Video: General structure of a passenger car in 3D. How does a car work? The structure of a car engine. Internal combustion engine (ICE) in 3D. General structure of a truck. Electrical equipment of a car: structure and main malfunctions
Nowadays, a car is no longer a luxury. Almost everyone can afford to buy it. But often very few people are familiar with the structure of a car, although it is very important for every driver to know what main parts, components and assemblies the vehicle consists of. First of all, this is necessary when some kind of car breakdown occurs, due to the fact that the owner is at least generally familiar with the design of the car, he can determine exactly where the malfunction occurred. There are a huge number of different brands and models of cars, but for the most part, all passenger cars have the same design. Let's analyze the structure of a passenger car.
Suspension
Windshield
Salon
Fuel system
Body
Transmission
Engine
Wheels and tires
Headlights
A passenger car consists of 5 main parts:
- body (supporting structure)
- chassis
- transmission
- internal combustion engine (gasoline or diesel)
- engine management system and electrical equipment
General structure of the car
The main components in the design of a car, as we wrote above, are:
- Engine;
- Body;
- Chassis;
- Electrical equipment.
All of them consist of many individual elements, parts, assemblies and assemblies.
The engine is the heart of the car. It is a source of mechanical energy and sets our car in motion. The most widespread in the automotive industry are internal combustion engines and diesel engines. However, in recent years, cars equipped with electric and hybrid engines have become increasingly popular.
The car body can have a frame or frameless design. As a rule, in modern passenger cars there is no frame, and all components and assemblies are attached directly to the body. That is why such a body is called a load-bearing body - this design solution for the vehicle allows its weight to be reduced as much as possible. We also advise you to familiarize yourself with the classification of cars by body type.
The car's chassis deserves special attention. It consists of many mechanisms whose tasks include transmitting torque from the power unit (engine) to the drive wheels, moving the car and controlling it. These groups of mechanisms are called transmission, chassis and vehicle control mechanism.
- The vehicle's transmission serves to transmit torque from the engine to the drive wheels, thereby allowing the torque to change in magnitude and direction. The transmission of a two-axle car with a front engine and rear-wheel drive usually consists of the following mechanisms: clutch, gearbox, driveline, final drive, differential and axle shafts.
- The chassis of a car consists of a frame or supporting body, front and rear axles, suspension (springs and shock absorbers), wheels and tires. Read more about the types and types of car suspensions.
- The driving mechanism of a car consists of a steering system and a braking system (with drum and disc brakes). It allows you to change the direction and speed of the car, stop it and hold it in place.
In addition to the above components, assemblies and mechanisms, absolutely all cars are equipped with electrical equipment, consisting of sources and consumers of electric current.
The electrical equipment of the car starts and allows the engine to work, illuminates and heats the interior of the car, allows you to move without problems in the dark and in bad weather, supports the anti-theft system, takes care of our safety on the road, turns the car into a concert hall or even a cinema, and performs many other useful and very important functions.
Internal combustion engine (ICE)
The main element of the car. Function – sets the car in motion.
The cars are equipped with gasoline, diesel engines and electric motors.
ICEs running on gasoline or diesel consist of: a block and cylinder heads, a camshaft, an exhaust system, an intake system (for air supply), a carburetor, and an injector.
Helical locking differential
Source:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qFrORHoL9H4 Helical locking differentials, in particular Torsen and Quaife, are much more advanced. Unlike all previous ones, created on the principle of “open differential with bevel gears + locking,” these models are designed completely differently. The peculiarity is in the tricky worm gears: when the torque on one of the shafts drops, the gears begin to wedge and the torque is immediately transferred to the other axis. That is, the differential does not even wait for the wheel to start slipping - it reacts to the deterioration of traction! Moreover, the harder the driver presses on the gas, the “tighter” the connection between the shafts: in the limit, one axle can account for up to 80% of the torque. It turns out that the differential is “clamped” when necessary - at the moment of acceleration, and when the gas is released it does not interfere with the independent rotation of the shafts.
Car chassis
A car chassis is a whole system that combines mechanisms that transmit engine energy to the drive wheels. The chassis consists of a transmission, chassis and control mechanisms.
The job of the transmission is to transfer energy from the engine to the wheels. The transmission consists of a gearbox (either manual or automatic - with automatic gear shifting without driver intervention), clutch, axle shaft and differential.
Transmission
Responsible for transmitting torque from the internal combustion engine to the wheels.
