If the expression “the main thing is to stop on time” in everyday communication concerns moral principles, then in the context of motor transport this expression can affect the material aspect of the life and health of the motorist.
There are no secondary units in the car, but the braking system should be a priority in car maintenance and repair. In the operation scheme of hydraulic brakes, the main ones are both the main and the working brake cylinders. Let's look at the operating principle, design, diagnostics, repair and replacement of this unit using the example of a common VAZ car.
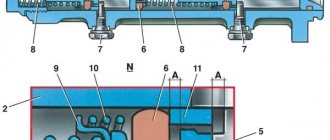
Brake master cylinder
The master cylinder is connected to the booster. This element is a housing to which the supply and return pipelines from the fluid reservoir are connected, and 3 pipelines leading to the brake mechanisms exit. There is one pipeline leading to the front brake mechanisms, and only one to the rear, leading to the regulator.
Inside this housing there are pistons that push the liquid into the pipelines. One of them is connected to the amplifier diaphragm rod. These are the main elements of the drive. The detailed design of the brake master cylinder is shown above.
Selection and purchase of GTZ
It is best to select a GTZ based on the car’s VIN code, although you can get by with the make, model and type of engine. The part does not have different options to choose from, so the only option to choose from is the manufacturer. Choose reliable brands, because the operation of the GTZ is critical to your safety. The website partreview.ru has good reviews for products from the brands TRW, ATE and LPR.
As mentioned above, sometimes you can get by by replacing parts of the GTZ repair kit. But if the housing itself or components not from the repair kit are worn out or damaged, the entire master brake cylinder is replaced.
Related terms
- ABS (Anti-lock braking system)
- Vacuum brake booster
Caliper device
Let's move on. The front axle mechanisms are disk ones, consisting of calipers with the main brake elements - pads, and brake discs.
A caliper is a body with cylinders made in it for the pistons. This model has two of them, one for each block. The support structure is shown in the figure.
The caliper pistons have the form of a glass, which is placed in their cylinders, but they can move along it. To prevent fluid leakage, the pistons are equipped with o-rings.
Pads are small metal plates onto which linings made of friction material are glued.
The brake disc is made of metal for better adhesion to the surface of the pads; its side surfaces are well processed so that there are no protrusions or shells on them.
The VAZ 2107 brakes work like this: the fluid moves into the caliper cylinders, where it begins to push out the pistons. They come out of the cylinders, pressing the pads against the disc.
Rear axle brake mechanism
The brake system of the VAZ-2107 rear axle has a different device. All its elements are hidden inside the brake drum:
The working brake cylinder of the VAZ 2107 has the following device: there is a body, also known as a cylinder, with two pistons placed in it. When exposed to fluid pressure, they come out of the cylinder.
The pads are metal, made in the shape of crescents, with friction clutches glued to their upper edge. The pads installed on the hub form a ring.
In the lower part, the pads are installed in the seats made under them, and in the upper part - in the grooves made in the pistons. To prevent the pads from moving apart spontaneously, they are tightened with springs. The parking brake mechanism is also located there.
avtoexperts.ru
The GTZ is an integral part of the brake system, which performs one of the key tasks - converting the force applied to the brake pedal to generate pressure in the system. The GTZ interacts through the “vacuum valve” rod with the brake pedal directly. The task of the GTZ is to evenly distribute pressure across all circuits.
In the photo: master brake cylinder of VAZ 2110
The brake cylinder is located on the brake “vacuum reservoir” cover. A brake fluid reservoir is mounted above it. The sections of the tank and the GTZ are interconnected by bypass holes, and are responsible for a specific section in the system. The reservoir itself is designed to replenish the loss of “brake fluid”. Visually, the tank has a transparent body, with a scale for monitoring the liquid level. In addition to the scale, sensors installed in the tank are used to signal the liquid level, displaying information on the “tidy”.
Location of GTZ
Types and design of GTZ
Structurally, gas turbine engines are divided into the following types:
• Single-circuit.
• Double-circuit.
For clarity, we will consider the design and principle of operation using the example of double-circuit GTZ. They are more popular than their predecessors. The latter were installed mostly on cars of the last century (various models of Moskvich, Zhiguli, GAZ, GAZ-53, 33 (first modification) trucks, etc. The dual-circuit system is considered more effective in terms of braking. Now it is equipped with Most of the modern cars are both domestic (Lada Kalina, Priora, “Ten” family, “Samar”, Granta, Vesta, Xray) and foreign (Renault Logan, Volkswagen Polo, KIA RIO, Hyundai Solaris, Opel Astra, Vectra, Chevrolet Lanos, Aveo, Cobalt, etc.) The advantages of a dual-circuit brake cylinder system are that if, for example, one circuit fails, the brakes on one pair of wheels are lost, but another circuit remains in the “battle” another pair of wheels, and therefore brakes, of which there are none.
