Everyone knows that the parking brake, which is popularly called the “handbrake,” should make it possible to park a car on a 25 percent slope. In this case, the lever should be installed in 3-5 positions. Most owners of a Lada Priora car do not know how to tighten the handbrake on a Priora, which will be discussed further.
I would like to immediately note that in order to perform this procedure as comfortably as possible, you will need to use an inspection pit or a lift.
Aspects indicating the need to adjust the handbrake
There are several ways that will help any car owner, without exception, to help with the question of whether it is advisable to adjust the hand brake
It is worth noting that there is no need to check the handbrake every day; it is important to pay attention to this detail every 30 thousand km.
To find out whether the handbrake needs to be adjusted, you need to park your car on a slight slope, then leave the car on the handbrake and put the gear in neutral. If the vehicle slowly but surely begins to move down an incline, then the vehicle's parking brake may not be working properly.
Of course, this problem can be solved by replacing the VAZ-2110 handbrake rod, however, as practice shows, it is quite enough to make a very simple adjustment of this part.
- The travel of a properly adjusted handbrake lever should not exceed 8 clicks. The optimal lever stroke is 6-7 clicks (this number varies depending on the car model; details for a specific VAZ model can be found in the operating instructions supplied with the car).
- After installing the new cable, the rear wheels of the car should be jacked up and try to spin them by hand. Rotation must be free.
- Now the brakes should be checked while driving. You need to drive 30-40 meters, then slow down using the parking brake. After braking, you need to get out of the car and touch the rear brake drum. It should not be hot, its temperature should not exceed the ambient temperature. If the drum gets so hot that it burns your hand, this means that the brake cable is too tight and should be loosened.
- To loosen the cable, you should put the car back on the inspection hole, unscrew the lock nut on the outer tip with a 13mm wrench, and then loosen the main fastening nut. After this, the locknut is tightened again.
- If the brake cable is too slack, it needs to be tightened. All steps are listed above, with one exception: the main nut on the tip should be tightened, not unscrewed.
- To independently check the reliability of the parking brake, you should find a slope with a ratio of 1:5 (that is, 1 meter high and 5 meters long), drive the car onto it, turn off the engine, put the car on the parking brake and squeeze the clutch. After these actions, the machine should remain in place and not roll downhill. If the car does roll, you should tighten the brake cable a little more.
As can be seen from our article, there is nothing difficult in replacing a brake cable and even a novice car enthusiast can do this task
The main thing you should pay attention to in this case is compliance with safety regulations. When changing a cable, it is very easy to get injured or get a chemical burn, so it is better not to carry out this operation alone, but to work together with an experienced auto mechanic
Main causes of failure
The main reason why such an important device may break and need to be replaced is mechanical wear of the handbrake. As you know, the basis of the system is a small cable that transmits forces from the lever to the mechanism. It actually turns on this node.
The operating conditions of the cable are quite complex - the constant load from the force that the driver transmits through the handbrake lever to the system, sooner or later, can damage the device.
Before you begin replacing the cable, it is strongly recommended that you understand the brake system:
However, the cable breaks extremely rarely - most often, the cables simply jump off. Or the tips fixed in the drum are ground with very long wheel bolts. Needs renovation. Also, the parking brake may not work due to wear on the rear drum brakes (as well as abrasion of the pads, depending on the design).
As a result, the unit ceases to perform the functions assigned to it - the handbrake simply does not hold. The parking brake needs to be replaced and subsequently adjusted. But not everything is so simple - in some cases, the device can be damaged during emergency braking of the car - as a result, it will require repair or replacement.
Often the metal is not completely ground, but the steel fibers are stretched and moving in the shell is very difficult. But it doesn’t matter what the reason for the parking brake failure is, why it doesn’t hold. The purpose of our article is to figure out how to solve the problem.
This material has been created to accurately determine whether the link is malfunctioning:
Malfunctions and their symptoms
Determining that a cable needs adjustment or replacement is quite simple. Signs of a faulty mechanism appear as follows:
- The handbrake is pressed effortlessly - the cable is loose, you need to tighten it.
- The mechanism does not respond to pressing the lever - the drive is torn or flew out, or the reason may be the wear of the rear pads.
- If the handbrake is stuck, the drive is damaged and needs to be replaced.
Having taken out the main element, you can visually determine its condition. Replacement is required in the following cases:
- Up to 2% are damaged or torn.
- The cable moves with difficulty even after applying lubricant.
- The drive tips have grooves.
If the adjustment does not help
There are not many cases when adjusting the parking brake did not have any effect. However, this is no reason to despair.
It is possible that the handbrake cable has broken. This is a rare occurrence, but all options need to be considered. Especially if your VAZ 2110 is not new. By the way, on newer models the cable also breaks if the car is used very intensively. The braking system is simply not designed for such loads.
Device diagram
There are several situations in which it is necessary to replace the parking brake cable:
- The cable broke;
- The tips gave way;
- The cable threads have stretches, which over time can turn into a full-fledged rupture;
- The cable is difficult to move inside the sheath even after abundant lubrication.
Assembly occurs in reverse order.
After installing the brake drums, you need to adjust the travel of the parking brake lever.
You must have with you:
- socket wrench with ratchet 10;
- extension;
- 2 open-end wrench for 13;
- WD-40 – 1 bottle.
To begin with, the car is installed on the pit. Next, use a 10 key to disconnect the metal protection. Then, to get to the adjustment mechanism, you need to disconnect the rubber ring from the front muffler mount and slide the casing. Now, to raise the handbrake, use a 13 key to screw in the internal screw, while listening to the number of clicks. Upon completion of the adjustment, the position is fixed, and the second screw is tightened to 13.
We hope our article was useful to you!
How much does it cost to tighten the handbrake and can you do it yourself?
Actually the question is rhetorical, as you understand in different regions, the cost can range from 200 to 1000 rubles. For example, in the capital, the price is often 500 – 1000, but in the regions you can raise it for 250 rubles.
And to be honest, the work itself only takes a few minutes, the main thing is to find a hole or a lift, a key of 10 and off you go. You need to tighten the middle bolt, the one that is in the middle, it is the handbrake, tighten the nut and thereby tighten the cables.
Of course, if they are rusty or torn, then everything is much more complicated; it is better to trust the master, because replacing the cables from the rear drums is not at all an easy task.
That's all, read our AUTOBLOG, I think it clarified the situation.
(11 votes, average: 4.36 out of 5)
Similar news
Rust converter composition. Can I do it myself?
How to unscrew a brake pipe. If it has soured and the edges are torn off.
Anti-squeak plates for brake pads. Why are i needed?