In passenger cars, the transmission includes a gearbox (gearbox) and a differential. In four-wheel drive performance vehicles, the transmission system also consists of a transfer case and an all-wheel drive system.
Cars are equipped with mechanical (manual transmission), automatic (automatic transmission), mechanical automated gearboxes, and variators.
The gearbox consists of:
- Carter;
- primary, secondary and intermediate shafts with gears;
- additional shaft and reverse gear;
- synchronizers;
- gear shift mechanism with locking and locking devices;
- shift lever.
Chassis
The main function is to soften impacts when the car moves over bumps and holes, and to ensure comfort.
Chassis includes: front/rear suspension, wheels. The suspension system includes: shock absorbers, springs, levers, silent blocks, bushings. It is also necessary to add steering rods and CV joints to the front suspension.
Modern models of powerful passenger cars are equipped with independent front/rear suspension. In the independent type of chassis, the wheels are mounted separately. This allows you to achieve maximum comfort when driving on uneven road surfaces.
Differential with disc lock.
Source:
Blocking is, of course, good, but I would like to somehow automate the process so that it would activate itself and only at the right moments. One type of automatic locking differential is a disc locking differential. They are designed in almost the same way as free differentials, but the shafts in them are connected to each other through spring-loaded clutches. That is, in the event of slipping, the disc lock can add a little torque to the lagging shaft - as much as the clutches can withstand before slipping begins. As a rule, this is quite a bit, which will compensate for only a slight drop in torque, for example, when the wheel hits dusty or wet asphalt.
Control mechanisms
These devices consist of a steering system that is connected to the front wheels by steering and brakes. Most modern cars use on-board computers, which themselves control the controls in some cases, and even make the necessary changes.
Here we note such an important part as what the car wheel consists of. Without him, the car simply would not have happened. This is truly one of the greatest inventions and consists of two components: a rubber tire, which can be tubed or tubeless, and a metal rim.
Steering
Responsible for maneuverability and turning of the car. The steering wheel is turned by the steering rack.
Steering device:
- lateral thrust;
- lower arm;
- pivot pin;
- upper arm;
- longitudinal thrust;
- steering bipod;
- steering gear;
- steering shaft;
- steering wheel.
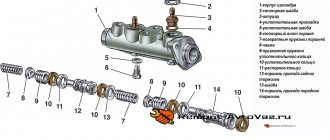
Brake system
Responsible for safety. Thanks to the brakes, the car stops. The braking system consists of : brake discs, pads, calipers, cylinders, circuits.
The higher the power of the internal combustion engine, the more powerful the braking system should be.
Brake system
The first system that allows the driver to safely drive a car is the brakes. Most braking systems use hydraulics to operate, using brake fluid.
For a passenger car, the brake system includes the following components and components:
- brake cylinders, discs, pads;
- brake pedal located in the cabin;
- hydraulic cylinder, brake system reservoir;
- vacuum booster;
- brake pipes (front, rear).
The car has three types of braking system: parking using a hand brake, medium spare, and working.
The list of car safety systems includes the brake system as the main one; body rigidity and the presence of passive safety elements are secondary.
Motor operation
To better understand the principle of operation, you need to understand in detail what a car engine consists of.
The body is the cylinder block. Inside there are channels that cool and lubricate the motor.
A piston is nothing more than a hollow metal glass with ring grooves on top.
The piston rings located at the bottom are oil scraper rings, and at the top are compression rings. The latter provide good compression and compression of the air-fuel mixture. They are used both to achieve tightness of the combustion chamber and as seals to prevent oil from entering there.
The crank mechanism is responsible for the reciprocating energy of the pistons to the crankshaft.
So, understanding what a car consists of, in particular its engine, let’s understand the principle of operation. The fuel first enters the combustion chamber, mixes with air there, the spark plug (in gasoline and gas versions) produces a spark, igniting the mixture, or the mixture ignites itself (in the diesel version) under the influence of pressure and temperature. The formed gases cause the piston to move downward, transmitting movement to the crankshaft, which causes it to rotate the transmission, where the movement is transferred to the wheels of the front, rear axle, or both, depending on the drive. A little later we will touch on what a car wheel consists of. But first things first.
Car interior or comfort zone
The interior of a modern car has a high level of comfort due to many vehicle systems. The air conditioning device ensures the creation of a comfortable microclimate inside the car, regardless of the weather outside. Some vehicle models are equipped with multi-zone climate control, which organizes the microclimate for each individual passenger.
