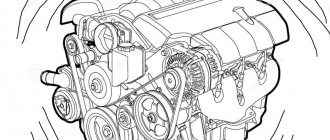
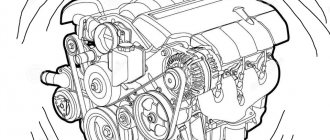
Internal combustion engines require a mixture of air and fuel to operate. The flammable compressed mixture pushes the pistons, which turn the crankshaft, and the car begins to move. Air enters the engine through a small throttle valve. And to control auxiliary devices, a vacuum is created.
Air leaks and its symptoms
The phenomenon of suction is associated with the penetration of air into the fuel tract of the machine.
It leads to a lean mixture and, as a result, greatly affects the operation of the engine, reducing its power and causing interruptions in operation. If air leaks occur in the intake manifold, the symptoms of the VAZ 2114 may be as follows:
- unstable idle speed;
- engine tripping;
- “sagging” during acceleration;
- increased gasoline consumption;
- difficult starting even at high air temperatures;
- a sharp drop in power (especially at speeds below 3,000 min-1).
If the engine stalls very often, this may also indicate that there is an air leak in the VAZ 2114. You can additionally verify the presence of this problem by using a car scanner. The presence of suction may be indicated by errors P0171 (very lean mixture) and P300 (misfire observed).
Stable engine operation at high speeds does not at all indicate the absence of suction, since it is most clearly manifested at low speeds. It is worth remembering this so as not to be misled and start looking for other causes of problems.
As soon as you notice that there are signs of air leaks, you should immediately begin searching for a possible place where it has entered the system.
Revealing
Let's look at different ways to detect air leaks into the engine through the injectors.
Spraying
Signs of suction are determined by spraying water (using a syringe) onto the hoses of a running engine. Liquid getting into cracks, holes, cracked hoses or a broken gasket causes a decrease in engine speed.
Another similar method is used to irrigate the same segment of nodes with ether, which leads to an increase in speed
. So, when identifying leak points, you should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the engine. To find the location of the leak, you can use the measurement of the degree of vacuum behind the throttle. In this case, the removed hose is connected to the throttle valve control element.
Video about identifying leaks using the spraying method
Smoke or steam generator
The duct locations are identified by a so-called steam generator, which is capable of detecting any breakdowns, cracks, or holes. An analogue of this device, often used by specialists, is a smoke generator.
The device detects leaks in internal cavities where there is air. Closing the throttle valve with some kind of plug, connect it to the intake manifold. Streams of smoke begin to leak through leaks and cracks.
Checking air leaks using a smoke generator
The device also checks for leaks in the exhaust system by plugging the exhaust pipe of the muffler. This is achieved by setting the piston of any cylinder to TDC
and the belief that valves are blocked. In this case, the smoke, having passed the open valves, flows into the exhaust system, revealing defects in the density of this area. For this purpose, the engine is started and in idle mode the possible appearance of a hiss or a specific whistle is heard.
Video about checking air leaks using a steam generator
Possible faults
Knowing possible areas of leakage, faults are identified:
If you do not hear any sounds, you can begin the process of pinching the hose going to the intake manifold.
The pinch operation is performed only with round nose pliers to avoid damage to the working sleeve.
By squeezing the sleeves of the VUT (vacuum brake booster) or mixture pressure regulator, you can hear stable engine operation. When you remove the tool (pliers), you feel a drop in speed. This defect indicates the presence of holes or cracks in the hose being tested.
. There may be malfunctions of the amplifier or the adsorber valve.
How does air leakage affect the operation of the internal combustion engine?
For reliable operation of the internal combustion engine, a sealed air intake system is needed. This is necessary for accurate preparation of the fuel mixture. The engine control unit prepares the air-fuel mixture based on the readings of the mass air flow sensor (MAF). The air passing through the mass air flow sensor is counted and transmitted to the control unit, which sends a signal to the injectors and opens them and keeps them open until the required amount of fuel is supplied to create the correct mixture. This operation of the internal combustion engine is correct, but when unwanted air leaks appear in the engine after the mass air flow sensor, its volume increases.
It turns out that the air flow sensor transmitted readings to the ECU about the same amount of air passing through it, but in fact, due to suction, the air volume is much larger than it should be, but the ECU does not know about it. Because of this, the fuel mixture is formed incorrectly.
