One of the main elements of a car’s ignition system, without which it is not possible to ignite the combustible mixture in the internal combustion engine cylinders, is the ignition module. By generating high voltage pulses, which creates a spark on the spark plugs, the module ensures ignition of the fuel mixture at a certain point in time.
This moment is determined by a preliminary setting corresponding to the factory parameters. Changing these parameters during vehicle operation can lead to problems in engine operation and serious malfunctions (even failure of the internal combustion engine).
Next, we will look at the design and operating principle of the module using the VAZ 2114 as an example, determine the main causes of the malfunction and how to eliminate them, and also describe several diagnostic methods.
Functions of the VAZ-2114 ignition module
The ignition module in the VAZ-2114 solves important problems in the functioning of the car:
- first creates pulses passing through high voltage;
- then transfers them to the spark plugs.
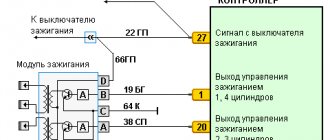
The power supply of the unit involves operation starting from the on-board system of the vehicle, the minus wire is controlled by the body of the car. The subtlety of the module’s operation is that it simultaneously produces 2 sparks, one of which occurs at the moment of maximum compression of the air-fuel mass, and the other depends on the release, which is why it is called idle.
As for the connection method, the spark plugs are connected to the 1st and 4th cylinder, and the idle sparks fit to the 2nd and 3rd cylinder structure.
Why does the MH fail?
The cause of failure of the ignition module is aging and insulation breakdown. Most often, the MZ fails along a vein of broken high-voltage wires, which causes a spark from the module to hit the housing, thereby exposing it to excessive currents.
Old spark plugs have high resistance due to carbon deposits, which can cause a breakdown in the housing, which leads to failure of the ignition module.
You should change spark plugs every 30-40 thousand kilometers, and also inspect high-voltage wires for breakdown.
What does the ignition module consist of?
The ignition module built into the VAZ-2114 consists of 2 high-power transformers and the same 2 electronic-based control units. One side of the product has 4 outputs at once; they are responsible for connecting the candles. To keep the structural components in their original form and protect them, the manufacturer provides a plastic coating. The weight of the entire structure slightly exceeds 1 kg.
The spark plugs suitable for the engine are fixed together with the ignition module by running high-voltage wiring. A device called a “controller” controls the process. First, he takes the performance indicators of the structure, then analyzes them and, finally, decides what should be changed to achieve optimal performance - the crankshaft rotation speed, the temperature reached by the coolant in the VAZ-2114, or the engine load.
Design
The design of the ignition module is quite complex, since it combines technology and electrics. The device serves to create high voltage transmitted to the spark plugs. It is this supplied current that is the basis for ignition.
The operation of the module ensures fuel combustion and, accordingly, engine operation. In very simple terms, the car won’t go anywhere without the module.
We recommend: Why is the exclamation mark on in the car and how to fix it?
For VAZ models, the use of two types of ignition modules is provided:
- Separate;
- Block.
Block ones differ in that the coils operate one per pair of spark plugs. These are the devices that are installed on the “fourteenth” model of the domestic automaker.
The coil distributes power to two candles at once, and its design includes the following elements:
- High voltage wires;
- Low voltage terminals;
- Secondary and primary winding;
- Core.
Separate modules, where the coils supply a separate circuit to each of the 4 sections, are distinguished by the output of high-voltage wires through a spring contact. Block ones are easier to check, they are easy to remove and return to their place.
It is noteworthy that with a size of 11x11x7 centimeters, this block weighs about 1.5 kilograms.
Frequent malfunctions of the VAZ-2114 ignition module
The following malfunctions occur in the VAZ-2114 ignition module:
- intermittency is formed at idle;
- power indicators leave much to be desired;
- the engine is not working correctly;
- in the paired operating mechanism, the cylinders are acting up (that is, the functioning of only one pair of cylinders can be heard);
- if the Check Engine light comes on.