Car seats now have many adjustments, so any driver or passenger can adjust the seats for a comfortable fit. The seats also have heating, cooling and even massage functions. Many cars are currently equipped with light and rain sensors, which undoubtedly creates driver comfort.
And don’t forget about the auxiliary systems: parking radar, surveillance cameras around the perimeter of the car, parking assistant. Multimedia devices allow you not only to listen to audio files, but also to watch videos and have Internet access; many systems have Bluetooth installed, which allows you to communicate by phone using multimedia without being distracted from driving the vehicle.
Active differentials
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Oabw1Jp5cg And finally, active differentials. The pioneer in this area is Mitsubishi, which equipped its Lancer Evolution with it. Taking a conventional open differential as a basis, the Japanese additionally connected the output shafts through two gears - high and low, the activation of which is controlled electronically using wet clutches. Thus, by using one gear or another, the computer can make one shaft spin faster or slower than another! The force, or rather the amount of torque transferred, is regulated by changing the degree of clutch slip. An active differential is installed on the rear axle of the car, giving it unprecedented stability in corners: where any other differential would have long ago “hanged” in a skid in response to adding gas, a car with such a differential is only more actively screwed into the turn. Off-road is not a problem either - if one wheel is stuck, the second one will tend to spin even faster. Below I have additionally attached a couple of pictures for clarity.
Electrical equipment
One of the most complex systems of passenger cars with many different elements and wires connecting them, entangling the entire car body, is electrical equipment, which serves to provide electricity to all electrical devices and electronic systems. Electrical equipment includes the following devices and systems:
- battery;
- generator;
- ignition system;
- light optics and interior lighting system;
- drives for electric motors of fans, windshield wipers, window lifts and other devices;
- heated windows and interior;
- all electronics of the automatic transmission, on-board computer and protective systems (ABS, SRS), engine management and others;
- power steering;
- anti-theft alarm;
- sound signal.
This is an incomplete list of devices included in the electrical equipment of a car and consuming electricity.
Every driver needs to know the structure of the car body and all its components in order to always maintain the car in good condition.
Car engine, its types
It is a complex of mechanisms that convert the thermal energy of the fuel burning in its cylinders into mechanical energy
. The heart of the car, its main unit is the engine. It is this part of the car that creates torque, which is transmitted to the wheels, causing the car to move in space. Today there are the following main types of car engines:
- ICE or internal combustion engine, which uses the energy of the fuel burned in its cylinders to produce mechanical energy;
- an electric motor powered by electrical energy from batteries or hydrogen cells (cars powered by hydrogen cells today are already available from most leading automakers as prototypes and are even in small-scale production);
- hybrid engines that combine an electric motor and an internal combustion engine in one unit, the connecting link between which is a generator.
According to the type of fuel burned, all internal combustion engines are divided into the following types:
- gasoline;
- diesel;
- gas;
- hydrogen, in which the fuel is liquid hydrogen (installed only on experimental models).
According to the design of internal combustion engines there are:
- piston;
- rotary piston;
- gas turbine.
Purpose and requirements
If the engine is called the heart of the car, then the body is its shell or body. Be that as it may, the body is the most expensive element of the car. Its main purpose is to protect passengers and internal components from environmental influences, to accommodate seats and other elements.
Car body
As an important structural element, the body is subject to certain requirements, including:
- corrosion resistance and durability;
- relatively small weight;
- required rigidity;
- optimal shape to ensure repair and maintenance of all vehicle components, ease of loading luggage;
- ensuring the necessary level of comfort for passengers and the driver;
- ensuring a certain level of passive safety in a collision;
- compliance with modern standards and design trends.
Main types
Before you understand what a car body is made of, you need to identify the main types of its design. Mass-produced passenger cars are produced in the following main types:
- sedan;
- hatchback;
- station wagon
There are other types, but these three are the main and most common.
The sedan body type is the most popular. The serial sedan has four doors for passengers, an engine compartment and a luggage compartment. This type of body is the most optimal for transporting passengers and small luggage.
A hatchback is a car with two doors for passengers, an engine compartment and a luggage compartment not shared with the passenger compartment. This type has limitations on the cargo it can carry, and is also not very convenient for transporting passengers. However, this implementation has its advantages. Cars in this type of body have a lower weight and size, which has a positive effect on its efficiency in relation to fuel consumption.
Station wagon passenger cars are designed for heavy loads. The luggage compartment of such cars is characterized by an increased volume, which does not prevent the interior from remaining at its full size. The station wagon design makes it possible to further expand the luggage compartment by folding the rear passenger seats.