The principle of operation of the VAZ 2110 hand brake
The fixation of the brake drums and wheels of the car occurs as a result of pressing the brake pads against them. They are driven by a lever through a system of cables, brackets and springs.
The tension of the cables (8) is set by a lever (2), and its fixation at a certain tension is set by a ratchet (11). You can remove the cable from the working position by pressing the button (1), disengaging the pawl (10) from the ratchet and lowering the lever to its lowest position.
Since the cable adjustment mechanism is located under the bottom of the car, a rubber seal (3) is installed on the rod (4), which prevents dirt and dust from entering the passenger compartment from the outside. For the same reason, the cables themselves are in a protective braid (9).
The tension of the cables (to the left and right wheels) of the hand brake is carried out simultaneously by moving the divider (5) along the rod (4) by tightening the nut (6) and fixing it with the lock nut (7).
At its core, the design of the parking brake system of the VAZ 2110 is quite simple. This is the secret of its reliability. The weak link in the system is considered to be the brake cables or, more precisely, their weakening. There are several reasons for this:
- brake pad wear;
- pulling the cable over time;
- weakening of fastening points.
The simplest solution and elimination of this problem is tightening the cables. Due to its simplicity and low labor costs, it is rare that a service will refuse to help a car enthusiast with this problem.
The asking price is from 250 to 500 rubles. We will consider the option with the minimum cost. That is, we will tighten the cable with our own hands.
Preparing for the process of tightening brake cables
Place:
- Garage with a pit;
- Overpass with free access to the bottom of the car;
- Lift.
Tool:
- Two open-end wrenches for 13. The presence of a head with a ratchet will help to significantly facilitate the work;
- Backlight (if necessary);
- Means for resuscitation of threaded connections (WD-40 or similar);
- Pliers;
- Metal brush;
- Grease (Litol, grease or the like);
- Rags, gloves.
Free time:
Minimum 30 minutes.
Step-by-step instructions for tightening the handbrake
The car is parked on an elevated place or above a garage pit with the engine turned off
The handbrake lever is in the down position. Important! If work is carried out immediately after turning off the engine, there is a risk of burns from the exhaust system. We clean the tension unit from dirt and rust with a wire brush. Spray the threaded connection with WD-40 or similar. We give the WD-40 and the threaded connection time to react and loosen the locknut. Tighten the tension nut five to six full turns. If screwing on the nut is quite difficult, it is advisable to hold the rod with pliers
This will eliminate the possibility of the rod turning and deformation of the place where it is attached to the lever. We check the operation of the handbrake from inside the car. If on the third or fourth click a clear difficulty is noticeable, the goal has been achieved. If the lever allows you to pull the cable until the seventh or eighth click, tighten it another five to six turns of the tension nut. We recheck the number of clicks. If the goal is achieved, fix the tension nut with a lock nut with sufficient force. This will eliminate the possibility of it unscrewing spontaneously. We lubricate the threads of the rod before and after the nuts - this will ensure that there are no problems during the subsequent tightening of the cables. We assemble the tool. We check the reliability of fixation. To do this, we put the car on the handbrake and try to move away. If the engine stalls immediately after releasing the clutch pedal, everything is fine. A good test for a handbrake is to place the car on a plane with an inclination angle of 16-20 degrees. A working mechanism should keep the car stationary, regardless of the load in the interior and luggage compartment.
Video instructions for tightening the handbrake on a VAZ 2110 can be found here:
What else should you pay attention to?
Ideally, both cables (for the left and right wheels) should synchronously press the pads against the brake drum. An experienced driver can check the consistency of the operation of the cables even while driving - the car with the handbrake should not skid (skid).
In a stationary state, this procedure has the following algorithm:
- you need to raise the rear axle of the car to the level when the wheels no longer touch the ground;
- Spin the wheels to the same speed and raise the handbrake.
If the wheels stopped synchronously, everything is in order; if the blocking occurred asynchronously, then there is a reason to check the parking brake yourself or go to a service station.
Brake system diagram VAZ 2111, 2112
Brake system diagram VAZ 2111, 2112
Operation of brake mechanisms.
1 — Shoe guide 2 — Guide pin 3 — Front brake brake pads 4 — Caliper 5 — Left front and right rear brake drive circuit hose 6 — Front brake wheel cylinder 7 — Wheel cylinder piston 8 — Piston O-ring 9 — Brake disc 10 — Piston stroke limit screw 11 — O-ring 12 — Thrust cup 13 — Piston return spring 14 — Right front and left rear brake drive piston 15 — O-ring spring 16 — Master cylinder reservoir 17 — Emergency fluid level sensor assembly 18 — Left drive piston front and right rear brakes 19 - Seal 20 - Vacuum booster 21 - Valve body 22 - Diaphragm 23 - Piston 24 - Vacuum booster valve 25 - Valve spring 26 - Pushrod return spring 27 - Air filter 28 - Pushrod 29 - Brake pedal return spring 30 — Pressure regulator piston 31 — Piston sleeve 32 — Seal 33 — Piston spring 34 — Pushrod O-rings 35 — Valve seat 36 — Valve spring 37 — Plug 38 — Valve 39 — Valve seat O-ring 40 — Pushrod 41 — Piston head seal 42 — Left front/right rear brake line 43 - Brake light switch 44 - Stop light switch tip 45 - Brake pedal 46 - Rod 47 - Valve body return spring 48 - Shoe tension spring 49 - Rear brake shoe 50 - Piston rear brake wheel cylinder 51 — Piston seal 52 — Thrust rings 53 — A-vacuum cavity 54 — B-atmospheric cavity 55 — C-channel connecting the atmospheric cavity with the internal cavity of the valve 56 — O-channel connecting the vacuum cavity with the internal cavity of the valve 57 - F-pressure force on the piston from its drive parts 58 - P1-fluid pressure in the main cylinder 59 - P2-fluid pressure in the wheel cylinders 60 - E.G-chambers of the pressure regulator connected to the main cylinder 61 - LN-chambers of the regulator pressure connected to the wheel cylinders 62 - K, M, H-gaps 63 - I. The pedal is not pressed 64 - II. Braking 65 - III. Disinhibition
When you press the brake pedal, it moves away from the tip 44 of the brake light switch, and the lamp circuit is closed, causing the brake lamp to light up. At the same time, the pusher 28 moves along with the piston 23 and the valve body 21. Following the piston, the valve moves under the action of spring 25 until it touches the valve seat. When adjacent to the seat, the valve separates chambers A and B. With further movement of the piston 23, its end moves away from the valve 24 and through the resulting gap, chamber B communicates with the atmosphere. Therefore, atmospheric air enters chamber B through filter 27, through the gap formed between the piston and valve, and then through channel C. Atmospheric air creates pressure on diaphragm 22.