Each of the circuits is responsible for a specific pair of wheels. So, if the car is rear-wheel drive, that is, there is a division, the first circuit is responsible for the front pairs of wheels, the second for the rear ones.
However, if we are talking about a front-wheel drive vehicle, then the distribution of responsibility occurs diagonally: L.P./P. Z. and P.P./L.Z.
The brake master cylinder has two main types:
• With bypass hole directly in the cylinder body.
• With bypass valve in the piston.
GTZ device
GTZ, where bypass valves are installed on the piston, are used for installation on cars with ABS systems. The fact is that in addition to bypass valves, such devices include valves to maintain excess pressure in different circuits, which is especially important when ABS is operating.
To make it clear, pistons are placed one behind the other in the brake cylinder body. The first piston is acted upon by a rod from the brake booster while the second piston is secured, essentially "free" and moved by increasing pressure or "direct" force from the other piston. In order for the pistons to “move” tightly along the cylinder, cuffs are installed at the edges. There is an additional seal in the space between the pistons. In addition, the device includes two springs, a travel stop, locking rings and a plug.
Principle of operation
From the pedal, a force is supplied to the first piston of the GTZ through the “vacuum chamber”, from which it begins to move. When moving, the holes in the cylinder are blocked, thereby increasing the pressure in the current section. Then, due to the pressure of the first section, the second piston begins to move, similarly blocking the hole of its “block”, increasing the pressure in it. When the desired pressure is reached, the machine slows down. Next, the springs “pull” the pistons back. Passing again through the same holes, the pressure decreases to its original value. Excess brake fluid used in operation is returned to the reservoir.
Operating principle of the master cylinder
In cases where there is a leak in the system of one of the circuits, the operation of the unit continues, but with some changes, including operational efficiency. If the leak occurs in the first “compartment,” then the first piston will move until it hits the second. Then, moving together until the plug, they will create pressure in the second “compartment”. But, if there is a leak in the second “block”, then the pressure in the first will not rise until both pistons meet and hit the plug. Only then will the pressure in the primary circuit increase and the brakes will apply.
Signs, malfunctions and resource
Let's talk about the signs and malfunctions of the GTZ. So:
1. Pedal dips. Serious damage is often due to the fact that the pistons do not work and, accordingly, do not generate the required pressure. As a result, the pads (especially if they are drum brakes) cannot compress sufficiently. It requires disassembling the part and purchasing the necessary spare parts or the unit as a whole.
Brake cylinder disassembled
2. Soft pedal. This often indicates that some air has accumulated in the system. The solution is simply simple - you need to bleed the system. To do this, unscrew the relief valve and press the pedal until “clean” liquid, without bubbles, flows out of the holes.
Pumping the GTZ
3. Depressurization of the cylinder. If you notice that the fluid is disappearing, the effectiveness of the brakes has decreased, inspect the outputs from the circuits, fittings, and connections. There should be no leaks, otherwise we determine what caused the leak: cuffs, elastic bands, or the body itself has cracked. If the latter, it is better to buy a new part. If there is a leak through the gaskets, then it is enough to get by with a “repair kit”.
brake fluid leaks
4. Piston jamming. Sometimes it happens that the “vacuum valve” rod breaks off during braking, and the pistons “wedge”, and therefore it is problematic to move the car. To solve the problem, you will need to completely disassemble the unit, draining the brake fluid.
5. Boiling of the brake fluid. Everyone has probably heard about routine fluid changes (depending on the class of car and model, the replacement period is about 40,000 km or two to three years). Boiling occurs due to the fact that a certain percentage of water accumulates in the liquid (usually 3-5% per year), which means the temperature load threshold decreases (from an average of 200 to 140-150 degrees). During boiling, part of the liquid, due to saturation with air, returns to the container; as a result, very little of it remains in the GTZ. As a result, “pedal failure”.
6. The cuffs are worn out, the return spring is broken. Many car enthusiasts for a long time cannot find the reason why the brakes “jam”, even while driving. As a rule, the reason lies in failed seals or springs. They begin to leak fluid, do not return the pistons to their original position, and the effectiveness of the brakes decreases. Sometimes even pieces of rubber that come off get into the channels and under the pistons, blocking their movement.