Viscous coupling
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sL6Suq5rnoM The principle of operation is quite simple. With a significant difference in the rotation speeds of the shafts, the liquid inside the coupling heats up and becomes more viscous, due to which more torque begins to be transmitted to the lagging shaft. It is often used as a center differential on vehicles with all-wheel drive to connect a second axle when the wheels of the first one slip. For cross-wheel locking, it is used in conjunction with a conventional open differential. Disadvantage: prone to overheating, which is why it cannot be used for a long time.
Material and manufacturing technology
The body of a modern passenger car is made of high-strength steel, which goes through several stages of processing. The small thickness of the metal used makes it possible to significantly reduce the overall weight of the machine, which has a positive effect on its dynamics and efficiency. Despite the small thickness of the steel, the body structure is designed in such a way that it is both light and strong.
On most modern cars, body parts are joined together by spot welding. This makes it possible to ensure reliable connections between elements and reduce the number of edges and sharp corners that are most vulnerable to corrosion. In the future, the automotive industry will use laser welding of parts. This approach minimizes the presence of bulges and depressions at the seams, and the body structure will become simpler and more reliable.
Chassis
Car muffler device
This component includes many units and components responsible for the machine’s ability to move.
Modern cars, as in the photo, are increasingly front-wheel drive
The main elements of the chassis include:
- pendant;
- wheels;
- driving axles.
Most modern passenger cars have an independent front suspension, which makes the car more controllable and stable at high speeds, and makes the ride more comfortable. This type of suspension has its own mounting system for each wheel. True, such cars have less repairability than rear-wheel drive cars.
Although the rear suspension is considered obsolete, it can still be seen on many cars. It is made in the form of a beam or, if the car has rear-wheel drive, in the form of a drive axle.
General body structure
To understand what a car body is made of, you should consider the main parts that make up its structure. For a simpler understanding, the structure of the car body can be divided into three compartments. What does the body consist of? The general layout of the parts is as follows:
- motor zone - designed to house the power unit and additionally performs the function of passive safety of the car;
- passenger part - needed to accommodate passengers and vehicle controls;
- luggage compartment – used for luggage;
Let's look at what each of these elements consists of in more detail.
The motor part consists of the following main parts:
- front upper and lower cross members;
- front side members;
- lower cross member for engine location.
The layout of the engine compartment is designed in such a way that in the event of a collision, the impact energy is absorbed by the side members and the front beam. By deforming, they reduce the load on the passenger compartment. This design increases the chances of the driver and passengers to protect themselves from injury in an accident.
The layout of the parts of the passenger compartment of a passenger car is as follows:
- lower front beam under the front window;
- front and rear roof cross members;
- roof side spar;
- front, side and rear pillars;
- thresholds;
- bottom;
- bottom reinforcing structures.
In other sources, the names of body parts may differ slightly, but this does not change the essence of the matter. The above diagram allows you to understand in general terms what the body consists of and what its structure is.
All parts of the passenger compartment of a passenger car have the necessary rigidity, which ensures reliable fastening of facing and functional parts. In addition, the design of the passenger part is made in such a way as to provide maximum passive protection in the event of side collisions.
The luggage compartment of a passenger car consists of a rear panel and wings. The layout of this compartment is designed in such a way that its structure allows it to withstand the loads of useful luggage, as well as provide passive safety in the event of impacts to the rear of the car.
The structure of the body of passenger cars depends on the model, manufacturer and other parts. However, in most mass-produced cars, the arrangement of body parts is approximately the same. Only sports cars and prototypes of conceptually new models, produced in quantities of several units, have a sharp difference. The body of such cars may have a different design.
Automatic transmission
A new type of transmission, which comes in several types:
- classical;
- semi-mechanical DSG;
- robotic;
- CVT.
The automatic transmission allows you to switch gears as smoothly as possible, maintaining the integrity of the clutch for a long time. Due to this, the automatic transmission can adapt to different driving styles. And options with manual shifting give the car excellent dynamics.
The device of the machine is quite complex. It consists of a hydraulic unit, planetary mechanisms, friction clutches and other equally important elements. Various sensors perform special functions here.
The automatic transmission is controlled via a selector. Operating modes depend on the selected position: P, N, R, D. On SUVs with a large number of operating ranges, additional modes are used: S, L, OFF, etc. There are also separate buttons such as Snow, Shift, Sport. They characterize the operation of the machine depending on external conditions.