Due to the difference in pressure in chambers A and B and the force of pressing the brake pedal, the valve body moves together with the rod 46, which in turn acts on the piston 18 of the main cylinder. When the piston 18 moves, the spacer ring moves away from the locking screw 10, and the sealing ring 11 is pressed by the spring 15 to the end of the piston groove. The compensation gap closes, and the main cylinder and reservoir are disconnected. With further movement of the piston 18 in the working cavity of the “left front - right rear brake” drive, fluid pressure is created, which is transmitted through pipelines to the wheel cylinders of the brake mechanisms. It also affects the floating piston 14, which, when moving, creates pressure in the “right front - left rear brake” circuit. Under increasing fluid pressure, the high-pressure rings 11 begin to expand and fit more tightly to the cylinder walls and to the end of the grooves, which improves the seal of the pistons in the cylinder.
As the pressure in the circuits increases, the force on the piston 30 of the pressure regulator increases, which tends to push it out of the regulator body. When the force from the fluid pressure begins to exceed the force from the elastic lever, the piston begins to move out of the housing. Following the piston, under the force of the pusher bushing spring and spring 36, the pusher 40 moves along with the bushing and rings 34. In this case, the gap M between the plate and the seat 35 increases, and the gaps H and K decrease. When the gap H is completely selected and the valve 38 isolates the chamber G from the chamber N, the pusher 40, together with the parts located on it, stops moving after the piston. From this point on, the pressure in chamber N will vary depending on the pressure in chamber L. As the force on the brake pedal increases further, the pressure in chambers E, G and L increases, and the piston will continue to move out of the housing.
Brake mechanism VAZ 2108/2109 (front view):
1 - Brake hose 2 - Guide pin mounting bolt 3 - Bleeding valve 4 - Wheel cylinder 5 - Cylinder to caliper mounting bolt 6 - Base mounting bolts
Brake mechanism VAZ 2108/2109 (side view):
1 - Wheel cylinder 2 - Piston 3 - Brake caliper base 4 - Brake disc 5 - Brake pads 6 - Caliper
At the same time, under the pressure of the liquid, the pusher bushing, together with the sealing rings 34 and the spring plate of the pusher bushing, will move towards the plug 37. At the same time, the gap M and the volume of the chamber N will decrease. As the volume of the chamber N decreases, the pressure in it, and therefore in the rear wheel drive, will increase and will almost always be equal to the pressure in the chamber L. When the gap K is completely selected, that is, the piston head 30 touches the seal 41, the pressure in the chamber L, and This means that in chamber N, it will increase to a lesser extent compared to chamber E and only due to throttling of the liquid between the piston head and seal 41. The dependence of the pressure in chambers L and E is determined by the ratio of the difference in the areas of the head and piston rod to the area of the head.
As the load on the car increases, the elastic lever 5 is loaded more, and the force on the piston from the lever 7 increases. This means that the moment the piston head touches the seal will be achieved at higher pressure in the master cylinder. Therefore, the efficiency of the rear brakes increases with increasing load on the vehicle.
Under fluid pressure, the pistons of the 7th and 50th wheel cylinders of the front and rear brakes move. In this case, the pistons 7 press the internal brake pads 3 to the disc 9, and the wheel cylinder assembly with the caliper 4 moves in the opposite direction under the force of the resulting reaction. A movable bracket presses the outer pad against the brake disc. When moving the pistons 50, part of the gap (1.25-1.65 mm) is selected between the shoulders of the thrust screws and rings 52. In this case, the pads 49 are pressed against the brake drum, creating a braking torque on the wheels. When the linings are worn, a gap of 1.25-1.65 mm is selected completely, and the thrust screws press on the shoulders of the thrust rings 52 with a force that ensures the shift of the rings along the cylinder mirror by the amount of wear of the linings. That is, the rings 52 will take a new position in the cylinders, again restoring the optimal gap between the pads and the drum.
If one of the circuits fails, the pressure regulator will operate part of its chambers, turning off the faulty circuit. Thus, if the “right front - left rear brake” circuit fails, the sealing rings 34 and the pusher bushing 40 under fluid pressure will move toward the plug 37 until the pusher bushing spring plate rests on the valve seat. The pressure in the rear brake will be regulated by a part of the regulator, which includes a piston 30 with a seal 41 and a housing sleeve into which the piston head fits. This part of the regulator will operate in the same way as with a working system.
When the “left front - right rear brake” circuit fails, the pressure of the fluid forces the pusher 40 along with its bushing and sealing rings 34 towards the piston 30, pushing it out of the housing. In this case, the gap M increases, and the gap H decreases. When valve 38 touches seat 35, the increase in pressure in chamber N stops, i.e. the regulator acts as a pressure limiter.
When the brake is released, the brake pedal and all parts of the vacuum booster take their original position under the action of springs, which leads to the cessation of the flow of atmospheric air into chamber B, and when valve 24 moves away from the seat, chambers A and B communicate with each other. The pistons 18 and 14 of the main cylinder, under the action of the return springs, are pressed against the stop screws 10. In this case, the spacer rings, resting against the screws 10, move the sealing rings 11 away from the ends of the piston grooves, as a result of which compensation gaps are formed through which the working cavities of the cylinder communicate with tank, i.e. the pressure in the circuits drops to atmospheric pressure.
Chambers E and G of the regulator communicate with chambers L and N. The springs of the rear brakes move the pads away from the drums by the amount of the gap between the nuts and the shoulders of the thrust rings 52, and the pistons of the wheel cylinders of the front brakes are moved away from the pads due to the elasticity of the sealing rings.
Hydraulic brake circuit diagram
Diagram of the brake system of VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 — front wheel brake mechanism 2 — left front-right rear brake line 3 — master brake cylinder 4 — right front-left rear brake line 5 — master brake cylinder reservoir 6 — vacuum brake booster 7 — rear wheel brake 8 — elastic brake pressure regulator drive lever 9 — brake pressure regulator 10 — brake pressure regulator drive lever 11 — brake pedal A — flexible front brake hose B — flexible rear brake hose
On the VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, a working brake system with diagonally separated circuits is used, which significantly increases the safety of driving the car. One circuit of the brake hydraulic drive ensures the operation of the right front and left rear brake mechanisms, the other brake circuit ensures the operation of the left front and right rear. If one of the circuits of the service brake system fails, the second circuit is used to stop the vehicle with sufficient efficiency. The hydraulic brake drive includes a vacuum booster 6 and a dual-circuit rear brake pressure regulator 9. The parking brake system on a VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 is driven by the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels.