Signs of air leaks
Incorrect formation of the fuel mixture leads to unstable operation of the internal combustion engine and with this problem the following symptoms are observed:
- Difficulty starting the engine when cold after a long period of inactivity;
- Unstable idling, speed jumps from 500 to 2000 rpm are observed;
- Increased engine vibration at idle;
- Loss of power and former dynamics of the car; to accelerate the car you need to press harder on the gas pedal;
- Fuel consumption increases;
These signs indicate a problem with the vehicle and require a quick solution to the problem. It should be noted that these symptoms can arise for other reasons, but checking the engine for air leaks is one of the number one points in solving problems in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Places where there may be suction
Air leakage can be anywhere where it passes to the combustion chamber, be it the intake corrugation or the receiver. There are several places where system depressurization occurs quite often.
Places of possible suction:
- Joints of the corrugation with the sensor and throttle assembly;
- Idle air control;
- Small breather;
- Vacuum brake booster;
- Absorber tubes;
- Injector rings;
- Intake receiver gaskets;
On cars with electronic injection
There are much more possible places for suction here. The most harmless and easily detectable air leak can form immediately behind the mass fuel flow sensor - in the cracked corrugation that goes from the air meter to the throttle. If the leak is in this exact place, it can be called luck, because such a defect can be detected visually and can be easily eliminated.
But air can be sucked in not only from the corrugation, but also from under the intake manifold gasket, and such suction can sometimes be noticed only when dismantling the manifold, and sometimes it is not visible even after removing the intake.
Air can be sucked in from vacuum hoses that have broken off the intake manifold. And it can also be very difficult to notice a small hose that has fallen out of its place of attachment.
In most cases, leaks can be detected using a smoke generator. But not always. This concerns suction from a faulty fuel tank ventilation valve. In this situation, unaccounted air will be sucked into the leak from the internal ventilation line of the fuel tank.
And if the intake manifold and fuel injector seals have already been replaced, all vacuum hoses have been checked, but the symptoms of air leaks do not go away, you should check the fuel tank ventilation valve. After all, if it has oxidized and is stuck in the open position, unaccounted air will constantly be sucked into the engine through it. This will lead to a lean mixture, loss of power and unstable engine operation.
The purpose of the fuel tank ventilation valve is to release excess gasoline vapors into the intake manifold, and if it gets stuck in the closed position, the plastic fuel tank may even crack (cars with such a defect are identified by a hissing sound when the fuel neck is unscrewed).
But bleeding occurs only occasionally, with mandatory preparation of all machine systems by the electronic unit. Therefore, the operation does not affect the stable operation of the engine. If the valve is stuck in the open position, it is through it that air will be sucked in.
A working valve will be closed when the engine is not running, so it can be removed and simply blown out. After this, you should connect 12-volt power to the valve contacts and just listen to whether the valve is opening/closing. Sounds indicating the functioning of the valve when it is directly connected to the battery indicate that the valve is working normally and the problem is not in it.
Symptoms of air leaks in the intake manifold of a VAZ 2114
All car engines, regardless of their type (with an injector or carburetor), operate on a mixture of fuel and air. The ratio of these components in the mixture is precisely calculated and regulated either electronically or mechanically.
But, sometimes it happens that additional air leaks occur, the mixture is “diluted” and the motorist can observe a serious loss of power in his car (which is especially noticeable at low speeds). We’ll talk about why this happens and how to correct this situation in today’s article.
Diagnostic methods
The engine's refusal to idle is a consequence of a lean mixture, caused by excess air in the fuel line.
This is accompanied by:
- Rusty fuel supply pipes.
- Fuel hoses that have dried out as a result of long use and are no longer held in place by clamps.
- Fuel filter with seal defects.
- Exhaust pipes that have lost their seal.
- Injection pump seals.
- Air entering through the manual lever of the fuel pump.
- Fuel pump seals.
- Obsolescence of seals.
First way
Diagnosis of the defect involves turning off the fuel pump and powering it from another vessel (for example, a plastic canister). Independent work will require a 3÷4 liter container, two transparent hoses, one meter long, and a pair of clamps. Observing cleanliness measures, the forward and return fuel lines from the injection pump are replaced with transparent tubes, and the air is removed from it.
One of the ways to remove suction is to clean the place of work and the location of the tank above the fuel pump. It is necessary to unscrew the “return” bolt, through which, according to the principle of a siphon, air escapes before fuel appears. The fitting bolt returns to its place. Running the engine for a few minutes removes any remaining air.
Video about diagnosing the fuel pump for air leaks
Second way
It consists of testing the fuel filter (standard), placing it below the injection pump
. The method is focused on determining suction through a filter. If there is no result, all tubes, tank, and hoses are checked. This method of powering gives precise indications of difficulty starting the engine.
