any motorist can repair the device if they have certain skills.
A mechanical carburetor is not so afraid of dirt and water, since their entry cannot completely damage it. This simultaneously conceals both the strength and weakness of the device. The carburetor needs to be adjusted quite often and must be cleaned compared to fuel injection, but it is more durable than electronic solutions when a number of conditions arise that are considered difficult or even extreme operating conditions.
Advantages and disadvantages of using carburetors
The advantages of carburetors include the high homogeneity of the mixture at the outlet; low cost and technological accessibility during production; comparative ease of maintenance and repair, maintainability without the need for special equipment. Unlike an injector, which requires electrical power, the operation of a carburetor occurs solely due to the energy of the air flow sucked in by the engine.
The main reason for the displacement of the carburetor from the automotive power system was the inability to provide a fuel-air mixture of an individual composition for each of the outbreaks. And the injection system with distributed injection operates in exactly this way, stably ensuring economical and environmentally friendly engine operation.
5 / 5 ( 1 voice )
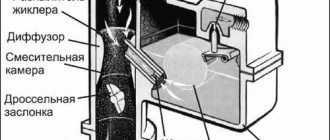
Mixing chamber. Dosing systems, economizers, ecostats
The mixing chamber ensures that tiny drops of gasoline, this “fog,” are mixed into the passing air stream. This function is performed by a diffuser - a specially narrowed section of the chamber. Thanks to this diffuser, the air passing through it is significantly accelerated. The movement of air during acceleration in the diffuser ensures the formation of a vacuum in the spray tube. Because of this, gasoline is constantly added and mixed into the passing stream.
The engine operates in various modes during operation. Therefore, fuel-air mixtures require different compositions, including those with a sharp change in the content of gasoline vapor fractions. To prepare a mixture of different concentrations, optimal for different engine operating modes, “advanced” carburetors are equipped with dosing devices. They come into operation or turn off at different times, or work simultaneously, providing the most optimal mixture composition for obtaining the best combination of power and efficiency in all engine modes. These metering systems are based on pneumatic compensation of the fuel-air mixture.
Economizers and econostats are additional parallel systems for supplying fuel to the mixing chamber. They enrich the air-fuel mixture only at high vacuum levels (i.e., close to maximum loads), when an economically generated mixture cannot meet the engine's needs. Economizers are equipped with forced control, pneumatic or mechanical.
Econostats are simply tubes of a certain cross-section, in some cases with emulsion channels, led into the space of the mixing chamber above the diffuser - into the zone where vacuum appears at maximum loads.
Device
Solex carburetors are manufactured for installation on 1.5-liter engines of VAZ cars.
Differences between SOLEKS and DAAZ:
- presence equipped with a solenoid valve that regulates the fuel supply at idle
- the presence of a heating system for the air-fuel mixture, which is connected by hoses to the engine cooling system.
The carburetor consists of a cover and a body, which includes:
- float chamber
- starting system
- idle system with electromagnetic valve
- main dosing system
- transition system
- econostat
- economizer with accelerator pump.
Tuning
The modernization is carried out in order to increase operating efficiency and to increase the power of the entire power unit. There are the following tuning options:
Replacing the valve needle and setting a new level in the float chamber. By performing this action, you can ensure more stable operation of the carburetor. We should not forget about preventing the appearance of an over-lean fuel mixture in high-power modes. By using a rubber locking needle, stable maintenance of a certain speed level can be achieved.
Solex carburetor disassembly diagram.
Throttle sawing. It is necessary to make the correct selection of cross-sections of the remote sensing holes, namely slightly smaller than optimal. When performing this action, CO2 emissions are reduced and gasoline consumption is reduced by approximately 2%. The idle mode will also undergo changes - there will be a more uniform division of the air-fuel mixture among the cylinders.
Diffuser polishing. This procedure is designed to reduce aerodynamic losses and increase flow speed.
There is also the option of independently upgrading the SOLEX carburetor. Its essence lies in smoothing corners, boring and grinding surfaces. The operation is carried out in the following sequence:
- dismantle and disassemble the carburetor
- separate the upper part of the carburetor from the body, clean it, rinse it and blow it with compressed air
- take out the throttle shaft and grind it off
- We disassemble and clean the lower part of the carburetor
- remove the dampers with axles
- We round the axis of the air damper
- We assemble the throttle mechanism and grind off all sharp corners and irregularities
- we install the accelerator pump tubes in both chambers
- Using sandpaper we smooth out the unevenness of the mixing chamber.
Carburetor of an internal combustion engine
See also the article about injection engines.