Vacuum booster
Vacuum brake booster for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112:
1 – vacuum booster housing 2 – booster housing cup 3 – rod 4 – adjusting bolt 5 – rod seal 6 – master cylinder flange O-ring 7 – diaphragm return spring 8 – booster stud 9 – tip mounting flange 10 – valve 11 – hose tip 12 – diaphragm 13 – amplifier housing cover 14 – sealing boot 15 – piston 16 – valve body protective cover 17 – air filter 18 – pusher 19 – pusher return spring 20 – valve spring 21 – valve 22 – valve body bushing 23 – rod buffer 24 – valve body A – vacuum chamber B – atmospheric chamber C, D – channels
The rubber diaphragm 12, together with the valve body 24, divides the cavity of the vacuum amplifier into two chambers: vacuum A and atmospheric B. Chamber A is connected to the engine inlet pipe through the check valve of the tip 11 and a hose. The 24 valve body is plastic. At the outlet of the cover, it is sealed with a corrugated protective cover 16. The valve body contains the main cylinder drive rod 3 with a support sleeve, rod buffer 23, valve body piston 15, valve assembly 21, pusher and valve return springs 19 and 20, air filter 17 , pusher 18. When you press the pedal, pusher 18, piston 15, and after them valve 21 move until they stop against the seat of the valve body. In this case, cameras A and B are separated. As the piston moves further, its seat moves away from the valve and through the resulting gap, chamber B is connected to the atmosphere. The air entering through filter 17, the gap between the piston and the valve and channel D, creates pressure on the diaphragm 12. Due to the difference in pressure in chambers A and B, the valve body moves along with the rod 3, which acts on the piston of the main cylinder. When the pedal is released, valve 21 moves away from the body seat and through the resulting gap and channel C of chambers A and B communicate with each other.
Pressure regulator drive
Brake pressure regulator drive for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 — brake pressure regulator 2.16 — brake pressure regulator mounting bolts 3 — pressure regulator drive lever bracket 4 — pin 5 — brake pressure regulator drive lever 6 — brake pressure regulator drive lever axis 7 — lever spring 8 — body bracket 9 — bracket fastenings of the brake pressure regulator 10 - elastic lever for the pressure regulator drive 11 - shackle 12 - shackle bracket 13 - washer 14 - retaining ring 15 - bracket pin A, B, C - holes
The brake pressure regulator regulates the pressure in the hydraulic drive of the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels on a VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, depending on the load on the rear axle of the car. The brake pressure regulator is included in both circuits of the brake system, and through the brake pressure regulator, brake fluid is supplied to both rear brake mechanisms.
The brake pressure regulator 1 is attached to bracket 9 with two bolts 2 and 16. In this case, the front bolt 2 simultaneously secures the fork bracket 3 of the lever 5 of the brake pressure regulator drive. A double-arm lever 5 is hinged on the pin of this bracket with a pin 4. Its upper arm is connected to an elastic lever 10, the other end of which is pivotally connected to the rear suspension arm bracket through an earring 11.
Bracket 3 together with lever 5 can be moved relative to the pressure regulator due to the oval holes for the fastening bolt. Thus, the force with which lever 5 acts on the piston of the brake pressure regulator is regulated.
Pressure regulator
Brake pressure regulator for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 - brake pressure regulator body 2 - piston 3 - protective cap 4, 8 - retaining rings 5 - piston bushing 6 - piston spring 7 - housing bushing 9, 22 - support washers 10 - pusher O-rings 11 - support plate 12 - bushing spring pusher 13 - valve seat O-ring 14 - valve seat 15 - sealing gasket 16 - plug 17 - valve spring 18 - valve 19 - pusher bushing 20 - pusher 21 - piston head seal 23 - piston rod seal 24 - plug A, D - chambers , connected to the main cylinder B, C - chambers connected to the wheel cylinders of the rear brakes K, M, H - gaps E - drainage hole.
The brake pressure regulator has four chambers: A and D connected to the master cylinder, B to the right wheel cylinder of the rear brakes, C to the left wheel cylinder of the rear brakes.
In the initial position of the brake pedal, the piston 2 is pressed by the lever 5 through the leaf spring 7 to the pusher 20, which, under this force, is pressed against the seat 14 of the valve 18. In this case, the valve 18 is pressed away from the seat, resulting in the formation of a gap H, as well as a gap K between the head piston and seal 21. Through these gaps, brake pressure regulator chambers A and D communicate with chambers B and C.
When you press the brake pedal, fluid flows through gaps K and H and chambers B and C into the wheel cylinders of the brake mechanisms. As the fluid pressure increases, the force on the piston increases, tending to push the piston out of the housing. When the fluid pressure force exceeds the force of the elastic lever, the piston begins to move out of the body, and after it, under the action of springs 12 and 17, the pusher 20 moves along with the sleeve 19 and rings 10. In this case, the gap M increases, and the gaps H and K decrease. When the gap H is completely selected and the valve 18 isolates chamber D from chamber C, the pusher 20, together with the parts located on it, stops moving after the piston. Now the pressure in chamber C will change depending on the pressure in chamber B. With a further increase in the force on the brake pedal, the pressure in chambers of the brake pressure regulator D, B and A increases, piston 2 continues to move out of the body, and sleeve 19 together with o-rings 10 and plate 11, under increasing pressure in chamber B, moves towards plug 16. At the same time, the gap M begins to decrease. Due to the decrease in the volume of chamber C, the pressure in it, and therefore in the brake drive, increases and will be practically equal to the pressure in chamber B. When the gap K becomes zero, the pressure in chamber B, and therefore in chamber C, will increase to a lesser extent degree than the pressure in chamber A due to throttling of the liquid between the piston head and seal 21.
The relationship between the pressure values in chambers B and A is determined by the ratio of the difference in the areas of the head and piston rod to the area of the head. As the vehicle load increases, the elastic lever 10 is loaded more and the force from the lever 5 on the piston increases, i.e. the moment of contact between the piston head and seal 21 is achieved at higher pressure in the main brake cylinder. Thus, the effectiveness of the rear brakes increases with increasing load.
If the brake circuit fails, the right front-left rear brake O-rings 10 and bushing 19, under the fluid pressure in chamber B, will move toward plug 16 until plate 11 rests on seat 14. The pressure in the rear brake will be regulated by part of the regulator, which includes piston 2 with seal 21 and bushing 7. The operation of this part of the regulator in the event of failure of the said circuit is similar to operation with a working brake system. The nature of the change in pressure at the output of the brake pressure regulator is the same as with a working brake system.