The origin of leaks in the fuel system of cars with a diesel engine is based on atmospheric pressure. It is higher than the pressure that is created when pumping fuel from a car tank. This is due to the replacement of brass fuel lines with rubber and plastic tubes and connecting them with clamps. Meanwhile, hoses made of such materials have a shorter service life. Reference is made to the fact that synthetic pipes in the engine compartment heat up, sag, rub, and, as they wear out, contribute to air leakage.
Thus, mechanical stress, overheating, and the use of cleaning agents capable of softening non-metallic materials and hermetic compounds can be attributed to the root causes of suction.
Video on how to eliminate air leaks from a fuel filter on a diesel engine
5 minutes to read. Published 08/01/2019
Internal combustion engines require a mixture of air and fuel to operate. The flammable compressed mixture pushes the pistons, which turn the crankshaft, and the car begins to move. Air enters the engine through a small throttle valve. And to control auxiliary devices, a vacuum is created.
“Suction” of foreign air into the carburetor
When foreign air enters the carburetor, the fuel mixture entering the car's engine cylinders becomes depleted.
The share of gasoline in it remains the same, but the share of air increases significantly. Such a composition simply does not ignite or ignites with difficulty and for a short time. Therefore, the engine may not start at all (either cold or hot), it may start and stall, unstable idling and “failures” are possible when starting off and in motion.
If the suspicion falls on the leakage of connections, seals and hoses, then it is necessary to check them as soon as possible.
General check for the presence of “suction” of foreign air into the carburetor
There is one effective way to check whether foreign air is being sucked into the carburetor. It is necessary to remove the air filter housing from it, start the engine, let it run for a while and then cover the top of the carburetor with your palm.
If the engine continues to operate with the air supply channels blocked, an attempt should be made to search for the location of this same “suction”.
If the carburetor stalls, look for the cause of the malfunction in something other than the “suction” of foreign air. Of course, this check does not claim to be exceptionally accurate, but in some cases it can help.
Possible places for foreign air to enter the carburetor
— Check how tightly the carburetor solenoid valve or the idle air system fuel nozzle holder is inserted in its place.
For a number of reasons, they sometimes get twisted and even lost. It is necessary to tighten the valve or holder, and if the engine begins to operate normally, by screwing or unscrewing the solenoid valve we achieve stable idle speed.
The fuel jet holder (on some carburetors is installed instead of the solenoid valve) must be screwed in with a little force.
solenoid valves for carburetors 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex and 2105, 2107 Ozone
It is also necessary to check whether the rubber sealing ring on the solenoid valve is damaged.
— Check the presence and condition of the rubber o-ring on the fuel mixture “quality” screw.
The image shows, as an example, a screw for adjusting the “quality” of the fuel mixture at idle speed of a 2107 “Ozone” carburetor with a rubber o-ring.
screw for adjusting the “quality” of the fuel mixture of the carburetor 2105. 2107 Ozone
— Check the tightness of the vacuum hoses
— From the ignition distributor (distributor) to the carburetor.
— From the vacuum brake booster to the intake manifold.
— Crankcase ventilation hose It is necessary to ensure that they are tightly seated on the fittings and that there are no cracks, cuts, punctures or abrasions.
Pinch the hoses near the carburetor fittings one by one and try to start the engine. If the air leak is blocked in this way, the engine will work normally. The image shows the location of possible “suction” of foreign air into the carburetor 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex.
places of possible “suction” of foreign air into the carburetor 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Check the tightness of the gaskets under the carburetor and intake manifold
If no gaps are visible visually and the whistle of sucked air is not audibly heard when the engine is cranked with the starter, then we try to tighten the carburetor and intake manifold mounting nuts. The tightening torque is 13 -16 N.m for the carburetor nuts, 21 -26 N.m for the intake manifold nuts. That is, there is no need to pull too hard, especially on a warm engine.
Tightening did not help, we remove the carburetor and change the gaskets, fortunately they are not expensive.
You can cover the connections being tested with soap foam or VD-40 liquid; a window will form at the point of “leakage” in the soap foam.
Vacuum hose repair
If your vacuum hose is damaged, you don't have to buy a new one. The hose is long. You can cut off the damaged part and reattach it to the engine.
The most common damage is at the ends of the tubes. Always ensure that the clamps are tight to prevent further leaks.
After repairs, start the engine and leave it idling. Listen for any hissing sounds.
If you decide to replace the vacuum hose, use one that is similar in length and diameter. Vacuum tubes are designed for specific locations, such as the brake booster or PCV (Power Crankcase Ventilation) system.