GTZ spring
7. Development of pistons and cylinder. It is not uncommon that after long-term operation, failure to replace the cuffs in a timely manner, wear forms on the pistons, as well as in the cylinder itself. The solution is to purchase a repair kit and replace the entire pistons with rubber bands. However, first check the condition of the cylinder; if it is worn out, then it is better to buy a new part; polishing and boring is not the best idea. Acceptable production is considered to be 0.15 mm.
Brake cylinder repair kit
The service life of the GTZ may vary depending on the model and make of the car. As a rule, “original” parts last at least 100,000 km, even on domestic cars. On some foreign cars, GTZs “survived” up to 250,000 km. The old Japanese models - Corolla, Land Cruiser - are often distinguished by their durability.
Conclusion
As you can see, the device is technologically quite complex, and the principle of operation seems incomprehensible to many. But, in fact, everything is simple, and the driver’s attention to this unit is required to a minimum, but still one should not forget about prevention. Change various seals, springs, in fact, these are consumables. Depending on the nature of the drive, they may not “survive” up to 100,000 km. Also, do not forget about the brake fluid replacement schedule.
Parking system
Although it engages the mechanism of the rear axle wheels, it is in no way connected with the working mechanism. It uses a cable as a drive connected to the handbrake located inside the car.
Under the car, this cable is divided into two parts, going into the rear axle mechanisms. Inside, the ends of the cable are connected to the drive lever, which in turn is connected to a spacer bar. The drive lever is connected to one of the pads.
When the handbrake is engaged, the cable pulls the lever, and since it rests against the bar, the pads are released. The toothed sector of the handbrake fixes the position of the lever when the pads are spread apart.
Where can I buy
Popular models and new items can be purchased in showrooms that sell accessories and spare parts for cars. Consultants will tell you what types of devices there are, how to choose, which company is better to buy, how much they cost, and how they differ.
If it is not possible to buy the necessary parts at your place of residence, the best inexpensive budget models can be ordered online from the online store of a manufacturer or auto parts dealer. This is available using the Yandex.Market aggregator or marketplaces that offer to purchase goods by type of vehicle, make or model of car. There are also descriptions, technical specifications, photos, as well as customer reviews. In addition, it is possible to select analogues of original parts.
In Moscow you can buy:
- GTZ at prices from 300 rubles (rear BELMAG 2105 (Bi-Bi)) to 21,992 rubles (VAG 2E0611917E (Autoperts777.ru));
- RTC - from 279 rubles (TTIALLI CF 701 (CARDONE)) to 6,597 rubles (DT SPARE PARTS 461850 (Autoperts777.ru)).
Pressure regulator
It is installed in the rear wheel drive and not only distributes fluid to the mechanisms, it also prevents possible skidding due to different forces on the mechanisms. This is done by limiting the supply of pressure to the mechanisms, depending on the position of the car body relative to the bridge.
The regulator is driven by a rod, one end of which is fixed to the rear axle, while it itself is fixed to the body. As the load on the rear axle increases, the body changes position relative to the axle; as a result, the rod puts pressure on the regulator piston, which adjusts the pressure supplied to the mechanisms.
The principle of operation of the VAZ-2107 brake system
If it is necessary to reduce speed, the driver presses the pedal. Its force is transmitted to the amplifier valve, which opens the required channel to supply atmospheric pressure to the membrane. The membrane is connected to a rod connected to the piston of the main cylinder. This rod displaces fluid into the pipelines leading to the operating mechanisms. Since the liquid is not compressed, all force is completely transferred to the mechanisms.
The liquid presses on the pistons of the working cylinders, and as they move out, they unclench (on drum bellows) or press the pads (on disk bellows) to the disk or drum connected to the wheel hubs. Due to the friction of the pads on the discs (drums), the rotation slows down.
Pneumatically driven
The last type of drive used in vehicles, pneumatic, has found greater use in trucks.
This type of work is identical to hydraulic, but compressed air acts as the working element.
The brief design of the system is as follows: there are the same drum brake mechanisms with a cam shaft. But this shaft is connected to a membrane-type working brake chamber.
Air supply lines connect to this chamber. Air pressure is provided by a compressor and under pressure it is stored in receivers.
The mechanism is controlled by a brake valve.
Principle of operation.
- The driver uses the pedal to open the air supply lines using the brake valve.
- Compressed air enters membrane-type working chambers.