If the brake circuit fails, the left front-right rear brake is moved by the pressure of the brake fluid, the pusher 20 with the bushing 19, sealing rings 10 towards the piston, pushing it out of the housing. The M gap increases and the H gap decreases. When valve 18 touches seat 14, the pressure increase in chamber C stops, i.e. The brake pressure regulator in this case acts as a pressure limiter. However, the achieved pressure value is sufficient for reliable operation of the rear brake.
There is a hole in housing 1, closed by plug 24. Liquid leakage from under the plug when it is squeezed out indicates a leak in rings 10.
Master cylinder with reservoir
Main brake cylinder with brake reservoir for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 — master cylinder body 2 — low-pressure sealing ring 3 — piston of the “left front-right rear brake” circuit drive 4 — spacer ring 5 — high-pressure sealing ring 6 — sealing ring pressure spring 7 — spring plate 8 — piston return spring 9 - washer 10 - locking screw 11 - drive piston of the "right front-left rear brake" circuit 12 - connecting sleeve 13 - reservoir 14 - emergency brake fluid level sensor A - gap
Brake master cylinder with sequential pistons. A brake tank 13 is mounted on the main brake cylinder body, in the filler neck of which a brake fluid level sensor 14 is installed. The high pressure O-rings 5 and the rear wheel cylinder rings are interchangeable.
Front wheel brake
Brake mechanism of the front wheel of VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 - brake disc 2 - pad guide 3 - caliper 4 - brake pads 5 - cylinder 6 - piston 7 - pad wear indicator 8 - o-ring 9 - guide pin protective cover 10 - guide pin 11 - protective cover
The front wheel brake mechanism is disc, with automatic adjustment of the gap between the pads and the disc, with a floating caliper and a brake pad wear indicator. The bracket is formed by a caliper 3 and a wheel cylinder 5, which are tightened with bolts. The movable bracket is bolted to pins 10, which are installed in the holes of the guide 2 of the pads. Lubricant is placed in these holes, rubber covers 9 are installed between the pins and the pad guide. Brake pads 4 are pressed against the grooves of the guide by springs, the inner one of which has a lining wear indicator 7. A piston 6 with a sealing ring 8 is installed in the cavity of the cylinder 5. Due to the elasticity of this ring, the optimal gap between the pads and the disk is maintained.
Rear wheel brake
Brake mechanism of the rear wheel of VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 — hub mounting nut 2 — rear wheel hub 3 — lower tension spring of brake pads 4 — brake shoe 5 — guide spring 6 — wheel brake cylinder 7 — upper tension spring 8 — expansion bar 9 — parking brake drive lever pin 10 — drive lever parking brake 11 - brake mechanism shield
The rear wheel brake mechanism on VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars is drum, with automatic adjustment of the gap between the brake pads and the brake drum. The automatic slack adjustment device is located in the wheel brake cylinder.
Wheel cylinder
Rear wheel brake cylinder for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112:
1 - brake pad stop 2 - protective cap 3 - brake cylinder body 4 - piston 5 - seal 6 - support plate 7 - spring 8 - cotters 9 - thrust collar 10 - thrust screw 11 - fitting A - slot on the thrust collar
The main element of the rear wheel brake cylinder is a split thrust collar 9, installed on the piston 4 between the shoulder of the thrust screw 10 and two cotters 8 with a gap of 1.25-1.65 mm. The thrust cuffs 9 are inserted into the brake cylinder with tension, providing a shear force of the cuff along the cylinder mirror of at least 343 N (35 kgf), which exceeds the force on the piston from the tension springs 3 and 7 (see Fig. 7) of the brake pads. When, due to wear of the brake linings, the gap of 1.25-1.65 mm is completely removed, the collar on the thrust screw 10 is pressed against the collar of the cuff 9, as a result of which the thrust cuff moves after the piston by the amount of wear of the brake linings. When the braking stops, the pistons are moved by the force of the tension springs until the crackers stop against the collar of the thrust collar. Thus, the optimal clearance between the brake pads and the brake drum is automatically maintained.
Parking brake system drive
Drive of the parking brake system of VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
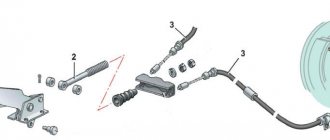
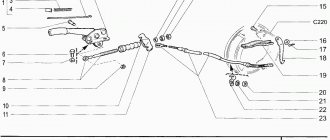
1 — button for fixing the hand brake lever 2 — parking brake lever 3 — protective cover 4 — rod 5 — cable equalizer 6 — adjusting nut 7 — lock nut 8 — cable 9 — cable sheath
The parking brake system on VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 vehicles with a mechanical drive acts on the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels. The parking brake drive consists of a lever 2, an adjusting rod 4, an equalizer 5, a cable 8, a lever 10 for the manual drive of the rear brake pads and an expansion bar 8.
Emergency brake fluid level sensor Emergency brake fluid level sensor for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
Emergency brake fluid level sensor for VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112 cars:
1 - protective cap 2 - sensor body 3 - sensor base 4 - o-ring 5 - clamping ring 6 - reflector 7 - pusher 8 - bushing 9 - float 10 - fixed contacts 11 - moving contact
Mechanical brake fluid emergency level sensor. The sensor housing 2 with the seal 4 is pressed to the base 3 by a clamping ring 5, which is screwed onto the neck of the brake reservoir. At the same time, the flange of the reflector 6 is pressed against the end of the neck. In this position, the clamping ring is held by two clamps made on the base 3. A pusher 7 passes through the hole in the base, connected to the float 9 by means of a sleeve 8. A movable contact 11 is located on the pusher, and on the sensor body — fixed contacts 10. The contact cavity is sealed with a protective cap 1. When the level of brake fluid in the brake reservoir drops to the maximum permissible level, the moving contact is lowered onto the fixed contacts and closes the circuit of the hazard warning lamp in the instrument cluster.
How to tighten the handbrake on a VAZ 2110? Replacing and adjusting the cable
Despite the fact that the hand (parking) brake is rarely used, VAZ 2110 owners quite often have problems with this unit - lack of reverse traction, weakening of the cable or breakage of the lever. Having discovered that the handbrake is not working properly, it is necessary to begin repairs immediately, since the safety of all road users depends on this unit. Most often the problem can be solved by adjusting the torso, but in some cases replacement will be necessary. This material describes in detail how to tighten and change this element of the brake system. Readers will also learn how malfunctions manifest themselves and what to do about them.
Purpose and location of the parking brake
The location of the handbrake is known to every VAZ 2110 driver - there is a lever installed between the front row seats, when pressed, braking occurs. The metal cable is a mechanical drive in this unit. By lowering the lever, the driver provides tension on the cable, which presses the rear brake pads to the wheel discs. Breakage of the lever is extremely rare, since the main load falls on the metal cable, as a result, after some time it loses the required tension.