Symptoms of air leaks in the intake manifold and check
Air leaks in the intake manifold are a common problem that manifests itself in unstable engine operation. Intake leakage leads to serious malfunctions; signs of air leakage in the intake manifold:
- the engine runs unevenly;
- the power unit shakes;
- RPM fluctuates.
However, it can be difficult to detect the area where air is being sucked in. For this reason, it is important to know how to check for air leaks in the intake manifold, as well as in the engine as a whole. Read more in our article.
Engine Inspection
To identify air leaks, you must first understand how the engine intake system works.
Air enters through the air filter. The throttle valve controls it by creating a vacuum. Know that a car is leaking air when it makes a hissing sound after starting.
Vacuum hoses wear out during operation and become brittle. This leads to their damage. Carefully inspect the hoses on the engine and replace them if necessary. The engines are different from each other. Refer to the repair manual for hose identification.
Signs of air leaks in the engine and finding the problem area
In modern electronically controlled internal combustion engines, the amount of air entering the cylinders is strictly taken into account by special sensors. But when the air flow finds an alternative path through a loose connection of parts, the normal operation of the power unit is disrupted due to a significant depletion of the combustible mixture. Determining air leaks in the intake manifold or other places is not an easy task; the symptoms that appear are too similar to many other problems. However, the problem of diagnosing this malfunction is completely solvable.
conclusions
The optimal methods for diagnosing air leaks in the intake manifold on your own remain the use of smoke and spraying the manifold, corrugations, and throttle bodies with a thin stream of flammable liquid. Good luck with your diagnostics and smooth roads!
It is necessary to repair the exhaust manifold if leaks are detected in it - cracks, fistulas, gasket breakdowns.
If there is any leakage of the exhaust system at the beginning of the tract: gasket, manifold, corrugation, flange, air is automatically sucked into the exhaust pipe due to the fact that the engine operates in cycles. A regulating lambda probe and an oxygen sensor are installed in the exhaust manifold of the muffler of all modern cars.
It reacts to the content of free oxygen in the exhaust gases / According to its readings, the control unit either enriches or depletes the mixture.
If there is a lot of oxygen, the mixture becomes richer.
When air enters from outside, the control unit always considers the mixture lean and gives the command to enrich it.
In this case, the fuel-air mixture becomes so rich that it does not have time to burn and floods the spark plugs. Fuel consumption increases, and it can be difficult to start driving at a traffic light or in a traffic jam.
Some of the unburned gasoline ends up in the muffler and catalyst.
In this case, the catalyst may melt and fail.
The exhaust manifold usually begins to crack even more due to overheating.
The lambda probe fails due to unburned gasoline and overheating.
Such a seemingly small malfunction as an exhaust gas leak can lead to big troubles.
This happens very often when a muffler is repaired poorly, the welding quality is poor, or the personnel who repaired your exhaust manifold or muffler exhaust pipe are incompetent.
Source
Symptoms of air leaks
Symptoms of engine air leaks are most often unambiguous:
- Uncertain start in the morning.
- Rough idle – idle speed fluctuates constantly and is below 1000 rpm. the engine may stall. On a car with a carburetor engine, the quality and quantity screw becomes insignificant for setting the XX mode since the air bypasses the XX channel.
- Power drop - in the intake tract on systems with MAF (mass air flow sensor) - low idle speed; on systems with a MAP sensor (absolute pressure sensor), on the contrary - increased idle speed, lambda errors, lean mixture, misfires.
- Increased fuel consumption - in order to start and continue driving, you need to constantly maintain high revs, while staying in a lower gear longer.
Signs of air leaks
First of all, uneven operation of the internal combustion engine should be alarming. Symptoms of the malfunction are also:
- startup problems;
- loss of power;
- increase in fuel consumption.
The most appropriate word to characterize engine operation is instability. This is not a clear shudder of the engine when it “trips”, rhythmically falls on one leg. This is a random oscillation, more characteristic of idling. Sudden stop. Difficulty in adjusting: I’ve just adjusted the idle speed evenly, balancing the quality and quantity of the mixture, when suddenly everything starts all over again. And this is some kind of rubber hose from shaking, it opens a crack, then becomes sealed again. Unpredictability and inadequacy are characteristic of this disease, but there is an exception to this rule.
Simple smoke generator
In general, I was standing at a checkpoint the other day. And in order not to waste time, I decided to bring to life an idea that had been exciting me for a long time - to assemble a simple smoke generator to check the intake manifold.