A standard carburetor has an air diffuser, which is designed as a tapering carburetor neck. The air passing through this constriction creates a reduced pressure. A hole with a small diameter through which gasoline is supplied is specially placed in this place. Ambient air pressure forces gasoline from the float chamber to exit into this hole in the air neck, then the fuel is sent to the intake manifold and then to the working area of the cylinders.
Since the engine operates over a wide speed range, it requires a different mixture composition, also in winter, when warming up, idling, in the medium speed range and under high load. Carburetors are equipped with various systems that help it do its job in various conditions. In addition to the components that will be described below, there are some components, including solenoids for stopping fuel injection and pressure drop dampers used in special cases. These parts are placed for various reasons and their removal can significantly affect the normal functioning of the engine.
Principle of operation
It is very difficult for a cold engine to start on a conventional air-fuel mixture. To alleviate this suffering, it was necessary to enrich this mixture.
To do this, a manual choke was installed in the carburetor, which was connected to a handle in the cabin using a cable. With the handle fully pulled out, the valve is closed, the mixture is rich. That is why it was possible to flood the candles. When we remove the handle, the damper opens, gradually normalizing the mixture.
We recommend reading: How did I fill 22 liters of AI-95 for 100 rubles? Sharing a secret
Classification of carburetors
- In the direction of flow of the fuel-air mixture - vertical and horizontal.
- According to the method of adjusting the nozzle cross-section and the formation of vacuum - with constant vacuum (the newest and most advanced carburetors made in Europe and Japan); with a constant nozzle cross-section - all serial carburetors up to the latest generations of these devices, including all those mass-produced in the USSR; with spool throttling - for the most part, horizontal carburetors for motorcycles, in which, instead of a throttle valve, the amount of mixture supplied is controlled by a slide valve.
- According to the number of mixing chambers – single-chamber and multi-chamber. It makes sense to use “double” carburetors, for example, on engines where the cylinders are located quite far from each other. Then each half injects the fuel-air mixture only into “its” cylinders. In addition to “paralleled” two- and four-chamber carburetors, there were also serial three-chamber carburetors (for example, “K-156” for the 3102 Volga). The 1st and 3rd mixing chambers were working in parallel here; they supplied the mixture to the 2nd – “pre-chamber”.
Why do you need a suction
From owners of gasoline vehicles equipped with a carburetor, you can hear the word “choke” or “choke”. Let's figure out what it is.
A little theory
Most internal combustion engines are designed to operate at temperatures around 90 degrees Celsius. This temperature regime is optimal for the engine, in which all temperature gaps are minimal, and the engine efficiency reaches its maximum.
But if the engine sits idle for several hours, it cools down to ambient temperature. Thermal clearances in a cooled engine are far from ideal, the oil is thick, the fuel evaporates worse and the engine does not “pull”.
To compensate for the loss of power and to reach operating mode faster, the engine requires an enriched fuel-air mixture.
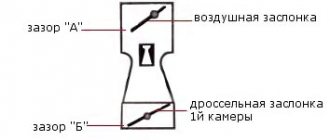
To enrich the mixture for stable operation of a cold engine, an air damper was invented. When the engine is warmed up, this damper should be open. When starting a cold engine and when it warms up, the damper is closed (or not closed completely).
Due to the fact that the damper is closed, less air enters the carburetor. In some carburetors, air passes through special channels. Once there is less air, the percentage of fuel in the mixture increases, the mixture becomes “rich”.
As technology improved, people tried to automate the process of starting and warming up. Designers have come up with enrichment devices that operate automatically.
For example, Honda mopeds have an electric enricher. It closes the additional gasoline supply channel using a needle as the engine operates.
In modern injection engines, the mixture composition is maintained by a computer, so a separate damper is not needed.
How to use the suction correctly
The air damper is mainly needed to start a cold engine. It is located on the left side of the moped and looks like a long curved lever.
The damper has only two positions:
- the damper is open - this is the working position, the damper lever is lowered down,
- The throttle is closed - this is the position for cold starting the engine. the throttle lever is raised up
How
The sequence of actions is quite simple:
- close the air damper completely (lift the lever up)
- turn on the ignition and start the engine
- let it work a little with the damper closed (literally 10-15 seconds)
- open the damper (lower the damper lever)
- let the engine idle for another minute (at this time I usually unfasten the moped, put the chain in the trunk, unlock the steering wheel, put on a helmet and gloves)
- remove the moped from the stand and you can start moving
Many moped owners complain that the moped will not start without a choke. I consider this to be normal (for a cold engine). This means that the carburetor works economically and does not waste gasoline.
It’s another matter if a moped with a warm engine refuses to move without suction. This indicates either a malfunctioning carburetor or a problem in the engine. In a properly warmed-up moped, the air damper should be fully open when moving.