The operation and maintenance manual for the VAZ 2110 states that at least once every six months it is necessary to carry out diagnostics of the brake system, including the parking brake. The traffic regulations have requirements for this unit - it must hold the car at a slope of 25 degrees. If the metal cable is not damaged, and the adjustment does not bring results, then the problem is in the rear brakes - this requires a full diagnosis from specialists.
Malfunctions and their symptoms
Determining that a cable needs adjustment or replacement is quite simple. Signs of a faulty mechanism appear as follows:
- The handbrake is pressed effortlessly - the cable is loose, you need to tighten it.
- The mechanism does not respond to pressing the lever - the drive is torn or flew out, or the reason may be the wear of the rear pads.
- If the handbrake is stuck, the drive is damaged and needs to be replaced.
Having taken out the main element, you can visually determine its condition. Replacement is required in the following cases:
- Up to 2% are damaged or torn.
- The cable moves with difficulty even after applying lubricant.
- The drive tips have grooves.
Replacing the cable
For work you will need a 10mm open end wrench, WD-40 lubricant, a set of screwdrivers, a 13mm open end wrench and a socket wrench. An inspection hole and a jack must be present in the garage or box. Replacing the cable is carried out as follows:
- The VAZ 2110 must be removed from the parking brake - to do this, lower the handbrake all the way to the floor. It is necessary to ensure that the restraint system of the VAZ 2110 is activated;
Remove the muffler from the suspension cushions and the resonator from the rear cushion
- The next step is to remove the brake drum from both rear wheels;
- Next you will need to get to the equalizer. This is the most difficult stage; the motorist needs to dismantle the muffler and remove the resonator located in the rear of the chassis. Next, you need to move the exhaust pipe down;
- Now you will have to crawl under the car and unscrew the adjusting elements (nuts), after which the equalizer can be dismantled;
- You need to remove the tip from the control;
- Also on the car body there is a bracket on which the tip stands;
Remove the end of the cable sheath from the bracket on the body - The handbrake is clamped with special brackets - they should be bent, but not damaged;
- Next, you need to disconnect the tip, having first removed the brake pad;
After removing the rear brake pad, disconnect the cable end from the lever - Having reached the rear axle beam, you should remove the last fastenings of the handbrake - the nuts. Done, the drive can be removed. Replacing the cable is done in the reverse order.
Adjustment
Tightening a cable is much easier than replacing it. The VAZ 2110 must be placed on a jack. The handbrake must be locked, after which you should find the adjusting bolt and nut - the work is done using two “13” keys.
Twist the nut until the cable is taut
The nut must be tightened until the rear wheelset stops moving. Next, you need to tighten the locknut. After this, you need to return the car to its original position, unlock it and check its operation.
Reasons why the handbrake does not work
Often the reasons are trivial, and the work itself only takes 10 minutes (more on that a little later), but now I’ll list the main points:
- Worn rear brake pads. Usually accompanied by a grinding noise when braking. Here, tighten, don’t tighten the cable, nothing will work. First you need to replace the pads, preferably on both wheels at once, because they wear out evenly.
- Incorrectly adjusted parking brake. This also happens, the adjusting bolt is simply loose - you need to tighten it.
- Cable wedge in sheath. This often happens over time, and often appears on 5 year old or older cars. The fact is that moisture gets between the sheath and the cable itself, after which the rust and the cable get stuck in the sheath. There are two ways here, either lubricate it and develop it so that it runs normally. Or you should replace the cables with new ones.
- Broken cable. Sometimes the cable breaks, both from the handle itself and under the car, it needs to be replaced.
- Ice or salt, reagents on the surface of the pads. It happens rarely, but it does happen, especially after driving through deep puddles. It is worth cleaning the pads with gentle pressure when driving short distances. All plaque should be cleared.
- Oil or brake fluid gets on the pads. For example, the working cylinder is leaking, or the rear axle seal may be leaking. Here you first need to remove the cause of the leak, then clean the pads. Of course, they will clean themselves after several braking cycles. If the “oiling” is strong, then you need to replace the pads with new ones, because the surface of the linings can be completely saturated with oil.
I know from experience that these are mainly the first four reasons. For example, on our VAZs, very often the cable in the sheath rusts from time to time, or it breaks, and you need to tighten it in time.
How to tighten the handbrake on a Prior? The auto industry breaks down as always - Fix the Car!
If the handbrake on a VAZ-2112 becomes difficult to hold, then you should not change it immediately, since the cable can be adjusted. If the mileage on the car is high, the rear pads on the car may wear out. This may reduce the effectiveness of the handbrake and the entire braking system. In this case, the handbrake cable will need to be tightened.
Handbrake diagram for VAZ-2112
For clarity, here is a diagram of a hand brake
1 - button that fixes the handbrake lever; 2 — hand brake lever; 3 — protective cover; 4 — handbrake rod; 5 — cable equalizer; 6 — adjusting nut; 7 - lock nut; 8 - cable; 9 — protective sheath of the cable.
In this scheme we need element number 6. It is he, and only him!
What is required for adjustment?
In order to adjust the handbrake you need a platform or lift. If there are no such devices, then you can simply hang the rear wheels on the “goats”. They can be installed under the car using a jack. It’s also worth taking two “13” keys and pliers.
Start:
- The car is installed on an overpass or “goats”. Hanging out your butt
- The lever position is set to the lowest possible position. We put the handbrake at the very bottom. Do not pay attention to the scuffs of the console; we conducted an experiment with non-standard armrests. The iron fastenings of the armrest are visible. The photo shows the editorial car
- Use a wrench to loosen the locknut. Adjusting nut
- The second wrench holds the adjusting nut.
- The adjusting nut should be tightened until the cable is tensioned. It must be remembered that the rod should be held with pliers when tensioning the cable. Tighten the adjusting nut
- After this, you should make sure that the full stroke of the handbrake lever is no more than 4 and no less than 2 clicks.
- When the stroke check is completed, the locknut is tightened. The adjustment is held with another key.
- If necessary, change the mechanism to a new one. Everything is rusty, we changed the adjustment mechanism
- After releasing the adjusted lever down, you should spin the rear wheels. When the lever is in its lowest position, the wheels should spin freely.
THIS IS INTERESTING: Chevrolet Cruze stove repair
If you cannot tighten the cable, then it should be replaced with a new one.