- The diaphragm is connected by a rod to the cam shaft rotation mechanism.
- Compressed air presses on the membrane, which deflects and pushes the rod, which acts on the mechanism and the shaft rotates, releasing the pads.
Types of maintenance work
Despite the fact that the system is not so complicated structurally, it requires periodic maintenance, including:
- Checking the fluid level in the system;
- Checking the degree of wear of friction clutches, pads, discs, drums;
- Bleeding the system to remove air;
- Checking the condition of the handbrake cables;
- Adjustment of cable tension;
- Adjusting the rear brake adjuster;
Before each trip, you must always check how much brake fluid is in the VAZ-2107 system. An insufficient amount of it can lead to the fact that the efficiency of the system can be significantly reduced due to air getting inside the pipelines. In addition, a decrease in level may indicate damage to pipelines and fluid leakage.
The elements of the mechanism should be checked every few months, this is especially true for the pads, since they wear out quite intensively. If necessary, worn elements are replaced.
Criterias of choice
In order to avoid mistakes when choosing, you need to pay attention to the recommendations and advice of vehicle manufacturers. After all, when installing products of other types or models, deterioration of the brake system cannot be ruled out, which directly affects traffic safety. In addition, the following points must be taken into account:
- connecting dimensions - measured by eye according to the old model or using a caliper;
- sealing elements - the material of the cuffs must be elastic in any climatic conditions - severe frost or heat;
- moisture and dust protection - rubber boots prevent dust and moisture from getting inside, preventing the development of corrosion and failure of the entire unit;
- bleeder fitting – installed on the RTC to remove air from the system. Easy to unscrew and check upon purchase.
Features of the braking system
One of the features of the VAZ-2107 brake circuit is the presence of a dual-circuit system. The essence of a dual-circuit system is that the working drive is divided into two parts, each of which supplies fluid to only two mechanisms, while the circuits do not interact with each other.
The presence of two circuits ensures the operability of the brakes of at least two wheels in the event of depressurization of one of the circuits. That is, even if the pipelines of one circuit are punctured, the second will remain fully operational, which will ensure the functioning of the brakes.
In the VAZ-2107, the circuits are divided in such a way that the drive of the front axle mechanisms is separated from the drive of the rear mechanisms. This allows you not only to maintain the functionality of the system when one of the circuits fails, but also to pump each circuit separately. That is, if one of the circuits is airy, then it needs to be pumped, but it is not necessary to service the second one.
This is only general information about how the VAZ-2107 brake system works, and does not include all the details on its maintenance and repair. In general, the brakes of this car work quite well, although some elements of it cause complaints from car owners.
Why is GTZ needed?
The GTZ converts the energy of pressing the brake pedal into the energy of compression of the brake fluid. And the force is transmitted very quickly through the system.
Its task is to provide braking force in at least one of the circuits of the braking system. If one part of the system fails, another circuit always remains operational. This allows the car to brake, although not as effectively.
In modern cars, the GTZ works in tandem with the ABS system - the latter regulates the braking force on the wheels by controlling the pressure through the main brake cylinder.
Video - do you need a pressure regulator or not?
Brake cylinder
- a component of the brake system, a power organ that converts compressed air pressure into mechanical energy, which is transmitted through the brake linkage to the brake pads, pressing them against the wheel rim or brake discs.
The brake cylinder body and covers are cast from cast iron or welded from steel. Inside the housing there are: a piston with a rubber sealing collar and a felt lubricating ring, a rod, and a release spring. The rod can be rigidly connected to the piston if the lever connected to it does not transmit bending force to it, or pivotally if the lever moves in an arc. In the rear cover of the brake cylinder there is a hole for supplying compressed air and a hole for installing a pressure gauge during testing, plugged with a plug. The front cover has a hole for draining condensate, and a rubber dust washer is installed in the neck of the cover.
The brake cylinder rod output must be within specified limits. When the rod comes out less than the norm, the wear of the brake pads increases and additional resistance to movement is created; when the rod comes out more than the norm, the compressed air consumption increases and the efficiency of the brake linkage decreases. The amount of rod output is determined at full service braking. If, during a control check of the brakes at the station, the value of the rod output exceeds the established standards, the car is not taken into account when calculating the brake pressure.
Brake cylinders are designed for a maximum pressure of 0.6 MPa. The pressure in the brake cylinders of freight cars in loaded mode should not exceed 0.44 MPa, in empty mode - 0.2 MPa, in the brake cylinders of passenger cars - 0.41 MPa.