If you suspect a faulty factory module in your car, then it's time to check the ignition module. It doesn’t hurt to make sure with your own hands that the wires are connected correctly and firmly; check that the spark plugs remain intact and are not damaged. Before you begin diagnostics and repair work, you need to stock up on protective equipment that will protect you from dangerous situations - the tool must be treated with insulating material, and gloves are required.
Examination
Often problems with MH begin after replacing high-voltage power wires. Many people may simply make a mistake by mixing up the connection points to the candles. The pin numbering scheme is presented below.
Also, owners of the injection-type VAZ-2114 often replace the standard wires with modern silicone analogues. This is absolutely impossible to do. Silicone high-voltage wires have significantly higher resistance. When replacing, it is also important to consider the length of each wire.
Standard wiring has the following parameters:
- The wire of cylinder 1 has a length of 56 cm and an operating resistance of 2.5 to 3.8 Ohms.
- A 44 cm long wire with an operating resistance of 2 to 3 Ohms goes to the second cylinder.
- 3 wire 36 cm long, resistance from 1.6 to 2.6 Ohms.
- 4 wire 32 cm long, resistance from 1.4 to 2.1 Ohm.
This is worth considering, since high resistance significantly reduces the spark discharge current.
Also, a problem with the ignition module may arise due to problems with the fuse responsible for its protection. The fuse is located behind the cover under the dash on the front passenger's side. This is the very first fuse located between relays 1 and 2. The element should be checked for the presence of a working jumper inside the housing. The test can be carried out visually, or using a tester in dial mode. Be sure to replace the burnt-out protective element with a complete analogue, rated 15 amperes.
It is also worth checking the incoming voltage. This requires:
- Set the tester to DC voltage measurement mode up to 20 volts.
- Connect the red test probe to the fuse terminal.
- Connect the black probe to ground.
- Turn on the ignition.
The voltmeter should give a reading equal to the battery charge. If there is voltage, it means it is reaching the ignition module.
Module
Many owners of the car described do not know how to check the VAZ-2114 ignition module using a multimeter. First you need to test the device with the engine running.
This requires:
- Start the power unit.
- Ask an assistant to keep the speed within idle.
- Wear a glove or take a dry cloth.
- Remove the power wires from the module sockets one by one.
Each removed wire must be brought to the power unit block. Without touching, a spark should discharge from the tip. A blue spark and a discharge accompanied by a crackling sound will indicate the necessary supply of discharge current. In this case, the engine should respond to the removed working wire by reducing the speed. If a wire is detected from which the spark does not come or it is quite weak, the engine speed will not change.
The previously described error codes from the on-board computer can also help in finding the wire with no spark.
For more effective testing, it is necessary to dismantle the ignition distribution device and carry out a test with a tester. This is easy to do if you follow these instructions.
First you need to dismantle the device. This is done as follows:
- Disconnect the ground terminal from the battery.
- Remove 4 high-voltage wires from the MZ sockets.
- Disconnect the electrical power plug.
- Unscrew the 3 nuts securing the module.
- Remove the device.
Next, a mandatory visual inspection of the device is carried out. The ignition module is a rather fragile device. The presence of defects on the housing, cracks and dents, can cause an internal short circuit. You also need to pay attention to the sockets for power cables. There should be no oxidation or dirt on the terminals. Any malfunctions should be eliminated by cleaning with a solvent. Next you need to check the connecting plug. Its contacts also need to be cleaned. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to check the VAZ-2114 ignition module with a multimeter.
Checking the connecting plug
First you need to check the incoming voltage to the module. This is done as follows:
- The multimeter is switched to voltmeter mode to measure DC voltage.
- The red measuring probe is connected to the incoming half of the module plug, with the central contact. It is he who is responsible for powering the device.
- The black test probe is connected to ground.
- Turn on the ignition.