Adjusting the handbrake after tensioning
After adjusting the brakes, you need to check them again. To do this, the car should be placed on a road with a slope of at least 23%. The car should be in neutral gear in this area and with the handbrake pulled up. If the handbrake brakes hold the car in this area, then the handbrake is adjusted correctly.
What to do when adjustment does not work
There are also cases when the above actions are not enough to adjust the handbrake. This can happen, for example, when the handbrake cable is broken. This happens on the VAZ-2112, although rarely. In such situations, the cable must be replaced. The cable also needs to be replaced when:
- The tips are loose.
- The cable itself begins to stretch, which will lead to its breakage during operation. HAIKU! The old cable is very worn out! For comparison, old and new handbrake cables
- Physical wear (scuffs and cracks) of the handbrake cables. Heavy wear on the handbrake cable
- It is quite difficult for the cable to move in the casing even after lubrication.
This replacement procedure does not require contacting a service station. Although this will require some time and skills from the driver, such work can be done independently.
It should also be remembered that when replacing the cable, certain conditions must be observed. To do this, the driver will need an assistant who will pull the cable.
Why do you tighten the handbrake?
The cable acts here as a drive. If the driver pulls the handbrake lever, then at the same time he uses the cable, which spreads the pads in the rear wheel.
If the handbrake is faulty, you just need to tighten the cable or replace it with a new one. On a VAZ-2112 it’s quite easy to do this with your own hands.
Need for adjustment
You can determine that the parking brake needs adjustment when checking. It is recommended to do it every 30,000 kilometers. This procedure should be done even if the handbrake seems to be working well.
The device must also be checked in cases where it does not work. For example, a car moves when the brake lever is applied.
Replacing the parking brake cable
Sometimes any adjustment does not bring the expected result. In this case, replacing the VAZ-2112 handbrake becomes the only correct solution to the problem. For what reasons does a car owner have to change the handbrake cable? First of all, the first indicator for replacement is its breakage and critical stretching, when adjustment does not lead to anything. In addition, if during an external inspection you notice damage and other signs of wear, in this case you also cannot do without replacement. Another reason for removing the old cable and installing a new one is its difficult movement inside the protective shell, even to the point of jamming, which makes normal operation of the entire system impossible.
Reasons for replacing the parking brake cable: difficult movement, external damage, critical stretching.
We will talk further about how to replace the VAZ-2112 parking brake cable, but before you begin, remove the brake drums on the rear wheels to disconnect the ends of the cable from the brake pads. To do this, naturally, the rear of the car must be suspended using a jack or a stationary lift. Perform all further operations following the following instructions:
- As in the case when it was necessary to tighten the cable, you need to loosen the lock nut on the rod and unscrew it, after which the adjusting nut can be unscrewed. This will allow you to remove the bracket from the rod, from which you need to remove both ends of the cable.
- Next, using a screwdriver, remove the ends of the cable from the hooks of the levers that drive the brake pads.
- Then the tips of the protective shell must be removed from the brackets located on the left and right sides of the bottom of the machine. Each bracket has a nut, by unscrewing which you can remove additional brackets from the arms.
As you may have noticed, the parking brake includes two cables and both of them must be removed for replacement. Installation of new cables is carried out in the reverse order of removal. This is exactly how the VAZ-2112 parking brake cable is replaced, just don’t forget to adjust the parking brake after the installation is complete. You could learn how to do this from the instructions given in this article.
Sources used:
- https://carfrance.ru/reguliruem-ruchnoj-tormoz-na-vaz-2110-svoimi-rukami/
- https://v-mireauto.ru/kak-podtyanut-ruchnik-na-vaz-2110/
- https://www.vazzz.ru/ne-derzhit-ruchnik-vaz-2110-dazhe-posle-natyazhki/
- https://carfrance.ru/kak-podtyanut-i-otregulirovat-ruchnik-na-vaz-2112-svoimi-rukami-video/
- https://carextra.ru/remont/natjazhka-i-zamena-ruchnika-na-vaz-2112.html
VAZ 2110: replacing the handbrake cable yourself
The parking or hand brake of a vehicle is designed for emergency braking in an emergency situation. The main purpose is when parking for more than 6 minutes with the engine turned off, the parking brake is activated by a lever. It is located between the front seats of the vehicle. On a VAZ 2110, replacing the handbrake cable is sometimes caused by the need to take care of safety. Replacing the VAZ 2110 parking brake cable can be done on your own.
What is a handbrake for?
Replacing the handbrake cable on a VAZ 2110
According to the current Traffic Rules, the handbrake of a VAZ must hold the vehicle on a slope of up to 25%. When lifting the lever up, it should produce from 2 to 8 clicks. If the car has been in operation for more than three years, then it is necessary to check the parking brake system. You can go to a car service center, where qualified specialists will carry out high-quality diagnostics. You also need to do this process yourself. Having stopped the car on a level surface, the lever rises all the way up with a smooth movement. In this case, the clicks are counted; there should be no more than 8 of them. When leaving the cabin, you need to apply force from behind, trying to move the car. If it rolls, then you will have to adjust the handbrake. After tightening the cable, the result is the same, which means that only one thing remains - to completely check the condition of the rear brake system.
Checking the rear brake system
Replacing parking brake cables on a VAZ 2110
- The car is installed on an overpass or in a garage in an inspection hole. Anti-roll bars are placed under the front wheels. The rear part is raised with jacks and reliable supports are installed. The lever goes all the way down.
- The rear drums are removed and checked for wear. They will not allow a lot of wear and tear. The rear brake pads are checked; their thickness should be more than 2/3 of the new pads. The condition of the cable is inspected from below; it should not have any abrasions or broken strands.
Replacement results
After assembly, you should check that the cable has been replaced correctly.
To do this you need:
- Raise the rear of the car using a jack, or drive it into a viewing hole;
- Lower the lever all the way down;
- Loosen the lock nut and tighten the adjusting nut until the cable is tensioned;
- Check the clicks, the norm is from 2 to 5;
- For reliability, tighten the lock nut, holding the adjusting nut from turning.
We check the operation of the handbrake: put the car on the handbrake and rotate the wheels. The rotation should be uniform and without friction.
To be more confident, choose a steep hill (with an approximate slope of at least 25%) and put the car on the handbrake. Costs? This means the replacement was done correctly.
Hand (parking) brake system on VAZ 2110
Handbrake If the handbrake malfunctions, it is recommended to make adjustments. And if it does not help, then repairs are carried out by replacing the faulty cable. On a car like the VAZ 2110, adjusting the cable is as simple as replacing it. If this malfunction is ignored, the car may move on its own, or you, on the contrary, will not be able to move.