The only suitable tools I had were a small knife and a triangular file without a handle.
A one and a half liter plastic bottle was also emptied of water. A half liter bottle of a certain drink was also purchased, which was quickly drained by my daughter
First of all, I cut the large and small bottles into two parts. I threw away the top part of the small bottle. In total, there are two lower parts left (small and large) and one upper part. I think it's clear.
I removed the hose from the crankcase ventilation valve fitting. I made a hole in the bottle cap with a file so that the removed hose would fit into it with force. Screwed the top of a large bottle onto the cap. This is the picture we got
From a different angle
Everything turned out tight
Then I dug a hole in the bottoms of both lower parts. The smaller one is the same size as a cigarette, and the upper one is the same size as the hoses from the compressor for inflating the wheels.
He shot a cigarette from the driver of the next car, lit it and inserted it into the hole of a smaller bottle, and shoved the whole thing upside down into the larger bottle.
I put it all into the top of the bottle and connected the car compressor
Here is a general view of this constructor
For a long time, the drivers of neighboring cars could not understand what I was doing so diligently, although many probably did not understand
As the experiment showed, this solution has the right to life because of its simplicity and speed of assembly. I spent half an hour at most. And then, while they were buying and drinking a drink, while they were chiseling holes in the knee with a file and shooting out cigarettes
It just needs to be modernized a little. You can insert not one cigarette, but several, so that there is more smoke. It’s even better to remember your childhood and use paper soaked in silica instead of cigarettes. I don’t know about you, but in childhood we often used smoke blowers made from such paper. There was smoke...
Also, the cap on the bottle must be screwed on through cheesecloth so that the ashes do not fly into the collector.
I will further improve it. True, this copy had to be thrown away, since during the check at the checkpoint they could have been mistaken for a drug addict.
I advise you to see what interesting solution our community member Pavel used to make a smoke generator from scrap materials
List of main reasons
Reasons why idle speed fluctuates
Incorrect operation of the power unit may be caused by a malfunction of certain elements:
- Failure of sensors:
- RXX;
- DMRV;
- DPKV;
- Lambda probe;
- DSA.
- The XX solenoid valve is faulty;
- The air filter is clogged;
- Heavy carbon deposits on candles;
- High-voltage wires are damaged or oxidized;
- Air leak in the intake manifold;
- Incorrect throttle position.
Methods for checking tightness
There are several ways to check for leaks. Some are faster than others, and some require expensive equipment. Consider the following methods to find the best solution for your case.
Inspect and check for loose hoses on the engine
The first place to check for vacuum leaks is the hoses on the engine. Check for cracks or loose fasteners. Each car has a unique vacuum tube pattern. Make sure the clamps are tight enough.
Try moving the clamps from the side. If they move easily, they need to be tightened. If you still cannot determine the location of the leak, inspect the surfaces further.
Spray soapy water around the intake area
This is probably the easiest and cheapest way to check for air leaks. Spray soapy water around the intake manifold and damaged hoses while the engine is running. You will see air bubbles in the leak areas.
Watch a video on how to look for air leaks using a soap solution:
Use a smoke generator
This is the professional way. Auto mechanics use it to check air leaks within a few minutes. But this will require expensive equipment.
Spray carburetor cleaner
There are those who use carburetor cleaner to detect air leaks. To do this, start the engine at idle speed. Spray cleaner onto areas you suspect of leaks. The engine speed will begin to increase when there is air leakage.
This is because carburetor cleaner will get into the engine and burn with the fuel.
This is a dangerous method for checking air leaks. Sprays are highly flammable. Have a fire extinguisher ready!
Air leak
When a car, when starting from a standstill (sharply), begins to choke for a second, and in some cases even stalls, this is 99% air leaks. Because excess air entering the engine cylinders causes a sharp leaning of the mixture and, as a result, difficulty in ignition. The engine runs rough and may stall at idle.
In this article we will learn to determine:
Sources
- Methods for assessing conformity No. 3 2008 / Not available. - M.: Standards and Quality, 2008. - 578 p.
- Kirillov A. A. Commentary on the Federal Law of July 20, 2012 No. 125-FZ “On the donation of blood and its components” (item-by-item); Justitsinform - M., 2013. - 631 p.
- Citizen and Law No. 07/2012 / Absent. — Moscow: St. Petersburg. [and others]: Peter, 2012. - 453 p.
- Citizen and Law No. 12/2014 / Absent. - Moscow: Mir, 2014. - 300 p.
- Corporate lawyer No. 09/2014 / Absent. - M.: MCFR, 2014. - 411 p.