Body layout
The load-bearing part of the car can consist of a frame and body, only the body, or be combined. The body that acts as a load-bearing part is called a load-bearing body. This type is most common on modern cars.
Also, the body can be made in three volumes:
- single-volume;
- two-volume;
- three-volume.
The single-volume one is made as a one-piece body that combines the engine compartment, passenger compartment and luggage compartment. This arrangement corresponds to passenger (buses, minibuses) and utility vehicles.
Double-volume has two zones of space. The passenger compartment, combined with the trunk, and the engine compartment. This layout includes hatchback, station wagon and crossover.
The three-volume one consists of three compartments: the passenger compartment, the engine compartment and the luggage compartment. This is a classic layout that sedans follow.
Body layout
Compression stroke
Compression itself (increasing pressure in the cylinder) does not begin immediately after the piston begins to move upward. The fact is that the fuel-air mixture, with the intake valve open, continues to flow into the cylinder for some time, despite the beginning of the pressure increase. Therefore, the closing of the intake valve must be coordinated with the nature of the mixture flow at its plate.
From the point of view of the best filling of the cylinder (and, accordingly, the greatest power), at the moment the intake valve closes, the mixture at the valve should stop, i.e. at this moment there is neither direct flow through the valve - into the cylinder, nor reverse flow - out of the cylinder. Here the process is greatly influenced by the design of the intake system, rotation speed, and throttle position. In general, the higher the rotation speed and the opening of the throttle valve, the longer the intake valve should be delayed in closing, given a constant length of the intake duct.
In practice, as a rule, a compromise option is chosen, but there are designs with variable valve timing (at which the closing delay of the intake valve changes) and with variable length of the intake system channels, which improve cylinder filling and engine parameters in a wide range of modes. Compromise solutions usually lead to deterioration of engine parameters due to reverse ejection of the mixture at low speeds and “undercharging” of the cylinder (i.e., reducing the amount of incoming mixture relative to the maximum possible) at high speeds. Engines with multi-valve heads (with three or four valves per cylinder) have a smaller delay in valve closure compared to traditional designs. When the piston moves upward with the valves closed, the fuel-air mixture is compressed. In this case, the pressure in the cylinder depends on the leakage of the mixture through the piston rings and valves. Their wear or damage, as well as scratches and scratches on the cylinder surface also increase mixture leakage through the piston rings. Under the influence of friction and pressure in the cylinder, the piston rings are pressed against the lower surfaces of the grooves, and the sealing of the cylinder cavity above the piston is achieved on one side at the junction of the rings with the surface of the cylinders, and on the other - along the lower end surfaces of the rings and grooves.
Rigidity
Rigidity is the property of a car body to resist dynamic and static loads during operation. It directly affects handling.
The higher the stiffness, the better the car's handling.
Rigidity depends on the body type, overall geometry, number of doors, car size and windows. The fastening and position of the windshield and rear windows also plays an important role. They can increase stiffness by 20-40%. To further increase rigidity, various reinforcement struts are installed.
Hatchbacks, coupes and sedans are considered the most stable. Typically, this is a three-volume layout that has additional partitions between the luggage compartment and the engine. Insufficient rigidity is shown by station wagon, passenger, and minibus bodies.
There are two stiffness parameters - bending and torsion. For torsion, resistance is checked under pressure at opposite points relative to its longitudinal axis, for example, when hanging diagonally. As already mentioned, modern cars have a solid monocoque body. In such structures, rigidity is provided mainly by side members, transverse and longitudinal beams.
How to learn to understand cars, including girls
Before a beginner gets on the road, he should get a license. To do this, he needs to complete a driving course. Among the many driving schools, we recommend choosing those that will provide initial information about the structure of the car and the principles of its operation. Naturally, in order to understand what the instructor is talking about, you need some knowledge of technology.
It would be a good idea to buy books and manuals about how to build a car in a store or find books on the Internet. They are divided into two types. The first ones talk about the principle of operation of the car as a whole.
Others pay attention to the description of a specific car model
By learning to correctly identify the types of car, you can choose the car that suits you best.
When buying your first car, it is important to talk to acquaintances and friends who already have driving experience. You can take them with you to the store or car market.
At the same time, you should remember the tips you receive, as they will be useful in the future.
How to choose the right first car:
To gain new knowledge, it is also useful to look at automobile magazines and special thematic forums on the Internet from time to time. From glossy publications you can learn about new products on the automotive market. Also there you can often find practical advice from car enthusiasts on how to get out of this or that difficult situation. On forums you can make useful acquaintances with colleagues.