You don’t have to go to a car service center to solve your problem. If you have some experience, understand the essence of the handbrake, and also apply the data from the repair and operation manual for the VAZ 2110, you can do everything yourself.
Is adjustment necessary?
First you need to determine whether the adjustment will really solve the problem of the handbrake malfunction.
Adjusting the parking brake
To do this, a small test is carried out. Moreover, it is recommended to do a similar procedure after every 30 thousand kilometers, even if you are sure that the parking brake works well.
Pulling up the handbrake
It is likely that you just need to tighten the parking brake on the VAZ 2110 to fix the problem.
- Drive to the inspection hole, from where it is most convenient to make adjustments. Another option is a lift. You'll find something here. This way you can easily get to the necessary nodes.
- Make sure the brake lever is in its lowest position.
- Take two keys. You will loosen the lock nut first and tighten the adjusting nut second.
- Tighten the adjustment nut until the cable is properly tensioned.
- It is strongly recommended to hold the rod when tightening the adjustment nut with pliers.
- Now make sure that the lever makes full travel in 2-4 clicks, no more.
- If after checking everything turned out to be good and the working stroke is correct, tighten the equalizer locknut while holding the adjustment nut with a second wrench.
- Release the handbrake lever down and turn the rear wheels by hand. Rotation should occur evenly without any jamming.
- But if the adjustment did not allow the cable to be tensioned, then the element must be replaced.
If the adjustment does not help
There are not many cases when adjusting the parking brake did not have any effect. However, this is no reason to despair.
Device diagram
There are several situations in which it is necessary to replace the parking brake cable:
- The cable broke;
- The tips gave way;
- The cable threads have stretches, which over time can turn into a full-fledged rupture;
- The cable is difficult to move inside the sheath even after abundant lubrication.
Replacement
There is one important condition - you will need an assistant. His task will be to strongly pull the cable, which will allow the equalizer to be installed correctly
The sequence of work to replace the cable is as follows:
- Lower the handbrake lever as far as possible;
- Remove the brake disc from the wheel where the element is being replaced;
- Remove the muffler from the suspension cushions and the resonator from the rear suspension;
- Lower the exhaust system down;
- Remove the adjusting nut and locknut;
- Remove the equalizer;
- Now remove the cable ends from the equalizer;
- Remove the tip of the equalizer shell from the bracket, which is located on the car body;
- Bend back the brackets that secure the cable;
- Remove the rear brake pad and remove the cable end from the lever;
- Slightly loosen the nut that secures the cable holder to the rear axle;
- Remove the cable from the holder, then from the bracket, and then pull it out through the brake spike;
- Place a new cable in its new location and perform the assembly procedure, following the reverse order of the indicated processes;
- Make sure that the cables in the bracket are positioned crosswise;
- After completing the installation of the new element, adjust the handbrake.
As you can see, the task does have certain nuances, but it is not difficult at all if you have some experience and rely on the VAZ 2110 operating manual. As a rule, everything is spelled out there.
It wouldn’t hurt to supplement your skills and knowledge with video tutorials or consultation with a friend from a service station. But if you are not confident in your own abilities, you should not risk replacing the handbrake cable yourself. It is better to spend more money, but entrust the work to specialists.
First adjustment steps
To begin adjusting the handbrake, you need to make sure that one of three elements is present and accessible: a lift, an inspection hole or an overpass.
An overpass is a type of engineering structure that is intended to lay a road or communications above the ground.
Homemade overpass for adjusting the handbrake on a VAZ 2110
At home, most often only the inspection hole is accessible. If you cannot take advantage of any of the above conditions, then you can make do with a kind of support trestles, which are a rigid structure installed under the rear part of the body after it has been lifted with a jack. In addition, you need to prepare two wrenches size “13”, as well as pliers.
Now you need:
- lower the parking brake lever to its lowest position;
One of the adjustment stages is to lower the handbrake lever
- using one key set to “13” you need to loosen the lock nut, while holding the adjusting nut with the second key;
Loosen the locknut and loosen the adjusting nut
- start tightening the adjusting nut and continue until the handbrake cable tightens or loosens slightly if it is too tight;
- While tightening the adjusting nut, you need to hold the rod in the handbrake mechanism with pliers.
That's not all, as there are a few steps left to complete the complete handbrake setup.
Need for adjustment
You can determine that the parking brake needs adjustment when checking. It is recommended to do it every 30,000 kilometers. This procedure should be done even if the handbrake seems to be working well.
The device must also be checked in cases where it does not work. For example, a car moves when the brake lever is applied.
At the same time, problems with the handbrake can lead to serious trouble if an uncontrolled car crashes into some obstacle or, even worse, into another car. Let's look at problems with the handbrake and how to fix them yourself without contacting specialists at a service station.
Advice! If the cable tension on the handbrake is insufficient, in addition to the handbrake, the car must be left “at speed”, this will protect you in case of unforeseen circumstances.
When the linings on the rear brake pads wear out and the drive cables are pulled out, a problem often arises in adjusting the handbrake stroke (parking handbrake). The examples that will be described in the article will help to cope with this problem not only for the VAZ-2110, but also for other domestically produced cars.
Is adjustment necessary?
First you need to determine whether the adjustment will really solve the problem of the handbrake malfunction.
Adjusting the parking brake
To do this, a small test is carried out. Moreover, it is recommended to do a similar procedure after every 30 thousand kilometers, even if you are sure that the parking brake works well.
Drive your vehicle to an area where there is a slight slope. Place the car on it, turn on the handbrake and shift to neutral. If the car starts to roll down, everything is obvious - the handbrake needs repair.
Which cable to choose
When choosing any car part, you must first of all be guided by its compatibility with your specific brand. Obviously, the cable from Chevrolet will not fit the Zhiguli. But there are times when people purchase unsuitable cables.
In our case, it is difficult to confuse anything. The handbrake cable of the VAZ 2114 is exactly the same as that of similar models of the domestic manufacturer. It can be found at any auto parts store. Several manufacturers produce cables, and all are usually of the same quality. This is understandable, the detail is not complicated.
There shouldn't be any problems when choosing. The prices are quite reasonable and there is not much difference. The only thing worth doing is to read on the packaging about compatibility with your car, just in case.
After following all the instructions, you can replace the handbrake cable on VAZ cars yourself. This will have to be done quite often, due to the design features of the brake system and its fragility. Having such skills is always useful. Now you know how to change the parking brake cable on a VAZ 2114.
The handbrake plays an extremely important role in ensuring driving safety. This element of the braking system not only serves to prevent a parked car from rolling, but can also help avoid a traffic accident. That is why it is necessary to always monitor the serviceability of its entire system. Now let's try to figure out how to tighten the handbrake.