The tester should show a voltage of 11.5–14 volts, equal to the battery charge.
Next, the incoming signal is checked. The voltmeter remains in the same position.
- The red probe of the tester is connected to contact “1” of the coming side of the plug. This contact is responsible for the distribution of pulse current for the cycle of candles 1–4.
- The black probe connects to ground.
- It is necessary to crank the starter a few turns.
The voltmeter should show pulse voltage. Contact “3” on the plug is checked in the same way.
Module plug
For this test, you need to switch the multimeter to resistance measurement mode. Next you need:
- Connect the red control probe to terminal “1”.
- Connect the black control probe to terminal “3”.
- The operating resistance should be within 0.5 Ohm.
In this way, both secondary windings of the ignition coils are checked. Any deviations in resistance will indicate an internal violation of the integrity of the winding.
Using the following test, the presence or absence of a short circuit is checked.
- The multimeter remains in resistance measurement mode.
- Connect the red test probe to the central contact of the plug.
- Connect the black test probe to the device body.
- The tester should not show any results. This will indicate that there is no internal short circuit. Any minimal resistance during this test is reason to replace the module.
The following check is needed to test the primary windings. The check is carried out as follows:
- The multimeter is switched to resistance measurement mode.
- Insert the red measuring probe into the “1” socket for high-voltage wires.
- Insert the black measuring probe into socket “4”.
- The operating resistance of the primary phase windings is 0.5 Ohm. Any data that differs from the nominal value can be recognized as the presence of an interturn short circuit in the primary winding of cylinders 1–4.
The test of sockets “2” and “3” is carried out in a similar way. Their operating resistance should also be 0.5 Ohm.
Additionally, you can check in the same way, but between sockets “1” and “2”. There are no internal connections between them. If there is resistance, the part is considered unsuitable for further use.
How to determine malfunctions in the ignition module at a service station
At a service station, diagnosing a VAZ-2114 factory module looks very simple - professional diagnostic equipment eliminates errors. Service station workers use an error code scanner and an application suitable for a computer diagnostic adapter. What errors are displayed on the display if the VAZ-2114 ignition module requires adjustment and repair?
- P3000-3004 – the car will not start;
- P0351 - indicates damage to the integrity of the windings of a pair of cylinders from 1 to 4;
- P0352 - determines the break in the section in the winding of 2-3 cylinders.
Symptoms of a problem
A large number of symptoms can be attributed to MH malfunctions, most often they are similar to a faulty spark plug and a malfunction of high-voltage wires.
If the following problems appear on your car, then most likely the ignition module is faulty:
- The engine is dual (two cylinders do not work at once) either 1-4 or 2-3. This is one of the reliable signs of a breakdown of the MH.
- The engine loses power and traction;
- When you press the gas pedal, jerks appear and the engine stutters;
- Difficulty starting the internal combustion engine when hot;
If such symptoms are detected on the car, it is necessary to check all the parts responsible for supplying the spark, spark plugs, wires and module.
Checking the condition of the ignition module with a multitester
In a VAZ-2114 injector with 8 valves, you can check the operation module using a multitester. All that remains is to arm yourself with a cunning device and determine the serviceability of the winding. During the procedure, follow the step-by-step instructions:
- Determine the operating format of the multitester in ohmmeter mode; it measures the resistance that occurs between the terminals of the secondary winding.
- Mount the probes by connecting the 1st and 4th cylinders to the terminals. Then fix to the 2nd and 3rd cylinders. An adequate result, indicating the absence of a breakdown in the winding, is approximately 5.4 kOhm; fluctuations in values of plus or minus 0.1 kOhm are acceptable. What you should pay attention to? The resistance between the terminals in a pair must correspond in terms of indicators to each other - be the same.
- If the difference is more than 100 Ohms, then we can say with confidence that the fault lies in the secondary winding.
How can I solve this problem? Only by replacing the ignition module.